1.python用缩进表示变量的归属
同一缩进的代码,称之为代码块
ps:布尔值位False数据有哪些:0,None,' ',[ ],{ }
变量名也可以用布尔值判断,变量名指向Ture,False # is_beautiful = True
注意Ture和Falese首字母必须大写
2.if
if 条件:
代码1
代码2
代码3
代码4
...
elif 条件:
代码1
代码2
代码3
代码4
...
else: # 不能单独使用,必须和if,while,for配合使用
代码1
代码2
代码3
代码4
...
if elif else 中有上往下检索且只会运行其中一个代码块,比如运行了if中的代码块将不会运行elif,else中的代码块,
运行了elif说明if中的条件不满足,将不会运行elif,else中的代码块。
gender = 'female'
age = 34
is_beautiful = True
if gender == 'female' and age > 18 and age < 30 and is_beautiful:
print('能不能加个微信啊,我很钟意你')
elif gender == 'female' and is_beautiful:
print('考虑一下')
else:
print('什么玩意儿')
print('正常执行结束')
3.if—in—在列表中选定结果
# if today in ['Monday','Tuesday','Wednesday','Thursday','Friday']:
# print('上班')
# elif today in ['Saturday','Sunday']:
# print('出去嗨')
if 嵌套:
gender = 'female' age = 24 is_beautiful = True is_success = False if gender == 'female' and age > 18 and age < 30 and is_beautiful: print('上去表白') if is_success: print('跟我走吧') else: print('你是个好人') elif gender == 'female' and is_beautiful: print('考虑一下') else: print('什么玩意儿') print('正常执行结束')
4.while条件循环
缩进,break:立即结束本层循环(只针对它所属于的那一个while有效)
continue:跳出本次循环,直接开始下一次循环
死循环:
while True:
1+1 #会加重处理器负荷
while+else:
#只有当while循环依据条件正常结束才会走else代码
如果是主动结束的break,那么不会走else
flag全局标志位与break区别,flag=ture,后令flag=Flase,会直接终结整段代码
无论flag在哪个位置:
# from_db_username = 'jason' # from_db_password = '123' # # flag = True # 定义一个全局的标志位 # while flag: # username = input("please input your username>>>:") # password = input("please input your password>>>:") # if username == from_db_username and password == from_db_password: # print('欢迎老板,我是23号技师,很高兴为您服务') # while flag: # cmd = input('please input your command>>>:') # if cmd == 'q': # flag = False # print('%s is running'%cmd) # else: # print('没钱滚蛋~') # # print("到点了")
5.for循环
可取字典的key: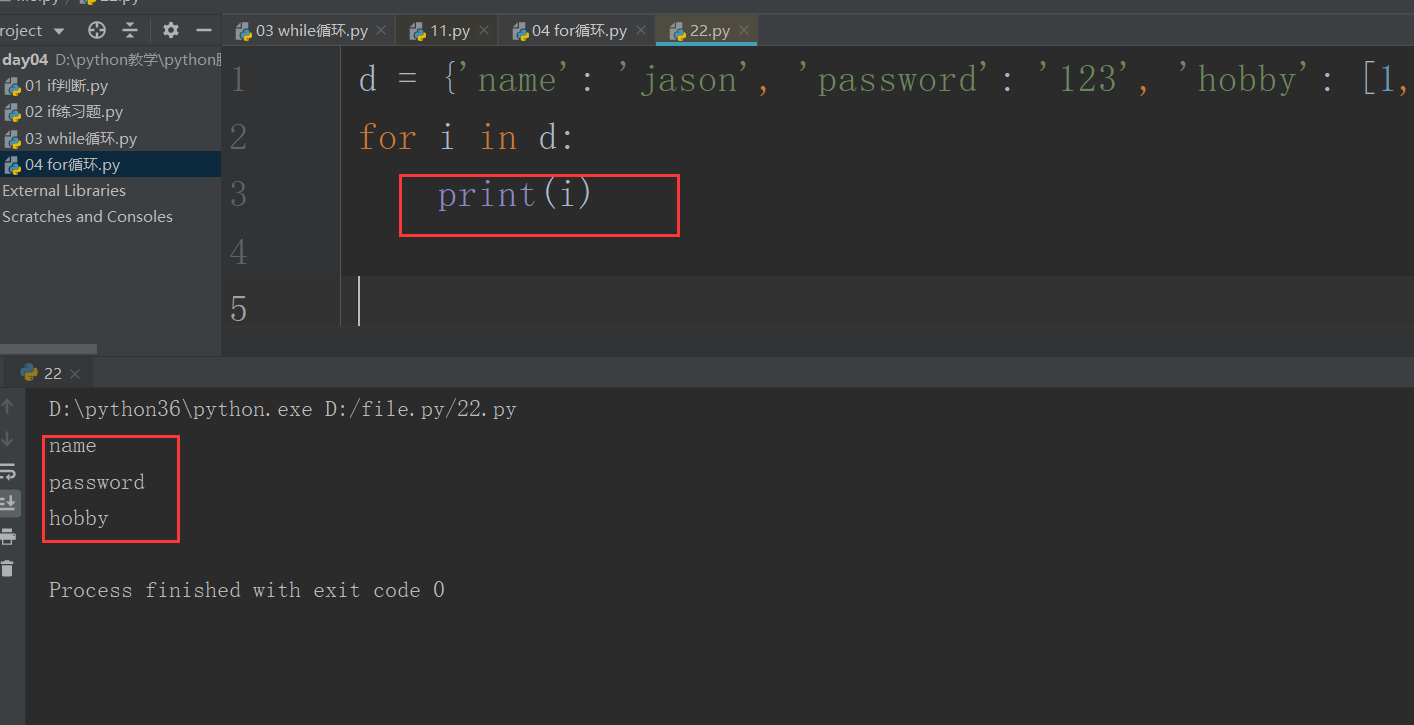
可取字典的value:

len() # 获取数据类型(容器类型)的个数,字符串是特例 获取的是字符串中字符的个数
range在python2与python3中的区别.其3(*****)
python2中
1.range其实就是一个列表
2.xrange其实就是你python3中的range
python3中
for i in range(1,10): # 顾头不顾尾
break结束循环
continue跳过当前条件
else除去上述语句之外,剩余的语句归为一类。
9*9乘法表:




