实验1 现代C++编程初体验
一、实验目的
- 体验现代C++标准库、算法库用法
- 灵活组合使用现代C++基础语言特性(数据表示、分支、循环、函数)和标准库,编程解决简单、基础问题
- 编程代码过程中,注意编码素养。关注代码表达,提升代码的可读性、易于维护性
二、实验准备
- 完整的c程序结构和书写规范。
- C程序的编写、编译、运行、调试方法。
- C语言中标识符命名规则、常量、变量;运算符、表达式及其混合计算规则。
三、实验内容
1. 实验任务1
以下为task1.cpp的源代码
1 // 现代C++标准库、算法库体验 2 // 本例用到以下内容: 3 // 1. 字符串string, 动态数组容器类vector、迭代器 4 // 2. 算法库:反转元素次序、旋转元素 5 // 3. 函数模板、const引用作为形参 6 7 #include <iostream> 8 #include <string> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 12 using namespace std; 13 14 // 声明 15 // 模板函数声明 16 template<typename T> 17 void output(const T &c); 18 19 // 普通函数声明 20 void test1(); 21 void test2(); 22 void test3(); 23 24 int main() { 25 cout << "测试1: \n"; 26 test1(); 27 28 cout << "\n测试2: \n"; 29 test2(); 30 31 cout << "\n测试3: \n"; 32 test3(); 33 } 34 35 // 函数实现 36 // 输出容器对象c中的元素 37 template <typename T> 38 void output(const T &c) { 39 for(auto &i: c) 40 cout << i << " "; 41 cout << endl; 42 } 43 44 // 测试1 45 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、string反转字符串 46 void test1() { 47 string s0{"0123456789"}; 48 cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl; 49 50 string s1{s0}; 51 reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end()); // 反转指定迭代器区间的元素 52 cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl; 53 54 string s2{s0}; 55 reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin()); // 将指定迭代区间的元素拷贝到指定迭代器开始的目标区间,并且在复制过程中反转次序 56 cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; 57 } 58 59 // 测试2 60 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector反转动态数组对象vector内数据 61 void test2() { 62 vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9}; 63 cout << "v0: "; 64 output(v0); 65 66 vector<int> v1{v0}; 67 reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end()); 68 cout << "v1: "; 69 output(v1); 70 71 vector<int> v2{v0}; 72 reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin()); 73 cout << "v2: "; 74 output(v2); 75 } 76 77 // 测试3 78 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector实现元素旋转移位 79 void test3() { 80 vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 81 cout << "v0: "; 82 output(v0); 83 84 vector<int> v1{v0}; 85 rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end()); // 旋转指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())之间的数据项,旋转后从迭代器v1.begin()+1位置的数据项开始 86 cout << "v1: "; 87 output(v1); 88 89 vector<int> v2{v0}; 90 rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end()); 91 cout << "v2: "; 92 output(v2); 93 94 vector<int> v3{v0}; 95 rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end()-1, v3.end()); 96 cout << "v3: "; 97 output(v3); 98 99 vector<int> v4{v0}; 100 rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end()-2, v4.end()); 101 cout << "v4: "; 102 output(v4); 103 }
