Lint工具
一、Lint是什么
Lint是ADT 16引入的静态代码检测工具(位于sdk/tools/bin/lint ),可以对Android工程的源文件进行扫描,找出在正确性、安全性、性能、易用性、无障碍性以及国际化等方面可能存在的bug和可优化提升的地方。
Lint默认包括几百个检测项,主要分为以下六类:
Valid issue categories: Correctness //编码错误或不完美,比如"WrongThread"表示可能在非UI线程调用widgets方法 Security //不安全的编码,比如“SetJavaScriptEnabled”表示WebView支持JavaScript Performance //对性能有影响的编码,比如"Wakelock"表示未正确释放屏幕锁,导致功耗增加 Usability //有更好的可用选项,比如"SmallSp"表示使用了小于12sp的尺寸 Accessibility //辅助选项,比如"ContentDescription"表示Image缺少ContentDescription属性 Internationalization //国际化,比如"RtlEnabled"表示使用了RTL属性但没有在manifext文件中设置android:supportsRtl为true
可以通过lint --list命令查看所有支持的检测项:
$lint --list
也可以通过lint --show <id> 命令查看某一检测项的详细介绍:
$ lint --show RtlEnabled RtlEnabled ---------- Summary: Using RTL attributes without enabling RTL support Priority: 3 / 10 Severity: Warning Category: Internationalization:Bidirectional Text To enable right-to-left support, when running on API 17 and higher, you must set the android:supportsRtl attribute in the manifest <application> element. If you have started adding RTL attributes, but have not yet finished the migration, you can set the attribute to false to satisfy this lint check.
除此之外,google还提供了自定义Lint检查规则的方法。
二、如何启动Lint检测
使用Android Studio时,无论何时构建应用,都会自动运行配置的Lint和IDE检查。但更多的时候,我们需要主动运行这些检测,并获取检测报告。
我们有两种方式启动Lint检测:
(1)命令行检测
我们可以在项目根目录下通过如下命令启动Lint检测:
./gradlew lint
检测完毕后可以看到类似如下结果:
> Task :lockscreen:lint Ran lint on variant debug: 335 issues found Ran lint on variant release: 335 issues found Wrote HTML report to file:///home/kevin/kevin/project/sysq/SystemUI/lockscreen/build/reports/lint-results.html Wrote XML report to file:///home/kevin/kevin/project/sysq/SystemUI/lockscreen/build/reports/lint-results.xml
检测报告被同时保存在lint-results.html和lint-results.xml两个文件中,打开后可以看到每个问题的详细描述和定位,以及修改建议:
<issue id="WrongConstant" severity="Error" message="Must be one of: View.LAYER_TYPE_NONE, View.LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, View.LAYER_TYPE_HARDWARE" category="Correctness" priority="6" summary="Incorrect constant" explanation="Ensures that when parameter in a method only allows a specific set of constants, calls obey those rules." errorLine1=" ViewCompat.setLayerType(getChildAt(i), layerType, null);" errorLine2=" ~~~~~~~~~"> <location file="/home/kevin/kevin/project/sysq/SystemUI/lockscreen/src/main/java/com/lenovo/artlock/LeatherViewPager.java" line="1793" column="52"/> </issue>
注:lint在jdk 9 和 jdk 11会报错,替换其他版本可以解决;另外,如果是window,则直接使用
gradlew lint
(2)手动运行检测
以Android Studio为例:
1.打开一个工程,选择要分析的项目、文件夹或文件
2.在菜单栏中依次选择Analyze > Inspect Code
3.查看检测范围和配置文件
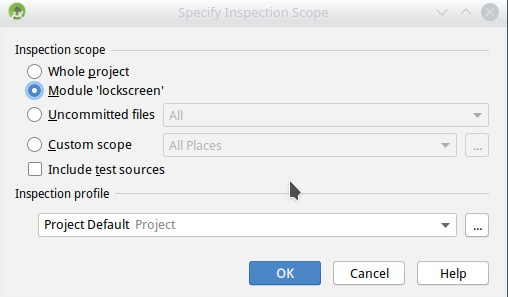
4.点击ok以运行检查
