Web后端学习笔记 Flask (12)Restful
Restful API规范
restful API是用于在前端与后台进行通信的一套规范,使用这个规范可以让前后端开发变得更加轻松:
1. 协议:http或者https
2. 数据传输格式:json
3. url链接:url链接中,不能有动词,只能有名词,并且对于一些名词,如果出现复数,就用复数的形式
4. http请求方法:
GET:在服务器上获取资源
POST:在服务器上新创建一个资源
PUT:在服务器上更新资源(客户端提供所有改变后的数据)
PATCH:在服务器上更新资源(只需提供需要改变的信息)
DELETE:从服务器上删除资源
举例:
GET/users/ :获取所有用户
POST/user/:创建一个用户
GET/user/id/:根据id获取一个用户
PUT/user/id/:更新某个id的用户信息(需要提供用户的所=所有信息)
PATCH/user/id/:更新某个id的用户信息(只需提供需要修改的数据)
DELETE/user/id/:删除一个用户
状态码:
| 状态码 | 原生描述 | 描述 |
| 200 | OK | 服务器成功响应客户端请求 |
| 400 | INVALID REQUEST | 用户发出的请求有误,服务器没有进行新建或者修改数据 |
| 401 | Unauthorized | 用户没有权限访问这个请求 |
| 403 | Forbidden | 因为某些原因禁止访问这个请求 |
| 404 | NOT FOUND | 用户请求的url不存在 |
| 406 | NOT Acceptable | 用户请求不被服务器接受,例如服务器期望客户端发送某个字段,但是没有发送 |
| 500 | Internal Server error | 服务器内部错误,比如出现了bug |
Restful插件:
通过 pip install flask-restful安装flask-restful插件
定义restful视图函数:如果使用flask-restful,那么定义视图函数的时候,需要继承自flask-restful.Resource这个类,然后再根据当前请求的method来定义响应的方法。类似于类视图的功能,可以分别定义get方法与post方法。
工具:postman做接口测试
from flask import Flask, render_template, request from flask_restful import Api, Resource import config app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(config) api = Api(app=app) class LoginView(Resource): def post(self): return {"username": "tom"} api.add_resource(LoginView, '/login/', endpoint='login') @app.route('/') def index(): return render_template("html/index.html") if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
注意事项:
1. endpoint是用来给url_for反转url的时候使用的。如果不写endpoint,那么将会使用视图的名字的小写来作为endpoint。
2. add_resource的第二个参数是访问这个视图函数的url,这个url和之前的route一样,也可以传递参数,并且这个方法还可以传递多个url来指定这个视图函数。
class LoginView(Resource): # 如果add_resource绑定了多个url,如果没有传参,可以将视图函数中的参数设置为None # 此时即使url中没有传递参数,也不会报错 def post(self, username=None): return {"username": username} api.add_resource(LoginView, '/login/<username>/', '/register/', endpoint='login')
注意事项:
1. 如果向返回json数据,那么就使用flask-restful,如果向渲染模板,那么好是采用视图函数或者类视图的方法。
2. url还是和之前的一样,可以传递参数。不同的是视图函数的是,可以绑定多个视图函数。
flask-restful参数
flask-restful插件提供了类似于WTForms来验证提交的数据是否合法,叫做reparse
class LoginView(Resource): # 如果add_resource绑定了多个url,如果没有传参,可以将视图函数中的参数设置为None # 此时即使url中没有传递参数,也不会报错 def post(self): parse = reqparse.RequestParser() parse.add_argument("username", type=str, help="用户名验证错误") parse.add_argument("password", type=str, help="密码验证错误") args = parse.parse_args() return {"username": args.get("username"), "password": args.get("password")} api.add_resource(LoginView, '/login/', endpoint='login')
在不传参数的时候,返回的结果:
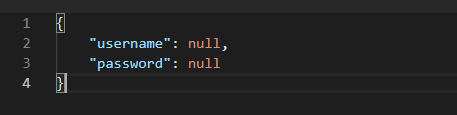
在post方法中传递参数之后,可以看到返回的结果:
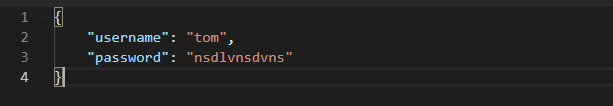
add_argument可以指定的字段:
1. default: 当没有传递相应参数的时候,设置这个参数的默认值
2. required:是否必须传递这一参数, 布尔值
3. type:指定提交的参数的类型,如果指定,那么将使用指定的数据类型来强制转换提交上来的值。
4. choices:选项,提交上来的值只有满足这个选项中的值才能验证通过
5. help:错误信息,如果验证失败,将会使用这个参数指定的值作为错误信息
6. trim:是否要取出前后的空格
type字段的值,可以使用python内置的数据类型,也可以使用flask-restful.input中的类型,例如:
url:判断传入的参数是否为url
regex:正则表达式
date:将这个字符串转换为datetime.date,如果转换失败,则会抛出异常
