dls的数论-Lucas定理及扩展
Lucas定理
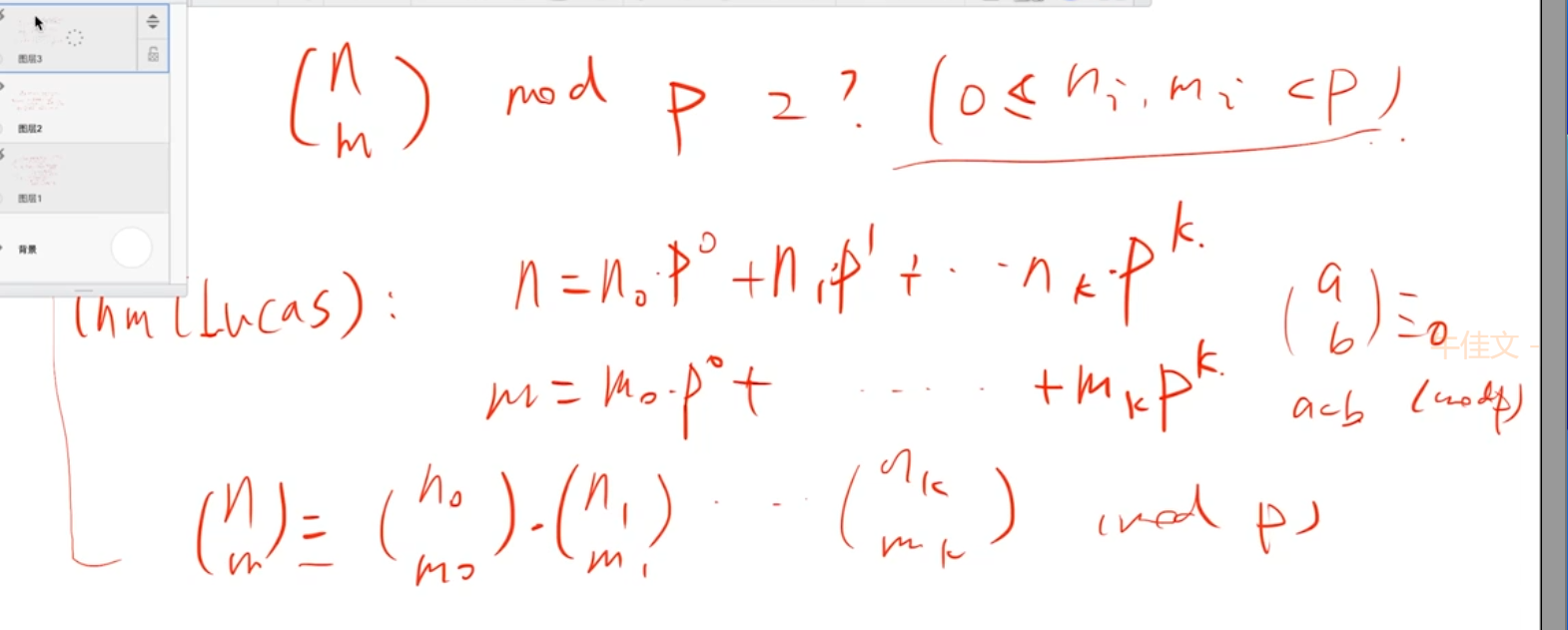
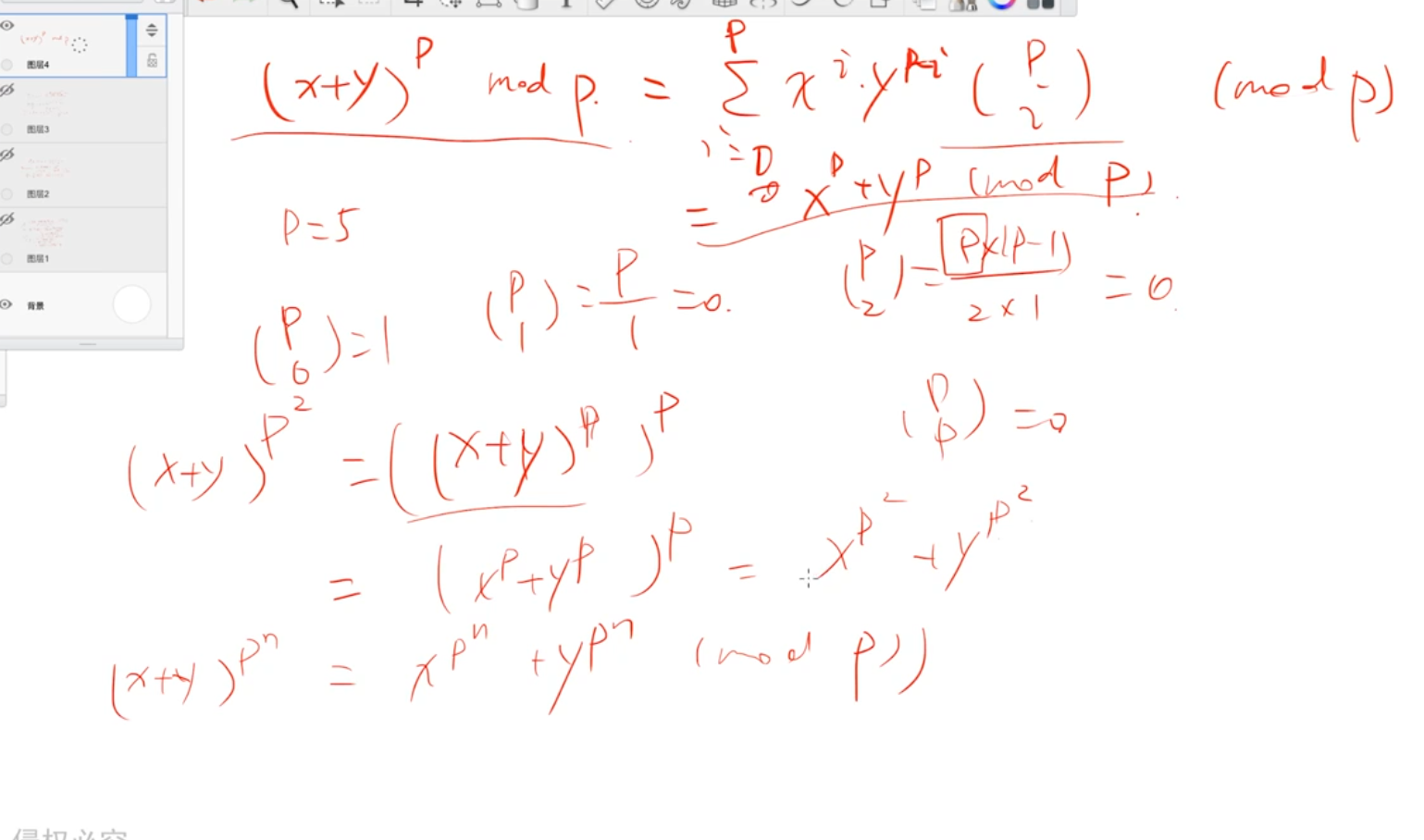

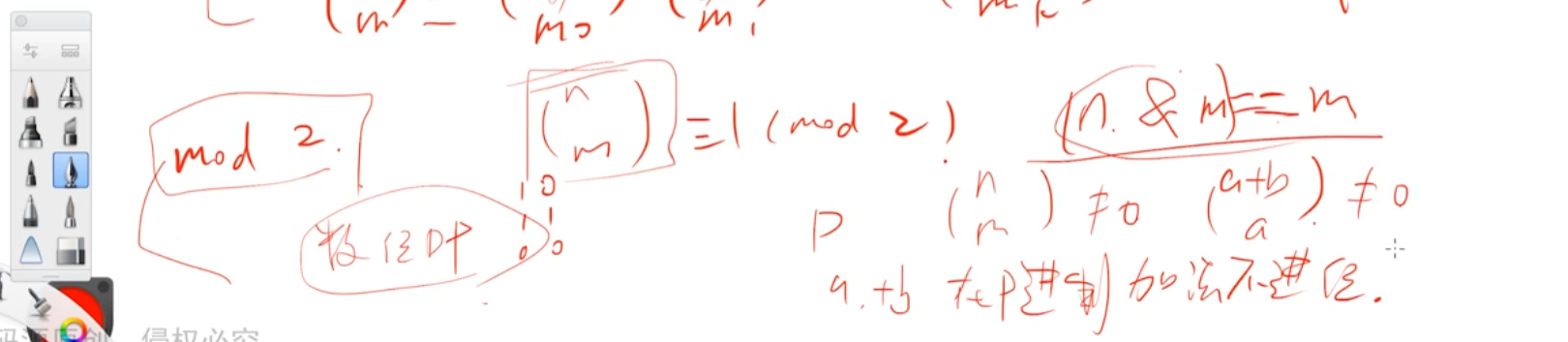
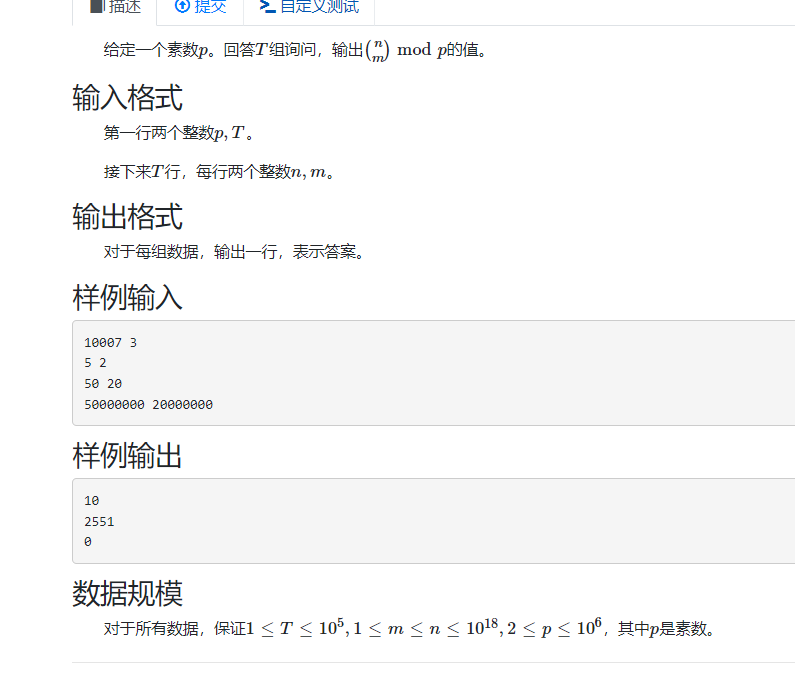
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int fac[N], inv[N];
LL p, T;
LL qmi(LL a, LL b, LL mod){
LL res = 1 % mod;
while(b){
if(b&1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
LL C(LL a, LL b){
if(b < 0 || b > a) return 0;
return (LL)fac[a] * inv[b] % p * inv[a - b] % p;
}
int main(){
scanf("%lld%lld", &p, &T);
fac[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= p - 1; i ++) fac[i] = (LL)fac[i - 1] * i % p;
inv[p - 1] = qmi(fac[p - 1], p - 2, p);
for(int i = p - 2; i >= 0; i --) inv[i] = (LL)inv[i + 1] * (i + 1) % p;
while(T--){
LL n, m; scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
LL ans = 1;
while( n > 0 || m > 0){
ans = ans * C(n % p, m % p) % p;
n /= p; m /= p;
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6+10;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
PII pq[N];
LL A[N], B[N], ans[N];
int fac[N], phipe, pr[N];
LL qmi(LL a, LL b, LL mod){
LL res = 1 % mod;
while(b){
if(b&1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
