Web前端JavaScript笔记(4)节点
如何获取元素节点的属性:
在Web前端JavaScript笔记(3)对象中,介绍了访问行间属性的方法,除此之外,系统还提供了三个方法访问元素的属性:
1. setAttribute:
2. getAttribute:
3. removeAttribute:
区别:
1. class属性的访问,class与className的区别
2. 行间的自定义属性,例如在 div中自定义属性,可以通过getAttribute方法访问到,但上一节中介绍的方法不支持自定义属性。
3. setAttribute还可以自定义属性并且进行赋值,其他的方法不支持。
4. 删除标签的属性,其他方法是没办法删除属性的,只能将属性设置为"",而removeAttribute()可以将属性删除。

5. innerHtml 获取标签间的内容,会解析文本
6. innerText 获取标签间的纯文本, 不会解析标签,设置纯文本
7. outerHTML 从外标签开始到外标签结束
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag = document.getElementById("div1"); // 访问行间属性 alert(tag.getAttribute("class")); alert(tag.getAttribute("title")); alert(tag.getAttribute("self")); // 访问自定义属性 tag.setAttribute("zx", "over"); // 设置自定义的属性 tag.removeAttribute("title"); alert(tag.innerHTML); // 获取标签之间的内容 alert(tag.innerText); alert(tag.outerHTML); } </script> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="box" title="hello" self="me"> <span>content</span> </div> </body> </html>
获取子节点:
系统提供的访问子节点的方法: (这些子节点共分为三类)
1. childNodes():访问当前节点下所有的子节点, 返回对象数组
2. lastChild():访问当前节点下最后一个子节点
3. firstChild():访问当前节点下第一个子节点
4. nextSibling: 当前节点的下一个兄弟节点
5. previousSibling:当前节点的上一个兄弟节点
同时,系统为每个节点提供了三个属性:
| nodeType | nodeName | nodeValue | |
| 元素节点 | 1 | 标签名 | null |
| 属性节点 | 2 | 属性名 | 属性值 |
| 文本节点 | 3 | #text | 文本内容 |
当标签出现换行,缩进的时候,系统也会把换行符,空格当作元素属性,所以通过childNodes获取到的元素子结点个数大于实际的子节点个数,可以通过以下的方法来去除这些空白符的影响:
【注】:下面的方法只能获取子结点中的元素节点
1. children : 只获取元素节点
2. firstElementChild:
3. lastElementChild:
4. nextElementSibling:
5. previousElementSibling:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag = document.getElementById("div1"); alert(tag.childNodes.length); alert(tag.childNodes[0]); alert(tag.childNodes[1]); alert(tag.childNodes[2]); alert(tag.lastChild); // 元素属性: alert(tag.childNodes[0].nodeType); alert(tag.childNodes[1].nodeType); alert(tag.childNodes[2].nodeType); } </script> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="box" title="hello" self="me"> <!--换行的时候会把换行符,空格也会算作元素--> <em>content</em> 节点 <strong>new node</strong> </div> </body> </html>
如何获取元素节点的属性节点:
系统提供了attributes方法用于获取元素节点上的所有属性节点: 获取到元素的属性节点
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag = document.getElementById("div1"); alert(tag.attributes); alert(tag.attributes.getNamedItem("title")); alert(tag.attributes["title"]); // 简便写法 } </script> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="box" title="hello" self="me"> <!--换行的时候会把换行符,空格也会算作元素--> 节点 </div> </body> </html>
DOM的节点操作:
// document.write()会覆盖掉原来页面上的内容
系统提供的节点操作的方法:
1. document.createElement () : 创建节点, 参数:标签名 返回值:创建好的标签
2. Node.appendChild(node):将某一个节点插入当前节点的子节点内
3. document.createTextNode(文本) 创建文本标签(纯文本,即使有标签也不会解析)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag_div = document.getElementById("div1"); let tag_btn = document.getElementById("btn1"); tag_btn.onclick = function () { let tag_p = document.createElement("p"); // 创建一个p标签 let text_content = document.createTextNode("hello javascript"); tag_p.appendChild(text_content); tag_div.appendChild(tag_p); } } </script> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="box"> <em>This</em> 节点 <strong>Content</strong> </div> <button id="btn1">节点操作</button> </body> </html>

每次点击按钮,会添加新的文本标签到div元素中
4. insertBefore() :格式: box1.parentNode.insertBefore(box2, box1);
功能:将box2添加到box1的前面
5. box1.parentNode.replaceChild(box2, box1); 用box2节点替换box1节点
6. node.cloneNode():克隆出一个新的node节点,返回值就是新创建的node节点, 只克隆节点本身
node.cloneNode(true):克隆node节点本身以及其所有的子节点
7. box.parent.removeChild(box):删除box节点
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag_div = document.getElementById("div1"); let tag_btn = document.getElementById("btn1"); tag_btn.onclick = function () { let tag_p = document.createElement("p"); // 创建一个p标签 let text_content = document.createTextNode("hello javascript"); tag_p.appendChild(text_content); document.body.replaceChild(tag_p, tag_div); // 替换节点 } } </script> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="box"> <em>This</em> 节点 <strong>Content</strong> </div> <button id="btn1">节点操作</button> </body> </html>
节点操作的案例:
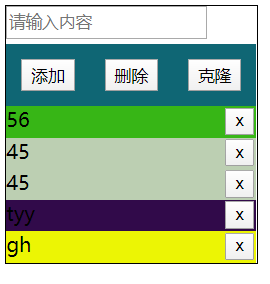
