Web前端JavaScript笔记(5)事件-拖拽
阻止默认行为和超链接
在浏览器上运行网页后,右击会弹出菜单,这属于浏览器的默认行为。如何禁止这一默认行为:
<script> window.onload = function () { document.oncontextmenu = function () { return false } } </script>
对于a链接,如果点击a链接后,会默认直接进行跳转,如何组织这一默认行为,在点击a连接后,想用户进行询问之后,在进行是否跳转。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag_a = $("baidu"); tag_a.onclick = function () { return confirm("Quit?"); // confirm会返回true和false }; } </script> </head> <body> <a id="baidu" href="https://ww.baidu.com" target="_blank">百度</a> </body> </html>
另一种方法,阻止超链接默认行为的方法,由系统提供的属性和方法实现:
1. preventDefault(); W3C, 阻止默认行为
2. window.event.returnValue = false; // IE浏览器,阻止默认行为
在实际应用中,需要自定义个能兼容不同浏览器的版本:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag_a = $("baidu"); tag_a.onclick = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; preventDefaultAction(e); alert("后续操作"); }; }; // 跨浏览器阻止默认行为 function preventDefaultAction(e) { if(e.preventDefault) { e.preventDefault(); } else { window.event.returnValue = false; } } </script> </head> <body> <a id="baidu" href="https://ww.baidu.com" target="_blank">百度</a> </body> </html>
拖拽实现:
1. mousedown
记录鼠标按下时鼠标相对于被拖拽的物体的位置:
offsetX = e.clientX - offsetX
offsetY = e.clientY - offsetY
2. mousemove
在鼠标一定的过程中,需要一致保持被拖拽物体与鼠标的相对距离
3. mouseup
取消拖拽
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag_div = $("box"); let absolute_x = 0; let absolute_y = 0; let current_x = 0; let current_y = 0; tag_div.onmousedown = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; absolute_x = e.clientX - tag_div.offsetLeft; absolute_y = e.clientY - tag_div.offsetTop; // 绑定鼠标移动事件 document上 document.onmousemove = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; current_x = e.clientX; current_y = e.clientY; tag_div.style.left = current_x - absolute_x + "px"; tag_div.style.top = current_y - absolute_y + "px"; } }; window.onmouseup = function () { document.onmousemove = null; }; } </script> <style> #box{ width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid black; background: #ffcf3f; position: absolute; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="box"></div> </body> </html>
对拖拽的改进,使得被推拽的物体不能超过屏幕的范围:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag_div = $("box"); let absolute_x = 0; let absolute_y = 0; let current_x = 0; let current_y = 0; tag_div.onmousedown = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; absolute_x = e.clientX - tag_div.offsetLeft; absolute_y = e.clientY - tag_div.offsetTop; // 获取窗口的大小 let window_width = document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth; let window_height = document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body // 绑定鼠标移动事件 document上 document.onmousemove = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; current_x = e.clientX; current_y = e.clientY; let adjust_x = current_x - absolute_x; let adjust_y = current_y - absolute_y; if(adjust_x < 0) { adjust_x = 0; } if(adjust_x >= window_width - tag_div.offsetWidth) { adjust_x = window_width - tag_div.offsetWidth; } if(adjust_y < 0) { adjust_y = 0; } if(adjust_y >= window_height - tag_div.offsetHeight) { adjust_y = window_height - tag_div.offsetHeight; } tag_div.style.left = adjust_x + "px"; tag_div.style.top = adjust_y + "px"; }; }; window.onmouseup = function () { document.onmousemove = null; } } </script> <style> #box{ width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid black; background: #ffcf3f; position: absolute; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="box"></div> </body> </html>
可以对上述的实现拖拽代码进行封装,成为一个独立的函数,放到too.js中可供使用
事件委托:
例如,对于如下的结构:
<body> <ul id="list"> <li>11</li> <li>22</li> <li>33</li> <li>44</li> </ul> </body>
需要给<li>标签添加相同的点击事件,按照之前的做法,是先获得所有的<li>标签,再通过循环为每一个<li>标签添加点击事件。如果需要在添加一个按钮,每次点击按钮后,都需要新增一个<li>标签,则新增的<li>标签是没有绑定点击事件的。
这样做的缺点是:
1. for循环添加相同的事件函数,浪费资源
2. 不能解决新增的节点事件绑定问题
解决方法:事件委托
A委托---->B代理,B执行动作,A受益
1. 找到当前节点的父节点或者祖先节点
2. 将事件添加到父节点或者祖先节点
3. 找到触发对象,判断触发对象是否满足条件,如果是执行后续操作