5.查看检测结果
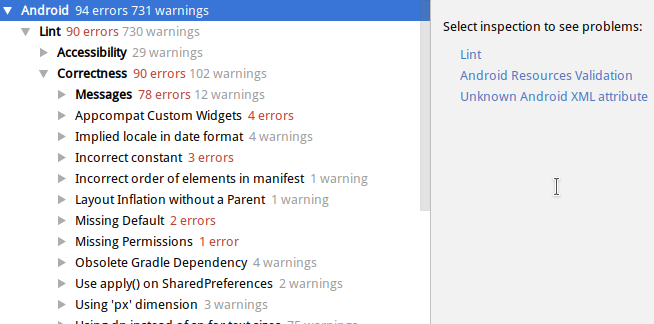
注:通过Custom scop可以自定义检测范文,Inspection profile可以指定或修改内置的lint配置文件,下面会详细介绍。
三、Lint配置文件
如果希望忽略一些检测项或调整其严重等级,可以通过修改配置文件lint.xml的方式。
Lint的工作流程如下:
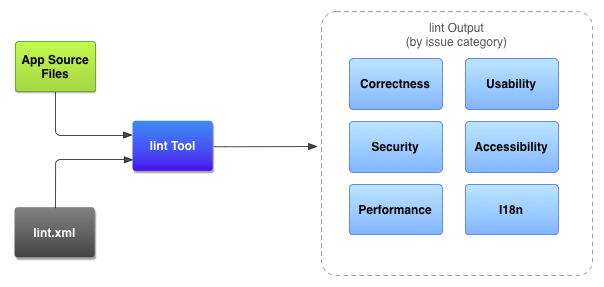
修改配置文件同样有两种方式:
(1)手动创建
如果是手动创建lint.xml文件,则将其放在Android项目的根目录下,其格式如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <lint> <!-- Disable the given check in this project --> <issue id="IconMissingDensityFolder" severity="ignore" /> <!-- Ignore the ObsoleteLayoutParam issue in the specified files --> <issue id="ObsoleteLayoutParam"> <ignore path="res/layout/activation.xml" /> <ignore path="res/layout-xlarge/activation.xml" /> </issue> <!-- Ignore the UselessLeaf issue in the specified file --> <issue id="UselessLeaf"> <ignore path="res/layout/main.xml" /> </issue> <!-- Change the severity of hardcoded strings to "error" --> <issue id="HardcodedText" severity="error" /> </lint>
在lint.xml定义的id会覆盖默认配置,未涉及的id则保持默认配置。
(2)Android Studio内置Lint配置文件
Android Studio内置了Lint和一些其他检查配置文件,通过第二部分中提到的Inspection profile选项可以修改。
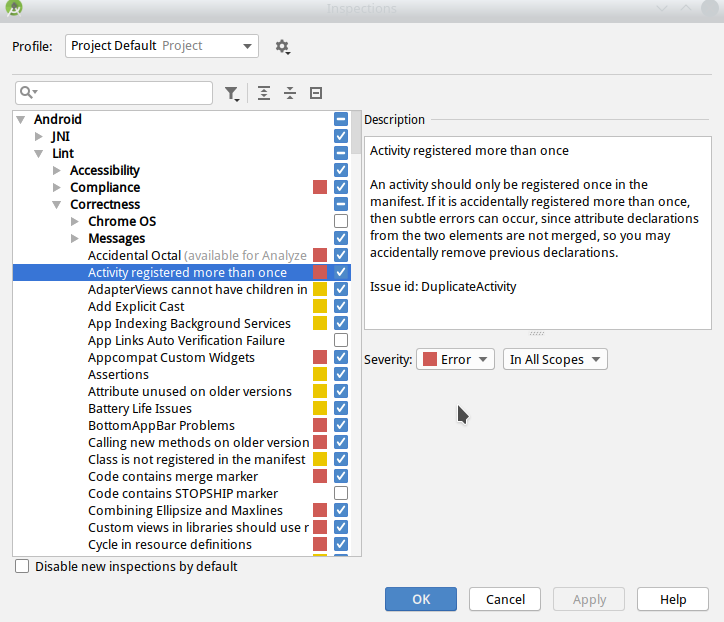
其中打√代表打开,Severity 代表严重等级,可以根据自己的需要修改。
Gradle中的lintOptions
除了上面修改单个issue的开关和严重等级,Gradle也提供了针对Lint运行方式的配置,可以在build.gradle中修改。
android { // 移除lint检查的error,可以避免由于编译条件太过严格而编译不过的问题 lintOptions { // 如果为 true,则当lint发现错误时停止 gradle构建 abortOnError false // 如果为 true,则只报告错误 ignoreWarnings true // 不检查给定的问题id InvalidPackage: Package not included in Android disable 'InvalidPackage' // 不检查给定的问题id 资源类型错误 disable "ResourceType" // 忽略因MissingTranslation导致Build Failed错误 "app_name" disable 'MissingTranslation' // 检查给定的问题 id enable 'RtlHardcoded','RtlCompat', 'RtlEnabled' // * 仅 * 检查给定的问题 id check 'NewApi', 'InlinedApi' // 配置写入输出结果的位置;它可以是一个文件或 “stdout”(标准输出) textOutput 'stdout' // 如果为真,会生成一个XML报告,以给Jenkins之类的使用 xmlReport false // 用于写入报告的文件(如果不指定,默认为lint-results.xml) xmlOutput file("lint-report.xml") // 如果为真,会生成一个HTML报告(包括问题的解释,存在此问题的源码,等等) htmlReport true // 写入报告的路径,它是可选的(默认为构建目录下的 lint-results.html ) htmlOutput file("lint-report.html") // 设置为 true, 将使所有release 构建都以issus的严重性级别为fatal //(severity=false)的设置来运行lint // 并且,如果发现了致命(fatal)的问题,将会中止构建 //(由上面提到的 abortOnError 控制) checkReleaseBuilds true // 设置给定问题的严重级别(severity)为fatal (这意味着他们将会 // 在release构建的期间检查 (即使 lint 要检查的问题没有包含在代码中) fatal 'NewApi', 'InlineApi' // 设置给定问题的严重级别为error error 'Wakelock', 'TextViewEdits' // 设置给定问题的严重级别为warning warning 'ResourceAsColor' // 设置给定问题的严重级别(severity)为ignore (和不检查这个问题一样) ignore 'TypographyQuotes' // 如果为 true,则检查所有的问题,包括默认不检查问题 checkAllWarnings true // 重置 lint 配置(使用默认的严重性等设置)。 lintConfig file("default-lint.xml") // 设置为 true,则当有错误时会显示文件的全路径或绝对路径 (默认情况下为true) absolutePaths true } }