LL cntp, cnts;
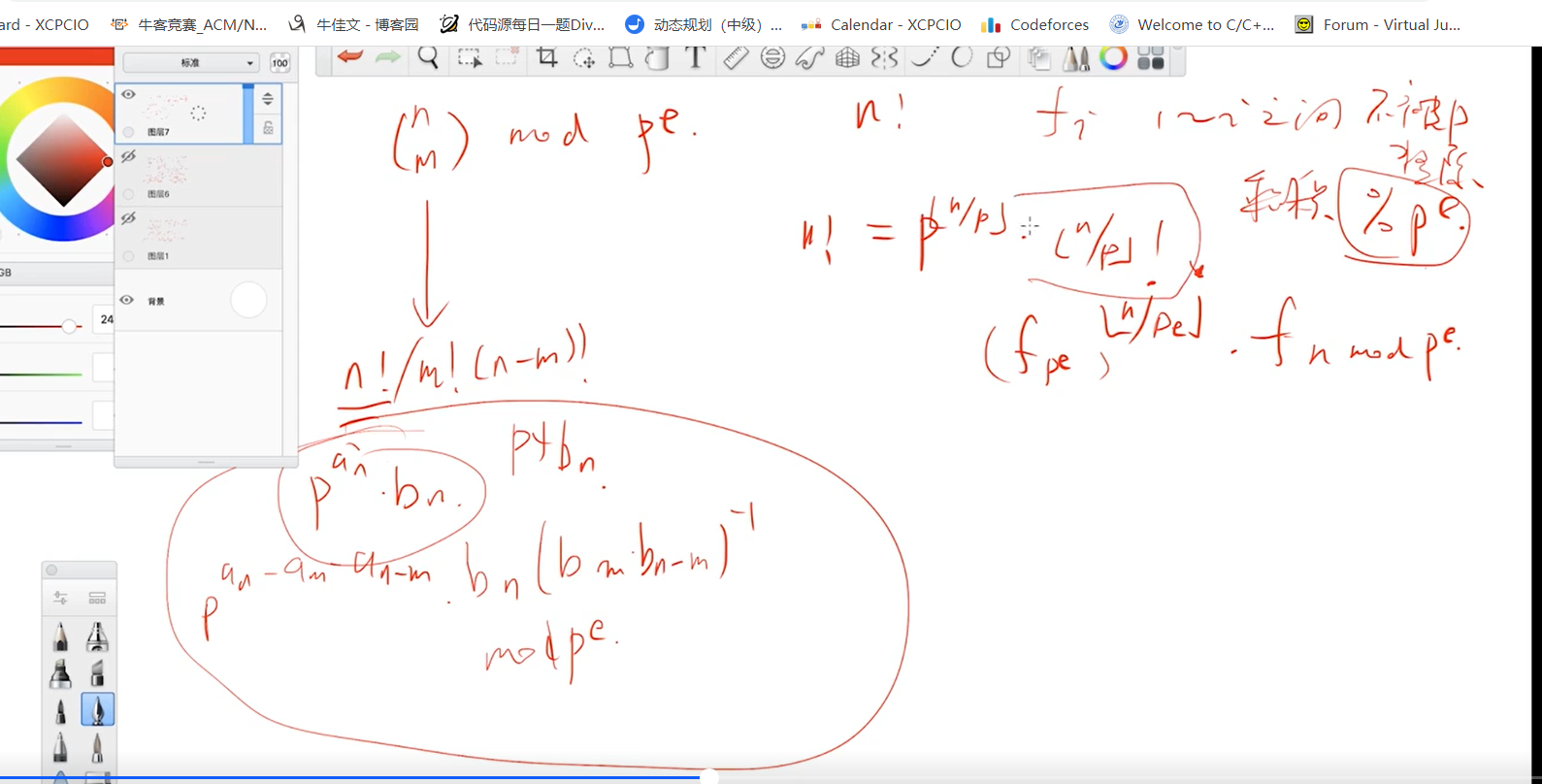
LL calc(LL a, LL p, LL pe, int w){
LL val = 1;
while(a){
cntp += a / p * w;
cnts += a / pe * w;
val = val * fac[a % pe] % pe;
a /= p;
}
return val;
}
LL C(LL a, LL b, LL p, LL pe){
cntp = 0, cnts = 0;
auto f1 = calc(a, p, pe, 1);
auto f2 = calc(b, p, pe, -1);
auto f3 = calc(a - b, p, pe, -1);
LL v1 = f1 * qmi(f2 * f3 % pe, phipe - 1, pe) % pe;
LL v2 = qmi(p, cntp, pe);
LL v3 = qmi(fac[pe], cnts, pe);
return v1 * v2 % pe * v3 % pe;
}
int main(){
int q, T;
scanf("%d %d", &q, &T);
int M = q, t = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= q; i ++){
if(q % i == 0){
int pe = 1;
while(q % i == 0) q /= i, pe *= i;
pq[t ++] = {i, pe};
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < t; i ++){
int pe = pq[i].second;
for(int j = 0; j < M; j ++){
if(j % pe == 1 && j % (M / pe) == 0){
pr[i] = j;
break;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < T; i ++) scanf("%lld %lld", &A[i], &B[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < t; i ++){
int p = pq[i].first, pe = pq[i].second;
fac[0] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= pe; j ++){
if(j % p == 0) fac[j] = fac[j - 1];
