jav核心(十四):集合类型操作:Collection、List、Set;Map集合;Iterator迭代器
一、java.util.List
1、List总结
- List中允许保存重复的数据;
- List中允许保存多个null;
- 常用实现类:ArrayList【推荐使用】、Vector、LinkedList;
- List中数据是有序的,按照数据添加顺序进行排序;
- 由于List是有序的,因此List新增加了一个方法:E get(int index) ,【Collection、Set接口均没有get(int index)方法】。
2、ArrayList和Vector的区别
(1)ArrayList和Vector,都是List接口的实现类。
| NO | 区别点 | ArrayList | Vector |
| 1 | 推出时间 | JDK1.2,属于新增类 | JDK1.0,属于旧类 |
| 2 | 性能 | 异步处理 |
同步处理
方法采用synchronized修饰,为同步方法
|
| 3 | 安全 | 非线程安全 | 线程安全 |
| 4 | 数据输出方式 | Iterator、ListIterator、foreach |
Iterator、ListIterator、foreach、
Enumeration
|
(2)ArrayList和Vector都是用数组实现的,主要有以下几个区别:
- Vector是多线程安全的,线程安全就是说多线程访问同一代码,不会产生不确定的结果。而ArrayList不是,这个可以从源码中看出,Vector类中的方法很多有synchronized进行修饰,这样就导致了Vector在效率上无法与ArrayList相比;
- 两个都是采用的线性连续空间存储元素,但是当空间不足的时候,两个类的增加方式是不同。
- Vector可以设置增长因子,而ArrayList不可以。
- Vector是一种老的动态数组,是线程同步的,效率很低,一般不赞成使用。
(3)适用场景分析:
- Vector是线程同步的,所以它也是线程安全的,而ArrayList是线程异步的,是不安全的。如果不考虑到线程的安全因素,一般用ArrayList效率比较高。
- 如果集合中的元素的数目大于目前集合数组的长度时,在集合中使用数据量比较大的数据,用Vector有一定的优势。
3、Vertor向量类型数据输出:Vertor --> Iterator | Enumeration
Java.util.Vertor是JDK1.0中设计的向量类型。后来在JDK1.2中新增了Collection、List、Set接口,为保持集合统一型,修改Vertor类的定义,使其实现了List接口。与新集合的实现不同,Vertor是同步的。
Java.util.Enumeration是JDK1.0中定义的接口,和Java.util.Iterator(JDK1.2出现)迭代器功能类似。其中Enumeration接口包含两个方法:
- hasMoreElements():测试此枚举是否包含更多的元素。
- nextElement():如果此枚举对象至少还有一个可提供的元素,则返回此枚举的下一个元素。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> vertor = new Vector<String>(); vertor.add("A"); vertor.add("B"); vertor.add("C"); //输出数据:使用迭代器Iterator Iterator<String> iterator = vertor.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ String data = iterator.next(); System.out.println(data); } System.out.println("*******"); //输出数据:使用Enumeration Enumeration<String> enumeration = ((Vector<String>) vertor).elements(); while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()){ String data = enumeration.nextElement(); System.out.println(data); } } }
//程序运行结果: A B C ******* A B C
二、Java.util.Set
1、Set总结
API描述:一个不包含重复元素的 collection。更正式地说,set 不包含满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素对 e1 和 e2,并且最多包含一个 null 元素。正如其名称所暗示的,此接口模仿了数学上的 set 抽象。
- Set不允许保存重复的数据【不同实现类,对重复数据的评定标准不一样】;
- 常用实现类:HashSet、TreeSet;
- HashSet允许保存一个null,TreeSet不允许保存null;
- HashSet中的数据是无序的;
- TreeSet中的数据是有序的,数据按照升序排列【通过调用数据元素的compareTo()方法进行排序,因此数据元素需要实现Comparable接口,否则会抛出ClassCastException异常】。
2、HashSet中,数据重复的评定标准:
当且仅当( e1.hashCode() == e2.hashCode() ) && e1.equals(e2) 为true时,才认定e1和e2重复。
(1)数据重复测试一:e1.equals(e2)为true时,hashCode()值必然相同的情况