from flask import Flask, render_template, request from flask_restful import Api, Resource, reqparse, inputs import config app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(config) api = Api(app=app) class LoginView(Resource): # 如果add_resource绑定了多个url,如果没有传参,可以将视图函数中的参数设置为None # 此时即使url中没有传递参数,也不会报错 def post(self): parse = reqparse.RequestParser() parse.add_argument("username", type=str, help="用户名验证错误", trim=True) parse.add_argument("password", type=str, help="密码验证错误", trim=True) parse.add_argument("age", type=int, help="年龄验证错误", trim=True) parse.add_argument("render", type=str, choices=["female", "male"], trim=True, help="性别填写错误") parse.add_argument("link", type=inputs.url, trim=True, help="url填写错误") parse.add_argument("phone", type=inputs.regex(r"1[3578]\d{9}"), trim=True, help="电话号码格式错误") args = parse.parse_args() return {"username": args.get("username"), "password": args.get("password"), "age": args.get("age"), "render": args.get("render")} api.add_resource(LoginView, '/login/', endpoint='login') @app.route('/') def index(): return render_template("html/index.html") if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
Flask-restful标准:
输出字段:
对于一个视图函数,可以指定好一些字段用于返回。在可以使用ORM模型或者自定义模型的时候,它会自动获取模型中的相应字段,生成json数据,然后再返回给客户端。这其中需要导入flask_restful.marshal_with装饰器,并且需要写一个字典,来指示需要返回的字段,以及该字段的数据类型。
from flask import Flask, render_template, request from flask_restful import Api, Resource, fields, marshal_with import config app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(config) api = Api(app=app) class ArticleView(Resource): resource_fields = { "title": fields.String, "content": fields.String } # 指定需要返回的字段 @marshal_with(resource_fields) def get(self): return {"title": "xxx", "content": "yyy"} api.add_resource(ArticleView, '/articles/', endpoint="articles") @app.route('/') def index(): return render_template("html/index.html") if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
有的字段没有值,在return的字典中没有写,也会返回为null值:
class ArticleView(Resource): resource_fields = { "title": fields.String, "content": fields.String } # 指定需要返回的字段 @marshal_with(resource_fields) def get(self): return {"title": "xxx"} # 即使此时content字段没有值,也会返回为null,这样就保证了接口比较规范 api.add_resource(ArticleView, '/articles/', endpoint="articles")
返回的结果:
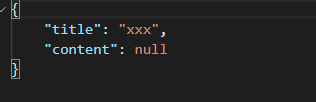
这种方式还有一个好处,就是如果相应的数据是一个模型,则可以直接返回模型的对象即可,而不用构建字典
from flask import Flask, render_template, request from flask_restful import Api, Resource, fields, marshal_with import config app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(config) api = Api(app=app) class Article(object): def __init__(self, title, content): self.title = title self.content = content article = Article(title="gone with wind", content="xsddkkjsdv") class ArticleView(Resource): resource_fields = { "title": fields.String, "content": fields.String } # 指定需要返回的字段 @marshal_with(resource_fields) def get(self): return article # 可以根据article对象中的属性自动构造字典,返回字典 api.add_resource(ArticleView, '/articles/', endpoint="articles") @app.route('/') def index(): return render_template("html/index.html") if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
复杂结构:
返回的字段的值任然是一个模型,则需要使用Nested()方法再定义一个字典,返回相应的字段
