西北大学2018第四届超萌新生赛题解
比赛网址:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/321#question
大家好,我是这次比赛负责人NE,
本次比赛志在"零板子也能AK",全程面向新生,不防AK
A 容斥定理,显然能被A如果暴力的减去$n/A,n/B,n/C$会冲突,例如2和3,会重复减去6,12等等,于是用容斥定理即可解决问题,
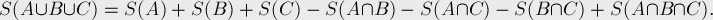
$S=x-(x/a+x/b+x/c-x/ab-x/ac-x/cb+x/abc),\ \ x=1000,000,000$
cin>>casn;
while(casn--){
ll a,b,c;
ll all=1000000000;
ll ans=0;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
ans=all/a+all/b+all/c-all/(a*b)-all/(a*c)-all/(b*c)+all/(a*b*c);
cout<<all-ans<<endl;
}
*原本这个题是ABC三个数都一定不是素数,被NE削弱了
B 计数,结构体排序,新生要学会使用sort函数和自定义cmp函数
如果会使用pair,就更方便了
int n,m,k;
cin>>n>>m;
vector<pair<int,int> > ans(m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) ans[i-1].second=i;
while(n--){
cin>>k;
while(k--){
int a;
cin>>a;
ans[a-1].first++;
}
}
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());
for(auto i:ans) cout<<i.second<<' '<<i.first<<endl;
return 0;
C找规律即可,不需要图论知识,注意会爆int
int casn;
long long n,m;
int main() {
cin>>casn;
while(casn--){
cin>>n>>m;
cout<<n*(n-1)/2-m<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
D一眼感觉可能是$bfs$,但是显然可以反向考虑,当前是$N$,如何最快的变成1?
显然,如果当前是奇数,无法整除二,只能减一,如果是偶数,除二的收益显然大于减一.
于是不断除二取余即可
while(cin>>n){
int ans=0;
while(n!=1){
if(n%2) ans++;
ans++;
n/=2;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
E照题意模拟即可,注意纯正九莲宝灯对手牌有要求
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 20;
struct Tile{
char type;
int id;
bool operator == (const Tile& T) const {
if (type == T.type && id == T.id) return 1;
else return 0;
}
}hand[maxn];
int getPower(char c) {
if (c == 'm') return 1;
else if (c == 'p') return 2;
else if (c == 's') return 3;
else return 4;
}
int main () {
int T; cin >> T;
while (T--) {
for (int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
string buf; cin >> buf;
hand[i].type = buf[1];
hand[i].id = buf[0] - '0';
}
sort(hand, hand + 13, [](Tile& a, Tile& b) {
if (getPower(a.type) < getPower(b.type)) return 1;
else if (getPower(a.type) > getPower(b.type)) return 0;
else if (a.id < b.id) return 1;
else return 0;
});
bool ans = 0;
//国士无双十三面
if (hand[0] == (Tile){'m', 1} && hand[1] == (Tile){'m', 9} && hand[2] == (Tile){'p', 1} &&
hand[3] == (Tile){'p', 9} && hand[4] == (Tile){'s', 1} && hand[5] == (Tile){'s', 9} &&
hand[6] == (Tile){'z', 1} && hand[7] == (Tile){'z', 2} && hand[8] == (Tile){'z', 3} &&
hand[9] == (Tile){'z', 4} && hand[10] == (Tile){'z', 5} && hand[11] == (Tile){'z', 6} &&
hand[12] == (Tile){'z', 7} &&
(hand[13] == hand[0] || hand[13] == hand[1] || hand[13] == hand[2] ||
hand[13] == hand[3] || hand[13] == hand[4] || hand[13] == hand[5] ||
hand[13] == hand[6] || hand[13] == hand[7] || hand[13] == hand[8] ||
hand[13] == hand[9] || hand[13] == hand[10] || hand[13] == hand[11] ||
hand[13] == hand[12])) ans = 1;
//纯正九莲宝灯
//判断花色是否一致
bool jiulianFlag = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < 14; i++) {
if (hand[i].type == 'z' || hand[i].type != hand[i - 1].type) {
jiulianFlag = 0;
break;
}
}
if (jiulianFlag) {
if (hand[0].id == 1 && hand[1].id == 1 && hand[2].id == 1 &&
hand[3].id == 2 && hand[4].id == 3 && hand[5].id == 4 &&
hand[6].id == 5 && hand[7].id == 6 && hand[8].id == 7 &&
hand[9].id == 8 && hand[10].id == 9 && hand[11].id == 9 &&
hand[12].id == 9) ans = 1;
}
//大四喜