运行结果:
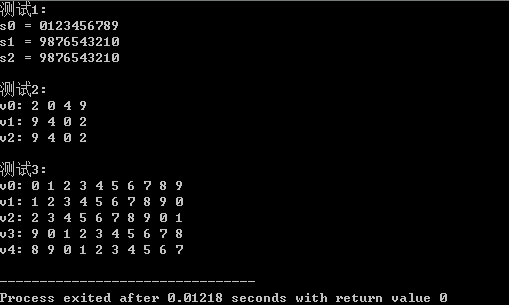
总结:
C++自带的算法库,在进行STL的使用后能大大简化代码和加快编程效率。对于字符串、容器内数据操作来说,反转元素次序(reverse)、旋转元素(rotate),排序(sort)的使用频率比较高,可以高效解决需要设计简单算法的一些编程问题。
2. 实验任务2
以下为task2.cpp的源代码
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <numeric> 6 #include <iomanip> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 // 函数声明 11 // 模板函数声明 12 template<typename T> 13 void output(const T &c); 14 15 // 普通函数声明 16 int rand_int_100(); 17 void test1(); 18 void test2(); 19 20 int main() { 21 cout << "测试1: \n"; 22 test1(); 23 24 cout << "\n测试2: \n"; 25 test2(); 26 } 27 28 // 函数实现 29 // 输出容器对象c中的元素 30 template <typename T> 31 void output(const T &c) { 32 for(auto &i: c) 33 cout << i << " "; 34 cout << endl; 35 } 36 37 // 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数 38 int rand_int_100() { 39 return rand() % 101; 40 } 41 42 // 测试1 43 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、排序 44 void test1() { 45 vector<int> v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10 46 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); // 产生[0, 100]之间的随机整数赋值给指定迭代器区间[v0.begin(), v0.end())内的每个数据项 47 cout << "v0: "; 48 output(v0); 49 50 vector<int> v1{v0}; 51 sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())内数据项进行升序排序 52 cout << "v1: "; 53 output(v1); 54 55 vector<int> v2{v0}; 56 sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1)内数据项进行升序排序 57 cout << "v2: "; 58 output(v2); 59 } 60 61 // 测试2 62 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值 63 void test2() { 64 vector<int> v0(10); 65 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); 66 cout << "v0: "; 67 output(v0); 68 69 auto iter1 = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 70 cout << "最小值: " << *iter1 << endl; 71 72 auto iter2 = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 73 cout << "最大值: " << *iter2 << endl; 74 75 auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 76 cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl; 77 cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl; 78 double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0)/v0.size(); 79 cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl; 80 81 cout << endl; 82 83 vector<int> v1{v0}; 84 cout << "v0: "; 85 output(v0); 86 sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); 87 double avg2 = accumulate(v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1, 0)/(v1.size()-2); 88 cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl; 89 }
运行结果:
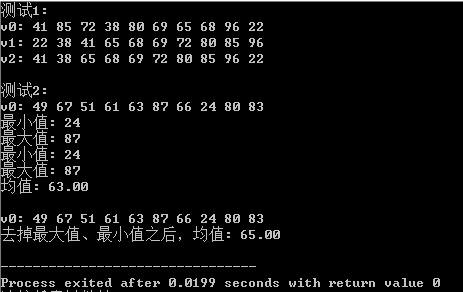
总结:
stl算法库中排序(sort)、赋值(generate);求最大值(max)、最小值(min)、均值(accumulate)等可以直接使用的函数算法对数据运算类型的编程问题以及编程中的化简效果好,可以提高编程的效率。
3. 实验任务3
编写程序,实现判断回文串。具体要求如下:
- 编写函数 bool is_palindrome(std::string s) 用于判断字符串s是否是回文串,是返回 true ,
