es之文档更新过程中并发冲突问题
ES是分布式的,也是异步并发的,我们的复制请求是并行发送的;这就意味着请求到达目的地的顺序是不可控制的,是乱序的;
如果是乱序的方式,很有可能出现这样的一个问题,新version的文档被旧version的文档覆盖掉—-数据丢失,或者直接抛异常;
TransportClient client = null;

Elasticsearch使用这个 _version 号来确保变更以正确顺序得到执行。如果旧版本的文档在新版本之后到达,它可以被简单的忽略。
我们可以利用 _version 号来确保 应用中相互冲突的变更不会导致数据丢失。我们通过指定想要修改文档的 version 号来达到这个目的。 如果该版本不是当前版本号,我们的请求将会失败。
新建一个文档,这个时候我们可以看到新文档的版本号_version=1:
PUT /website/blog/1/_create
{
"title" : "this is title" ,
"txt" : "just do it"
}
现在尝试通过重建文档索引来保存修改数据:
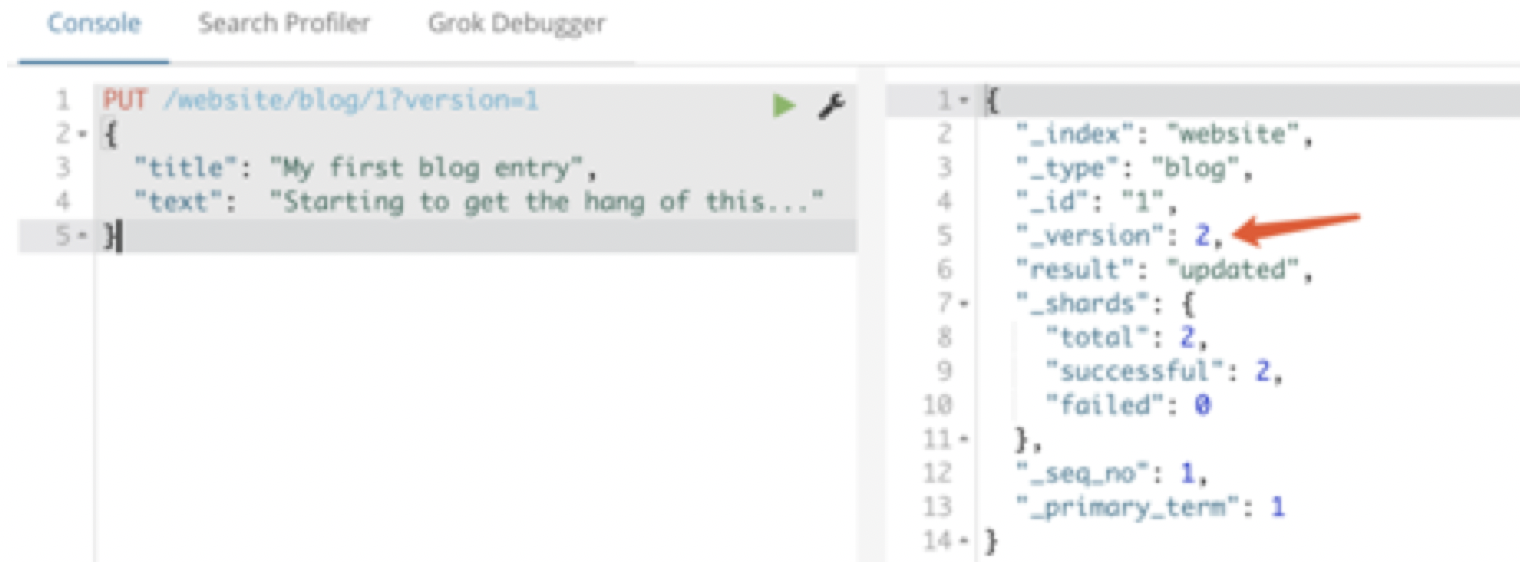
请求成功,并且响应体告诉我们 _version 已经递增到 2
PUT /website/blog/1?version=1
{
"title" : "this is test" ,
"txt" : "just do it"
}
