C++ STL学习笔记(2) 容器结构与分类
接着学习侯捷老师的C++ STL!
在使用容器的时候,需要明白容器中元素之间在内存里的关系是什么样的,是连续的,还是非连续的。
容器可以分为两类:
1. sequence container , 即序列容器
a. Array 连续空间 , 大小固定,不能扩充

b. Vector 后部可以扩充(当然扩充工作由Allocator完成),我们只需将元素放进去即可

c. Deque 双向的队列,前后都可以扩充

d. List 链表, 双向链表
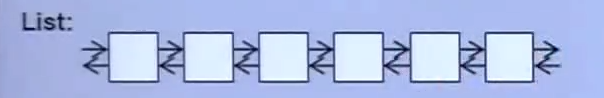
e. Forward-List ; c++ 11 引进, 单向链表
2. associative container , 即关联式容器 (key,value)
a. set,内部用红黑树实现。(红黑树:一种高度平衡的二叉树,会自动调整左右的大小,方便查找),对于set, 它的key就是value
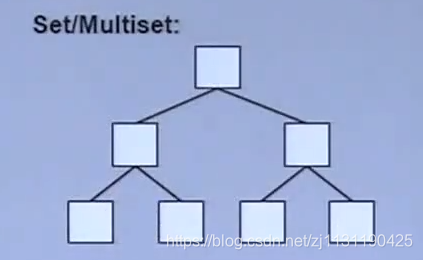
multiset,放入的元素的内容可以有重复。set则不能重复。
b.map: 具有key和value
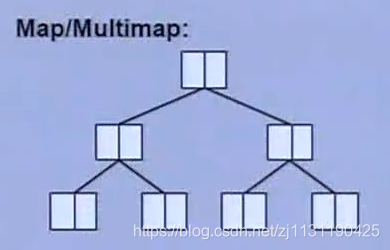
multimap,放入的元素的key可以有重复。map则不能重复。
3. unordered container, 可翻译为不定序, 元素放入容器中,其次序是不定的,也可以看作一种关联式容器
a. unordered set/multiset

b. unordered map/multimap
上面的不定序用哈希表来表示的话会更加的直观:
侯捷老师PPT中的哈希表的结构:
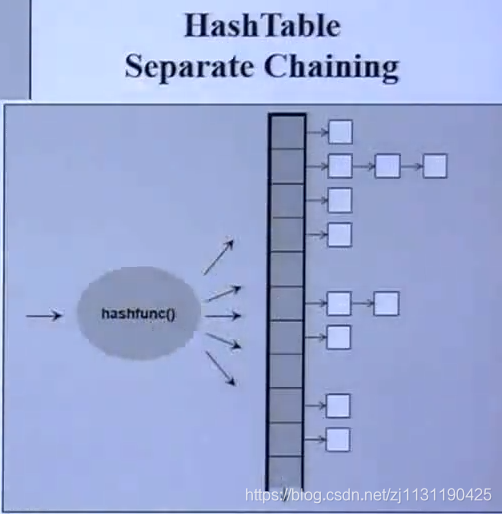
通过哈希表,也能很好的解释为什么上述的容器可以翻译为不定序。
可以将上述的每个一深色的方块看作一个bucket,每个篮子中的元素用链表表示(seperate chaining), hash可以理解为:假如有二十个空间,现在放入一个元素进去,元素放入的位置需要通过计算得到,假设元素a经过计算需要放到第三个位置去,元素b经过计算也要放到第三个位置去,这时就会发生碰撞。一种解决方法是:通过一定的计算方式将他们分开放置。另一种方法是:既然碰撞,索性都放到同一个bucket中,以链表表示。这是目前最好的做法。
这样做面临一个问题: 如果一个bucket的链表太长,而查找的元素恰好又在最后一个,那么在查找过程中,这个bucket的链表查找效率会非常低,所以会对bucket的链表长度做某一些限制,如果链表长度超过限制,则会将所有的元素都打散重新进行计算排列位置,这就是为什么会称为不定序的原因。因为每次放入一个元素,原来的排列顺序可能会被打乱。
(void 类型的指针)
1. aray测试:
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <array> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::array<int, arraySize> c; std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(0, 100); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { c[i] = u(e); } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.data() << endl; // return pointer to mutable data array 返回指针 数组中第一个元素的地址 cout << c.size() << endl; // 大小 cout << c.front() << endl; // 第一个元素 cout << c.back() << endl; // 最后一个元素 return 0; }
2. 容器vector放入元素,且排序
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf #include <string> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::vector<std::string> c; std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.push_back(std::string(buf)); } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.data() << endl; // return pointer to mutable data array 返回指针 cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.front() << endl; cout << c.back() << endl; cout << c.capacity() << endl; // 实际的空间的大小 vector中内存分配以两倍增长的 timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 std::string target("3456"); // 查找 auto iter = ::find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // :: 全局函数 if (iter == c.end()) cout << "Not find string" << endl; else cout << "Find string " << *iter << endl; std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; return 0; }
3. list双向链表