实现在输入框中输入内容,点击添加之后可以添加一条记录,点击删除按钮可以删除最后一条记录,点击克隆按钮可以克隆最后一条记录:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let input_tag = $("input_text"); let bottom_section = $("bottom"); $("add").onclick = function () { let input_content = input_tag.value; if(!input_content){ alert("请输入内容"); } else{ // 开始创建节点 let node = document.createElement("div"); let text_node = document.createTextNode(input_content); let btn_node = document.createElement("button"); let btn_text_node = document.createTextNode("x"); btn_node.appendChild(btn_text_node); node.appendChild(text_node); node.appendChild(btn_node); node.style.background = randomColor(); bottom_section.appendChild(node); input_tag.value = ""; // 清空输入框 updateItemsButtons(); } }; $("delete").onclick = function () { let last_node = bottom_section.lastChild; bottom_section.removeChild(last_node); updateItemsButtons(); }; $("clone").onclick = function () { let last_node = bottom_section.lastChild; let clone_node = last_node.cloneNode(true); // 深拷贝 bottom_section.appendChild(clone_node); updateItemsButtons(); }; function updateItemsButtons() { // 对每条记录上的删除按钮绑定函数 let child_nodes = bottom_section.children; // 只获取div元素节点 let btn_arr = []; for(let i=0; i<child_nodes.length; i++) { btn_arr.push(child_nodes[i].firstElementChild); //console.log(child_nodes[i].children); } // 对标签绑定事件函数 for (let i=0; i<btn_arr.length; i++) { // console.log(btn_arr[i]); btn_arr[i].index = i; btn_arr[i].onclick = function () { bottom_section.removeChild(child_nodes[this.index]); } } } } </script> <style> #container{ width: 200px; border: 1px solid black; } #top{ width: 100%; height: 30px; } #top input{ height: 20px; line-height: 30px; margin: 0 auto; } #middle{ width: 100%; height: 50px; border: none; display: flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content: space-around; background: #0f6674; } #middle button{ /*width: 25%;*/ height: 50%; align-self: center; /*margin-top: 10px;*/ } #bottom{ } #bottom div{ height: 25px; position: relative; } #bottom div button{ position: absolute; top: 1px; right: 2px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="container"> <div id="top"> <input type="text" id="input_text" placeholder="请输入内容"> </div> <div id="middle"> <button id="add">添加</button> <button id="delete">删除</button> <button id="clone">克隆</button> </div> <div id="bottom"> <!--<div>content<button>x</button></div>--> </div> </div> </body> </html>
选项卡:
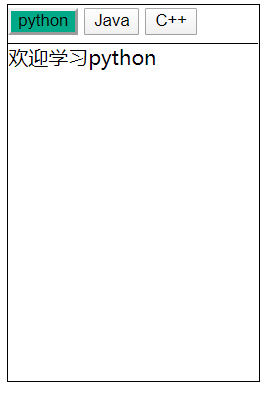
实现选项卡切换的时候,呈现选定状态的样式以及下方显示相对应的内容:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function(){ let btn_arr = $("buttons"); let buttons = btn_arr.getElementsByTagName("button"); let content_box = $("content"); let contents = content_box.getElementsByTagName("div"); // 为按钮添加事件绑定函数 for (let i=0; i<buttons.length; i++) { buttons[i].index = i; buttons[i].onclick = function () { for (let j=0; j<buttons.length; j++) { buttons[j].className = ""; contents[j].style.display = "none"; } this.className = "active"; contents[this.index].style.display = "block"; } } } </script> <style> #container{ width: 200px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid black; } #container #buttons{ height: 30px; } #container #content{ border-top: 1px solid black; } .active{ background: #00aa88; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="container"> <div id="buttons"> <button class="active">python</button> <button>Java</button> <button>C++</button> </div> <div id="content"> <div style="display: block">欢迎学习python</div> <div style="display: none">欢迎学习Java</div> <div style="display: none">欢迎学习C++</div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
offset系列方法-快速获取当前页面上的宽,高,距左距离和距右距离:
1. offsetWidth:
2. offsetHeight:
3. offsetLeft:
4. offsetTop:
区别:
通过node.style.width / height获取的是html盒模型中content的大小
offsetWidth / offsetHeight获取的是盒模型中content+padding+border的大小
offsetLeft / offsetTop得到的是距离页面左上角的距离
文档碎片:
利用文档碎片可以大幅提高文档的运行效率:
应用:例如需要在页面上创建10万个节点,将10万个节点全部添加到页面上
提示: 官方提示的计时器: console.time("hh") 代码 console.timeEdn();
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function(){ //创建十万个节点,没创建一个,插入一个到body中 console.time("test1"); for (let i=0; i<100000; i++) { let new_tag = document.createElement("div"); document.body.appendChild(new_tag); } console.timeEnd("test1"); // 官方提供的计时器 // // 先创建所有节点,在插入节点 console.time("test2"); let node = document.createElement("div"); // 先创建一个标签 for (let i=0; i<100000; i++) { let new_node = document.createElement("div"); node.appendChild(new_node); } document.body.appendChild(node); console.timeEnd("test2"); // 官方提供的计时器 } </script> </head> <body> </body> </html>
第二种方法插入节点的速度更快,称之为文档碎片操作。
数组元素的遍历方法:
1. for循环
2. for-in
3. for-each方法:
<script> window.onload = function(){ let arr = [1,4,2,3,4,2]; for (let i=0; i<arr.length; i++) { console.log(i); } for(let elem in arr){ console.log(elem); } arr.forEach(function (item, index, arr) { console.log(item); }) } </script>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)