else fac[j] = (LL)fac[j - 1] * j % pe;
}
phipe = (LL)pe * (p - 1) / p;
for(int j = 0; j < T; j ++){
ans[j] = (ans[j] + C(A[j], B[j], p, pe) * pr[i] % M) % M;
}
}
for(int j = 0; j < T; j ++) printf("%lld\n", ans[j]);
return 0;
}


#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int n, G, pr[N];
PII pq[N];
int A[N], B[N], fac[N], phipe;
LL ans;
LL qmi(LL a, LL b, LL mod){
LL res = 1 % mod;
while(b){
if(b&1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
LL cntp, cnts;
LL calc(LL a, LL p, LL pe, int w){
LL val = 1;
while(a){
cntp += a / p * w;
cnts += a / pe * w;
val = val * fac[a % pe] % pe;
a /= p;
}
return val;
}
LL C(LL a, LL b, LL p, LL pe){
cntp = 0, cnts = 0;
LL f1 = calc(a, p, pe, 1);
LL f2 = calc(b, p, pe, -1);
LL f3 = calc(a - b, p, pe, -1);
LL v1 = f1 * qmi(f2 * f3 % pe, phipe - 1, pe) % pe;
LL v2 = qmi(p, cntp, pe);
LL v3 = qmi(fac[pe], cnts, pe);
return v1 * v2 % pe * v3 % pe;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &G);
if(G % 999911659 == 0){
puts("0");
return 0;
}
int M = 999911659 - 1, t = 0;
int m = M;
for(int i = 2; i <= m; i ++){
if(m % i == 0){
int pe = 1;
while(m % i == 0) m /= i, pe *= i;
pq[t ++] = {i, pe};