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <list> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::list<std::string> c; // 双向链表 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.push_back(std::string(buf)); } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.max_size() << endl; // 最大的元素个数 cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.front() << endl; cout << c.back() << endl; timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 std::string target("3456"); // 查找 auto iter = ::find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // :: 全局函数 if (iter == c.end()) cout << "Not find string" << endl; else cout << "Find string " << *iter << endl; std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; timer.reset(); c.sort(); // 排序 std::cout << "Sort Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; return 0; }
4. forward_list单向链表
这个的用法于双向链表list基本相同
6. deque 双向队列
一个容器占用一定的内存后,就不能再向外扩充了。而是以别的方式进行扩充,例如,对于vector,它是按照每次两倍的内存进行扩充的,但是它的扩充策略是先找到另一块两倍大小的内存,然后再将其原来的内容复制过去。
那么deque的扩充策略是什么样的,两端都可以扩充?
deque的内部结构:
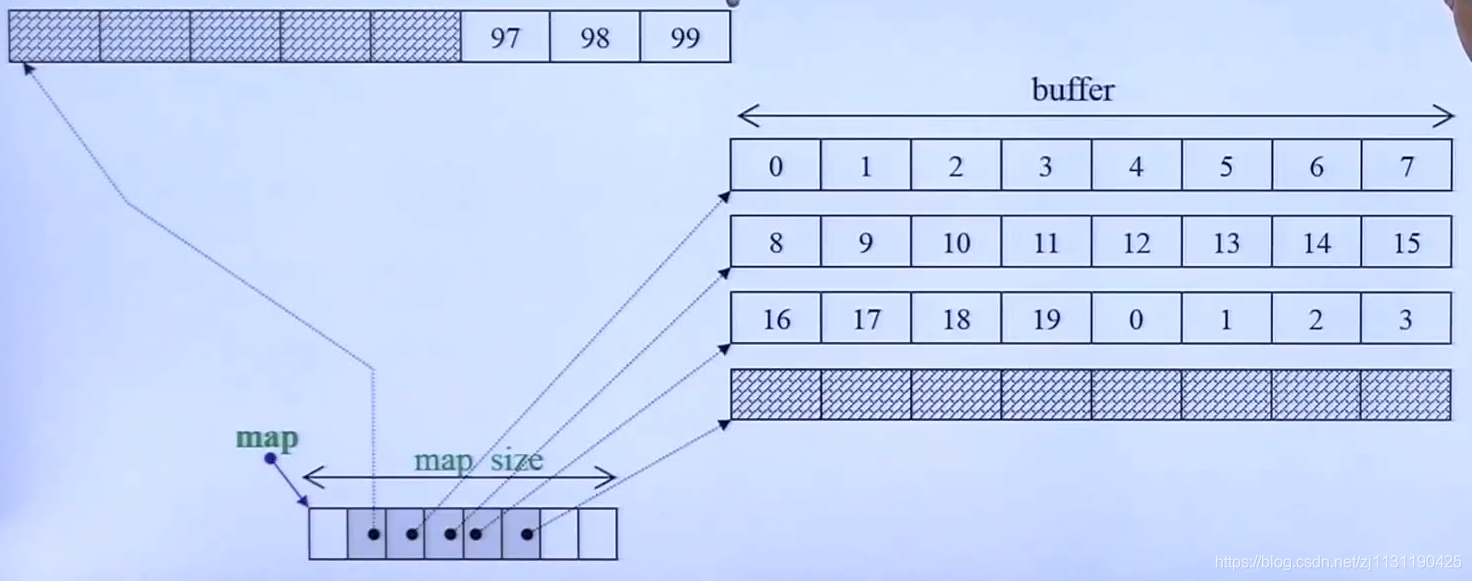
可以看出deque是分段连续的,map中存储指针,每个指针指向一段连续的buffer,当一个buffer放满元素的时候,会自动分配下一个buffer。其中buffer是连续的。
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <deque> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::deque<std::string> c; // 双向链表 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.push_back(std::string(buf)); // c.push_front(std::string(buf)); } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.max_size() << endl; // 最多能存储的元素个数 cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.front() << endl; cout << c.back() << endl; timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 std::string target("3456"); // 查找 auto iter = ::find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // :: 全局函数 if (iter == c.end()) cout << "Not find string" << endl; else cout << "Find string " << *iter << endl; std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; return 0; }
7. stack, 我们非常熟悉的栈,出战,入栈操作
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <stack> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::stack<std::string> c; // 双向链表 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.push(std::string(buf)); // c.push_front(std::string(buf)); } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; return 0; }
8. queue,用法于stack非常类似,不做详细的介绍了
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <queue> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::queue<std::string> c; // 双向链表 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.push(std::string(buf)); // c.push_front(std::string(buf)); } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; return 0; }
对于stack和queue,它们内部实际上是通过deque实现的,所以也可以将他们称为容器适配器。
关联式容器
1. 使用multiset容器
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <set> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::multiset<std::string> c; // 双向链表 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.insert(std::string(buf)); //set inset } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.max_size() << endl; // 关联式容器的查找 std::string target("3456"); timer.reset(); auto iter = ::find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // 通用的find函数 if (iter == c.end()) { cout << "Not found!" << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } else { cout << "found target " << *iter << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 auto pItem = c.find(target); // multiset内部的find函数 返回指针 if (pItem == c.end()) { cout << "Not found!" << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } else { cout << "found target " << *pItem << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } return 0; }