int z1cnt = 0;
int z2cnt = 0;
int z3cnt = 0;
int z4cnt = 0;
int dasixiJiang1 = 15;
int dasixiJiang2 = 15;
for (int i = 0; i < 14; i++) {
if (hand[i] == (Tile){'z', 1}) z1cnt++;
else if (hand[i] == (Tile){'z', 2}) z2cnt++;
else if (hand[i] == (Tile){'z', 3}) z3cnt++;
else if (hand[i] == (Tile){'z', 4}) z4cnt++;
else if (dasixiJiang1 == 15) dasixiJiang1 = i;
else dasixiJiang2 = i;
}
if (z1cnt == 3 && z2cnt == 3 && z3cnt == 3 && z4cnt == 3 && hand[dasixiJiang1] == hand[dasixiJiang2]) ans = 1;
cout << (ans ? "YES" : "NO") << endl;
}
}
F利用相似三角形模拟即可
也可以用圆外点到圆割线与切线的关系等价计算,此方法所有计算都可以在整数下进行,无精度误差
从圆外一点引圆的两条割线,这一点到每条割线与圆交点的距离的积相等,(切线也满足)
typedef long long ll;
int main() {
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--) {
ll fx,fy,rx,ry,r;
int n;
scanf("%lld %lld %lld %lld %d",&fx,&fy,&rx,&r,&n);
ry=fy;
ll len=(fx-rx)*(fx-rx)-r*r;
ll cnt=0;
ll all=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
ll y0,data;
scanf("%lld %lld",&y0,&data);
all+=data;
ll a=fy-y0;
ll b=-fx;
ll c=y0*fx;
ll d=(a*rx+b*ry+c)*(a*rx+b*ry+c);
ll R=r*r*(a*a+b*b);
if(d<=R) {
all=all-min(data,len);
}
}
printf("%lld\n",all);
}
}
*原本不保证高度相同,存在相切的情况,且存在直线相交但射线不相交的情况,且输出为误导性的"四舍五入到整数位",被NE削弱了
G显然卖萌值的前缀和在正整数域内为一个单调递增级数,可以近似理解为$N^3$,函数,估算可知$10^18$所需要的卖萌次数不会超过$10^6$数量级(实际为140000左右)
因此,预处理出前缀和,保证在数组中,对于每次询问,进行二分查找即可,复杂度约为$O(10^6+Tlog(10^6))$
记忆力好的直接用公式二分也行
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(15);
const int N = 15e5;
vector<long long> pre(N);
int n;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
pre[i] = 1LL * i * i;
pre[i] += pre[i - 1];
n = i;
if(pre[i] > (long long)1e18) break;
}
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
long long k;
cin >> k;
auto it = lower_bound(pre.begin(), pre.begin() + n, k);
if(*it > k) it--;
long long ans = *it;
cout << ans << '\n';
}
H根据行列的关系可以推公式
$A = (x_{min}+x_{max})(x_{max}-x_{min}+1)/2$
$B=(x_{max}-x_{min}+1)$
$C=(y_{min}+y_{max})(y_{max}-y_{min}+1)/2$
$D=(y_{max}*(y_{{max}}+1)*(2y_{max}+1)-(y_{min}-1)(y_{min})(2y_{min}-1))/6$
$Ans = A * C + B * (C-D)$
或者
可以先转化为原来矩阵的位置,直接算,更方便
设$a = xmax-xmin$,$b=ymax-ymin$。可以把每个元素对应到原矩阵上的位置,就会发现是求原矩阵中一个平行四边行中所有元素的和。平行四边形的顶点分别是$(xmin,ymin),(xmax,ymin),(xmin-b,ymin+b),(xmax-b,y+b)$。
对于第$ymin+i(i<=b)$列的所有所需要的元素,它们的和为$(ymin+i)*(xmin+xmax-2*i)*(xmax-xmin+1)/2$
然后只需要对上式的i从0到b求和即可。
最后的式子是$(a+1)*b*(ymax*(xmax+xmin)+(xmin+xmax-2*ymin)*(b+1)/2-(b+1)*(2*b+1))/2$
同时还要注意除法需要用到分母对于1000000007的模逆元
int T;
cin>>T;
ll inv = powmod(6,mod-2);
while(T--) {
ll u,v,x,y; //u:xmin,v:xmax,x:ymin,y:ymax
cin>>u>>x>>v>>y;
ll a = (u+v) * (v-u+1) / 2 % mod;
ll b = (v-u+1)%mod;
ll c = (x+y)*(y-x+1)/2%mod;
ll d = y*(y+1)%mod*(2*y+1)%mod - (((x-1)*x%mod*(2*x-1)%mod)%mod+mod)%mod;
d = d * inv % mod;
ll ans = a * c % mod+ b * ((c - d) % mod + mod)% mod;
ans %= mod;
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
I 显然$O(n^2)$的暴力会超时,于是考虑优化
建立两个标记l,r,对于区间[l,r]维护其中的种类数, 如果已经满足,就保存一次答案,并尝试删除$l$处的元素,并使$l=l+1$,直到不再满足答案为止,当前不满足答案时,尝试将$r+1$处的元素加入,使得$r=r+1$
显然,每个数组位置只会被遍历至多2次,复杂度$O(n)$
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e6+10;
int a[maxn], num[maxn];
int main() {
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--) {
int n, m, k;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", a+i);
if(a[i] > k) a[i] = 0;
}
