EF Core 封装方法Expression<Func<TObject, bool>>与Func<TObject, bool>区别
unc<TObject, bool>是委托(delegate)
Expression<Func<TObject, bool>>是表达式
Expression编译后就会变成delegate,才能运行。比如
Expression<Func<int, bool>> ex = x=>x < 100;
Func<int, bool> func = ex.Compile();
然后你就可以调用func:
func(5) //-返回 true
func(200) //- 返回 false
而表达式是不能直接调用的。
===========================
案例:不正确的查询代码造成的数据库全表查询。
//错误的代码 Func<QuestionFeed, bool> predicate = null; if (type == 1) { predicate = f => f.FeedID == id && f.IsActive == true; } else { predicate = f => f.FeedID == id; } //_questionFeedRepository.Entities的类型为IQueryable<QuestionFeed> _questionFeedRepository.Entities.Where(predicate);
上面代码逻辑是根据条件动态生成LINQ查询条件,将Func类型的变量作为参数传给Where方法。
实际上Where要求的参数类型是:Expression<Func<TSource, bool>>。
解决方法:
不要用Func<TSource, bool>,用Expression<Func<TSource, bool>>。
//正确的代码 Expression<Func<QuestionFeed, bool>> predicate=null; if (type == 1) { predicate = f => f.FeedID == id && f.IsActive == true; } else { predicate = f => f.FeedID == id; } _questionFeedRepository.Entities.Where(predicate);
框架中加入了EF,使开发效率大大加快,但是项目做出来之后,数据稍微多一点,页面的加载速度就会非常慢。经过层层详细的排查之后,发现是项目封装的EF工具类有问题。
/// <summary> /// 按条件查询 /// </summary> /// <param name="whereLambda">lambda表达式</param> /// <returns>IQueryable 泛型集合</returns> public IQueryable<T> LoadItems(Func<T, bool> whereLambda) { return MyBaseDbContext.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).AsQueryable(); }
方法的参数whereLambda,其类型为Func<T, bool> ,在调用LoadItems方法时,通过SQL Server Profiler检测生成的sql语句,你会发现它只生成了一条查询全部结果的语句。然后通过一步步断点调试发现,将数据全部加载完毕后,还会根据查询条件whereLambda进行很多次的循环,才能把最终结果返回。
并且当调用带条件参数的查询方法时,都会遇到这个问题。不过当发现问题之后,基本也就能解决问题了。随后我们发现了与Func<TObject, bool> 非常相似的类型Expression<Func<TObject, bool>>
Expression<Func<TObject, bool>>为表达式类型,它会带上查询条件一并生成sql语句,将查询结果返回,大大提高查询效率。
修改后的方法:
/// <summary> /// 按条件查询 /// </summary> /// <param name="whereLambda">lambda表达式</param> /// <returns>IQueryable 泛型集合</returns> public IQueryable<T> LoadItems(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda) { return MyBaseDbContext.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).AsQueryable(); }
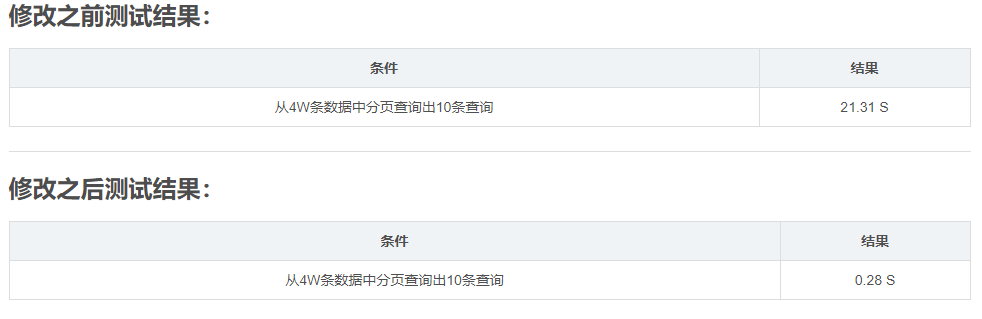
修改之后需要注意:
修改为表达式类型后按照之前的思路写可能会报错
LINQ to Entities 不识别方法“System.String ToString()”,因此该方法无法转换为存储表达式。
LINQ to Entities 不识别方法“…get_Item(Int32)”,因此该方法无法转换为存储表达式。
错误原因:
因为底层方法的参数Lambda,由委托类型改为表达式类型。因此咱们写的Lambda表达式里面不能存在C#的方法,比如 ToString()、ToInt()等等。因为表达式类型不能识别。
解决方案:
将Lambda中用到的参数,在外面定义成变量。然后再放到Lambda表达式中。
举例:
//修改之前 listQuestionTypeDetails = this.CurrentDal.LoadItems(u => u.ExamQuestionTypeEntity.QuestionTypeId == enQuestionType.QuestionTypeId.ToString()).ToList(); //修改之后 String questionTypeId = enQuestionType.QuestionTypeId.ToString(); listQuestionTypeDetails = this.CurrentDal.LoadItems(u => u.ExamQuestionTypeEntity.QuestionTypeId == questionTypeId ).ToList();
总结:Expression<Func<TObject, bool>>与Func<TObject, bool>
Func<TObject, bool> 委托类型,使用这个类型执行查询时会查询表中的全部数据,加载到内存中然后在根据条件循环进行筛选。
Expression<Func<TObject, bool>> 表达式类型,使用该类型作为参数时,会将查询条件一并添加到sql语句中查询出结果。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号