c++数据结构与算法 图
图的定义:
图:用线或者边连接在一起的节点集合。G=(V,E)
当且仅当(i,j)是图的边,则称节点i,j是邻接的。
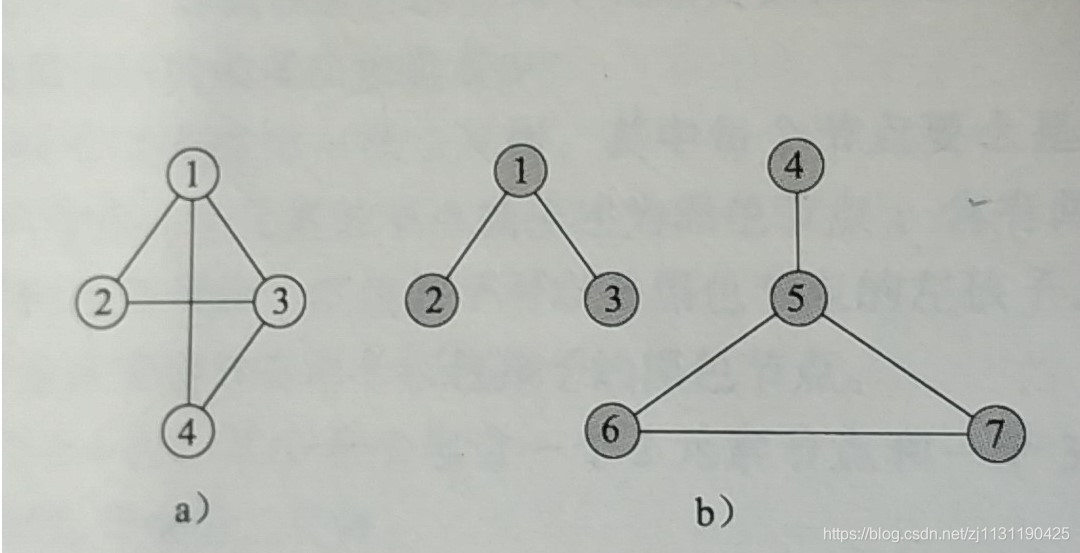
有向图和无向图;
加权图;
一条路径,如果除第一个和最后一个节点之外,其他节点各不相同,则这条路径称为简单路径;
生成树:设G是一个无向图,G是联通的,当且仅当G的每一对顶点之间都有一条路径。假设G是联通的,但G的有些边对联通来说是不必要的,去掉这些边依然联通
子图:如果图H的顶点和边的集合分别是G的顶点和边的集合的子集,那么图H是G的子图。
环路:起点和终点相同的简单路径称为环路:
没有环路的联通无向图是一棵树,一个G的子图,如果包含G的所有顶点,且是一棵树,则成为G的生成树。
图的特性:
1.在无向图中,与节点i相关联的边的数目称为节点i的度,假设在图G中,节点的数量为n,边的数量为e,则有:
即所有顶点的度数之和为边的数目的两倍,因为每一条边都与两个节点相连。
在具有n个节点的图中,边的最小数目是0, 最大的数目是,每个节点与其他n-1个节点连接,则n个节点共有n*(n-1)条边,再出去重复的:则最后为n*(n-1)/2
同理:
在有向图G中,节点的度分为入度和出度:
图的ADT:
无权图的描述:
邻接矩阵,邻接链表,邻接数组
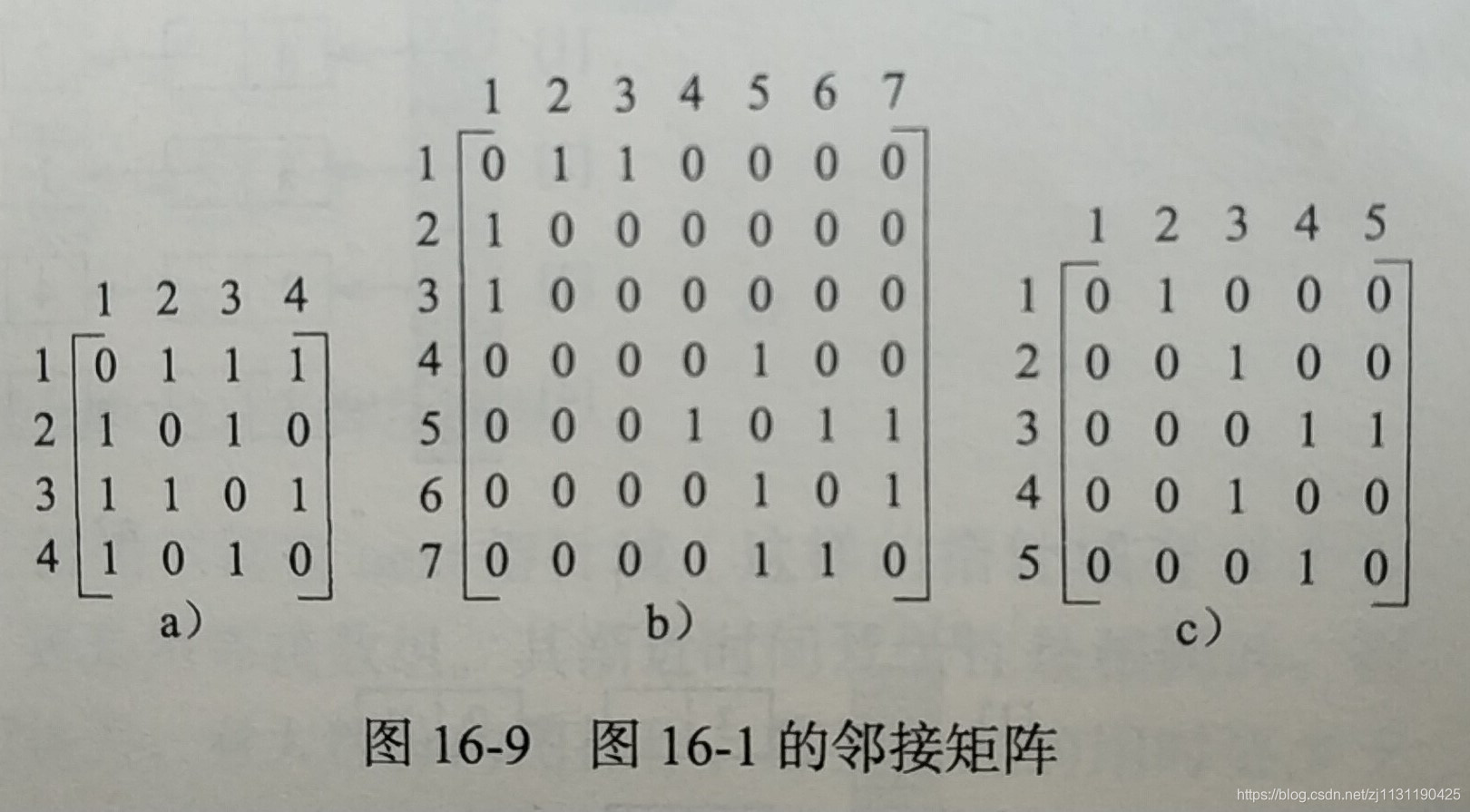
1.邻接矩阵:
n个节点的图: n*n的邻接矩阵,矩阵元素值为0,1(代表连接,或者不连接)、
无向图的邻接矩阵是对称的,所以只需存储上三角或者下三角。
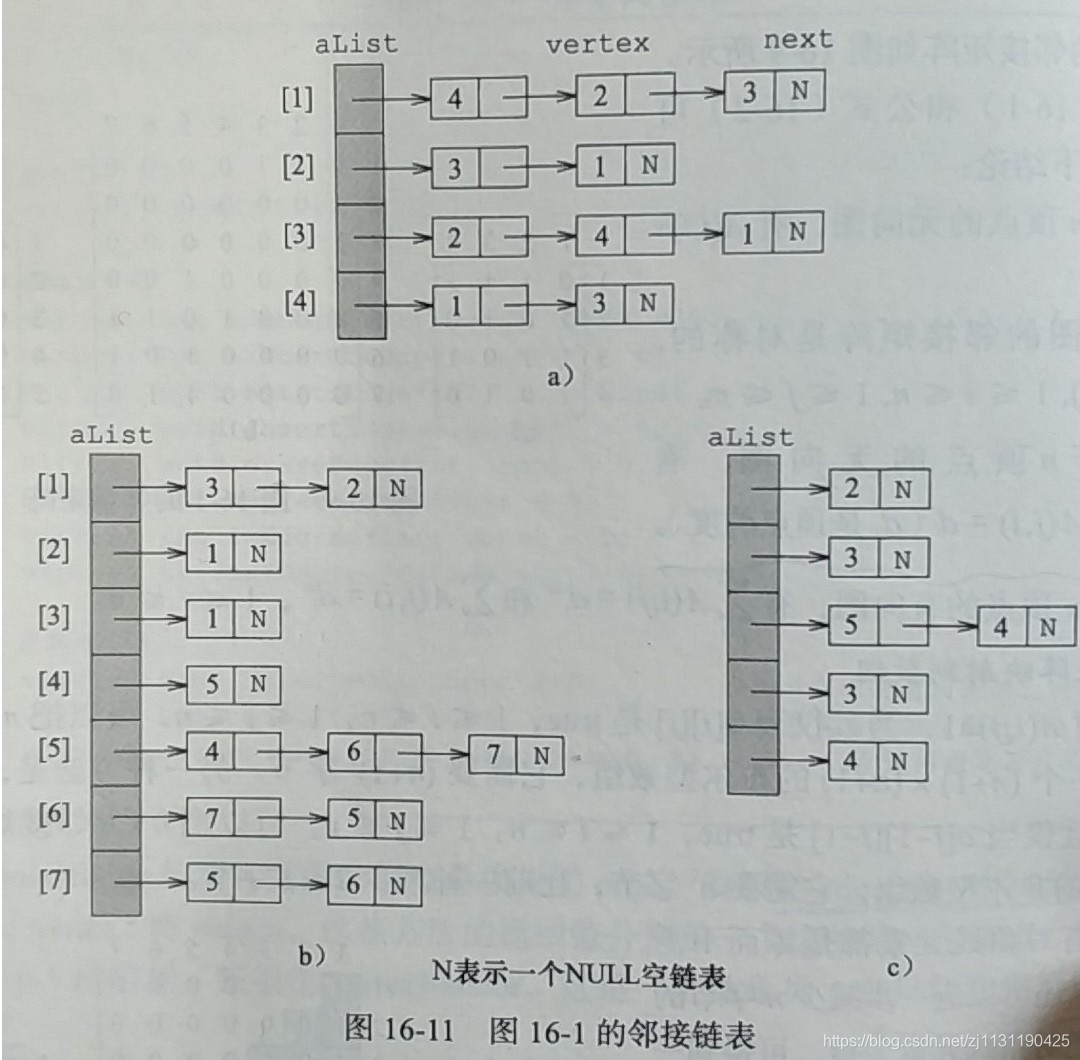
2. 邻接链表
节点i的邻接表是一个线性表,它包含所有邻接于节点i的节点。
在邻接链表米描述中,图的每个节点都有一个邻接表,可以使用一个保存链表的数组保存所有的顶点。
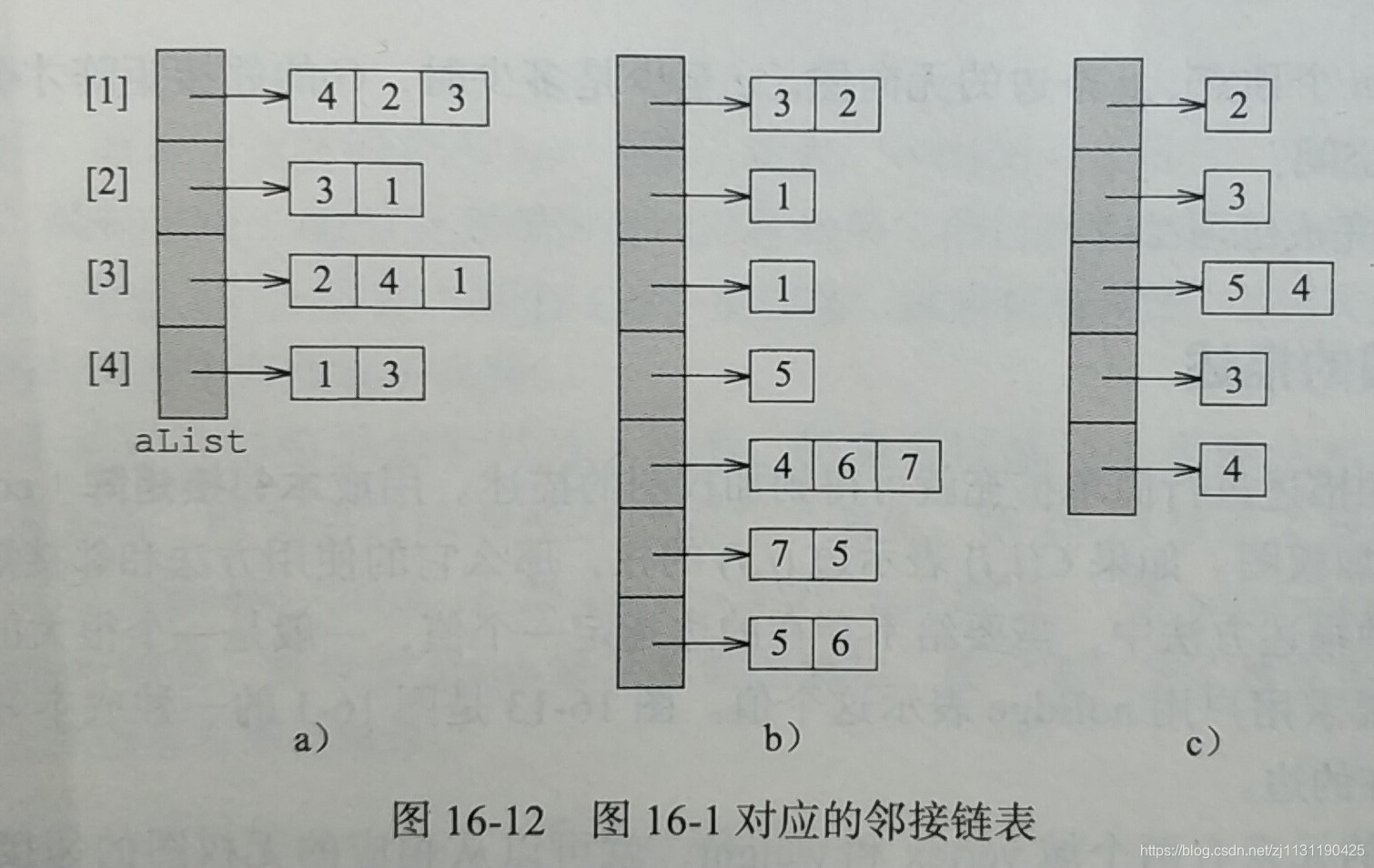
3. 邻接数组
在邻接数组中,每一个节点的线性表使用一个数组线性表表示而不是链表。
加权图的描述:
对无权图的描述稍作扩充即可表示加权图的描述
图的ADT实现:(邻接矩阵)
基类实现: graph.h文件
// 图的ABC实现
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H
template<typename T>
class graph
{
public:
virtual ~graph() {};
// ADT
virtual int numberOfVertices() const=0; // 返回节点数量
virtual int numberOfEdges() const=0; // 返回边的数量
virtual bool existEdge(int i, int j) const=0; // 返回某条边(i,j)是否存在
virtual void insertEdge(edge<T>* e) =0; // 插入一条边
virtual void eraseEdge(int i, int j) =0; // 删除一条边
virtual int degree(int i) const=0; // 节点i的度 无向图
virtual int outDegree(int i) const=0; // 出度
virtual int inDegree(int i) const=0; // 入度
// others;
virtual bool directed() const=0;
virtual bool weighted() const=0;
};
#endif 一共有四种图,无权无向图,加权无向图,无权有向图,加权有向图
其中每种图都可以有三种实现方法:邻接矩阵,邻接链表,邻接数组
1. 邻接矩阵类的实现:
因为需要有在图中插入边的操作,所以定义类edge,表示需要插入的边:
