池化与采样
TensorFlow2教程完整教程目录(更有python、go、pytorch、tensorflow、爬虫、人工智能教学等着你):https://www.cnblogs.com/nickchen121/p/10840284.html
Outline
- Pooling
- upsample
- ReLU
Reduce Dim
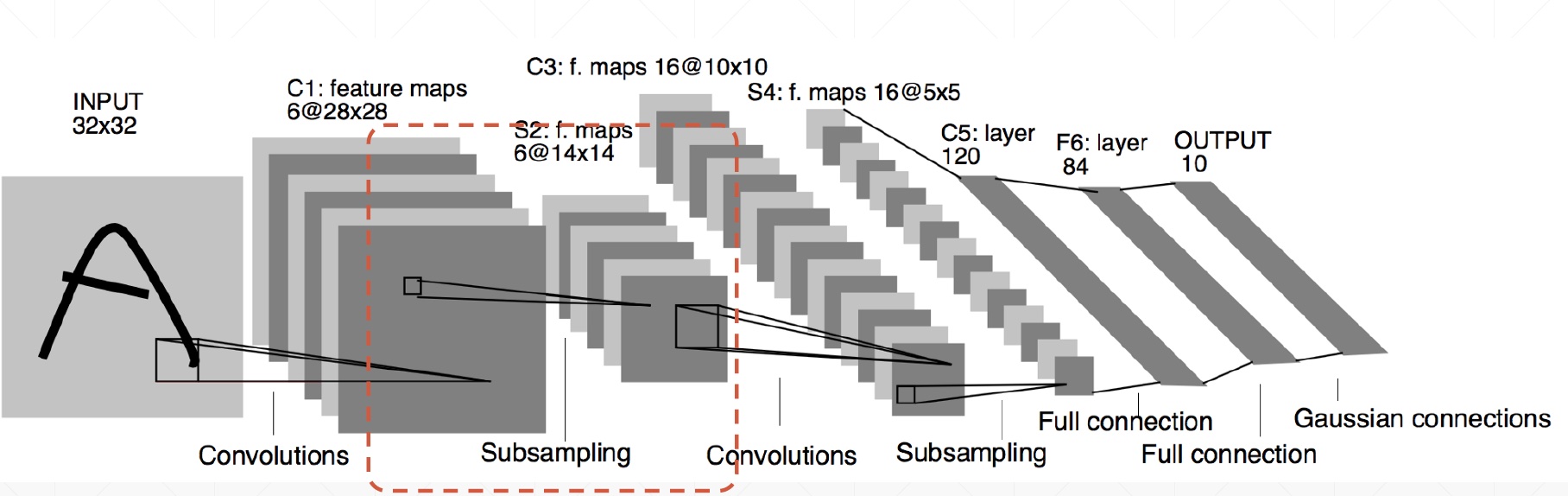
subsample
Max/Avg pooling
- stride = 2
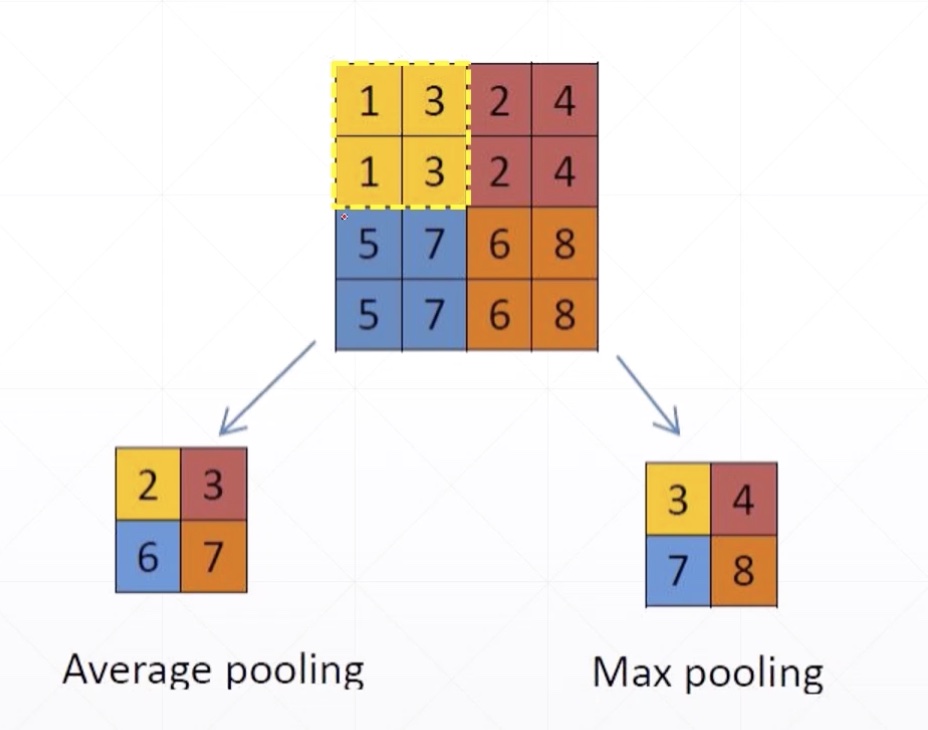
Strides
- stride = 1
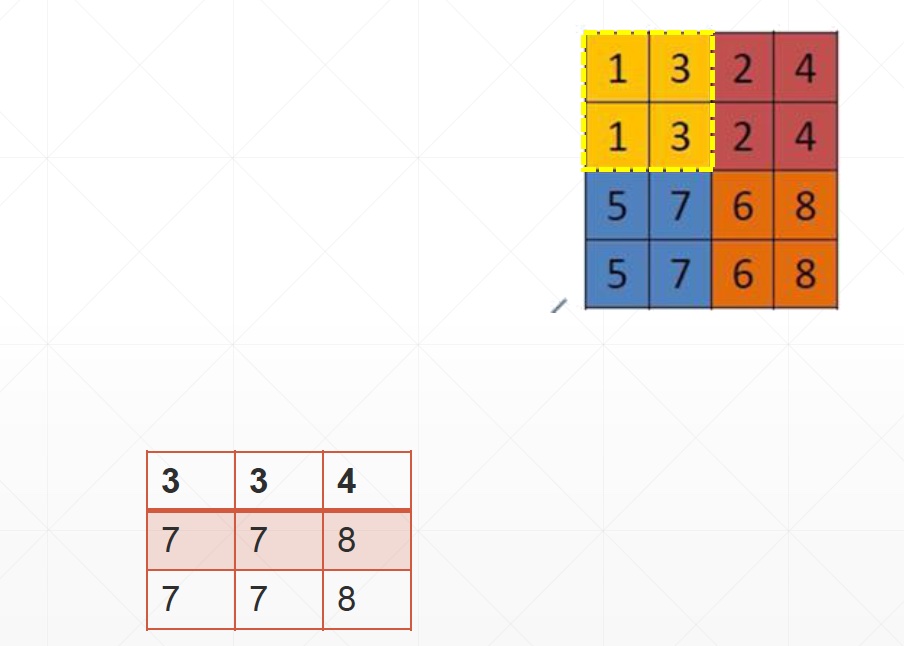
For instance
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
x = tf.random.normal([1, 14, 14, 4])
x.shape
TensorShape([1, 14, 14, 4])
pool = layers.MaxPool2D(2, strides=2)
out = pool(x)
out.shape
TensorShape([1, 7, 7, 4])
