js运算符、优先级
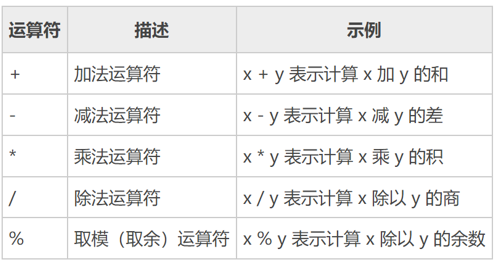
算数运算符
var x=15; var y=10;
console.log(x % y); //5
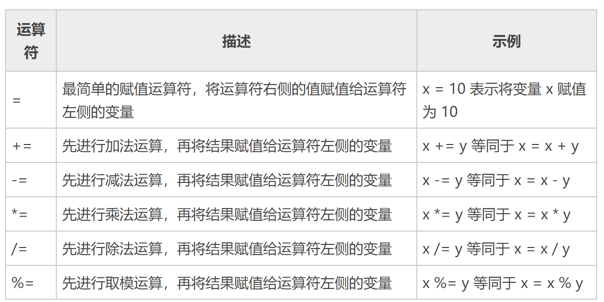
赋值运算符
字符串运算符
+和+=运算符除了可以进行数学运算外,还可以用来拼接字符串,其中: +运算符表示将运算符左右两侧的字符串拼接到一起; +=运算符表示先将字符串进行拼接,然后再将结果赋值给运算符左侧的变量。
var x = "Hello ";
var y = "World!";
x += y;
console.log(x); // 输出:Hello World!
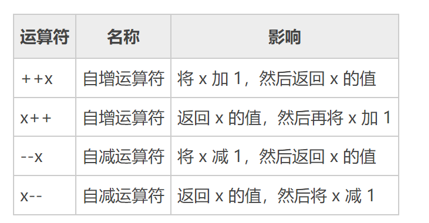
自增自减
var x = 10;
console.log(++x); // 输出:11
console.log(x); // 输出:11
var y = 10;
console.log(y++); // 输出:10
console.log(y); // 输出:11
var b=5;
console.log(b++ + ++b); //5 + (6+1) =12
console.log(b) //7
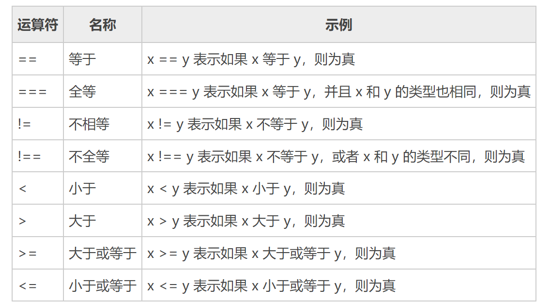
比较运算符
var x = 25;
var z = "25";
console.log(x == z); // 输出: true
console.log(x === z); // 输出: false
逻辑运算符
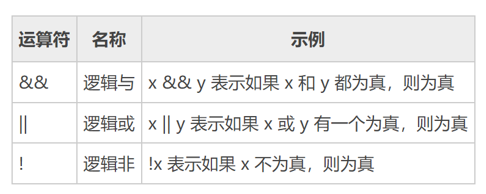
逻辑运算符的运算结果是一个布尔值
var year = 2021;
// 闰年可以被 400 整除,也可以被 4 整除,但不能被 100 整除
if((year % 400 == 0) || ((year % 100 != 0) && (year % 4 == 0))){
console.log(year + " 年是闰年。");
} else{
console.log(year + " 年是平年。");
}
如果运算符两个都是值,不是判断语句
1.表达式1 && 表达式2
第一个表达式值为真,返回第二个表达式
第一个表达式为假,返回第一个表达式
2.表达式1 || 表达式2
第一个表达式值为真,返回第1个表达式
第一个表达式为假,返回第2个表达式
console.log((3 > 4) && 9); //9 console.log(1 && 0); //0 console.log(0 && 1); //0
console.log((3 + 4) || 9); //7 console.log(1 || 0); //1 console.log(0 || 1); //1
console.log(null && 5); //null
console.log(undefined && 7) // undefined
console.log("123" && 8); //8
console.log("" && 8); //""
三元(目)运算符
条件表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2 ;
条件为true,返回表达式1的结果 否则,返回表达式2的结果
var x = 11, y = 20;
x > y ? console.log("x 大于 y") : console.log("x 小于 y"); // 输出:x 小于 y
位运算符(了解)
运算符优先级
运算符的执行顺序称为运算符的优先级,优先级高的运算符先于优先级低的运算符执行运算。
例如: w=x+y*z;
运算符的优先级可以通过使用圆括号来改变
例如为了让加法先执行,乘法后执行,可以修改上面的表达式为: w=(x+y)*z;
优先级 运算符
1 小括号
2 ++ -- !
3 算数运算符 先 * / % 后 + -
4 > >= <
5 == != ===
6 先&& 后 ||
7 =


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号