edge.h文件:
#ifndef EDGE_H
#define EDGE_H
template<typename T>
class edge // 一条边
{
private:
int vertex1;
int vertex2;
T weight;
public:
/*
edge()
{
vertex1 = 0; // 节点1
vertex2 = 0; // 节点2
weight = 0; // 权重
}
*/
edge(int v1, int v2) // 无权边
{
vertex1 = v1;
vertex2 = v2;
weight = 1;
}
edge(int v1, int v2, T w)
{
vertex1 = v1;
vertex2 = v2;
weight = w;
}
int getvetex1()
{
return vertex1;
}
int getvetex2()
{
return vertex2;
}
T getweight()
{
return weight;
}
};
#endif在图中插入边和删除边的时候,需要首先检测的边的合法性:如果不合法,程序需要抛出异,这个由自定义的异常类实现:
invalidVertextExcept.h文件:
#ifndef INVALID_VERTEX_H
#define INVALID_VERTEX_H
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
class invalidVertex : public runtime_error
{
public:
invalidVertex() : runtime_error("The vertex must between 1 and n")
{
}
};
#endif
同时,再调用还未定义的方法的时候,程序也需要抛出异常,这个由自定义异常类undefinedMethedEXcept实现:
undefinedMethedExcept.h文件:
#ifndef INVALID_VERTEX_H
#define INVALID_VERTEX_H
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
class invalidVertex : public runtime_error
{
public:
invalidVertex() : runtime_error("The vertex must between 1 and n")
{
}
};
#endif
图的数据结构实现:
adjacencyWeightedG.h文件:
#ifndef ADJACENCYWEIGHTEDG_H
#define ADJACENCYWEIGHTEDG_H
#include <iostream>
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\graph.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\edge.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\invalidVertextExcept.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\undefinedMethodExcept.h"
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class adjacencyWgraph : public graph<T>
{
private:
int n; // 节点个数
int e; // 边的数目
T** matrix; // 邻接矩阵
T noEdge; // 表示不存在的边的值
public:
adjacencyWgraph(int vertex_num, T theNoEdge); // 构造函数
adjacencyWgraph(adjacencyWgraph<T>& gar); // 拷贝构造函数
~adjacencyWgraph(); // 析构函数
int numberOfVertices() const;
int numberOfEdges() const;
bool directed() const;
bool weighted() const;
bool existEdge(int i, int j) const;
void insertEdge(edge<T>& theEdge);
void eraseEdge(int i, int j);
int degree(int i) const;
int outDegree(int i) const;
int inDegree(int i) const;
void outputMatrix() const;
void addNode(); // 在图种增加一个节点
};
template<typename T>
adjacencyWgraph<T>::adjacencyWgraph(int vertex_num, T theNoEdge)
{
// 节点数
if(vertex_num<0)
{
//cout << "Number of vertex must >= 0" << endl;
//exit(0);
throw invalidVertex();
}
n = vertex_num; // 节点数
e = 0;
noEdge = theNoEdge;
// 创建邻接矩阵
matrix = new T*[n+1];
for(int i=0; i<n+1; i++)
{
matrix[i] = new T[n+1];
}
// 初始化邻接矩阵
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
matrix[i][j] = noEdge; // 初始化为不存在的边值
}
}
}
template<typename T>
adjacencyWgraph<T>::adjacencyWgraph(adjacencyWgraph<T>& gra)
{
n = gra.n;
e = gra.e;
noEdge = gra.noEdge;
matrix = new T*[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
matrix[i] = new T[n+1];
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
matrix[i][j] = gra.matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
template<typename T>
adjacencyWgraph<T>::~adjacencyWgraph()
{
for(int i=0; i<n+1; i++)
{
delete [] matrix[i];
}
delete [] matrix;
}
template<typename T>
int adjacencyWgraph<T>::numberOfVertices() const
{
return n;
}
template<typename T>
int adjacencyWgraph<T>::numberOfEdges() const
{
return e;
}
template<typename T>
bool adjacencyWgraph<T>::directed() const
{
return true;
}
template<typename T>
bool adjacencyWgraph<T>::weighted() const
{
return true;
}
template<typename T>
bool adjacencyWgraph<T>::existEdge(int i, int j) const
{
// 返回是否存在一条边
if(i<1 || j<1 || i>n || j>n || matrix[i][j]==noEdge)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
template<typename T>
void adjacencyWgraph<T>::insertEdge(edge<T>& theEdge) // 插入一条边
{
int v1 = theEdge.getvetex1();
int v2 = theEdge.getvetex2();
// 判断边的合法性
if(v1<1 || v2<1 || v1>n || v2>n)
{
//cout << "The edge is invalid" << endl;
//return;
throw invalidVertex();
}
if(matrix[v1][v2]==noEdge)
{
e++; // 如果是插入新的边
}
matrix[v1][v2] = theEdge.getweight(); // 插入一条边
}
template<typename T>
void adjacencyWgraph<T>::eraseEdge(int i, int j)
{
if(i<1 || j<1 || i>n || j>n)
{
//cout << "The edge is invalid" << endl;
//return;
throw invalidVertex();
}
else if(matrix[i][j]==noEdge)
{
cout << "The edge not exist" << endl;
return;
}
else
{
matrix[i][j] = noEdge;
e--; // 边的条数
}
}
template<typename T>
int adjacencyWgraph<T>::degree(int i) const
{
//cout << "undefined method" << endl;
//exit(0);
throw undefinedMethod();
}
template<typename T>
int adjacencyWgraph<T>::outDegree(int i) const
{
// 先判断节点的合法性
if(i<1 || i>n)
{
throw invalidVertex();
}
int count = 0;
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
if(matrix[i][j]!=noEdge)
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
template<typename T>
int adjacencyWgraph<T>::inDegree(int i) const
{
// 检查节点合法性;
if(i<1 || i>n)
{
throw invalidVertex();
}
int count = 0;
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
if(matrix[j][i]!=noEdge)
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
template<typename T>
void adjacencyWgraph<T>::outputMatrix() const
{
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
cout << matrix[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
template<typename T>
void adjacencyWgraph<T>::addNode()
{
T** old;
old = matrix;
n = n+1; //节点的数量+1
matrix = new T*[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
matrix[i] = new T[n+1];
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
{
matrix[i][j] = noEdge; // 初始化邻接矩阵
}
}
// 将原来的数据复制过来
for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=n-1; j++)
{
matrix[i][j] = old[i][j];
}
}
// 释放内存
for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++)
{
delete [] old[i];
}
delete [] old;
}
#endif
在类种添加了一个新的方法,addNode(),用于在图中增加新的节点。
测试代码:
mian.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\adjacencyWeightedG.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\edge.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
cout<<"Hello C-Free!"<<endl;
adjacencyWgraph<int> graphy(5, 0);
graphy.outputMatrix();
// 声明一些边
edge<int> edge1(3, 4, 9);
edge<int> edge2(4, 3, 11);
edge<int> edge3(2, 1, 3);
edge<int> edge4(4, 6, 11); // 不满足条件的
edge<int> edge5(3, 4, 9);
cout << "insert edges in graph-->" << endl; // 插入边
graphy.insertEdge(edge1);
graphy.insertEdge(edge2);
graphy.insertEdge(edge3);
try
{
graphy.insertEdge(edge4); // 异常测试
}
catch(invalidVertex& ex)
{
cout << ex.what() << endl;
}
graphy.outputMatrix();
graphy.insertEdge(edge5);
// 插入重复的边
cout << "The edge number is " << graphy.numberOfEdges() << endl;
cout << "The edge (3, 4) exist: " << graphy.existEdge(3, 4) << endl;
// 删除一条边
try
{
graphy.eraseEdge(4, 3);
}
catch(invalidVertex& ex)
{
cout << ex.what() << endl;
}
graphy.outputMatrix();
cout << "The edge number is " << graphy.numberOfEdges() << endl;
// 测试没有定义的方法
try
{
graphy.degree(4);
}
catch(undefinedMethod& ex)
{
cout << ex.what() << endl;
}
// 测试入度和出度
cout << "The out degree is " << graphy.outDegree(1) << endl;
// 测试 addNode()
cout << "Add node in graphy: " << endl;
graphy.addNode();
graphy.outputMatrix();
// 插入线的节点
cout << "Insert edge in new graph: " << endl;
edge<int> edge6(6, 5, 3);
try
{
graphy.insertEdge(edge6);
}
catch(invalidVertex& ex)
{
cout << ex.what() << endl;
}
graphy.outputMatrix();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
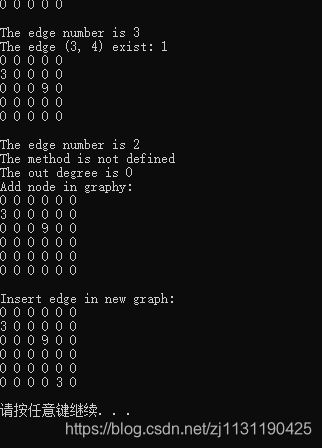
通过从上面的类继承和重载其中的一些方法,可以实现无向图的数据结构:
图的遍历:
例如需要从一个顶点开始,搜索所有可以到达的顶点,所谓顶点u是从顶点v可到达的,是指有一条从v到u的路径,这种路径搜索方法常有两种:广度优先搜索(breadth first search, BFS) 和深度优先搜索(depth first search, DFS), DFS效率更高,使用的更多。
1. 广度优先搜索。 BFS
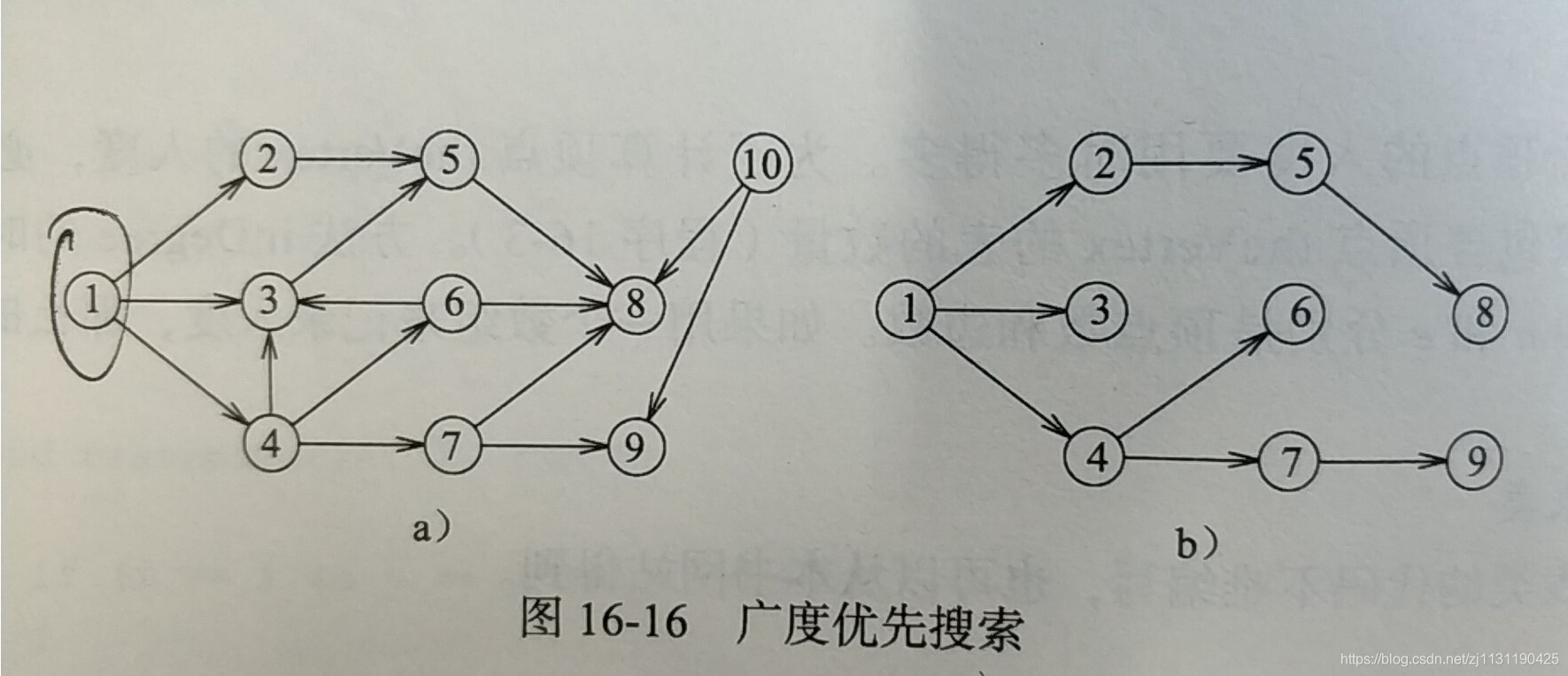
假设要从顶点1开始搜索所有的可到达的顶点,可以采用:1.先确定邻接于顶点1的所有顶点集合{2,3,4}.在确定邻接于{2,3,4}的所有顶点集合{5, 6,7},再确定邻接于{5,6,7}的顶点结合{8,9}
所以从顶点1 可到达的顶点集合为{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}
这种方法称为BFS,可以使用队列实现。BFS和二叉树层次遍历相似:
例如再上面的利用邻接矩阵实现的图中定义新的方法BFS:
template<typename T>
vector<int> adjacencyWgraph<T>::bfs(int node)
{
if(node<1 || node>n) // 节点不满足图的限制
{
throw invalidVertex();
}
queue<int> q;
vector<int> result; // 保存满足条件的节点
int label[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
label[i] = 0; // 作为标记, 未到达的顶点都标记为0
}
//label[node] = 1; // 节点node已经到达:
q.push(node); // 将node压入队列
while(!q.empty())
{
int node_tmp = q.front(); // 弹出度列首端的元素
label[node_tmp] = 1; // node_tmp已经到达
q.pop();
// 寻找从node_tmp可到达的节点
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(i==node_tmp)
{
continue;
}
else
{
if(matrix[node_tmp][i] != noEdge && label[i]==0) // 从node_tmp可以到达的顶点
{
// 从node_tmp到节点 i 有边且 节点 i 没有到达过
q.push(i); // 将可到达的顶点压入队列
