函数优化实战
TensorFlow2教程完整教程目录(更有python、go、pytorch、tensorflow、爬虫、人工智能教学等着你):https://www.cnblogs.com/nickchen121/p/10840284.html
Himmelblau function
- \(f(x,y)=(x^2+y-11)^2+(x+y^2-7)^2\)
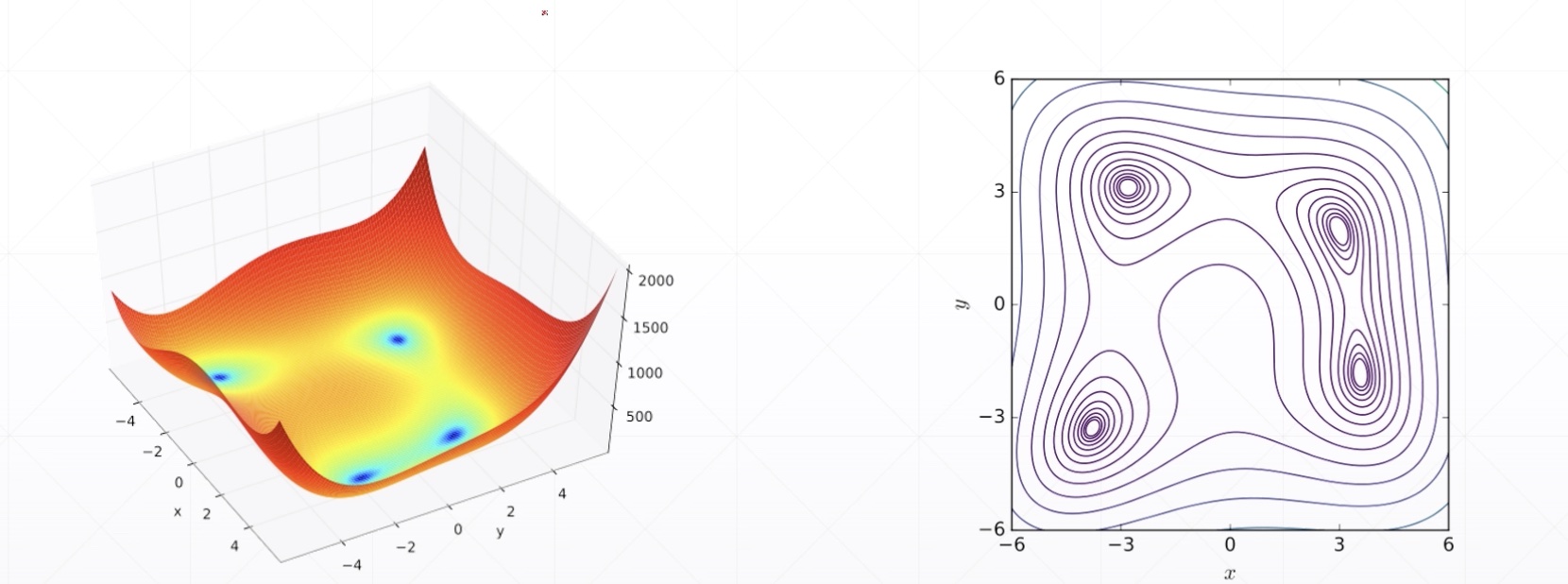
Minima
- f(3.0,2.0)=0.0
- f(-2.8,3.1)=0.0
- f(-3.7,-3.2)=0.0
- f(3.5,-1.84)=0.0
Plot
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
def himmeblau(x):
return (x[0]**2 + x[1] - 11)**2 + (x[0] + x[1]**2 - 7)**2
x = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
y = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
print(f'x_shape: {x.shape},y_shape: {y.shape}')
# 生成坐标点
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print(f'X_shape: {X.shape},Y_shape: {Y.shape}')
Z = himmeblau([X, Y])
fig = plt.figure('himmelblau')
ax = Axes3D(fig)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.view_init(60, -30)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
plt.show()
x_shape: (120,),y_shape: (120,)
X_shape: (120, 120),Y_shape: (120, 120)

Gradient Descent
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.constant([-4.,0.])
for step in range(200):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([x])
y = himmeblau(x)
grads = tape.gradient(y,[x])[0]
x -= 0.01 * grads
if step % 20 == 0:
print(f'step: {step}, x: {x}, f(x): {y}')
step: 0, x: [-2.98 -0.09999999], f(x): 146.0
step: 20, x: [-3.6890159 -3.1276689], f(x): 6.054703235626221
step: 40, x: [-3.7793102 -3.283186 ], f(x): 0.0
step: 60, x: [-3.7793102 -3.283186 ], f(x): 0.0
step: 80, x: [-3.7793102 -3.283186 ], f(x): 0.0
step: 100, x: [-3.7793102 -3.283186 ], f(x): 0.0
step: 120, x: [-3.7793102 -3.283186 ], f(x): 0.0
step: 140, x: [-3.7793102 -3.283186 ], f(x): 0.0
step: 160, x: [-3.7793102 -3.283186 ], f(x): 0.0
step: 180, x: [-3.7793102 -3.283186 ], f(x): 0.0

