C++数据结构与算法 队列的应用之图元识别
图元识别:
数字化图像可以看作m*m的矩阵,单色如图中,像素点的值为0,1.值为0的点表示背景,为1的点表示图元上的一个点。两个相邻的图元像素是同一个图元的像素,图元识别就是给同一个图元的像素做标记。
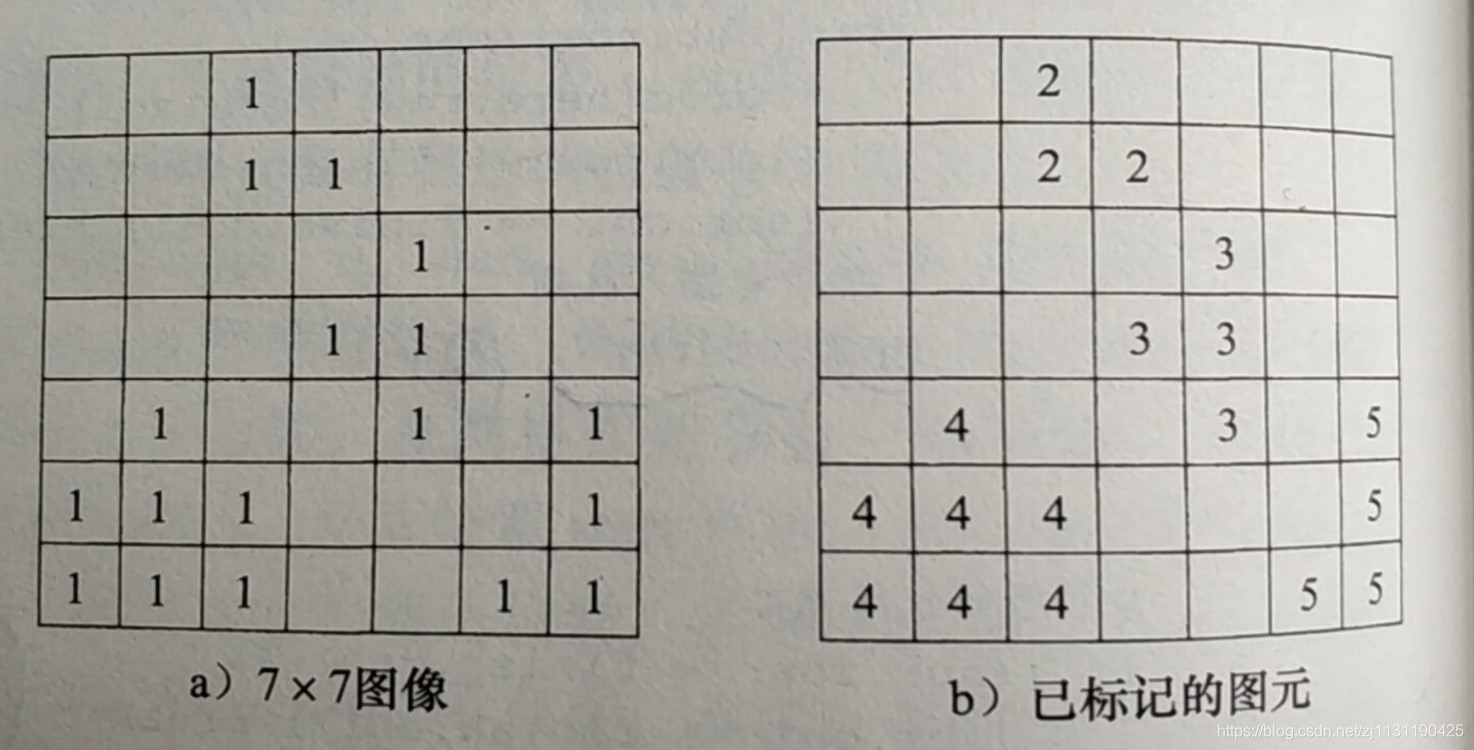
原理如上图所示。
算法思路:
通过扫描像素来识别图元,采用逐行扫描的方式,当扫描到一个未标记图元像素的时候,给他一个图元标记,将其作为一个新图元种子,通过识别标记所有与该种子相邻的元素,来寻找到剩余的像素点。与种子相邻的像素点称为1-间距像素,然后识别和标记与1-间距相邻的所有未标记的像素,这些像素称为2-间距像素。接着标记与2-间距相邻的像素点。直到标记完所有的像素点为止。
算法实现:
#include <iostream> #include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\dequeue\external_file\queue.h" using namespace std; // 迷宫 template<typename T> void print_array(T **a, int size) { for(int i=0; i<size; i++) { for(int j=0; j<size; j++) { cout << a[i][j] << " "; } cout << endl; } cout << endl; } class position // 存储位置坐标 { public: int row; int col; position() { row = 0; col = 0; } position(int row, int col) { this->row = row; this->col = col; } /* void add_offset(position& ps) { row += ps.row; col += ps.col; } */ }; void labelCompents(int** graph, int graphSize) // 标记图元 { // 参数:原始图像, 图像大小 // 给图像的边缘添加一层背景(0) int** new_graph = new int*[graphSize+2]; for(int i=0; i<graphSize+2; i++) { new_graph[i] = new int[graphSize+2]; } for(int i=0; i<graphSize+2; i++) { for(int j=0; j<graphSize+2; j++) { if(i==0 || i==graphSize+2-1) // 图元添加背景像素 { new_graph[i][j] = 0; } else if(j==0 || j==graphSize+2-1) // 图元添加背景像素 { new_graph[i][j] = 0; } else { new_graph[i][j] = graph[i-1][j-1]; } } } cout << "原始图像: " << endl; print_array(new_graph, graphSize+2); // 寻找图元 // 初始化偏移量 position offset[4]; // 向右偏移 index=0 offset[0].row = 0; offset[0].col = 1; // 向下偏移 index=1 offset[1].row = 1; offset[1].col = 0; // 向左偏移 index=2 offset[2].row = 0; offset[2].col = -1; // 