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < t; i ++){
int pe = pq[i].second;
int Mi = M / pe;
for(int j = 0; j < M; j += Mi){
if(j % pe == 1){
pr[i] = j; break;
}
}
}
int T = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n / i; i ++){
if(n % i == 0){
A[T] = n, B[T ++] = i;
if(n / i != i) A[T] = n, B[T ++] = n / i;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < t; i ++){
int p = pq[i].first, pe = pq[i].second;
fac[0] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= pe; j ++){
if(j % p == 0) fac[j] = fac[j - 1];
else fac[j] = (LL) fac[j - 1] * j % pe;
}
phipe = (LL)pe * (p - 1) / p;
for(int j = 0; j < T; j ++){
ans = ( ans + (LL)C(A[j], B[j], p, pe) * pr[i] % M ) % M;
}
}
printf("%lld\n", qmi(G, ans, 999911659));
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int n, G, pr[N];
PII pq[N];
int fac[N], phipe;
PII A[N];
int T;
LL ans;
LL qmi(LL a, LL b, LL mod){
LL res = 1 % mod;
while(b){
if(b&1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
LL cntp, cnts;
LL calc(LL a, LL p, LL pe, int w){
LL val = 1;
while(a){
cntp += a / p * w;
cnts += a / pe * w;
val = val * fac[a % pe] % pe;
a /= p;
}
return val;
}
LL C(LL p, LL pe){
cntp = 0, cnts = 0;