# 定义一个restful视图 class ArticleView(Resource): resource_field = { "title": fields.String, "content": fields.String, "author": fields.Nested({ # User类型 "username": fields.String, "email": fields.String }), "tags": fields.Nested({ "name": fields.String }) } @marshal_with(resource_field) def get(self, article_id): article = db.session.query(Article).filter(Article.id == article_id).first() return article api.add_resource(ArticleView, '/articles/<article_id>/', endpoint="article")
使用field.Nested()之后,返回的的数据如下所示:
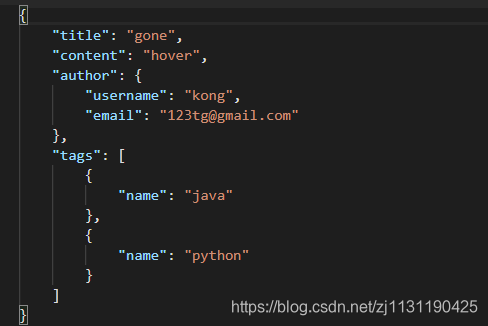
重命名属性:
在读取模型中的某个字段之后,需要用一个新的名字将其返回,可以使用attribute属性实现:
例如,需要将article中的title属性返回,并赋予一个新的属性名:
# 定义一个restful视图 class ArticleView(Resource): resource_field = { "article_title": fields.String(attribute="title"), # 改变属性的名字 "article_content": fields.String(attribute="content"), "article_author": fields.Nested({ # User类型 "username": fields.String, "email": fields.String }, attribute="author"), "article_tags": fields.Nested({ "name": fields.String }, attribute="tags") } @marshal_with(resource_field) def get(self, article_id): article = db.session.query(Article).filter(Article.id == article_id).first() return article api.add_resource(ArticleView, '/articles/<article_id>/', endpoint="article")
返回结果:
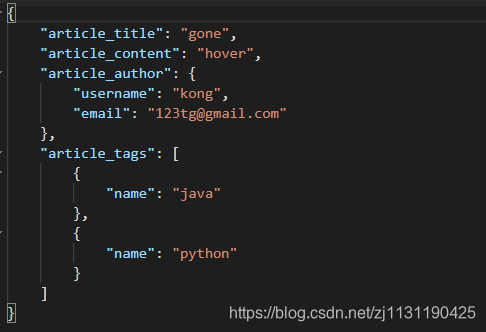
默认值:
在resource_field中定义的一些字段,如果模型中没有与之对应的字段,则该字段的值会被设置为null返回。除此之外,还可以给没有的字段设置默认值,最后返回的该字段的值就是默认值,而不是null.
class ArticleView(Resource): resource_field = { "article_title": fields.String(attribute="title"), # 改变属性的名字 "article_content": fields.String(attribute="content"), "article_author": fields.Nested({ # User类型 "username": fields.String, "email": fields.String }, attribute="author"), "article_tags": fields.Nested({ "name": fields.String }, attribute="tags"), "read_cnt": fields.Integer(default=100) } @marshal_with(resource_field) def get(self, article_id): article = db.session.query(Article).filter(Article.id == article_id).first() return article api.add_resource(ArticleView, '/articles/<article_id>/', endpoint="article")
此时返回的read_cnt字段的值就是默认值100:
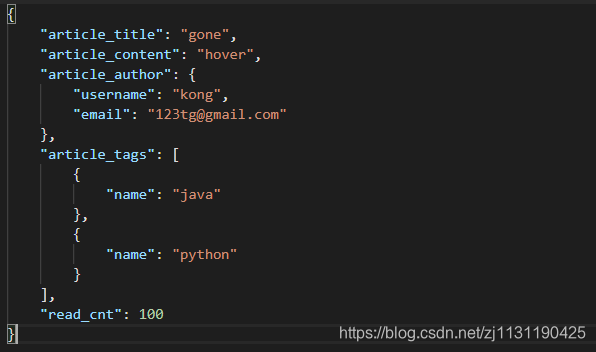
Flask-restful细节:
1. flask-restful结合蓝图使用
在flask-restful中使用蓝图,需要将蓝图定义到一个单独的文件即可,此时在定义api的时候,以蓝图为参数,而不用再以app作为定义api的参数,在主app主注册蓝图:
例如,定义蓝图的文件,articleViews.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from flask import Blueprint from flask_restful import Resource, fields, marshal_with, Api from models import User, Article, Tag from exts import db article_bp = Blueprint("article", __name__, url_prefix="/article") api = Api(article_bp) # api # 定义一个restful视图 class ArticleView(Resource): resource_field = { "article_title": fields.String(attribute="title"), # 改变属性的名字 "article_content": fields.String(attribute="content"), "article_author": fields.Nested({ # User类型 "username": fields.String, "email": fields.String }, attribute="author"), "article_tags": fields.Nested({ "name": fields.String }, attribute="tags"), "read_cnt": fields.Integer(default=100) } @marshal_with(resource_field) def get(self, article_id): article = db.session.query(Article).filter(Article.id == article_id).first() return article api.add_resource(ArticleView, "/<article_id>/", endpoint="article")
在主app.py文件中注册蓝图:
