数据结构与算法笔记(二) 线性表(数组描述)
c++常用的数据描述方法是数组描述和链式描述,线性表可以用来说明这两方法,先介绍数组描述的线性表。后面再介绍链式描述的线性表。
C++ STL容器vector和list相当于线性表的数组描述和链式描述。数组描述方法将元素存储在一个数组中,所有元素依次存储在一片连续的存储空间,这就是所谓的顺序表
数据对象和数据结构:
数据对象是一组实例或值。 // 数据实例 理解:数据对象int, 5是数据对象 int 的实例。 还有string, digit之类的数据对象
数据对象通常会有一系列i相关的操作或者函数,把数据对象的实例转换为该对象的另一个实例。或者转化为其他数据对象的实例
数据结构:数据结构是一个数据对象,同时这个对象的实例以及构成实例的元素都存在着联系,而这些联系有相关的函数决定。
数据结构研究的是数据对象的描述以及相关函数的具体实现。
1.线性表数据结构:
线性表也称有序表,它的每一个实例都是元素的有序集合。线性表实例的形式,其中,
是线性表的元素,i是索引,n是线性表的长度。元素可以看成原子,他们本身的结构金额线性表无关。
线性表可以用抽象数据类型来说明(abstract data type, ADT):即说明它的实例,也说明它的操作
LinearList
{
实例:
有限个元素的集合
操作:
empty();
size();
get(index);
indexOf(x); // 返回元素的索引值
erase(index); // 删除某个元素
insert(index, x); // 插入元素
output(); // 输出线性表
创建();
撤销();
}
可以用抽象类来描述上面的数据类型LineraList
template<typename T>
class linearList
{
public:
virtual ~linearList() {}; // 析构函数
virtual bool empty() const=0;
virtual int size() const=0;
virtual T& get(int index) const=0;
virtual int indexOf(T x) const=0;
virtual void erase(int index) const=0;
virtual void insert(int index, T& x) const=0;
virtual void output() const=0;
}
上面的类相当于数据结构LinearList的基类,这是一个抽象类。
数组描述:
在数组描述中,用数组来存储线性表的元素。我们需要一个映射,使得数组的每一个元素对应线性表的一个元素。可以用公式表示为:
location(i) = i
即: 第i个线性表中的元素在数组中的位置是i.
改变数组的长度:
增加或者减少新的数组长度,首先要建立一个具有新长度的数组,把旧数组的元素复制到新的数组。
template<typename T>
void changeLength1D(T*& a, int oldLength, int newLength)
{
if(newLength<0)
throw illegalParameterValue("New length must >= 0");
T* temp = new T[newLength];
int number = min(oldLength, newLength); // 复制的元素个数
copy(a, a+number, temp);
delete []a ; // 释放老数组的内存空间
a = temp;
}
arrayList类:
定义一个Linearlist(抽象类)的派生类:这个派生类继承了基类的方法的同时,也要定义一些自己特有的方法
arrayList类的基类:linearlist中定义一些纯虚函数(注意春熙函数的定义方法),所以linearList类是一个抽象类
虚函数virtual functiuonName() const=0表示的是定义为纯虚函数,这个纯虚函数是只读函数
虚函数virtual functiuonName()=0表示的是定义为纯虚函数,这个纯虚函数不是只读函数
linearlist.h
#ifndef LINEAR_LIST_H
#define LINEAR_LIST_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T> // 定义一个抽象类
class linearList
{
public:
// 抽象类中的纯虚函数
virtual ~linearList() {}; // 析构函数
virtual bool empty() const=0;
virtual int size() const=0;
virtual T& get(int index) const=0;
virtual int indexOf(const T& x) const=0; // 这里定义的是虚函数,虚函数virtual functiuonName() const=0表示的是定义为纯虚函数,这个纯虚函数是只读函数
virtual void erase(int index) = 0; // 这里定义的是虚函数,虚函数virtual functiuonName()=0表示的是定义为纯虚函数,这个纯虚函数不是只读函数
virtual void insert(int index, T x) = 0;
// virtual void output(ostream& out) const=0;
};
#endif
arrayList.h
// 定义模板类: lineaList的派生类
#ifndef ARRAY_LIST_H
#define ARRAY_LIST_H
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\linearlist.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class arrayList : public linearList<T>
{
private: // 数据域
T* element;
int arrayLength; // 一维数组的长度
int listSize; // 线性表长度
//void checkIndex(int index) const;
public:
arrayList(); // 无参构造函数
arrayList(int capacity); //构造函数
arrayList(const arrayList& array); // 拷贝构造函数