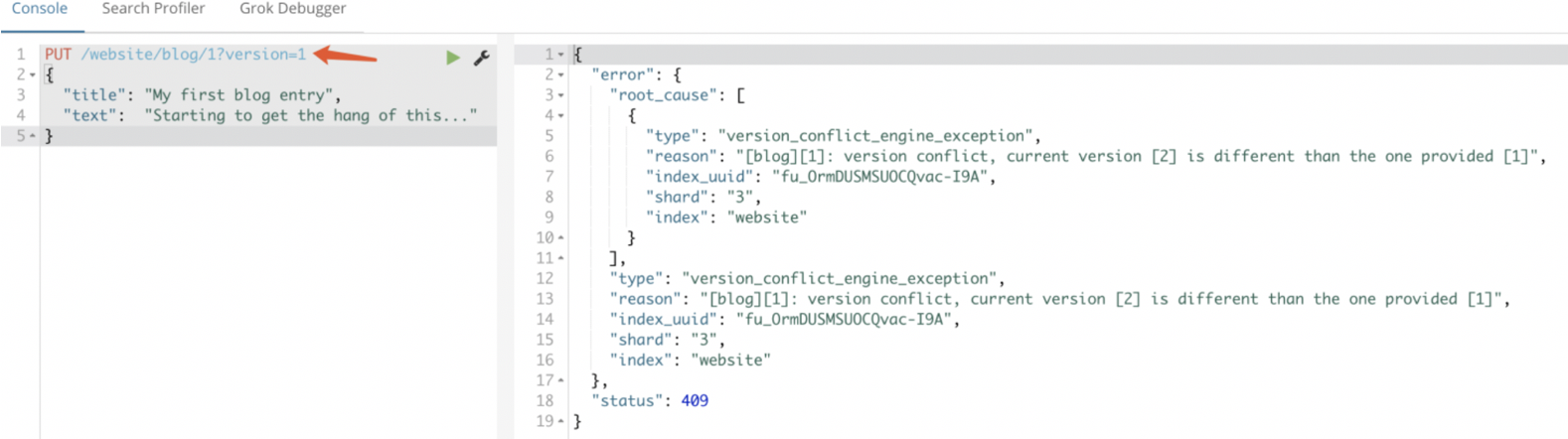
然而,如果我们重新运行相同的索引请求,仍然指定 version=1 , Elasticsearch 返回 409 ConflictHTTP 响应码,和一个如下所示的响应体:
以上通过version的控制,可以让es在并行情况下操作而不出现丢失数据的现象,这种乐观锁的操作是比较常用的;
上面我们讲到的是基于version进行版本的控制。在分布式环境下,只要version不同,那么修改就会报错;
而通过外部系统进行控制:version_type=external,只有当你提供的version比es中的_version大的时候,才能完成修改
| _version | version_type=external |
|---|---|
| 只有_versioin相同,才会执行修改 | 只有当你提供的version比es中的_version大的时候,才能完成修改 |
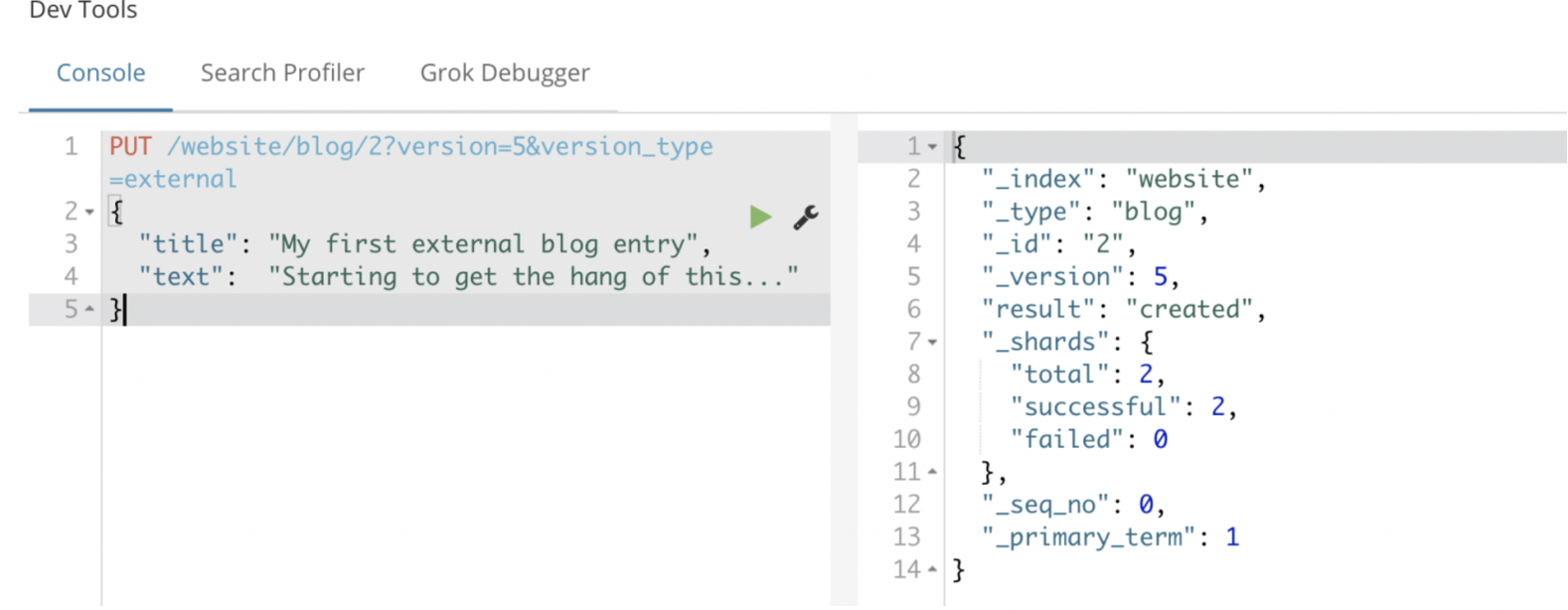
例如,要创建一个新的具有外部版本号 5 的博客文章,我们可以按以下方法进行:
PUT /website/blog/2?version=5&version_type=external
{
"title": "My first external blog entry",
"text": "Starting to get the hang of this..."
