std::vector::push_back()
定义:
void push_back (const value_type& val);
作用:
Add element at the end
Adds a new element at the end of the vector, after its current last element. The content of val is copied (or moved) to the new element.
注意:
This effectively increases the container size by one, which causes an automatic reallocation of the allocated storage space if -and only if- the new vector size surpasses the current vector capacity.
说明:
如果是push_back(container),会发生容器元素的复制 (这里的container指的是vector、map...)
参考---cplusplus.com
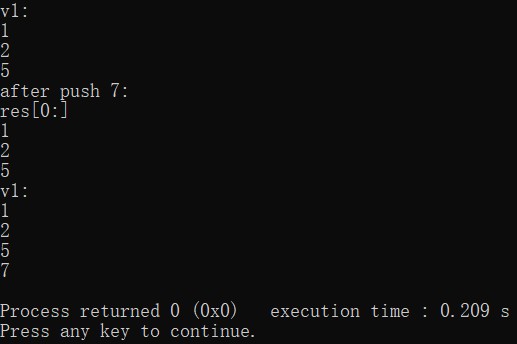
实验1:
源码:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
vector<int>& v=v1;
v.push_back(5);
cout<<"v1:"<<endl;
for(int i:v1) {
cout<<i<<endl;
}
res.push_back(v1);
cout<<"after push 7:"<<endl;
v.push_back(7);
cout<<"res[0:]"<<endl;
for(int i:res[0]) {
cout<<i<<endl;
}
cout<<"v1:"<<endl;
for(int i:v1) {
cout<<i<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果:
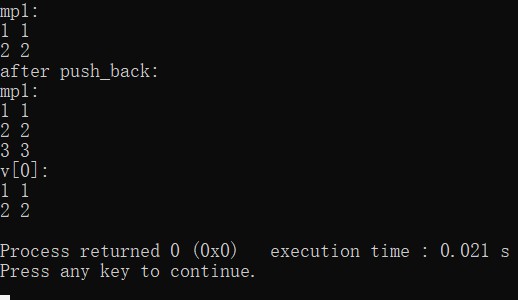
实验二:
源码:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<map<int,int>> v;
map<int,int> mp1;
mp1.insert(std::pair<int,int>(1,1));
mp1.insert(std::pair<int,int>(2,2));
cout<<"mp1:"<<endl;
for(std::pair<int,int> e:mp1) {
cout<<e.first<<" "<<e.second<<endl;
}
v.push_back(mp1);
mp1.insert(std::pair<int,int>(3,3));
cout<<"after push_back:"<<endl;
cout<<"mp1:"<<endl;
for(std::pair<int,int> e:mp1) {
cout<<e.first<<" "<<e.second<<endl;
}
cout<<"v[0]:"<<endl;
for(std::pair<int,int> e:v[0]) {
cout<<e.first<<" "<<e.second<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果: