C++数据结构与算法(九) 树,优先级队列,最大堆的实现
树:
用来表示具有结构层次的数据,应用:
软件工程技术:模块化技术
根:
子树:
在树中,每个元素都代表一个节点。
树的级: 根是一级,根的孩子是二级,一次往下,有三级,四级。。。
树的高度(深度): 树中级的个数
树中元素的度:一个元素的度指其孩子的个数,一棵树的度是其元素的度的最大值
二叉树:
定义:一棵二叉树t是有限个元素的集合,当二叉树非空时,其中有一个元素是根,余下的元素被划分为两颗二叉树,称为t的左子树和右子树。
二叉树和树的区别:
1. 每个元素恰好又两棵子树。
2. 元素的子树是有序的,有左右之分
3. 树的子树是无序的
4. 二叉树可以为空
二叉树的特性:
1. 一个二叉树有n个元素,则它有n-1条边。(除过根节点外,所有元素有且只有一个父节点)
2. 二叉树的高度为h,则他的元素个数x满足
3. 一棵二叉树有n个元素(n>0),则它的高度h满足
4. 高度为h的二叉树有个元素,则称为满二叉树
5 完全二叉树:
对于高度为h的满二叉树,
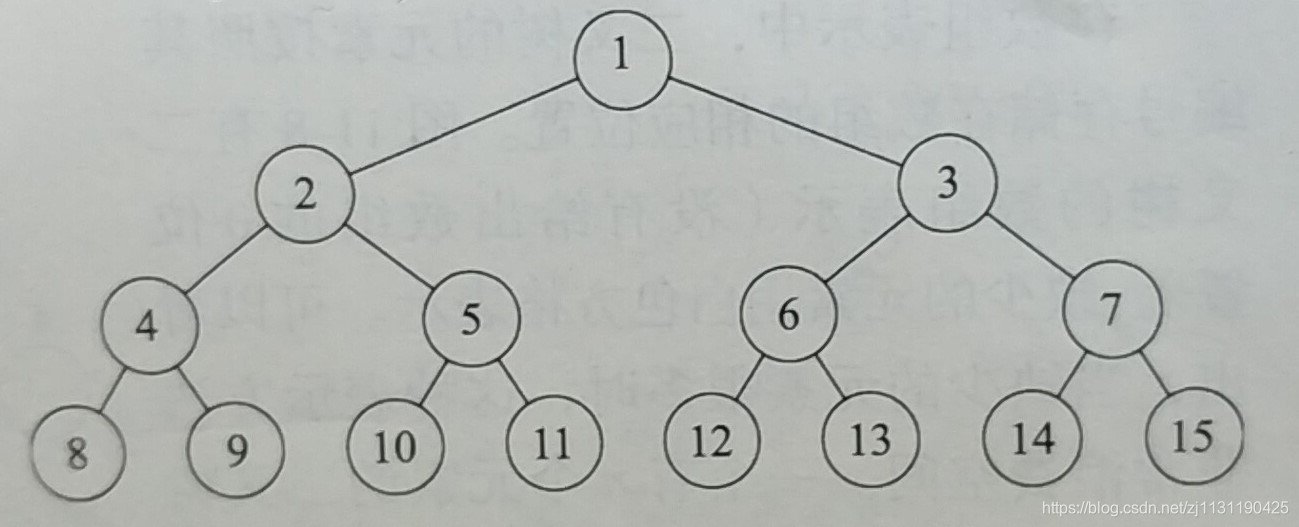
按照从左到右,从上到下的顺序编号,从1-2^h-1, 从二叉树中删除k个编号为2^h-i的元素(1<=i<=k), 所得到的二叉树被称为完全二叉树。
6. 假设一个完全二叉树的编号为i, 1<=i<=n,则有一下关系:
a. i=1, 则该元素为根节点,i>1,其父节点的编号为[1/2]
b. 2i>n, 则该元素没有左孩子,否则,左孩子的编号为2i
c 2i+1>n, 该元素无右孩子, 否则右孩子的编号为2i+1
二叉树描述:
1. 数组描述:
在数组描述中,二叉树中的元素按照其编号存储在数组的相应位置

可以看到,具有n个节点的二叉树,可能最多需要2^n个存储空间来存储(右斜二叉树),这样会浪费大量的存储空间,只有当二叉树缺少的元素数目较少时,才会用到数组描述
2.链表描述
用一个节点描述二叉树的一个元素,系欸但包含是两个指针(leftchild, rightchild)和数据域,先实现二叉树结点的数据描述
template<typename T>
struct binaryTreeNode // 定义二叉树的节点
{
T element;
binaryTreeNode<T>* leftchild; // 左子树
binaryTreeNode<T>* rightchild; // 右子树
binaryTreeNode()
{
leftchild = NULL;
rightchild = NULL;
}
binaryTreeNode(T value)
{
element = value;
leftchild = NULL;
rightchild = NULL;
}
binaryTreeNode(T value, binaryTreeNode<T>* theleftchild, binaryTreeNode<T>* therightchild)
{
element = value;
leftchild - theleftchild;
rightchild = therightchild;
}
};
由于一个n个节点的树有n-1条边,所以值为NULL的指针个数为2*n-(n-1) = n+1个
二叉树常用操作:
有四种常用的二叉树遍历方法:
1.前序遍历
2.中序遍历
3.后序遍历
4 层次遍历
且者四种遍历方法的时间复杂度均为O(n)
二叉树的ADT:
// 二叉树的抽象基类
#ifndef BINARY_TREE_ABC_H
#define BINARY_TREE_ABC_H
template<typename T>
class binaryTreeABC
{
public:
virtual bool empty() const=0;
virtual int size() const=0;
virtual void preOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0; // 前序遍历
virtual void inOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0; // 中序遍历
virtual void postOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0; // 后序遍历
//virtual void levelOrder(void (*),(T*)) = 0; // 层级遍历
// void (*) (T*)是一种函数类型,其参数是T*, 返回值为void
};
#endif
二叉树的实现
binaryTree类的是实现:
#ifndef BINARY_TREE_H
#define BINARY_TREE_H
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\binaryTree\external_file\binaryTreeABC.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
struct binaryTreeNode // 定义二叉树的节点
{
T element;
binaryTreeNode<T>* leftchild; // 左子树
binaryTreeNode<T>* rightchild; // 右子树
binaryTreeNode()
{
leftchild = NULL;
rightchild = NULL;
}
binaryTreeNode(T value)
{
element = value;
leftchild = NULL;
rightchild = NULL;
}
binaryTreeNode(T value, binaryTreeNode<T>* theleftchild, binaryTreeNode<T>* therightchild)
{
element = value;
leftchild - theleftchild;
rightchild = therightchild;
}
};
template<typename E>
class binaryTree : public binaryTreeABC<binaryTreeNode<E> >
{
private:
binaryTreeNode <E>* root; // 根节点
int treeSize; // 节点个数
static void (*visit)(binaryTreeNode<E>* t); // 访问函数 静态数据成员visit
// visit是一个函数指针, 返回值void, 参数 binaryTreeNode*
static void preOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);
static void inOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);
static void postOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);
//static void levelOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);
static void dispose(binaryTreeNode<E> *t) // 删除一个节点
{
delete t;
}
public:
binaryTree(); // 构造方法
~binaryTree(); // 析构方法
bool empty() const
{
return treeSize==0;
}
int size() const
{
return treeSize;
}
void preOrder(void (*theVisit) (binaryTreeNode<E>*)) // 公有的方法 函数签名()
{
visit = theVisit;
preOrder(root); // 这里调用的是私有的preOrder()函数
// 在实际的应用中,用户只能通过实例化的对象调用公有的方法,公有的方法内,调用了私有的方法
}
void inOrder(void (*theVisit) (binaryTreeNode<E>*))
{
visit = theVisit;
inOrder(root);
}
void postOrder(void (*theVisit) (binaryTreeNode<E>*))
{
visit = theVisit;
postOrder(root);
}
//void levelOrder(void (*) binaryTreeNode<E>*);
void erase()
{
postOrder(dispose);
root = NULL;
treeSize = 0;
}
};
// 类的实现
template<typename E>
binaryTree<E>::binaryTree()
{
root = NULL;
treeSize = 0;
}
template<typename E>
binaryTree<E>::~binaryTree()
{
erase();
}
// 实现类中私有的方法
template<typename E>
void binaryTree<E>::preOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{
// 前序遍历
if(t!=NULL) // 通过递归的方法访问系欸但
{
visit(t);
preOrder(t->leftchild);
preOrder(t->rightchild);
}
}
template<typename E>
void binaryTree<E>::inOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{
// 中序遍历
if(t!=NULL)
{
//binaryTree<E>::visit(t);
inOrder(t->leftchild);
visit(t);
inOrder(t->rightchild);
}
}
template<typename E>
void binaryTree<E>::postOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{
// 后序遍历
if(t!=NULL)
{
postOrder(t->leftchild);
postOrder(t->rightchild);
visit(t);
}
}
//template<typename E>
//void binaryTree<E>::levelOrder(void (*) (binaryTreeNode<E*))
#endif修改版二叉树代码如下:
对上面的二叉树的代码实现做了一些修改,问题已经改正:binaryTree.h文件
#ifndef BINARY_TREE_H
#define BINARY_TREE_H
// #include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\binaryTree\external_file\binaryTreeABC.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
struct binaryTreeNode // 定义二叉树的节点
{
T element;
binaryTreeNode<T>* leftchild; // 左子树
binaryTreeNode<T>* rightchild; // 右子树
binaryTreeNode()
{
leftchild = NULL;
rightchild = NULL;
}
binaryTreeNode(T value)
{
element = value;
leftchild = NULL;
rightchild = NULL;
}
binaryTreeNode(T value, binaryTreeNode<T>* theleftchild, binaryTreeNode<T>* therightchild)
{
element = value;
leftchild = theleftchild;
rightchild = therightchild;
}
};
// 实现二叉树的类
template<typename T>
class binaryTree
{
private:
binaryTreeNode<T>* mroot; // 二叉树根节点
int treeSize; // 二叉树的节点个数
// 定义一些函数
int getHeight(binaryTreeNode<T>* root); // 获取二叉树的高度;
void addNode(T value, int direction, binaryTreeNode<T>*& root); // 给二叉树添加节点
void distory(binaryTreeNode<T>*& root);
void preOrder(binaryTreeNode<T>* root); // 前序遍历
void inOrder(binaryTreeNode<T>* root); // 中序遍历
void postOrder(binaryTreeNode<T>* root); // 后序遍历
public:
binaryTree(T rootValue); // 构造函数
~binaryTree(); // 析构函数
bool empty() const;
int size() const;
int getHeight();
void addNode(T value, int direction);
void distory();
void preOrder();
void inOrder();
void postOrder();
//void levelOrder(); // 二叉树的层次遍历需要用到队列,用于存储二叉树的
};
template<typename T>
binaryTree<T>::binaryTree(T rootValue) // 构造函数, 创建根节点
{
mroot = new binaryTreeNode<T>(rootValue);
treeSize = 1;
}
template<typename T>
binaryTree<T>::~binaryTree()
{
distory(mroot);
//mroot = NULL;
treeSize = 0;
}
template<typename T>
bool binaryTree<T>::empty() const
{
return treeSize==0;
}
template<typename T>
int binaryTree<T>::size() const
{
return treeSize;
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::addNode(T value, int direction, binaryTreeNode<T>*& root)
{
// 添加一个节点
// 参数: value: 节点值 int:0/1 left or right root: 根节点 指针类型的引用
//cout << "AddNode " << value << " " << direction << endl;
if(direction == 0) // 左节点
{
if(root->leftchild == NULL) // 插入节点
{
root->leftchild = new binaryTreeNode<T>(value); // 左孩子
treeSize++;
}
else if(root->rightchild == NULL) // 再判断右孩子
{
root->rightchild = new binaryTreeNode<T>(value);
treeSize++;
}
else
{
addNode(value, direction, root->leftchild);
}
//treeSize++;
}
else
{
if(root->rightchild == NULL) // 右孩子
{
root->rightchild = new binaryTreeNode<T>(value);
treeSize++;
}
else if(root->leftchild == NULL) // 再判断左孩子
{
root->leftchild = new binaryTreeNode<T>(value);
treeSize++;
}
else
{
addNode(value, direction, root->rightchild);
}
//treeSize++;
}
//return root;
//cout << "Add Finished!" << endl;
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::addNode(T value, int direction)
{
//cout << "test: " << mroot->leftchild << endl;
addNode(value, direction, mroot);
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::distory(binaryTreeNode<T>*& root) // 有参数的distory函数
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
distory(root->leftchild);
distory(root->rightchild);
delete root;
}
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::distory()
{
distory(mroot);
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::preOrder(binaryTreeNode<T>* root) // 有参数的
{
if(root != NULL)
{
cout << root->element << " ";
preOrder(root->leftchild);
preOrder(root->rightchild);
}
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::preOrder()
{
cout << "前序遍历:";
preOrder(mroot);
cout << endl;
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::inOrder(binaryTreeNode<T>* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
inOrder(root->leftchild);
cout << root->element << " ";
inOrder(root->rightchild);
}
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::inOrder()
{
cout << "中序遍历:";
inOrder(mroot);
cout << endl;
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::postOrder(binaryTreeNode<T>* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
postOrder(root->leftchild);
postOrder(root->rightchild);
cout << root->element << " ";
}
}
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::postOrder()
{
cout << "后序遍历:";
postOrder(mroot);
cout << endl;
}
template<typename T>
int binaryTree<T>::getHeight(binaryTreeNode<T>* root) // 获取二叉树的高度
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
int dep_L = getHeight(root->leftchild); // 左部分
int dep_R = getHeight(root->rightchild); // 右部分
return (dep_L>dep_R)? dep_L+1: dep_R+1;
}
}
template<typename T>
int binaryTree<T>::getHeight()
{
return getHeight(mroot);
}
#endif测试代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\binaryTree\external_file\binarytree.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
binaryTree<int> tree(0);
for(int i=1; i<=4; i++)
{
tree.addNode(i, 0);
}
for(int i=1; i<=4; i++)
{
tree.addNode(i, 1);
}
cout << "Tree size: " << tree.size() << endl;
tree.preOrder();
tree.inOrder();
tree.postOrder();
cout << "The tree height is: " << tree.getHeight() << endl;
return 0;
}

关于二叉树的层次遍历方法:
层次遍历中。需要从底层到顶层,从左到右进行遍历,所以需要用到队列。
关于队列的实现请参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zj1131190425/article/details/88090905
template<typename T>
void binaryTree<T>::levelOrder(binaryTreeNode<T>* root)
{
queue<binaryTreeNode<T>*> q; // 队列,用于保存二叉树的节点
while(root!=NULL)
{
cout << root->element << " ";
if(root->leftchild!=NULL) // 保存当前节点的左右孩子
q.push(root->leftchild);
if(root->rightchild!=NULL)
q.push(root->rightchild);
try
{
root = q.front(); // 更新root的值
}
catch(queueEmptyException& ex)
{
return;
}
q.pop();
}
}
void binaryTree<T>::levelOrder(binaryTreeNode<T>* root)
{
levelOrder(mroot);
} ----------------------------------------------分割线-----------------------------------------------------
优先级队列:
与队列不同,优先级队列中的元素出队列顺序由元素的优先级决定。
实现优先级队列效率较高的数据结构是堆:堆是一颗完全二叉树,所以使用数组表示效率最高。优先级队列是一个或者多个元素的 集合,每个元素都有一个优先权。优先级队列的操作,push(), pop(), top().
最大优先级队列:查找删除从优先级最高的元素开始
最小优先级队列: 查找删除从优先级最低的元素开始
优先级相同的,按照任意顺序处理:
堆:
大(小)根树: 每个节点的值都大于(小于)其子节点的树
大根堆:一个大根堆既是大根树也是完全二叉树
小根堆:。。。
因为堆是完全二叉树,因此可以用数组进行描述
堆的插入和删除操作:
堆的插入和删除操作必须要保证堆的结构的不变(依然保持为大根树或者小根树),所以把新元素插入新的节点,需要沿着从新节点到根节点的路径,执行一趟起泡操作,将新元素与父节点的元素进行比较交换,直到后者大于或者等于前者为止。
堆的删除操作,删除的是根节点的元素,所以删除了根节点的元素后,需要对大根堆的布局进行重新调整。
详细介绍一下关于大根堆的删除,插入,和初始化操作:
插入操作:

例如,在a中所示的大根堆中插入元素21,因为大根堆一定是完全二叉树,所以插入的位置是一定的。需要进行的操作是:把新元素插入新的节点,需要沿着从新节点到根节点的路径,执行一趟起泡操作,将新元素与父节点的元素进行比较交换,直到后者大于或者等于前者为止。
例如:将1插入,则不会改变大根堆的结构,所以直接插入到元素2的左孩子位置
如果插入元素5,则会破坏大根堆的结构5>2,所以需要将元素2移动到其左孩子的位置,再将5插入到原来2的位置
如果插入的是30,则需要将2移动到其左孩子位置,将根节点20移动到2的位置,将30插入根节点。
插入的过程:
template<typename T>
void maxheap<T>::push(T theElement) // 在大堆根中插入元素
{
ensureLength(); // 先检测数组长度, 动态分配内存大小
int currentNode = heapSize+1; // 新节点的编号
while(currentNode!=1 && element[currentNode/2]<theElement) // currentNode==1的时候就到达根节点了,所以不用再进行比较了//直接插入根节点
{
// element[currentNode/2]<theElement 要插入元素位置的父节点小于插入元素,则不能直接插入到当前位置//
element[currentNode] = element[currentNode/2]; // 将父节点移动到插入位置
currentNode /= 2;
}
element[currentNode] = theElement;
heapSize++;
}删除操作:
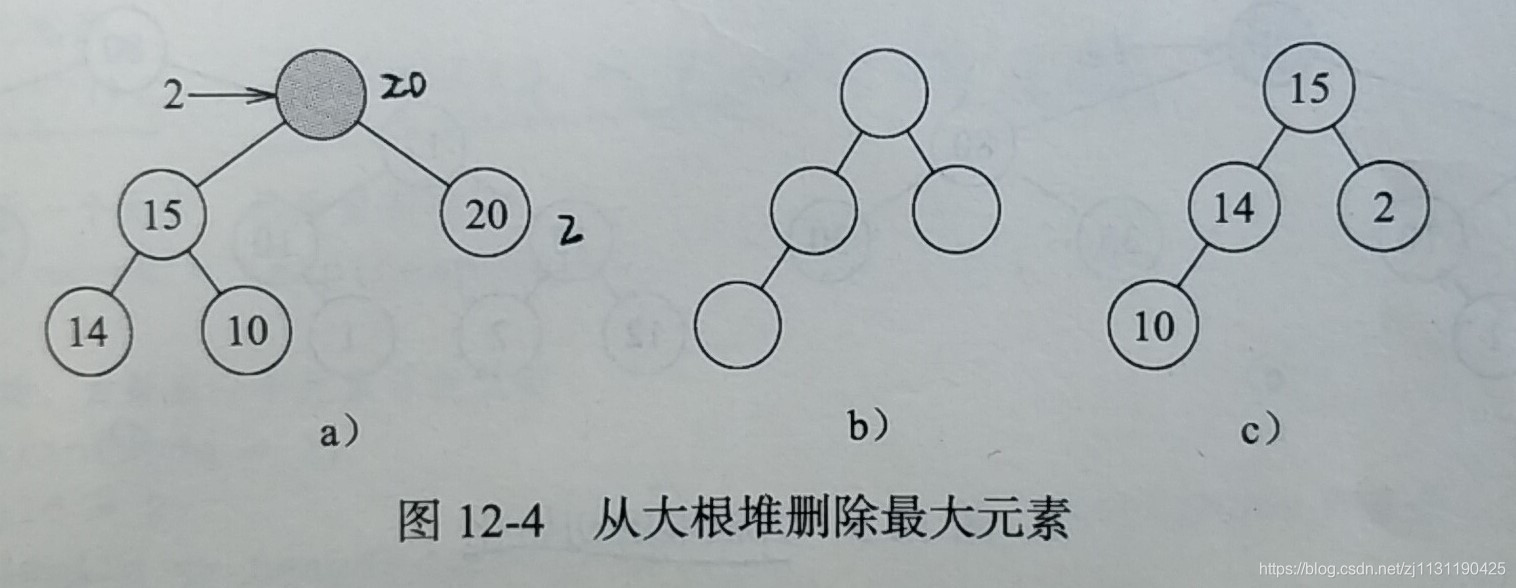
假设要对图12-3所示的大堆根执行删除操作:删除元素21,则大堆根的结构需要重新组织。将元素2取出,删除2所在的节点,得到一个完全二叉树,但此时根节点为空,且2不能放入根节点,所以需要把根节点的左右孩子中的较大者移到根节点。此时位置3为一个空位,且位置3没有左右孩子,所以可以将2插入到位置3.
假设接着继续删除,删除元素20后,大根堆的结构如图12-4(b)所示。此时需要调整元素的位置。在12-4(a)中,将元素10取出(始终是最后一个元素取出),根节点的左右孩子中较大的元素15放入根节点,元素14>10,所以14上移到位置2,元素10放入位置3.
删除过程:
template<typename T>
void maxheap<T>::pop() // 删除大堆根的根元素
{
if(heapSize==0)
{
throw heap_empty_exception(heapSize);
}
// 删除根元素
element[1].~T();
T last_element = element[heapSize--]; // 获取最后一个元素 // heapsize-1
// 重新建堆
// 寻找最后一个元素的插入位置
int currentNode = 1;
int child = 2; // currentNode的孩子
while(child<=heapSize) // 这里是child<=heapSize,即使剩余最后两个元素也需要重构最大堆
{
// 找到currentNOde的大孩子
if(child<=heapSize && element[child]<element[child+1])
{
child++;
}
if(last_element>=element[child]) // 找到插入的位置
{
break;
}
// 否则
element[currentNode] = element[child]; // 将大孩子网上移动
currentNode = child;
child *= 2;
}
element[currentNode] = last_element; // 插入位置
} 最大堆的完整代码实现:
1.最大堆的实现, maxHeap.h文件:
// maxheap实现
// 因为最大堆是完全二叉树,
// 所以采用数组描述
#ifndef MAXHEAP_H
#define MAXHEAP_H
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\binaryTree\external_file\heapEmptyException.h"
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class maxheap
{
private:
int arrayLength;
int heapSize;
T* element; // 堆中的元素
void ensureLength();
public:
maxheap(int length=10); // 构造函数
~maxheap();
bool empty() const;
int size() const;
void initilize(T *theHeap, int theSize); // 初始化一个非空的大堆根;
void push(T theElement); // 插入一个元素
T top(); // 返回根节点的元素
void pop(); // 删除根节点的元素
void print_heap();
};
template<typename T>
maxheap<T>::maxheap(int length)
{
heapSize = 0; // 堆中元素的个数
arrayLength = length;
element = new T[arrayLength+1]; // 堆中元素编号从位置1开始
}
template<typename T>
maxheap<T>::~maxheap() // 析构函数
{
delete [] element;
}
template<typename T>
void maxheap<T>::ensureLength()
{
// 动态分配内存的大小
if(heapSize>=arrayLength-1) // 编号原因,所以减一
{
T* old = element;
element = new T[2*arrayLength+1];
for(int i=1; i<=heapSize; i++)
{
element[i] = old[i];
}
delete [] old;
arrayLength = 2*arrayLength+1;
}
// 如果元素很少,也需要重新分配内存空间
if(heapSize>1 && heapSize<arrayLength/4) // 动态减少内存空间
{
T* old = element;
element = new T[arrayLength/4+1];
for(int i=1; i<=heapSize; i++)
{
element[i] = old[i];
}
delete [] old;
arrayLength = arrayLength/4+1;
}
}
template<typename T>
bool maxheap<T>::empty() const
{
return heapSize==0;
}
template<typename T>
int maxheap<T>::size() const
{
return heapSize;
}
template<typename T>
void maxheap<T>::initilize(T* theHeap, int theSize) // 初始化非空的大堆根
{
delete [] element;
// element = theHeap;
heapSize = theSize; // 获取堆中元素的个数
ensureLength(); // 动态分配内存
for(int i=0; i<theSize; i++)
{
element[i+1] = theHeap[i]; // 因为再堆中的元素编号是从1开始的
}
// 重构大堆根
for(int root=heapSize/2; root>=1; root--) // heapsize/2是最后一个元素的父节点
{
T root_element = element[root]; // 对应的父节点
int child = root*2; // 父节点的左孩子
while(child<=heapSize)
{
if(child<heapSize && element[child] < element[child+1])
{
child++; // 此时child是左右孩子中的较大者
}
if(root_element>=element[child]) // 根节点与大孩子比较
{
break; // 不用进行调整
}
// 否则需要调整位置 child/2是根节点的位置
element[child/2] = element[child];
child *= 2; // 为了跳出while循环
}
element[child/2] = root_element;
}
}
template<typename T>
T maxheap<T>::top()
{
return element[1]; // 返回大根堆的根;
}
template<typename T>
void maxheap<T>::push(T theElement) // 在大堆根中插入元素
{
ensureLength(); // 先检测数组长度, 动态分配内存大小
int currentNode = heapSize+1; // 新节点的编号
while(currentNode!=1 && element[currentNode/2]<theElement) // currentNode==1的时候就到达根节点了,所以不用再进行比较了//直接插入根节点
{
// element[currentNode/2]<theElement 要插入元素位置的父节点小于插入元素,则不能直接插入到当前位置//
element[currentNode] = element[currentNode/2]; // 将父节点移动到插入位置
currentNode /= 2;
}
element[currentNode] = theElement;
heapSize++;
}
template<typename T>
void maxheap<T>::pop() // 删除大堆根的根元素
{
if(heapSize==0)
{
throw heap_empty_exception(heapSize);
}
// 删除根元素
element[1].~T();
T last_element = element[heapSize--]; // 获取最后一个元素 // heapsize-1
// 重新建堆
// 寻找最后一个元素的插入位置
int currentNode = 1;
int child = 2; // currentNode的孩子
while(child<=heapSize) // 这里是child<=heapSize,即使剩余最后两个元素也需要重构最大堆
{
// 找到currentNOde的大孩子
if(child<=heapSize && element[child]<element[child+1])
{
child++;
}
if(last_element>=element[child]) // 找到插入的位置
{
break;
}
// 否则
element[currentNode] = element[child]; // 将大孩子网上移动
currentNode = child;
child *= 2;
}
element[currentNode] = last_element; // 插入位置
}
template<typename T>
void maxheap<T>::print_heap()
{
//int height = (int)(log(heapSize+1)/log(2));
cout << "The heap: ";
for(int i=1; i<=heapSize; i++)
{
cout << element[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
#endif 当最大堆在删除元素时,如果堆中没有元素,则抛出异常:这一功能由自定义的异常类heap_empty_exception实现:
heapEmptyException.h文件
#ifndef HEAP_EMPTY_EXCEPTION
#define HEAP_EMPTY_EXCEPTION