~arrayList(); //析构函数
// ADT方法:abstract data type 抽象数据类型
bool empty() const; // 线性表是否为空
int size() const;
T& get(int index) const;
int indexOf(const T x) const;
void erase(int index);
void insert(int index, T x);
//void output(ostream& out) const;
// 其他方法
int capacity() const;
// 重载流插入运算符
// friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayList<T>& array_list); // 重载流插入运算符 <<只能以友元函数的形式重载
void output() const;
// 添加新的方法
void clear();
void push_back(T x); // 在线性表的最右端添加元素
T& pop_back(); // 在线性表的最右端删除元素, 且把值返回来
};
// 模板类的实现
// 无参数构造函数
template <typename T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList()
{
arrayLength = 5; // 初始数组的大小10
listSize = 0;
element = new T[arrayLength];
}
// 有参数的构造函数
template <typename T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(int capacity)
{
if(capacity<1)
{
// cout << "The Initial capacity= " << capacity << " Must > 0" << endl;
//throw invalid_argument("The Initial capacity must bigger than zero");
// cout << "Parameter wrong" << endl;
}
this->arrayLength = capacity;
this->listSize = 0;
this->element = new T[arrayLength];
}
// 拷贝构造函数
template <typename T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(const arrayList& array_list)
{
arrayLength = array_list.arrayLength;
listSize = array_list.listSize;
element = new T[arrayLength];
for(int i=0; i<listSize; i++)
{
element[i] = array_list.element[i];
}
}
// 析构函数
template<typename T>
arrayList<T>::~arrayList()
{
delete [] element;
}
// ADT方法, 抽象数据类型 arralyList基本方法实现
template<typename T>
bool arrayList<T>::empty() const
{
return listSize==0;
}
template<typename T>
int arrayList<T>::size() const // 返回线性表的长度
{
return listSize;
}
template<typename T>
T& arrayList<T>::get(int index) const
{
return element[index];
}
template<typename T>
int arrayList<T>::indexOf(const T x) const
{
int i;
bool found_flag = false;
for(i=0; i<listSize; i++)
{
if(element[i]==x)
{
found_flag = true;
break;
}
}
return (found_flag)?i:-1;
}
template<typename T>
void arrayList<T>::erase(int index) // 删除线性表中的某个元素
{
// 添加索引的检查函数 checkindex中定义一个异常类
for(int i=index; i<listSize-1; i++)
{
element[i] = element[i+1];
}
listSize--;
}
template<typename T>
void arrayList<T>::insert(int index, T x) // 插入一个元素
{
//int old_listSize = listSize; // 线性表的原来长度
//listSize++; // 插入元素后线性表的长度
if(listSize>=arrayLength) // 现象表中的元素个数超出数组的大小
{
arrayLength *= 2; // 增加数组的大小
T* old = element;
element = new T[arrayLength]; // 新数组
//int i;
for(int i=0; i<listSize; i++)
{
element[i] = old[i]; // 先把element中的元素复制过来
}
delete [] old; // 释放old_ListSize的内存
}
// 再执行插入操作
int j;
for(j=listSize-1; j>=index; j--)
{
element[j+1] = element[j];
}
element[++j] = x;
listSize++;
}
template<typename T>
int arrayList<T>::capacity() const // 返回数组的大小
{
return arrayLength;
}
template<typename T>
void arrayList<T>::clear()
{
listSize = 0; // 线性表长度为0