这里有必看介绍一下运行的结果: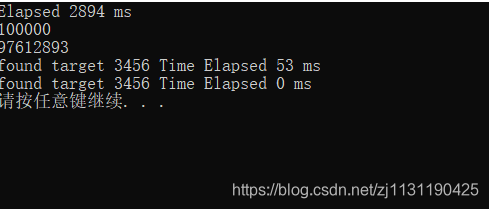
可以看到,set内部的find函数比通用的::find()函数速度快很多,set内部利用红黑树实现,所以它的查找速度是非常快的。但是也可以发现,关联式容器在插入数据的时候,速度还是相当慢的。
2. 使用容器multimap
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <map> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::multimap<int, std::string> c; // key, value std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.insert(std::pair<int, std::string>(i, std::string(buf))); //map inset } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.max_size() << endl; // 关联式容器的查找 // std::string target("3456") int target = 300; timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 auto pItem = c.find(target); // multiset内部的find函数 返回指针 if (pItem == c.end()) { cout << "Not found!" << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } else { // 输出key,value的值 cout << "found target " << pItem->first << " | " << pItem->second << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } return 0; }
3. unordered_multiset
不定序, 这种multiset的实现是通过hash table进行的,而不是经典的红黑树

// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <unordered_set> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::unordered_multiset<std::string> c; // 不定序, 通过hash table实现 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.insert(std::string(buf)); //map inset } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.max_size() << endl; cout << c.max_bucket_count() << endl; cout << c.bucket_count() << endl; // bucket的数量 // 关联式容器的查找 std::string target("3456"); // int target = 300; timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 auto pItem = c.find(target); // multiset内部的find函数 返回指针 if (pItem == c.end()) { cout << "Not found!" << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } else { // 输出key,value的值 cout << "found target " << *pItem << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } int bucket_cnt = c.bucket_count(); // 遍历一下bucket for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << "Bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements" << endl; } return 0; }
可以查看hash table中数据存储的具体情况,例如可以看到bucket的数量,以及bucket中存储的元素个数
运行结果:
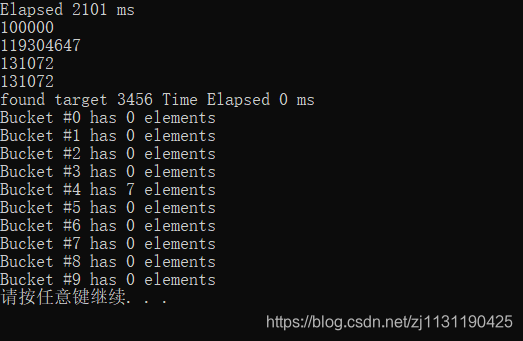
从结果可以看到,bucket的数量居然是大于元素的个数,实际上,bucket的个数确实是大于元素个数,因为从上面的hash table图可以发现,有的bucket中存放了多个元素,有的hash table中却是空的。bucket的个数大于元素个数是为了避免一个bucket过长(会降低查找元素的效率),所以每当元素个数大于bucket的个数的时候,bucket的个数就会按照两倍扩充,然后将元素打散,重新按照一定的规则计算元素放置的位置。
4. unordered multi_map
与上面的multi_set类似