所以可以通过上述的操作,实现<li>标签委托<ul>,此时只需要为<ul>标签添加事件函数,同时新增的<li>节点也可以响应点击事件,这个事件是<li>委托给ul的。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let btn = $("add"); let tag_ul = $("list"); // 找到li的父节点 tag_ul.onclick = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; let target_e = e.target || window.event.srcElement; // 获取事件对象 if(target_e.nodeName.toLowerCase() === "li") // 判断触发对象是否满足条件 { target_e.style.background = "red"; } }; let cnt = 1; // 增加新节点 btn.onclick = function () { let newLi = document.createElement("li"); newLi.innerHTML = (cnt++ * 1111).toString(); tag_ul.appendChild(newLi); } } </script> <style> </style> </head> <body> <button id="add">增加</button> <ul id="list"> </ul> </body> </html>
可以利用事件委托对前面的增加记录案例进行改进:
这样只需要添加一个点击就可以实现所有按钮绑定事件:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let input_tag = $("input_text"); let bottom_section = $("bottom"); $("add").onclick = function () { let input_content = input_tag.value; if(!input_content){ alert("请输入内容"); } else{ // 开始创建节点 let node = document.createElement("div"); let text_node = document.createTextNode(input_content); let btn_node = document.createElement("button"); let btn_text_node = document.createTextNode("x"); btn_node.appendChild(btn_text_node); node.appendChild(text_node); node.appendChild(btn_node); node.style.background = randomColor(); bottom_section.appendChild(node); input_tag.value = ""; // 清空输入框 // updateItemsButtons(); } }; $("delete").onclick = function () { let last_node = bottom_section.lastChild; bottom_section.removeChild(last_node); // updateItemsButtons(); }; $("clone").onclick = function () { let last_node = bottom_section.lastChild; let clone_node = last_node.cloneNode(true); // 深拷贝 bottom_section.appendChild(clone_node); // updateItemsButtons(); }; // 事件委托 bottom_section.onclick = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; let target = e.target || window.event.srcElement; // 找到触发对象 if(target.nodeName.toLowerCase() === "button") // 要转换成小写 { bottom_section.removeChild(target.parentNode); // 删除当前对象的父节点 } }; input_tag.onkeydown = function (ev) { // 给输入框添加快捷键 let e = ev || window.event; let key_code = e.keyCode || e.which; // 判断回车键 if(e.ctrlKey && key_code===13) { $("add").onclick(); } } } </script> <style> #container{ width: 200px; border: 1px solid black; } #top{ width: 100%; height: 30px; } #top input{ height: 20px; line-height: 30px; margin: 0 auto; } #middle{ width: 100%; height: 50px; border: none; display: flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content: space-around; background: #0f6674; } #middle button{ /*width: 25%;*/ height: 50%; align-self: center; /*margin-top: 10px;*/ } #bottom{ } #bottom div{ height: 25px; position: relative; } #bottom div button{ position: absolute; top: 1px; right: 2px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="container"> <div id="top"> <input type="text" id="input_text" placeholder="请输入内容"> </div> <div id="middle"> <button id="add">添加</button> <button id="delete">删除</button> <button id="clone">克隆</button> </div> <div id="bottom"> <!--<div>content<button>x</button></div>--> </div> </div> </body> </html>
事件监听器:
传统的事件绑定,需要先获取到相应的节点,再去绑定事件,但是在一些场景中,这种传统的方法不能够满足需求:
1. 例如,对一个按钮重复绑定同一个是按,当事件被触发的时候,前面的事件会被后面的事件覆盖
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let btn = $("add"); btn.onclick = function () { alert("点击1"); }; btn.onclick = function () { alert("点击2"); }; } </script> <style> </style> </head> <body> <button id="add">增加</button> </body> </html>
当点击按钮后只能出现"点击2","点击1"会被覆盖掉。
而事件监听器是另一种绑定事件的方式,addEventListener()用于向指定元素添加事件句柄,IE8以下不支持,火狐和谷歌支持/
removeEventListener()删除事件监听器。
addEventListener("click", functionName, bool):
第一个参数表示需要监听的操作,例如click
第二个参数表示绑定的事件函数,函数名或者匿名函数
第三个参数表示 true: 事件捕获,false事件冒泡, 默认/ 事件捕获:与事件冒泡案例中的顺序正好相反。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let btn = $("add"); btn.addEventListener("click", function () { alert("点击1"); }, false); btn.addEventListener("click", function () { alert("点击2"); }, false); } </script> <style> </style> </head> <body> <button id="add">增加</button> </body> </html>
而利用事件监听器就可以执行所有绑定的事件。利用事件监听器,可以给标签绑定多个事件函数,同时,也能够精确的去删除标签上绑定的某一个事件函数,但是传统事件绑定方法,一是会后绑定的事件函数会覆盖掉前面的事件函数,在一个是,如果需要删除事件函数,则会将所有的事件函数都删除。(node.onclick = null)