memset(num, 0, sizeof num);
int l = 0, r = 0, ans = 1e7, len = 0;
num[0] = 1e7;
for(r = 0; r < n; r++) {
if(a[r] != 0 && num[a[r]] == 0) len++;
num[a[r]]++;
while(len >= k) {
if(a[l] != 0 && num[a[l]] == 1) {
len--;
ans = min(ans, r-l+1);
}
num[a[l]]--;
l++;
while(l < n && a[l] == 0) l++;
}
}
if(ans == 1e7) printf("-1\n");
else printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
J 首先,一个集合内出现多次的元素没有意义,所以要去重,去重后的数组最大为100,
然后如果暴力每个集合选一个,复杂度显然爆炸
但是可以发现等价的枚举方式,即先结合前2个数组,将结果再结合第3个数组...以此类推,每次结合一个新数组后,值域会增加,最后的总复杂度就是$O((N*(N+1)/2)*3e2*3e2)$
可以理解为简单的分组背包
存在更优秀的做法,例如不断两两结合(原本std要用这个,但是和背包拉不开数量级,索性不卡了..
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL_DEFINE
freopen("data.in", "rt", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
auto _start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(15);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<bool>> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int k;
cin >> k;
a[i].resize(301);
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[i][x] = true;
}
}
vector<vector<bool>> dp(n, vector<bool>(30001));
for (int i = 0; i <= 300; i++) {
if (a[0][i]) {
dp[0][i] = true;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 300; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k <= i * 300; k++) {
if (dp[i - 1][k] && a[i][j]) {
dp[i][k + j] = true;
}
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 30000; i++) {
ans += dp[n - 1][i];
}
cout << ans << '\n';
#ifdef LOCAL_DEFINE
auto _end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
cerr << "elapsed time: " << chrono::duration<double, milli>(_end - _start).count() << " ms\n";
#endif
return 0;
}
K排序之后,从编号[l,r]里面选出来的集合
如果包含a[l] a[r],那么他们都是a[l]*a[r],该值的贡献次数就是2^(r-l-1)
把答案表达式进行简单的因子提取,会发现对于每个右端点
(a[0]*2^(r-1)+a[1]*2^(r-2)+...a[r-1]*2(0) ) *a(r)
发现可以用类似秦九昭算法的方法来从进行O(n)计算
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
const int maxn = 1e5+10;
ll a[maxn];
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%lld", a+i);
sort(a, a+n);
ll last = 0, ans = 0;
for(int i = n-2; i >= 0; i--) {
last = (last*2%mod+a[i+1])%mod;
ll tmp = a[i]*last%mod;
ans += tmp;
ans %= mod;
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
L由于购买策略是"当前钱够就买",所以并不是带的钱越多能买的罐子数量越多(无单调性)
比如最多能带5元,商店有3个罐子,价格分别为5 1 1.如果带4元能买2个罐子,而带5元只够买一个.所以并不能用二分.注意到罐子的数量*每个罐子的最大价格最多只有3e5,则可以使用枚举法,枚举带的钱数,设罐子价格总和为sum,则只需要从1元枚举到min(sum+1,n).
对于每次枚举,判断是否能买m个罐子即可.
注意特殊样例
100 1 1
0
答案应为 1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int jar[305],n,m,k;
bool check(int money){
int buy=0;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
if(money>=jar[i]){
money-=jar[i];
buy++;
}
if(money==0||buy>=m)
break;
}
return buy>=m;
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
cin>>jar[i];
int len=min(k*1001,n);
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++)
if(check(i))
return cout<<i<<endl,0;
cout<<"poor chicken tail wine!"<<endl;
}
M简单思考发现,一定可以删除到0,接下来考虑所有数字二进制转化,把所有数字或起来,二进制下的1的个数即为答案
*原本题面写的是,全部清空的最少操作次数,NE觉得这个题太水,今早灵基一动,改成了尽量少
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int m;
cin >> m;
while(m--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
sum |= a[i];
}
int ans = __builtin_popcount(sum);
cout << ans << '\n';
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号