/** * 按照规范重写Book类的equals()方法、hashCode()方法 */ class Book { private int price; private String name; public Book(int price, String name) { this.price = price; this.name = name; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Book book = (Book) o; return price == book.price && Objects.equals(name, book.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(price, name); } @Override public String toString() { return this.name + "--" + this.price; } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Book book = new Book(100, "java开发"); Book book1 = new Book(100, "java开发"); Book book2 = new Book(100, "设计模式"); Book book3 = new Book(10, "abc"); System.out.println("*********"); System.out.println(book.hashCode()); //-1166307760 System.out.println(book1.hashCode()); //-1166307760 System.out.println(book2.hashCode()); //1100964814 System.out.println(book.equals(book1)); //true System.out.println(book.equals(book2)); //false System.out.println("*********"); Set<Book> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); hashSet.add(book); hashSet.add(book1); //book1 与 book 重复,不进行保存 hashSet.add(book2); //book2 不重复 hashSet.add(book3); //book3 不重复 System.out.println(hashSet); } }
//程序执行结果: ********* -1166307760 -1166307760 1100964814 true false ********* [设计模式--100, abc--10, java开发--100]
(2)数据重复测试二:e1.equals(e2)为true,但hashCode()值不同的情况
class Book { private int price; private String name; public Book(int price, String name) { this.price = price; this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return this.name + "--" + this.price; } //任何对象之间比较,均返回true public boolean equals(Object o) { return true; } //使用随机数生成hashCode public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(Math.random()); } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Book book = new Book(100, "java开发"); Book book1 = new Book(100, "java开发"); Book book2 = new Book(100, "设计模式"); System.out.println("*********"); System.out.println(book.hashCode()); System.out.println(book1.hashCode()); System.out.println(book2.hashCode()); System.out.println(book.equals(book1)); System.out.println(book.equals(book2)); System.out.println("*********"); Set<Book> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); hashSet.add(book); hashSet.add(book1); //book1 与 book 重复 hashSet.add(book2); //book2 不重复 System.out.println(hashSet); } }
//程序执行结果 ********* 920603493 -1541131927 1273275611 true true ********* [java开发--100, 设计模式--100, java开发--100]
3、TreeSet中,数据重复的评定标准:
当且仅当 e1.compareTo(e2) 返回结果为0时,认为e1、e2重复。
TreeSet不使用equals()、hashCode()方法进行判定。
class Book implements Comparable{ private int price; private String name; public Book(int price, String name) { this.price = price; this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return this.name + "--" + this.price; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { return true; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash("1111"); } @Override public int compareTo(Object o) { return 1; } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Book book = new Book(100, "java开发"); Book book1 = new Book(100, "java开发"); Book book2 = new Book(100, "设计模式"); System.out.println("*********"); Set<Book> hashSet = new TreeSet<>(); hashSet.add(book); hashSet.add(book1); hashSet.add(book2); System.out.println(hashSet); } }