pool = layers.MaxPool2D(3, strides=2)
out = pool(x)
out.shape
TensorShape([1, 6, 6, 4])
out = tf.nn.max_pool2d(x, 2, strides=2, padding='VALID')
out.shape
TensorShape([1, 7, 7, 4])
upsample
- nearest
- bilinear
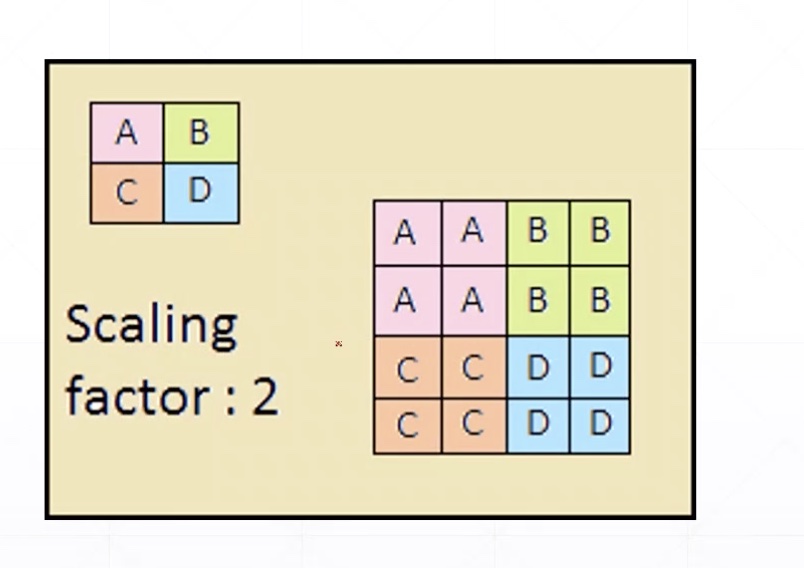
UpSampling2D
x = tf.random.normal([1, 7, 7, 4])
x.shape
TensorShape([1, 7, 7, 4])
layer = layers.UpSampling2D(size=3)
out = layer(x)
out.shape
TensorShape([1, 21, 21, 4])
layer = layers.UpSampling2D(size=2)
out = layer(x)
out.shape
TensorShape([1, 14, 14, 4])
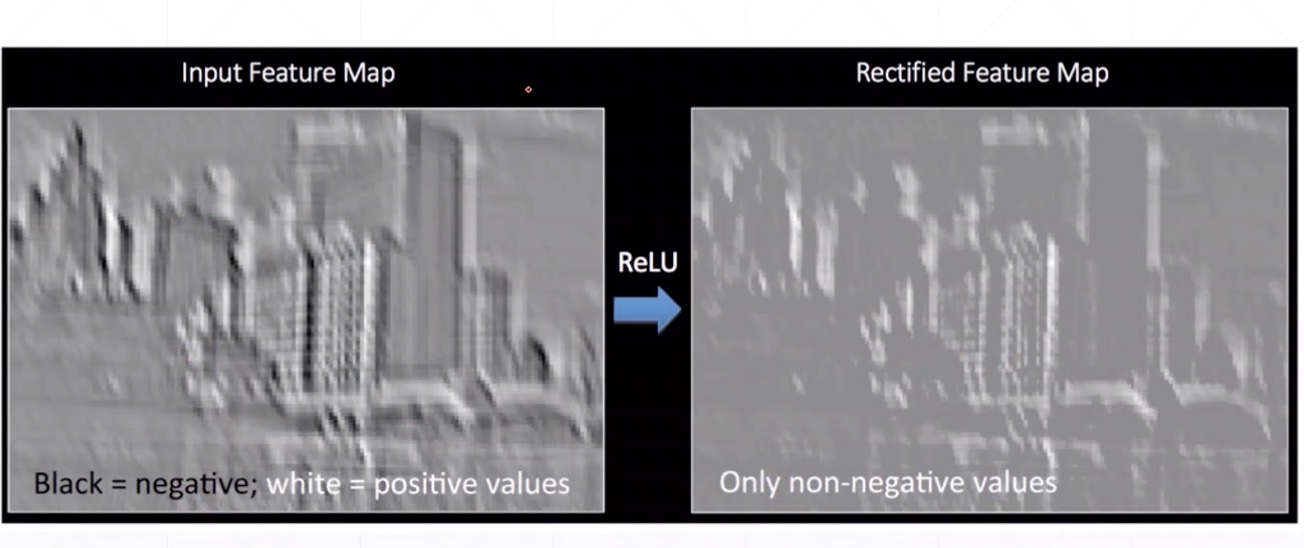
ReLu

x = tf.random.normal([2,3])
x
<tf.Tensor: id=76, shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[-0.30181265, 0.39785287, -0.78380096],
[ 0.6593401 , -0.40962896, -0.3656048 ]], dtype=float32)>
tf.nn.relu(x)
x
<tf.Tensor: id=76, shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[-0.30181265, 0.39785287, -0.78380096],
[ 0.6593401 , -0.40962896, -0.3656048 ]], dtype=float32)>
layers.ReLU()(x)
<tf.Tensor: id=80, shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[0. , 0.39785287, 0. ],
[0.6593401 , 0. , 0. ]], dtype=float32)>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号