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <unordered_map> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::unordered_multimap<int, std::string> c; // 不定序, 通过hash table实现 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.insert(pair<int, std::string>(i, std::string(buf))); //map inset } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.max_size() << endl; cout << c.max_bucket_count() << endl; cout << c.bucket_count() << endl; // bucket的数量 // 关联式容器的查找 // std::string target("3456"); int target = 300; timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 auto pItem = c.find(target); // multiset内部的find函数 返回指针 if (pItem == c.end()) { cout << "Not found!" << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } else { // 输出key,value的值 cout << "found target " << pItem->first << " | " << pItem->second << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } int bucket_cnt = c.bucket_count(); // 遍历一下bucket for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << "Bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements" << endl; } return 0; }
5 set集合,于multi_set的用法类似
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <set> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::set<std::string> c; // 不定序, 通过hash table实现 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c.insert(std::string(buf)); //map inset } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.max_size() << endl; // 关联式容器的查找 std::string target("3456"); // int target = 300; timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 auto pItem = c.find(target); // multiset内部的find函数 返回指针 if (pItem == c.end()) { cout << "Not found!" << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } else { // 输出key,value的值 cout << "found target " << *pItem << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } return 0; }
5 map,与multi_map的用法类似
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "Timer.h" #include <random> #include <map> #include <cstdlib> // qsort snprintf abort #include <string> #include <stdexcept> const int arraySize = 100000; using std::cout; using std::endl; int compare(void* x, void* y) { return (*(int*)x - *(int*)y); // 指针类型转换 } int main() { Timer timer; // 计时器 std::map<int, std::string> c; // 不定序, 通过hash table实现 std::default_random_engine e; // 默认的随机数引擎 std::uniform_int_distribution<int> u(1000, 20000); e.seed(10); // 设置生成随机数的种子 char buf[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { try { int rnd = u(e); //随机数 std::snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", rnd); // 将随机数写入c_string c[i] = std::string(buf); // map可以用这种写法 } catch (std::exception& exp) { cout << exp.what() << endl; // 会抛出标准异常类中的异常 bad_alloc std::abort(); // 退出程序 } } std::cout << "Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << std::endl; cout << c.size() << endl; // vector中的实际元素的个数,arraySize; cout << c.max_size() << endl; // 关联式容器的查找 // std::string target("3456"); int target = 300; timer.reset(); // 计时器归零 auto pItem = c.find(target); // multiset内部的find函数 返回指针 if (pItem == c.end()) { cout << "Not found!" << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } else { // 输出key,value的值 cout << "found target " << pItem->first << " | " << pItem->second << " Time Elapsed " << timer.elapsed() << " ms" << endl; } return 0; }
后续的unordered set, unordered map的用法与前面的都很相似。
----------------------------------------------------------分割线--------------------------------------------------------------





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)