}
}
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(label[i]==1)
{
result.push_back(i); // 记录可到达的顶点
}
}
return result;
}测试图:
假设有下面的图:
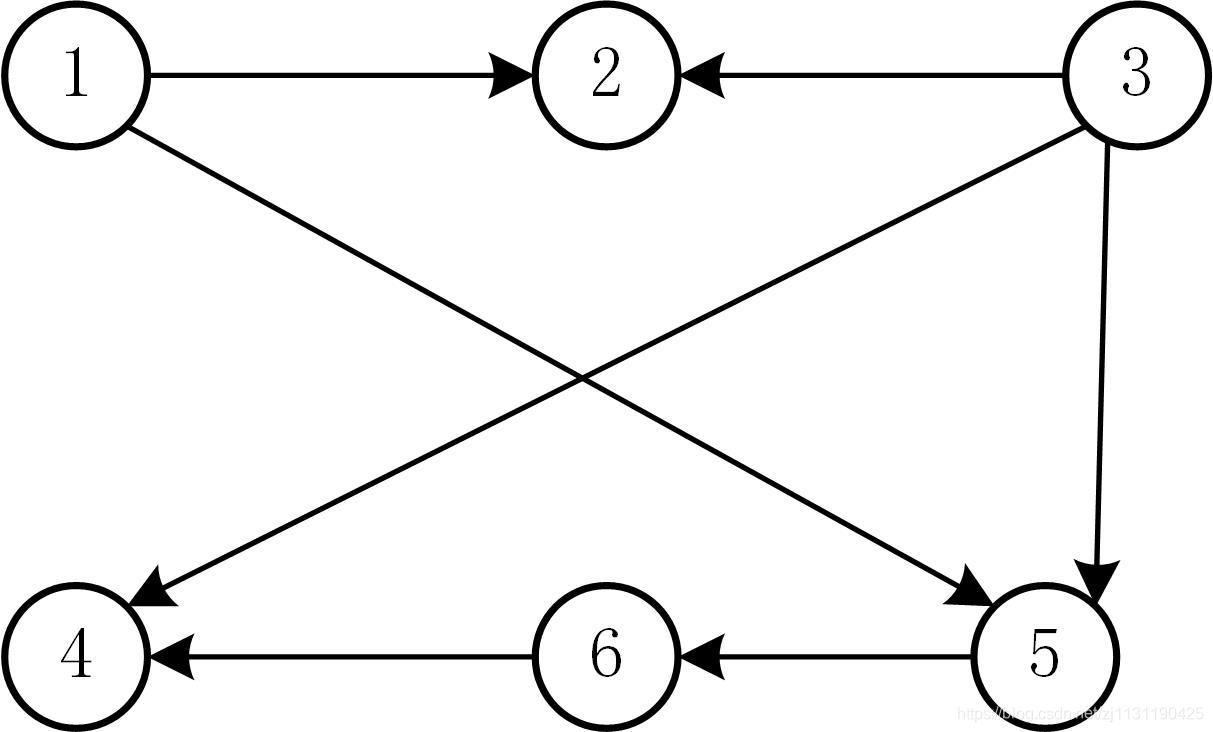
从节点1可到达的顶点为:{1,2,,4,5,6}
测试代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\adjacencyWeightedG.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\edge.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
cout<<"Hello C-Free!"<<endl;
adjacencyWgraph<int> graphy(6, 0);
graphy.outputMatrix();
// 声明一些边
edge<int> edge1(1, 2, 9);
edge<int> edge2(1, 5, 11);
edge<int> edge3(3, 1, 3);
edge<int> edge4(3, 5, 11); // 不满足条件的
edge<int> edge5(3, 4, 9);
edge<int> edge6(5, 6, 9);
edge<int> edge7(6, 4, 9);
cout << "insert edges in graph-->" << endl; // 插入边
graphy.insertEdge(edge1);
graphy.insertEdge(edge2);
graphy.insertEdge(edge3);
graphy.insertEdge(edge4);
graphy.insertEdge(edge5);
graphy.insertEdge(edge6);
graphy.insertEdge(edge7);
graphy.outputMatrix();
vector<int> res = graphy.bfs(3);
for(int i=0; i<res.size(); i++)
{
cout << res[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果: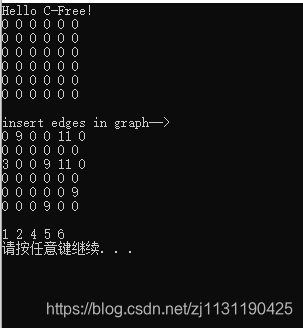
深度优先搜索
深度优先搜索是另一种搜索方法,在迷宫问题中已经使用过这种方法: 迷宫问题博客
这里没有采用递归的方法实现,而是采用堆栈的方法:思路和迷宫问题相近:
template<typename T>
vector<int> adjacencyWgraph<T>::dfs(int node)
{
if(node<1 || node>n) // 节点不满足图的限制
{
throw invalidVertex();
}
stack<int> node_stack;
vector<int> result;
int label[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
label[i] = 0;
}
node_stack.push(node); // 将node压入栈
label[node] = 1; // node标记
while(!node_stack.empty())
{
int tmp_node = node_stack.top();
// node_stack.pop();
//label[tmp_node] = 1; // 标记节点
// 寻找tmp_node的邻接节点
bool find_flag = false; // 标志位