低版本浏览器需要兼容事件监听器:
1. attachEvent()
2. detachEvent()
function addEvent(node, eventType, funcName) { if (node.addEventListener) // 判断是否支持 { node.addEventListener(eventType, funcName, false); } else { node.attachEvent("on" + eventType, funcName); } } function removeEvent(node, eventType, funcName) { if(node.removeEventListener) { node.removeEventListener(eventType, funcName); } else { node.detachEvent("on" + eventType, funcName); } }
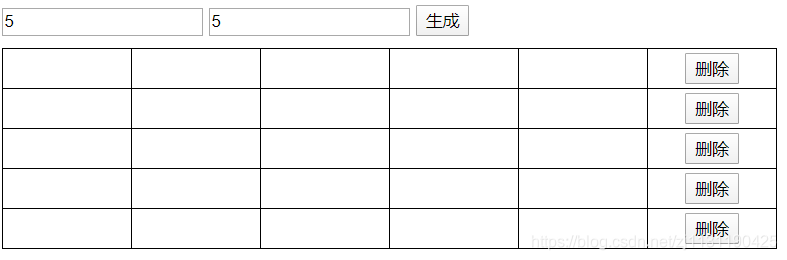
案例:动态生成表格
输入表格的行数和列数,自动生成表格:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let btn = $("gen"); let row = $("row"); let col = $("col"); let table = $("t1"); btn.onclick = function () { let row_num = row.value; let col_num = col.value; if(!row_num || !col_num) { alert("请输入完整的行列"); } else { let row_max = parseInt(row_num); let col_max = parseInt(col_num); if (isNaN(row_max) || isNaN(col_max)) //行列必须是数字 { alert("行列必须是数字"); } else { for(let row_cnt=0; row_cnt<row_max; row_cnt++) { // 控制行数 let tr = document.createElement("tr"); // 创建行 for (let col_cnt=0; col_cnt<col_max; col_cnt++) { let td = document.createElement("td"); tr.appendChild(td); } let td_del = document.createElement("td"); td_del.innerHTML = "<button>删除</button>"; tr.appendChild(td_del); table.appendChild(tr); } } } }; table.onclick = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; let target = e.target || window.event.srcElement; if(target.nodeName.toLowerCase() === "button") { table.removeChild(target.parentNode.parentNode); } }; } </script> <style> #t1 tr td{ width: 100px; height: 30px; border: 1px solid black; } #t1 tr td:last-child button{ display: block; margin: 0 auto; } #t1{ border: 1px solid black; border-collapse: collapse; margin-top: 10px; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="text" placeholder="行数" id="row"> <input type="text" placeholder="列数" id="col"> <button id="gen">生成</button> <table id="t1"> </table> </body> </html>
效果如下图所示:
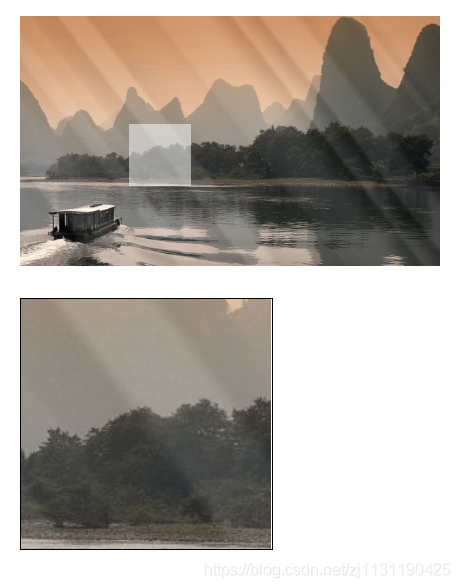
案例:放大镜
在图片中,随着鼠标的移动,图片的局部区域会在另一个地方被放大一定的倍数:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { let tag_mark = $("mark"); let tag_sourcePic = $("source-pic"); let tag_largePic = $("large-pic"); let tag_img = tag_largePic.getElementsByTagName("img")[0]; tag_sourcePic.onmouseover = function () { tag_mark.style.display = "block"; }; tag_sourcePic.onmouseout = function () { tag_mark.style.display = "none"; }; tag_sourcePic.onmousemove = function (ev) { let e = ev || window.event; let temp_x = e.clientX - tag_sourcePic.offsetLeft -tag_mark.offsetWidth /2; let temp_y = e.clientY - tag_sourcePic.offsetTop - tag_mark.offsetHeight/2; if (temp_x < 0){ temp_x = 0; } if (temp_x > tag_sourcePic.offsetWidth - tag_mark.offsetWidth) { temp_x = tag_sourcePic.offsetWidth - tag_mark.offsetWidth; } if (temp_y < 0) { temp_y = 0; } if (temp_y > tag_sourcePic.offsetHeight - tag_mark.offsetHeight) { temp_y = tag_sourcePic.offsetHeight - tag_mark.offsetHeight; } tag_mark.style.left = temp_x + "px"; tag_mark.style.top = temp_y + "px"; // 放大效果 tag_img.style.left = temp_x * -3.2 +"px"; tag_img.style.top = temp_y * -3.2 + "px"; } } </script> <style> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } #source-pic{ width: 336px; height: 200px; position: absolute; left: 20px; top: 25px; } #source-pic img{ display: block; width: 100%; height: 100%; } #source-pic #mark{ width: 50px; height: 50px; opacity: 0.5; background: white; position: absolute; left: 0; top: 0; display: none; } #large-pic{ width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid black; position: absolute; left: 20px; top: 250px; overflow: hidden; } #large-pic img { position: absolute; left: 0; top: 0; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="source-pic"> <img src="../picture/others/timg1.jpg" alt=""> <div id="mark"></div> </div> <div id="large-pic"> <img src="../picture/others/timg1.jpg" alt=""> </div> </body> </html>










【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)