//程序执行结果 ********* [java开发--100, java开发--100, 设计模式--100]
4、说明:一般情况下,比较两个对象是否相同,通过hashCode()和equals()方法判断
- 首先判断hashCode()值是否相等,如果不相等,则认为e1、e2不相同;如果相等,则继续判断e1.equals(e2)是否为true,若为true则认为e1、e2相同,否则认为e1、e2不相同;
- Comparable的compareTo()方法只是作为对象的排序使用,但并不能真正区分两个对象是否相同。
三、Java.util.Map
1、Map总结
- 将键映射到值的对象。一个映射不能包含重复的键;每个键最多只能映射一个值。
//语法定义
public interface Map<K,V>
2、Map接口中的方法
| NO | 方法名称 |
| 1 |
将指定的值与此映射中的指定键相关联(可选操作)。
|
| 2 |
返回此映射中映射到指定键的值。
|
| 3 |
返回此映射中包含的映射关系的 set 视图。
|
| 4 |
public Set<K> keySet()
返回此映射中包含的键的 set 视图。
|
3、HashMap和HashTable的区别
HashMap是JDK1.2中用来代替HashTable的类,也就是说建议使用HashMap,不要使用HashTable。
| NO | 区别点 | HashMap | HashTable |
| 1 | 推出时间 | JDK1.2,属于新增类 | JDK1.0,属于旧类 |
| 2 | 性能 | 异步处理 |
同步处理
方法采用synchronized修饰
|
| 3 | 安全 | 非线程安全 | 线程安全 |
| 4 | 是否允许null | 允许key或value为null | key和value均不能为null |
(1)基本功能上的区别:
- 同步性: HashTable的方法是同步的,HashMap是不同步的。所以在多线程场合要手动同步HashMap。
- 对Null的支持: HashTable不允许null值(key和value都不可以),HashMap允许null值(key和value都可以,只容许有一个null值的key,可以有多个null值的value)。
- 数据输出方式:HashTable可以使用Enumeration和Iterator,HashMap只可以使用Iterator。
(2)底层存储数据的区别
- HashTable中hash数组默认大小是11,增加的方式是 old*2+1。HashMap中hash数组的默认大小是16,而且一定是2的指数。
- 哈希值的使用不同,HashTable直接使用对象的hashCode。而HashMap重新计算hash值,而且用与代替求模。
//HashTable : 计算哈希值 int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
//HashMap : 计算哈希值 int hash = hash(k); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //HashMap通过key,重新计算hash值 static int hash(Object x) { int h = x.hashCode(); h += ~(h << 9); h ^= (h >>> 14); h += (h << 4); h ^= (h >>> 10); return h; } //HashMap使用新计算出的hash值进行求模 static int indexFor(int h, int length) { return h & (length - 1); }
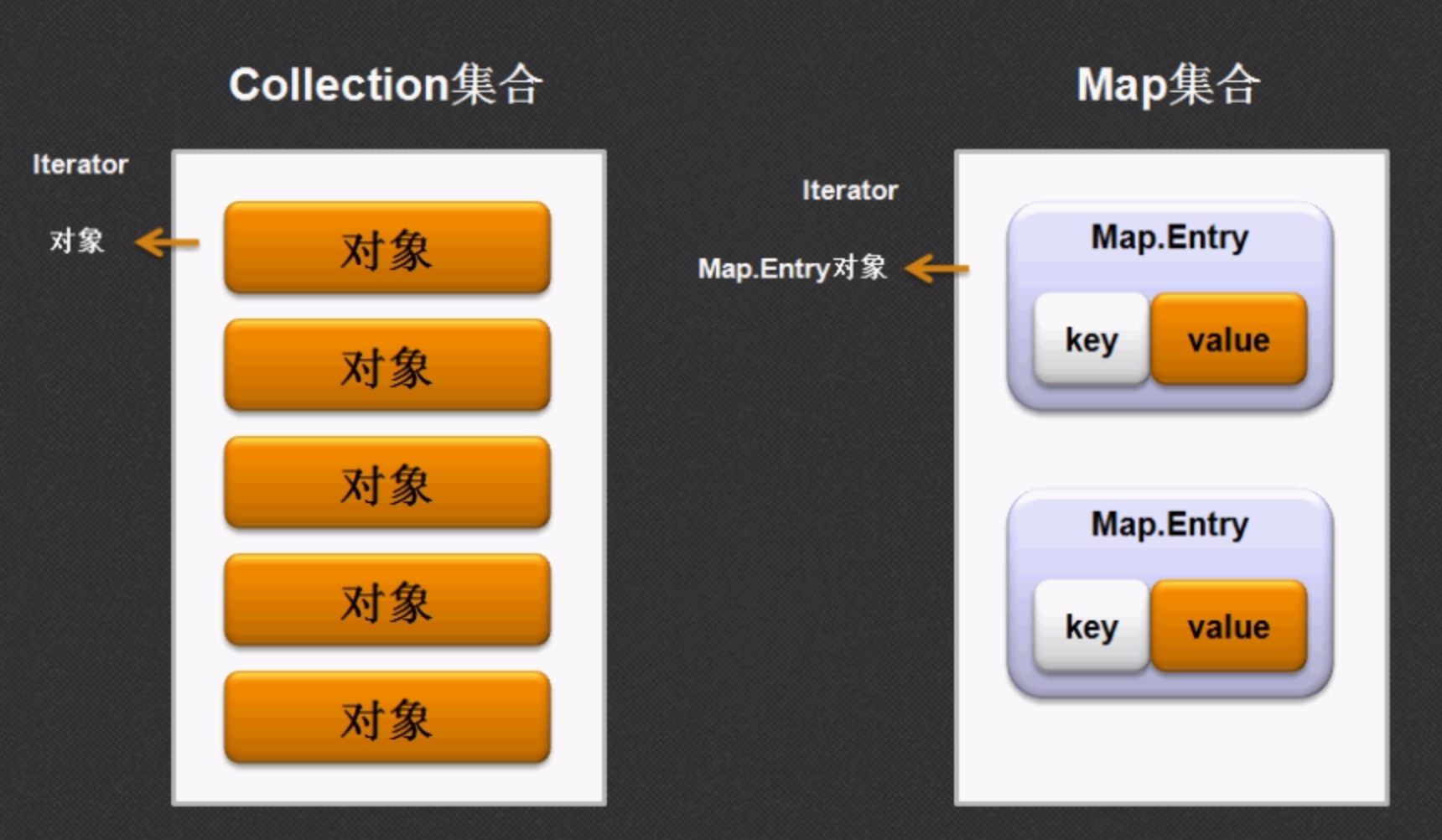
4、将Map中的数据,通过迭代器输出:Map —> Set —> Iterator
- 调用Map.entrySet()方法,将Map集合转换为Set集合,其中Set中的泛型为:Map.Entry<K,V>;
- 调用Set.iterator()方法,将Set集合转换为Iterator迭代器,泛型依然是:Map.Entry<K,V>;
- 调用Iterator的hasNext()、next()方法,循环取出Map.Entry<K,V>接口对象;
- 调用Map.Entry接口的getKey()获取key、getValue()获取value。
class Book { private int price; private String name; public Book(int price, String name) { this.price = price; this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return this.name + "--" + this.price; } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Book book = new Book(100, "java开发"); Book book1 = new Book(100, "java开发"); Book book2 = new Book(56, "设计模式"); System.out.println("*********"); Map<String,Book> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("book",book); map.put("book1",book1); map.put("book2",book2); //将Map中的数据,通过迭代器输出:Map —> Set —> Iterator Set<Map.Entry<String,Book>> set = map.entrySet(); Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Book>> iterator = set.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ Map.Entry<String,Book> entry = iterator.next(); String key = entry.getKey(); Book value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+" : "+value); } } }
//程序执行结果 ********* book2 : 设计模式—56 book1 : java开发--100 book : java开发--100