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(tmp_node==i)
{
continue;
}
else
{
if(matrix[tmp_node][i]!=noEdge && label[i]==0)
{
//找到节点i;
find_flag = true;
node_stack.push(i); // 将找到的节点压入堆栈
label[i] = 1; // 标记此节点已经到达
break;
}
}
}
if(!find_flag)
{
node_stack.pop();
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(label[i]==1)
{
result.push_back(i);
}
}
return result;
}测试:同样使用上面六个节点的图进行测试:
测试代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\adjacencyWeightedG.h"
#include "E:\back_up\code\c_plus_code\graph_project\external_file\edge.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
cout<<"Hello C-Free!"<<endl;
adjacencyWgraph<int> graphy(6, 0);
graphy.outputMatrix();
// 声明一些边
edge<int> edge1(1, 2, 9);
edge<int> edge2(1, 5, 11);
edge<int> edge3(3, 1, 3);
edge<int> edge4(3, 5, 11); // 不满足条件的
edge<int> edge5(3, 4, 9);
edge<int> edge6(5, 6, 9);
edge<int> edge7(6, 4, 9);
cout << "insert edges in graph-->" << endl; // 插入边
graphy.insertEdge(edge1);
graphy.insertEdge(edge2);
graphy.insertEdge(edge3);
graphy.insertEdge(edge4);
graphy.insertEdge(edge5);
graphy.insertEdge(edge6);
graphy.insertEdge(edge7);
graphy.outputMatrix();
vector<int> res = graphy.dfs(1);
for(int i=0; i<res.size(); i++)
{
cout << res[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
测试结果:

应用:
1.在途中寻找路径:
a. 最长路径
b. 最短路径
2.检测一个图是否是连通图:
对每一个节点。执行BFS或者DFS,判断此节点是否能到达其他所有的节点,即可判断图是否为连接图
3. 生成树
在一个具有n个顶点的无向连通图中,从任何一个顶点开始进行BFS,所有的顶点都将被加上标记,可以到达n-1个当点,正好构成n-1条边;这些路径构成了一个联通子图,称为图的生成树。
广度优先生成树:按照BFS得到的生成树
深度优先生成树:按照DFS得到的生成树
---------------------------------------------------------end-----------------------------------------------------------------



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号