向上偏移 index=3 offset[3].row = -1; offset[3].col = 0; int direction_number = 4; // 一个方格相邻位置的个数 queue<position> q1; position current_position; // 当前的位置 position neighbor; // 相邻位置 int id = 1; // 图元的标号 // 开始扫描图像 for(int i=0; i<graphSize+2; i++) { for(int j=0; j<graphSize+2; j++) { if(new_graph[i][j]==1) { new_graph[i][j] = ++id; // 将这个位置标记为当前位置,也是图元种子 current_position.row = i; current_position.col = j; while(true) { for(int cnt=0; cnt<direction_number; cnt++) { // 确定相邻的位置 neighbor.row = current_position.row + offset[cnt].row; neighbor.col = current_position.col + offset[cnt].col; if(new_graph[neighbor.row][neighbor.col]==1) // 相邻位置满足条件 { new_graph[neighbor.row][neighbor.col] = id; q1.push(neighbor); } } if(q1.empty()) { break; // 当前编号标记完毕,寻找下一个编号 } current_position = q1.front(); q1.pop(); } } } } cout << "标记后的图元: " << endl; print_array(new_graph, graphSize+2); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int map_size = 10; int input_map[10][10] = { {0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1}, {1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1}, {1,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1}, {1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0} }; // 数据转换 int** map_in = new int*[map_size]; for(int i=0; i<map_size; i++) { map_in[i] = new int[map_size]; } for(int i=0; i<map_size; i++) { for(int j=0; j<map_size; j++) { map_in[i][j] = input_map[i][j]; } } // 将原始地图转换为指针的形式 labelCompents(map_in, map_size); return 0; }
运行结果:

上述的图元标记算法中应用到了很多迷宫最短路径中的方法:https://blog.csdn.net/zj1131190425/article/details/88086506
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)