#include <stdexcept>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class heap_empty_exception : public runtime_error
{
private:
int heap_size;
public:
heap_empty_exception(int heap_size):runtime_error("Heap is empty")
{
this->heap_size = heap_size;
}
void display_error()
{
cout << "The heap size is " << heap_size << endl;
}
};
#endif测试代码:main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\binaryTree\external_file\binarytree.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\binaryTree\external_file\maxHeap.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
maxheap<int> heap;
int a[] = {1,4,7,2,3,9,15,21,10,11,14};
heap.initilize(a, 11);
heap.print_heap();
heap.push(2);
heap.push(3);
heap.push(29);
heap.print_heap();
cout << "pop 操作:" << endl;
cout << "-------------------------------------------" << endl;
while(!heap.empty())
{
//cout << heap1.top() << " ";
heap.print_heap();
heap.pop();
}
cout << endl;
// 堆的应用:堆排序
cout << endl << "堆排序: " << endl;
maxheap<int> heap1;
int b[] ={2,3,8,91,12,78,23,10,9,1,33,54};
heap1.initilize(b, 12);
heap1.print_heap();
cout << "-------------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "排序结果: " << endl;
while(!heap1.empty())
{
cout << heap1.top() << " ";
heap1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
cout << endl << "-------------异常类测试------------------" << endl;
try
{
heap1.pop();
}
catch(heap_empty_exception& ex)
{
cout << ex.what() << endl;
ex.display_error();
}
return 0;
}
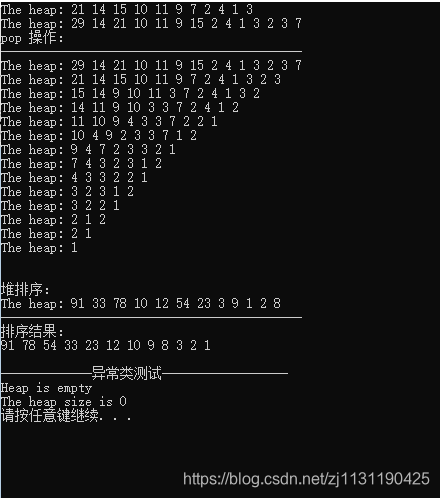
运行结果:
左高树:
上述的堆是一种隐式数据结构,在数组中的存储是隐式的,虽然它的时间效率高,空间利用率高,但是这种数据结构没有存储树的结构信息,当涉及到其他一些应用的时候(两个优先级队列合并),就需要树的结构信息了。左高树就能满足这种需求。
一棵二叉树,如果让一部分特殊的节点代替树中的空子树,则称之为扩充二叉树。补充的节点称为外部节点,原有的节点称为内部节点。
定义s(x)是从内部节点x到其子树的外部节点所有路径中最短的一条,若x是外部节点,则s值为0.若x是内部节点,则:
s = min{s(L), s(R)}
左高树: 当且仅当任何内部节点x的左孩子值的s大于等于右孩子的s值。
堆排序:
堆可以实现n个元素的排序,所需的时间为O(nlogn),首先用n个待排序的元素来初始化一个大根堆,然后从堆中逐个删除元素,每次删除的都是最大的元素。初始化的时间为O(n),每次删除的时间为O(logn),因此总的时间为O(nlogn).
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------


