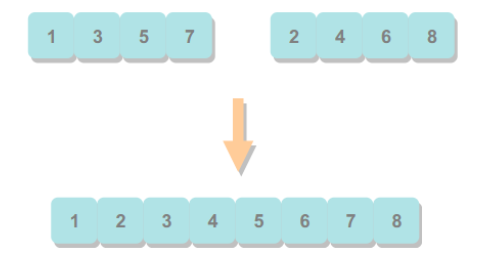
归并排序
归并排序的思想是将数组分成两部分,分别进行排序,然后归并起来
1 public class MergeSort { 2 public void mergeSort(int[] num, int start, int end) { 3 if (start < end) { 4 int mid = (start + end) / 2; 5 mergeSort(num, start, mid); 6 mergeSort(num, mid + 1, end); 7 merge(num, start, mid, end); 8 } 9 } 10 public void merge(int[] num,int start, int mid, int end){ 11 int[] tempArray = new int[end - start + 1]; 12 int p1 = start; 13 int p2 = mid + 1; 14 int p = 0; 15 while (p1 <= mid && p2 <= end){ 16 if (num[p1] <= num[p2]){ 17 tempArray[p++] = num[p1++]; 18 }else { 19 tempArray[p++] = num[p2++]; 20 } 21 } 22 while (p1 <= mid){ 23 tempArray[p++] = num[p1++]; 24 } 25 while (p2 <= end){ 26 tempArray[p++] = num[p2++]; 27 } 28 for (int i = 0;i < tempArray.length;i++){ 29 num[start + i] = tempArray[i]; 30 } 31 } 32 33 public void mergeSort(int[] num){ 34 mergeSort(num,0,num.length - 1); 35 } 36 37 public static void main(String[] args) { 38 MergeSort mergeSort = new MergeSort(); 39 int[] array={5,8,6,7,9,4,3,2,1}; 40 mergeSort.mergeSort(array); 41 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); 42 } 43 }
快速排序
快速排序通过一个切分元素将数组分为两个子数组,左子数组小于等于切分元素,右子数组大于等于切分元素,将这两个子数组排序也就将整个数组排序了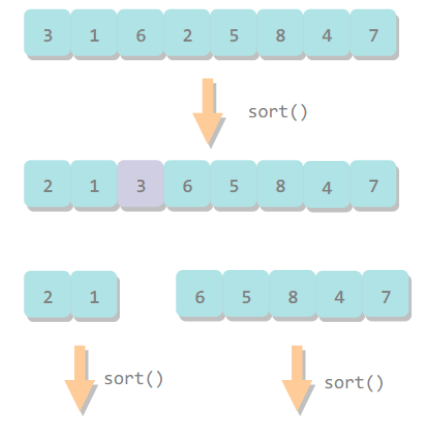
public class QuickSort { private int partition(int[] num, int start, int end) { int pivot = num[start]; int left = start; int right = end; while (left != right) { while (left < right && num[right] > pivot) { right--; } while (left < right && num[left] <= pivot) { left++; } if (left < right) { int p = num[right]; num[right] = num[left]; num[left] = p; } } int p = num[left]; num[left] = num[start]; num[start] = p; return left; } public void quickSort(int[] num, int start, int end) { if (start >= end) { return; } int pivotIndex = partition(num, start, end); quickSort(num, start, pivotIndex - 1); quickSort(num, pivotIndex + 1, end); } public void quickSort(int[] num) { quickSort(num, 0, num.length - 1); } public static void main(String[] args) { QuickSort quickSort = new QuickSort(); int[] num = {4,7,6,5,3,2,8,1}; quickSort.quickSort(num); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num)); } }
堆排序
把最大元素和当前堆中数组的最后一个元素交换位置,并且不删除它,那么就可以得到一个从尾到头的递减序列,从正向来看就是一个递增序列,这就是堆排序
构建堆
无序数组建立堆最直接的方法是从左到右遍历数组进行上浮操作
一个更高效的方法是从右至左进行下沉操作,如果一个节点的两个节点都已经是堆有序,那么进行下沉操作可以使得这个节点为根节点的堆有序
叶子节点不需要进行下沉操作,可以忽略叶子节点的元素,因此只需要遍历一半的元素即可
public class HeapSort { public void downAdjust(int[] num, int parentIndex,int length){ int temp = num[parentIndex]; int childIndex = 2*parentIndex + 1; while (childIndex < length){ if (childIndex + 1 < length && num[childIndex + 1] > num[childIndex]){ childIndex++; } if (temp >= num[childIndex]){ break; } num[parentIndex] = num[childIndex]; parentIndex = childIndex; childIndex = 2 * parentIndex + 1; } num[parentIndex] = temp; } public void heapSort(int[] num){ for (int i = (num.length - 2)/ 2;i >= 0;i--){ downAdjust(num,i, num.length); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num)); for (int i = num.length - 1;i > 0;i--){ int p = num[i]; num[i] = num[0]; num[0] = p; downAdjust(num,0,i); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1,3,2,6,5,4,7,8,9,10,0}; HeapSort heapSort = new HeapSort(); heapSort.heapSort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); } }
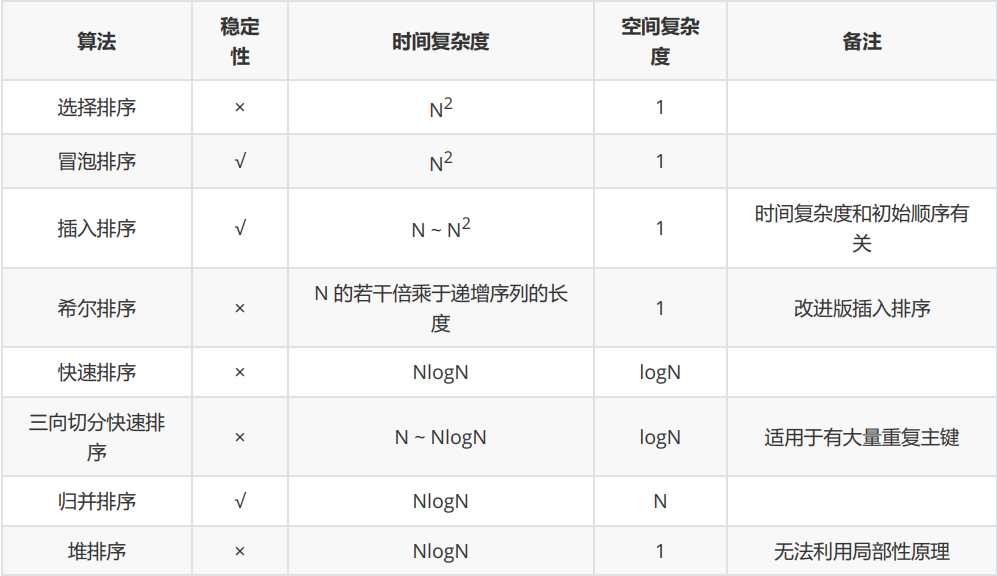
排序有哪些?
什么排序O(N2),什么排序O(NlogN),什么排序稳定,什么排序不稳定
快排,归并原理,可以做到稳定吗
数据结构中散列表说一下?Hash冲突有什么解决方法?