from flask import Flask, render_template, request import config from exts import db from models import User, Article, Tag from articleViews import article_bp app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(config) db.init_app(app=app) app.register_blueprint(article_bp) # 注册蓝图 @app.route('/') def index(): user = User(username="kong", email="123tg@gmail.com") article = Article(title="gone", content="hover") article.author = user tag1 = Tag(name="java") tag2 = Tag(name="python") article.tags.extend([tag1, tag2]) db.session.add(article) db.session.commit() return "Hello" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
其中models文件为定义ORM模型的文件:models.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from exts import db class User(db.Model): __tablename__ = "user" id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) username = db.Column(db.String(50), nullable=False) email = db.Column(db.String(50), nullable=False) # tag和article之间是多对多的关系 article_tag = db.Table("article_tag", db.Column("article_id", db.Integer, db.ForeignKey("article.id"), primary_key=True), db.Column("tag_id", db.Integer, db.ForeignKey("tag.id"), primary_key=True), ) class Article(db.Model): __tablename__ = "article" id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) title = db.Column(db.String(100), nullable=False) content = db.Column(db.Text) author_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey("user.id")) author = db.relationship("User", backref="articles") tags = db.relationship("Tag", secondary=article_tag, backref="articles") class Tag(db.Model): __tablename__ = "tag" id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True) name = db.Column(db.String(50))
2. flask-restful渲染模板
falsk-restful规定的数据交互的形式是JSON,所以即使返回渲染的模板(及render_templlate(html文件)),此时在浏览器中显示的还是字符串形式的,而不会当作html代码被浏览器解析:此时需要借助一个装饰器,@api.representation("text/html")来定义一个函数,在这个函数中对html代码进行封装,再进行返回
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from flask import Blueprint, render_template, make_response from flask_restful import Resource, fields, marshal_with, Api from models import User, Article, Tag from exts import db article_bp = Blueprint("article", __name__, url_prefix="/article") api = Api(article_bp) # api @api.representation("text/html") # 保证restful也能够通过render_template渲染模板 def output_html(data, code, headers): # data是字符串形式的html文本 resp = make_response(data) # 构造Response对象 return resp # 定义一个restful视图 class ArticleView(Resource): resource_field = { "article_title": fields.String(attribute="title"), # 改变属性的名字 "article_content": fields.String(attribute="content"), "article_author": fields.Nested({ # User类型 "username": fields.String, "email": fields.String }, attribute="author"), "article_tags": fields.Nested({ "name": fields.String }, attribute="tags"), "read_cnt": fields.Integer(default=100) } @marshal_with(resource_field) def get(self, article_id): article = db.session.query(Article).filter(Article.id == article_id).first() return article class ArticleListView(Resource): def get(self): return render_template("html/list.html") # 此时,restful返回的依然是字符串形式的html文本,不能被浏览器解析 api.add_resource(ArticleView, "/<article_id>/", endpoint="article") api.add_resource(ArticleListView, '/list/', endpoint="list")





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)