[Usaco2004Feb]Cow Marathon 树的直径
本人水平有限,题解不到为处,请多多谅解
本蒟蒻谢谢大家观看
题目:传送门
先来说下什么是树的直径
树的直径:一棵树中两个节点所经过的权值和最大即为树的直径,
即树中所有最短路径长度中的最大值
图示:
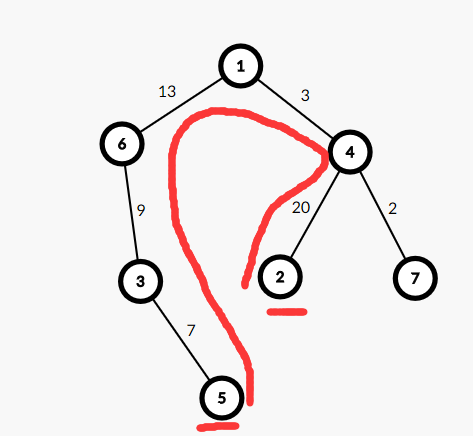
红笔所画的即为树的直径,由 2→5 所经过的所有点为树的直径,权值和为:20+3+13+9+7==52
即ans==52
法一:跑两遍dfs
先从任意一点P出发,找离它最远的点Q,再从点Q出发,找离它最远的点W,W到Q的距离就是树的直径
证明:博客
其实可以根据上面一幅图感性理解一下,分两种情况。
1:若P在直径上,毫无疑问,Q一定在直径的端点上(左右端点),所以保证了W&Q的距离就是树的直径
2:若P不在直径上,例如令P==7时,其Q也一定在直径端点上,这时Q==5,所以也可证明W&Q的距离就是树的直径
先以P为根做一遍dfs,再以Q为根再做一遍dfs,f[Q]为自己到自己的值为0,dfs(Q,0)表示其父亲节点为0
code:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n,m; 4 int tot,ver[100010],edge[100010],head[100010],nxt[100010]; 5 int x,y,z,ans,hhh; 6 char ch; 7 int f[101000]; 8 bool v[1000010]; 9 void add(int x,int y,int z) 10 { 11 ++tot; 12 ver[tot]=y; 13 edge[tot]=z; 14 nxt[tot]=head[x]; 15 head[x]=tot; 16 } 17 inline long long read(){ 18 register long long x(0), f=1; register char c(getchar()); 19 while(c<'0'||'9'<c){ if(c=='-') f=-1; c=getchar(); } 20 while('0'<=c&&c<='9') 21 x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48), c=getchar(); 22 return x*f; 23 } 24 void dfs(int x,int fa) 25 { 26 for(int i=head[x];i;i=nxt[i]) 27 { 28 int y=ver[i],z=edge[i]; 29 if(y==fa)continue; 30 f[y]=f[x]+z; 31 if(f[y]>ans) 32 { 33 ans=f[y]; 34 hhh=y; 35 } 36 dfs(y,x); 37 } 38 } 39 int main() 40 { 41 n=read(); 42 m=read(); 43 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 44 { 45 x=read(); 46 y=read(); 47 z=read(); 48 cin>>ch; 49 add(x,y,z); 50 add(y,x,z); 51 } 52 f[1]=0; 53 dfs(1,0); 54 f[hhh]=0; 55 dfs(hhh,0); 56 cout<<ans; 57 return 0; 58 }
法二:树形dp
对于每个节点我们要记录两个值:
f1 [ i ] 表示以 i 为根的子树中,i 到叶子结点距离的最大值
f2 [ i ] 表示以 i 为根的子树中,i 到叶子结点距离的次大值
对于一个节点,它到叶子结点距离的最大值和次大致所经过的路径肯定是不一样的
这样做就是,先看能否更新最大值,若能,它的次大值就是原先的最大值,再更新它的最大值;若不能,就看能不能更新次大值,若能,就更新,不能就不管它
这样的话,最后的答案 answer = max { f1 [ i ] + f2 [ i ] }
为什么这样做是正确的呢?
我们跑一遍样例
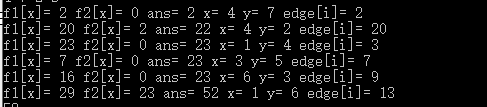
我们可以发现前两个样例是做
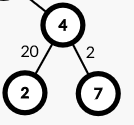
的树的直径,以4为根最大值为20,次大值为2
第三个样例是做以1为根的树上直径
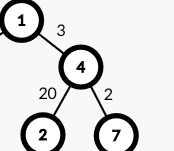
此时以1为根的最大值的链为23,然而因为这时f2[1]没有这个值,所以这时f2[1]为0,此时ans就从4的链转到了1的链来了。
之后就依次类推……

code:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int N=1e6+10; 4 int n,m,tot,ans; 5 int f1[N],f2[N]; 6 int head[N],ver[N],edge[N],nxt[N]; 7 char ch; 8 void add(int x,int y,int z) 9 { 10 tot++; 11 nxt[tot]=head[x]; 12 head[x]=tot; 13 ver[tot]=y; 14 edge[tot]=z; 15 } 16 void dp(int x,int fa) 17 { 18 for(int i=head[x];i;i=nxt[i]) 19 { 20 int y=ver[i]; 21 if(y==fa) 22 continue; 23 dp(y,x); 24 if(f1[x]<f1[y]+edge[i]) 25 { 26 f2[x]=f1[x]; 27 f1[x]=f1[y]+edge[i]; 28 // cout<<"f1[x]= "<<f1[x]<<" f2[x]= "<<f2[x]<<" edge[i]= "<<edge[i]<<" x= "<<x<<" y= "<<y<<endl; 29 } 30 else if(f2[x]<f1[y]+edge[i]) 31 f2[x]=f1[y]+edge[i]; 32 ans=max(ans,f1[x]+f2[x]); 33 //cout<<"f1[x]= "<<f1[x]<<" f2[x]= "<<f2[x]<<" ans= "<<ans<<" x= "<<x<<" y= "<<y<<" edge[i]= "<<edge[i]<<endl; 34 } 35 } 36 int main() 37 { 38 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 39 for(int i=1,x,y,z;i<=m;i++) 40 { 41 scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); 42 add(x,y,z); 43 add(y,x,z); 44 cin>>ch; 45 } 46 dp(1,0); 47 printf("%d",ans); 48 return 0; 49 } 50 /* 51 7 6 52 1 6 13 E 53 6 3 9 E 54 3 5 7 S 55 4 1 3 N 56 2 4 20 W 57 4 7 2 S 58 */

