vue之循环遍历v-for
1.背景
2.遍历数组

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!-- 开发环境版本,包含了有帮助的命令行警告 --> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!--<script src="./js/vue.js"></script>--> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h3>{{title}}</h3> <h4>1.遍历数组</h4> <h4>订单列表如下(不取下标)</h4> <ul> <li v-for="item in orderList"> {{item.orderName}}---- {{item.price}}---- {{item.num}} </li> </ul> <h4>合计:{{allPrice}}</h4> <h4>订单列表如下(取下标)</h4> <ul> <li v-for="(item,index) in orderList"> {{index+1}}. {{item.orderName}}---- {{item.price}}---- {{item.num}} </li> </ul> <h4>合计:{{allPrice}}</h4> </div> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { title: '循环遍历v-for简单使用', name: 'ldp', orderList: [ {orderName: '方便面', price: 3, num: 6}, {orderName: '鸡腿', price: 8, num: 1}, {orderName: '手机', price: 39, num: 4}, {orderName: '鱼', price: 12, num: 9} ] }, computed: { allPrice: function () { // 高阶函数 all表示每次的结果,item表示循环出来的每个对称 , reduce 函数的第二个参数表示 all=0开始累加 return this.orderList.reduce((all, item) => { return all + item.price * item.num }, 0) } } }); </script> </body> </html>
3.遍历对象

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!-- 开发环境版本,包含了有帮助的命令行警告 --> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!--<script src="./js/vue.js"></script>--> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h3>{{title}}</h3> <h4>遍历对象</h4> <ul> <li v-for="(value,key,index) in product"> {{value}}--- {{key}}--- {{index}}---</li> </ul> </div> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { title: '循环遍历v-for简单使用', name: 'ldp', product: { orderName: '方便面', price: 3, num: 6 } } }); </script> </body> </html>
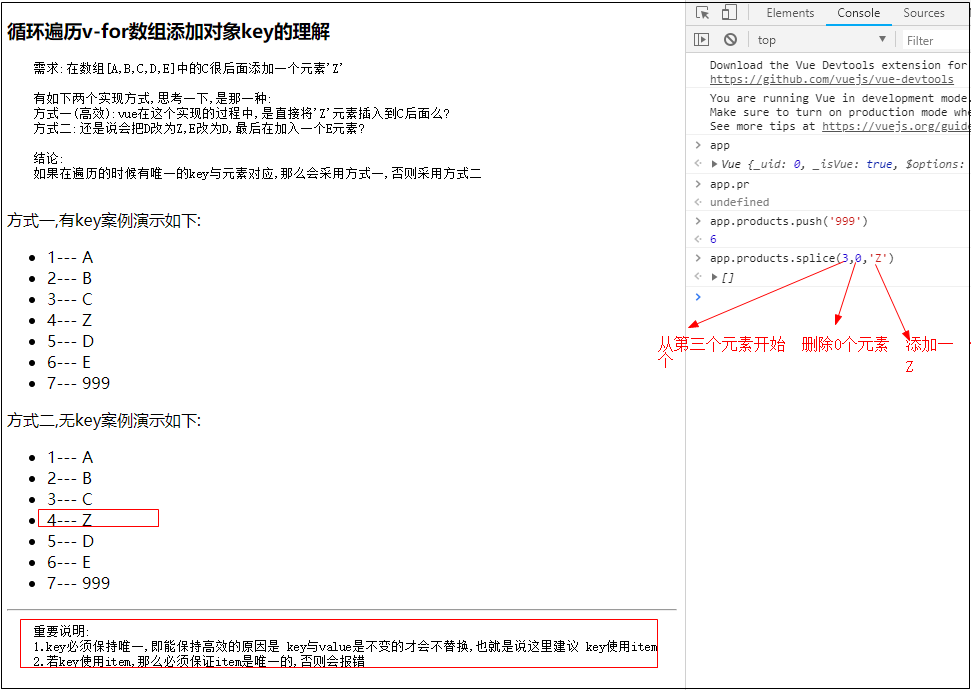
4.关于遍历中的key
5.数据数组变动中的方法
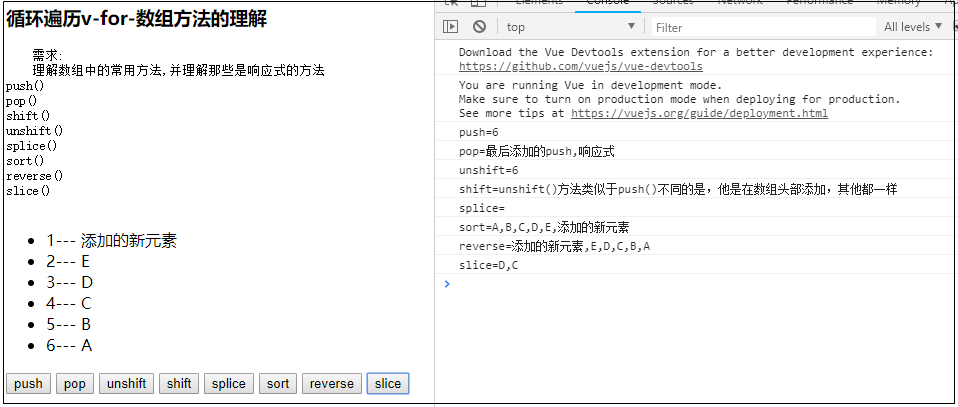