注:如果只想对某以特定问题进行检查,可以使用check命令,check命令会覆盖disable和enable命令;同时abortOnError设置为false是必要的,这样可以防止lint检查提前结束。
四、常见问题处理
首先我们需要知道,规则是死的,代码是活的,并非所有的Lint警告都需要通过修改代码来解决,有些警告可以被当成善意的提醒,我们可以通过一些标注来忽略它。
如果是java代码,可以通过注解@SuppressLint("警告名称"),如
@SuppressLint(“HandlerLeak”) @SuppressLint(“all”) //如果不清楚警告名称,可以直接忽略all
如果是xml文件,可以通过属性tools:ignore="警告名称",如
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" tools:ignore="TextFields,HardcodedText,UselessParent"> <!--如果不清楚警告名称,可以直接忽略all --> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" tools:ignore="all">
下面列举一些常见的警告,以及推荐的处理方式:
(1)[Accessibility] Missing contentDescription attribute on image
原因:为了照顾一些视力不好的小伙伴,我们在使用Image相关组件(如ImageView或ImageButton)时,需要添加contentDescription属性,以便通过声音等途径告知图片中的内容。
方案:添加contentDescription属性
(2)To get local formatting use getDateInstance(), getDateTimeInstance(), or getTimeInstance(), or use new SimpleDateFormat(String template, Locale locale) with for example Locale.US for ASCII dates.
(3)Consider using apply() instead; commit writes its data to persistent storage immediately, whereas apply will handle it in the background
(4)This <FrameLayout> can be replaced with a <merge> tag
(5)This Handler class should be static or leaks might occur (anonymous android.os.Handler)
(6)Use new SparseIntArray(...) instead for better performance
(7)Use a layout_height of 0dp instead of fill_parent for better performance
(8)This Cursor should be freed up after use with #close()
(9)This tag and its children can be replaced by one <TextView/> and a compound drawable
(10)android:singleLine is deprecated: Use maxLines="1" instead
(11)Must be one of: Context.POWER_SERVICE, Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE, Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE, Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE
.getSystemService("window");
方案:改为常量
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
(12)@id/message_name can overlap @id/cancel_button if @id/message_name grows due to localized text expansion
android:maxEms="6"
(13)the resource 'R.color.aqua' appears to be unused
原因:无用资源
方案:删除
(14)Avoid object allocations during draw/layout operations (preallocate and reuse instead)
原因:在draw和layout和onMeasure方法中最好不要创建对象,因为这些方法在一次显示过程中会根据父布局的需要不止一次的调用。
方案:将其new方法提取出来。
(15)Avoid using sizes smaller than 12sp: 8sp
原因:避免使用尺寸小于12 sp:8 sp,其实就是想告诉你小于12sp真的太小啦,系统建议你改成12sp,因为他觉得12sp已经很小了,不建议比12sp还小
方案:不要小于12sp
(16)Field can be converted to a local variable
原因:字段可以转换为一个局部变量
方案:转换为一个局部变量


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号