delete [] element; // 释放原来的内存
arrayLength = 5;
element = new T[arrayLength]; //分配较小的内存
}
/*
template<typename T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayList<T>& array_list)
{
for(int i=0; i<listSize; i++)
{
out << element[i] << " ";
if(i%10==0)
out << endl;
}
out << endl;
}
*/
template<typename T>
void arrayList<T>::output() const
{
if(listSize == 0)
{
cout << "Empty array !" << endl;
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<listSize; i++)
{
cout << element[i] << " ";
if((i+1)%10==0)
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
template<typename T>
void arrayList<T>::push_back(T x)
{
if(listSize>=arrayLength) // 需要扩充数组的大小
{
arrayLength *= 2;
T* old = element;
element = new T[arrayLength];
for(int i=0; i<listSize; i++)
{
element[i] = old[i];
}
delete [] old; // 释放内存
}
element[listSize++] = x; // 在线性表的最右端插入元素
}
template<typename T>
T& arrayList<T>::pop_back()
{
T& tmp = element[listSize-1];
listSize--;
return tmp;
}
#endif
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <time.h>
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\linearlist.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\arraylist.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\digui\external_file\chain.h"
using namespace std;
// 实现友元函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
arrayList<double> array(3);
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
array.insert(i, i*i);
}
cout << "array capacity is " << array.size() << endl;
array.output();
array.erase(4);
array.output();
array.insert(4, 10);
array.output();
array.clear();
cout << "array capacity is " << array.size() << endl;
array.output();
array.push_back(1.23); // 分配的最小内存5
array.push_back(2.3);
array.push_back(3.3);
array.push_back(9.6);
array.push_back(9.1);
array.push_back(11.2);
array.push_back(3.1415);
array.output();
double num = array.pop_back();
cout << "The pop number is " << num << endl;
array.output();
return 0;
}
运行结果: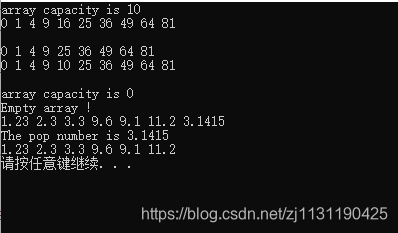
再动态的增加数组的长度的时候,每次为什么不是+1,+2,而是加倍:
无论数组每次增加多少,都不影响每一次最坏的插入操作时间 ,但是影响连续插入时的渐进时间复杂度,假设从长度为1的表开始插入数据,每次都插入到表尾,所以不需要移动表里的元素,时间复杂度是
。
假设执行次插入操作,则n次插入的时间为T:
其中A是执行插入操作的时间复杂度:
数组增加长度的操作,代码如下
//int old_listSize = listSize; // 线性表的原来长度
//listSize++; // 插入元素后线性表的长度
if(listSize>=arrayLength) // 现象表中的元素个数超出数组的大小
{
arrayLength *= 2; // 增加数组的大小
T* old = element;
element = new T[arrayLength]; // 新数组
//int i;
for(int i=0; i<listSize; i++)
{
element[i] = old[i]; // 先把element中的元素复制过来
}
delete [] old; // 释放old_ListSize的内存
} 对于B来说,如果数组长度按照+1,则数组改变长度的时间是:
则:
如果数组的长度每次增加两倍:
n次插入操作,,其中k就是执行数组扩容的次数,每次扩容的时间复杂度2的k次方,也即数组扩容前
个元素进行复制
所以k次插入数组扩容的时间复杂度是B,则
所以有:
这就是数组长度每次都增加两倍的原因:
-------------------------------------------------------分割线---------------------------------------------------------------
添加新的方法,对arrayList进行修改
1.当线性表中的元素个数小于数组长度的1/4时,数组长度减半
2. 添加异常类checkIndex();