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!-- 开发环境版本,包含了有帮助的命令行警告 --> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!--<script src="./js/vue.js"></script>--> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h3>{{title}}</h3> <pre> 需求: 理解数组中的常用方法,并理解那些是响应式的方法 push() pop() shift() unshift() splice() sort() reverse() slice() </pre> <ul> <li v-for="(item,index) in products"> {{index+1}}--- {{item}}</li> </ul> <button @click="push">push</button> <button @click="pop">pop</button> <button @click="unshift">unshift</button> <button @click="shift">shift</button> <button @click="splice">splice</button> <button @click="sort">sort</button> <button @click="reverse">reverse</button> <button @click="slice">slice</button> </div> <script> let app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { title: '循环遍历v-for-数组方法的理解', name: 'ldp', products: ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'] }, methods: { // 在数组最后添加元素,响应式的方法 // push()方法在数组的尾部添加一个或者多个元素,并返回数组的新长度。注意的是,改变的是原数组的值,返回的是新数组的长度 push() { let data = this.products.push("最后添加的push,响应式") console.log("push=" + data) }, // pop()方法删除数组的最后一个元素,并返回它的删除值。也是改变原数组,返回的是删除的值。 pop() { let data = this.products.pop() console.log("pop=" + data) }, // unshift()方法类似于push()不同的是,他是在数组头部添加,其他都一样 unshift() { let data = this.products.unshift("unshift()方法类似于push()不同的是,他是在数组头部添加,其他都一样") console.log("unshift=" + data) }, // shift()方法则类比pop()方法。 shift() { let data = this.products.shift() console.log("shift=" + data) }, // Array.splice()方法,用来删除或插入元素,会修改原数组! // //第一个参数是截取的起始位置(包括),第二个参数是截取(删除)的个数,之后的参数就是添加在元数组的新值 splice() { // 从第二个开发删除0个,添加一个新元素 let data = this.products.splice(2, 0, '添加的新元素') console.log("splice=" + data) }, // Array.sort()方法,返回排序后的数组。如果数组包含undefined,会被排到数组的尾部。如果不带参数的调用sort(),数组元素以字母表顺序排序。 sort() { let data = this.products.sort() console.log("sort=" + data) }, // 返回逆序数组(倒叙排列数组)[ Array..reverse() ] reverse() { let data = this.products.reverse() console.log("reverse=" + data) }, // Array.slice()方法,返回指定数组的片段或者子数组。不会改变原数组 // 第一个参数是截取开始的位置(包括),第二个参数是截取结束的位置(不包括) slice() { let data = this.products.slice(2, 4) console.log("slice=" + data) } } }); </script> </body> </html>
6.简易购物车练习

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!-- 开发环境版本,包含了有帮助的命令行警告 --> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!--<script src="./js/vue.js"></script>--> </head> <style> table { border: 2px solid cadetblue; border-collapse: collapse; border-spacing: 0; } th, td { border: 2px solid cadetblue; } </style> <body> <div id="app"> <h3>{{title}}</h3> <pre> 需求: 做一个简易购物车 </pre> <table> <thead> <tr> <th>序号</th> <th>品名</th> <th>零售价</th> <th>购买数量</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for="(item,index) in products"> <td>{{index+1}}</td> <td>{{item.orderName}}</td> <td>{{item.price}}</td> <td> <button @click="decrement(index)">-</button> {{item.num}} <button @click="increment(index)">+</button> </td> <td> <button @click="del(index)">删除</button> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> 总计:{{totalPrice}} </div> <script> let app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { title: '循环遍历-购物车案例', name: 'ldp', products: [ {orderName: '方便面', price: 3, num: 6}, {orderName: '鸡腿', price: 8, num: 1}, {orderName: '手机', price: 39, num: 4}, {orderName: '鱼', price: 12, num: 9} ] }, computed: { totalPrice() { // 高阶函数 return this.products.reduce((total, item) => { return total + item.num * item.price }, 0) } }, methods: { increment: function (index) { console.log("---执行加一") this.products[index].num++ }, decrement: function (index) { console.log("---执行减一") if (this.products[index].num > 1) { this.products[index].num-- } else { console.log("---在减就没有了") } }, del(index) { this.products.splice(index, 1) } } }); </script> </body> </html>
完美!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号