}
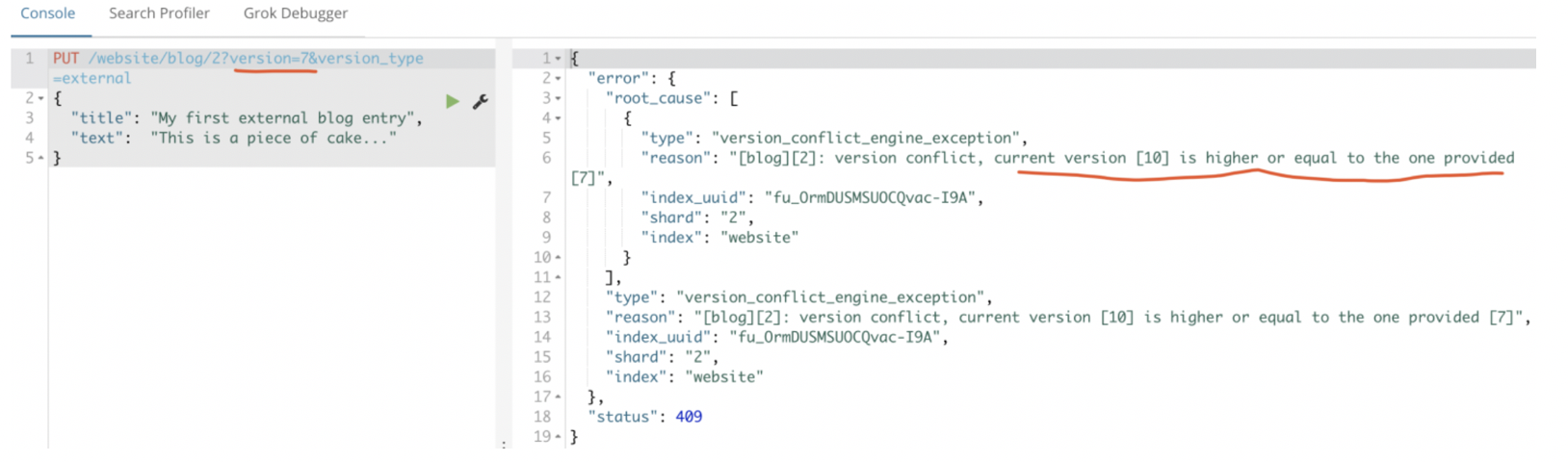
现在我们更新这个文档,指定一个新的 version 号是 10 :
PUT /website/blog/2?version=10&version_type=external
{
"title": "My first external blog entry",
"text": "This is a piece of cake..."