LL v1 = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < T; i ++){
LL f = calc(A[i].first, p, pe, A[i].second);
v1 = v1 * qmi(f, phipe + A[i].second, pe) % pe;
}
LL v2 = qmi(p, cntp, pe);
LL v3 = qmi(fac[pe], cnts, pe);
return v1 * v2 % pe * v3 % pe;
}
int main(){
int m; scanf("%d", &m);
int M = m;
int t = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= m; i ++){
if(m % i == 0){
int pe = 1;
while(m % i == 0) m /= i, pe *= i;
pq[t ++] = {i, pe};
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < t; i ++){
int pe = pq[i].second;
int Mi = M / pe;
for(int j = 0; j < M; j += Mi){
if(j % pe == 1){
pr[i] = j; break;
}
}
}
int s, cnt2; scanf("%d %d", &s, &T);
T ++; A[0] = {s, 1};
for(int i = 1; i < T; i ++){
int a; scanf("%d", &a);
A[i] = {a, -1};
s -= a;
}
if(s < 0){
puts("Impossible");
return 0;
}
if(s > 0) A[T ++] = {s, -1};
for(int i = 0; i < t; i ++){
int p = pq[i].first, pe = pq[i].second;
fac[0] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= pe; j ++){
if(j % p == 0) fac[j] = fac[j - 1];
else fac[j] = (LL) fac[j - 1] * j % pe;
}
phipe = (LL)pe * (p - 1) / p;
ans += C(p, pe) * pr[i];
ans %= M;
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}

