纯C 实现 strpos substr strspilt str_trim
在C 语言中没有C++ 好用的 spilt 方法 (STL 带的也不怎么好用)
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int Cstrpos(char *haystack, const char *needle) 7 { 8 char *p; 9 p = strstr(haystack, needle); 10 if(p) 11 { 12 return p - haystack; 13 } 14 return -1; 15 } 16 17 int Csubstr(char *haystack, int start, int len, char *out) 18 { 19 int i; 20 for(i=0; i<len; i++) 21 { 22 out[i] = haystack[start+i]; 23 } 24 return 0; 25 } 26 27 char *Csplit(char *haystack, const char *needle, char *out) 28 { 29 int start, end, offset, i; 30 //match start 31 if(0 == memcmp(haystack, needle, strlen(needle))) 32 { 33 start = Cstrpos(haystack, needle); 34 if(-1 == start) 35 { 36 return NULL; 37 } 38 } 39 else 40 { 41 start = 0; 42 } 43 end = Cstrpos(haystack+start, needle); 44 if(-1 == end) 45 { 46 end = strlen(haystack) - start; 47 } 48 offset = end; 49 50 for(i=0; i<offset; i++) 51 { 52 out[i] = haystack[i]; 53 } 54 haystack += i+1; 55 56 return haystack; 57 } 58 59 int main(int argc, char **argv) 60 { 61 //char *str = "123,456,789"; //2个测试字符串 62 char *str = "123"; 63 cout<<str<<endl; 64 65 int pos1; 66 pos1 = Cstrpos(str, ","); 67 cout<<pos1<<endl; 68 69 char out[10] = {0}; 70 71 //Csubstr(str, 1, 3, out); 72 //cout<<out<<endl; 73 74 cout<<"+++++++++++++++++++++"<<endl; 75 76 memset(out, 0, 10); 77 str = Csplit(str, ",", out); 78 cout<<out<<endl; 79 80 cout<<"+++++++++++++++++++++"<<endl; 81 82 memset(out, 0, 10); 83 str = Csplit(str, ",", out); 84 cout<<out<<endl; 85 86 87 cout<<"+++++++++++++++++++++"<<endl; 88 89 memset(out, 0, 10); 90 str = Csplit(str, ",", out); 91 cout<<out<<endl; 92 93 cout<<"+++++++++++++++++++++"<<endl; 94 95 memset(out, 0, 10); 96 str = Csplit(str, ",", out); 97 cout<<out<<endl; 98 99 return 0; 100 }
因为也包含了测试程序 使用 cout 输出,所以使用 g++ 编译,执行。但3个函数是 可以移值到 ARM 、 KEIL、STM32 中的。
测试123,456,789

测试123
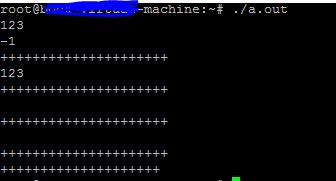
这个,目前还有一个缺点,分隔符只支持1个字符。
补发一个,实现的 str_trim 函数 需要头文件 #include <ctype.h>
1 static void str_trim(char *str) 2 { 3 int len; 4 char *copy; 5 char *end, *start; 6 7 len = strlen(str); 8 copy = (char *)malloc(len + 1); 9 10 if(! copy) 11 { 12 logd("malloc error \n"); 13 return ; 14 } 15 16 memset(copy, 0, len + 1); 17 strcpy(copy, str); 18 start = copy; 19 end = start + len - 1; 20 21 while(end >= start) 22 { 23 if(! isgraph(*end)) 24 { 25 *end = '\0'; 26 end--; 27 } 28 else 29 { 30 break; 31 } 32 } 33 34 len = strlen(copy); 35 end = start + len - 1; 36 while(start <= end) 37 { 38 if(! isgraph(*start)) 39 { 40 start++; 41 } 42 else 43 { 44 break; 45 } 46 } 47 48 strcpy(str, start); 49 free(copy); 50 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号