}

version_type=external能够修改的条件就是:提供的版本号必须比_version大
如果此时插入版本号比现在的_version小的,就会报错:
3:重复提交retry_on_conflict
elasticsearch设计的目的就是多用户的海量数据操作;
那么可能存在这样场景:A进程接收到请求尝试去检索(retrieve)和重建索引(reindex)某个文档C,B进程也接收到请求检索(retrieve)和重建索引(reindex)文档C;
那么这个时候就会出现:其中一个进程提前修改了文档C,然后另一个进程在做检索的时候,因为_version改变了,所以匹配不到文档C,操作就会失败,然后数据丢失
这就是在并发操作的时候经常出现的现象;
解决:
对于多用户的更新操作,文档被修改了并不要紧,如果出现了匹配不到的现象,我们只要重新在操作一遍就可以了;所以需要使用关键字retry_on_conflict(默认0)
POST /website/pageviews/1/_update?retry_on_conflict=5
{
"script" : "ctx._source.views+=1",
"upsert": {
"views": 0
}
}
retry_on_conflict=5 代表如果出现失败,最大可以重复五次的update操作
5.7.6:悲观锁控制【无用】
类似传统数据库————mysql,在处理并发的时候,为了防止出现冲突的问题,就会使用悲观锁;
这种方法被关系型数据库广泛使用,它假定有变更冲突可能发生,因此阻塞访问资源以防止冲突。
一个典型的例子是读取一行数据之前先将其锁住,确保只有放置锁的线程能够对这行数据进行修改(想想java中的synchronize)。
5.7.6.1:全局锁(无用)
只允许一个线程进行执行更新操作,这样能够避免并发性问题,在es中,全局锁是将一份文档是否存在作为依据
获取一个全局锁:
PUT website/blog/1/_create
{}
这样就上锁了,然后使用java的多线程做测试,在里面修改数据
TransportClient client = null;
如果另一个进行想同时在创建一个website/blog/1 就会抛异常
释放全局锁:
全局锁必须通过删除来释放:
DELETE website/blog/1
优点:操作非常简单,非常容易使用,成本低 缺点:你直接就把整个index给上锁了,这个时候对index中所有的doc的操作,都会被block住,导致整个系统的并发能力很低
5.7.6.2:document文档锁(无用)
这种锁比全局锁的粒度小,因为全局锁是锁定整个index,那么文档所就是针对单个文档完成锁定
上锁的方式依赖groovy脚本:/config/scripts
vim documentLock.groovy 【脚本需要上传到所有节点】
if ( ctx._source.process_id != process_id ) { assert false }; ctx.op = 'noop';
脚本的意思:
如果当前传入的process_id和设定的process_id不一致,就抛异常assert false
如果一致的,返回'noop'
插入一个文档:
PUT website/blog/1
{
"id" : 1,
"process_id" : 234
}
对当前文档上文档锁:
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"upsert": { "process_id": 234 },
"script": {
"lang": "groovy",
"file": "documentLock",
"params": {
"process_id": 234
}
}
}
注意,当前设定的"process_id": 234,如果此时换一个"process_id" : 123,那么就会抛异常:assert false
比如:
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"upsert": { "process_id": 123 },
"script": {
"lang": "groovy",
"file": "documentLock",
"params": {
"process_id": 123
}
}
}
注意:如果传入的是"process_id": 234,传入正确参数,直接返回ctx.op = 'noop'
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"upsert": { "process_id": 234 },
"script": {
"lang": "groovy",
"file": "documentLock",
"params": {
"process_id": 234
}
}
}
如何释放悲观锁 , 删除对应的process_id数据即可:
DELETE website/blog/1
{
"query": {
"term": {
"process_id": 234
}
}
}
文档级锁可以实现细粒度的访问控制,但是当文档数量达到百分甚至上千万的时候,这种方式开销是比较昂贵的
5.7.6.3:共享锁和排它锁(无用)
共享锁:数据是共享的,多个线程可以获取同一个数据的共享锁,然后对这个数据执行读操作 排它锁:只能有一个线程获取排它锁,然后执行更新操作
在config/scripts下 vim gongxiang_paita.groovy
if (ctx._source.lock_type == 'exclusive') {
assert false
} else {
ctx._source.lock_count++
}
脚本意思:
如果其他线程共享:ctx._source.lock_count++
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"upsert": {
"lock_type": "shared",
"lock_count": 1
},
"script": {
"lang": "groovy",
"file": "gongxiang_paita"
}
}
如果其他线程添加排他锁'exclusive',那么抛异常:
(1):将共享share标记修改成排他exclusive标记
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"doc" : {
"lock_type": "exclusive"
}
}
(2):修改成排他标记后,在尝试共享修改操作,报错
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"upsert": {
"lock_type": "shared",
"lock_count": 1
},
"script": {
"lang": "groovy",
"file": "gongxiang_paita"
}
}
如何释放锁:
Vim unlock.groovy
if (ctx._source.lock_type == "shared") {ctx._source.lock_count --};
if (ctx._source.lock_count == 0) { ctx.op = 'delete' };
脚本意思:
ctx._source.lock_type == "shared" 则lock_count—
当lock_count == 0,那么删除/website/blog/1
(1):GET website/blog/1 查看一下,当前是共享锁还是排它锁;
(2): 如果是排他锁,需要修改会共享锁
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"doc" : {
"lock_type": "shared"
}
}
(3):释放共享锁
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"upsert": {
"lock_type": "shared",
"lock_count": 1
},
"script": {
"lang": "groovy",
"file": "unlock"
}
}
这样就释放了共享锁;