- 否则,返回 false 。
- 在main函数中,输入字符串,调用 is_palindrome , 输出结果,要求支持多组输入。
以下为task3.cpp的源代码
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> bool is_palindrome(std::string s); int main() { using namespace std; string s; while(cin >> s) cout << boolalpha << is_palindrome(s) << endl; } bool is_palindrome(std::string s) { std::string w(s); reverse(s.begin(),s.end()); if(w==s) { return true; } else{ return false; } }
运行结果:
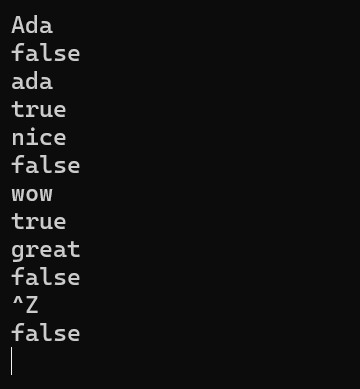
总结:使用reserve自带函数,使得判断的编程过程大大方便了。
4. 实验任务4
编写程序实现进制转换。具体要求如下:
- 编写函数 std::string dec_to_n(x, n) 实现把一个十进制数x转换成n进制,结果以字符串形式
- 返回。如果第2个参数没有指定,默认转换成二进制。
- 在main函数中,输入十进制整数,调用函数 dec2n 得到转换成指定进制的字符串,输出。要求支持多组输入。
以下为task4.cpp的源代码
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2); int main() { using namespace std; int x; while(cin >> x) { cout << "十进制: " << x << endl; cout << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << endl; cout << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << endl; cout << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << endl << endl; } } std::string dec2n(int x,int n) { char arr[50000]={}; itoa(x,arr,n); std::string s; for(auto &i:arr) s+=i; return s; }
运行结果:
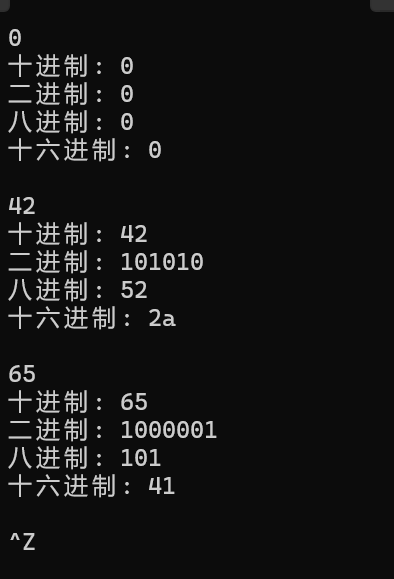
5. 实验任务5
编写一个程序,在屏幕上打印字母密文对照表。
代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { int i; cout<<setw(2)<<" "; for(i=1;i<27;i++) { cout<<setw(2)<<char(96+i); } int w=0,cnt=64; while(w<26){ w++; cnt++; cout<<'\n'<<setw(2)<<w; for(i=1;i<27;i++) { cnt++; if(cnt>90) { cnt-=26; } cout<<setw(2)<<char(cnt); } } return 0; }
运行结果:

总结:
本题主要是对格式控制以及函数综合的使用。
6. 实验任务6
编写一个程序,实现自动生成算术运算题目并自动评测。具体要求如下:
- 程序运行后,自动生成10道10以内的算术运算题目。
- 运算式(包括=)在程序运行时自动生成。运算式=右侧的答案由用户输入
- 算术运算包括:加、减、乘、除。生成题目时,运算随机。
- 两个操作数限制在[1, 10]区间内的整数。
- 当生成的随机运算是减法时,要求第一个操作数>第二个操作数
- 当生成的随机u那算时除法时,要求第一个操作数能整除第二个操作数整除
- 用户完成10道测试后,屏幕给出正确率,要求以百分号形式输出,保留小数点后两位。
- 多次运行程序时,每次生成的题目与上次不同。
代码如下:
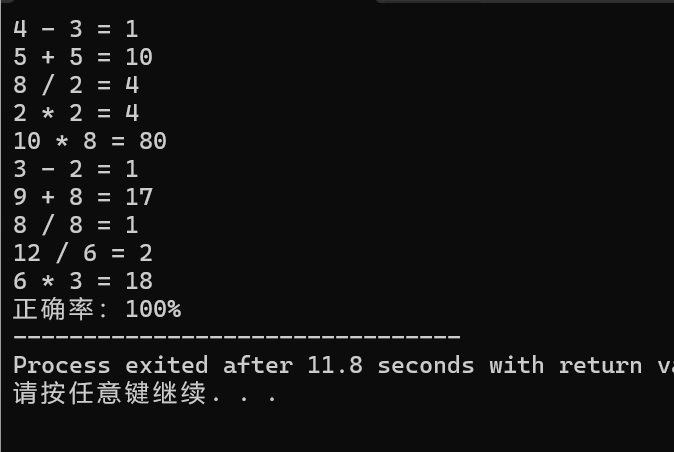
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int compansion(char ow,int a,int b){ if(ow == '+') { return a+b; } else if (ow == '-') { return a-b; } else if (ow == '*') { return a*b; } else return a/b; } int main() { char www[4]={'+','-','*','/'}; int curr = 0; for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ srand(time(0)); char ow = www[rand()%4]; int a,b; if(ow == '-'){ a = rand()%9+2; b = rand()%(a-1)+1; } else if(ow == '/'){ b = rand()%10+1; a = b*(rand()%10/b+1); } else a = rand()%10+1,b=rand()%10+1; cout<<a<<" "<<ow<<" "<<b<<" = "; int ans; cin>>ans; if(ans == compansion(ow,a,b)) curr++; } cout<<"正确率:"<<1.0*curr/10*100<<setprecision(2)<<"%"; return 0; }
运行结果:
四、实验总结
此部分书写内容:
本次实验学会了C++的各种运行规范,以及使用C++自带的函数进行编写代码,大大减少了编写的工作量与简易程度,经过实验,C++的知识更加丰富了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号