Web前端Javascript笔记(6)正则表达式
在web前端中,假设用户需要提交表单,在表单提交到服务器进一步处理之前,Javascript程序会检查表单,以确认用户输入的信息是符合规范要求的。这些工作可以使用正则表达式完成,正则表达式是一个描述字符模式的对象,ECMAscript的RegExp类表示正则表达式。在正则表达式中,定义了功能强大的【模式匹配】,【文本检索】,【替换】函数。
正则表达式创建: ig忽略大小写和全局匹配,全局匹配表示是匹配/替换 所有的满足条件的,否则只返回第一个
<script>
let box0 = new RegExp("box", "ig"); // 匹配字符串(主体),匹配模式(修饰符)
let box1 = RegExp("box", "ig"); // 匹配字符串(主体),匹配模式(修饰符)
let box2 = /box/ig;
</script>正则表达式对象的属性和方法:
1. test
格式是: 正则.test(string): 在字符串中匹配正则是否存在, 返回布尔值
2.exec
格式是: 正则.exec(string): 在字符串中匹配正则是否存在, 返回数组,数组中存储的是匹配到的字符,匹配失败返回的是null
3. 在字符串中的很多方法都可以使用正则表达式:参数是正则表达式
match() , 在字符串中匹配是否有合法的正则,返回值: 数组和null
replace(), 字符串.replace(oldstr/ RegExp, newstr), 用新的字符串匹配就的字符串,旧的字符串可以用正则表示
返回值: 替换成功的新字符串
split() ,字符串分割,分隔符可以是正则表达式,返回值是分割后的字符串
search(), 字符串搜索,参数可以是正则表达式, 返回值:>=0的下标, 否则返回值为-1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
let box = RegExp("are"); // 匹配字符串(主体),匹配模式(修饰符)
let sen = "How are you";
alert(box.test(sen));
let box1 = RegExp("are", "i"); // 忽略大小写
let sen1 = "How Are you";
alert(box1.test(sen1));
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>元字符:
在正则表达式中有特殊含义的字符
1. 单个数字和字符的元字符
"."表示可以匹配任何单个字符
[ ] 匹配单个范围内的字符 , 例如[a-z][A-Z][0-9], 匹配单个数字或者字母,[a-zA-Z0-9_],匹配单个数字,字母或者下划线
[^]与[ ]匹配的内容相反,例如 [^0-9]匹配处0-9之外的单个字符
\w 匹配数字,字母或者下划线,等价于[a-zA-Z0-9_]
\W 与\w正好相反
\d 表示匹配单个数字,等价于[0-9]
\D表示匹配非数字
2. 重复字符:(假设x代表任意的单个字符)
x? 表示匹配0或者1个字符x
x* 表示匹配任意多个字符x
x+ 表示匹配1或者多个字符x(至少一个)
x{m,n}匹配至少m个,最多n个字符
x{n} 表示必须匹配n个字符x
(xyz)+ 此时括号里面的内容xyz是当作单个字符去处理的
3. 空白字符
空白字符包括:
(null字符,空格字符,进纸字符,换行字符,回车字符,制表符等等)
\s 匹配任意单个的空白字符
\S 匹配任意单个的非空白字符
4. 锚字符
^ 行首匹配
$ 行尾匹配
例如: ^g.*d$ 匹配的字符串必须以g开头,以d结尾。
5. 替代字符
| 表示或运算字符
6. 修饰符
i 忽略大小写
g 全局匹配
m 换行匹配
7.转义字符:
\. 代表本来 . 字符的意思
\* 代表本来*字符的意思
正则表达式应用:
1. 匹配压缩文件
<script>
let reg = /^\w+\.(zip|rar|gz)$/;
let file_name = "shell.rar";
alert(reg.test(file_name));
</script>2. 匹配手机号
<script>
let phone_reg = /^1[0-9]{10}/
alert(phone_reg.test("18834659876"));
</script>3. 验证身份证号:
<script>
let id_reg = /^[1-9]\d{16}(\d|x)$/i;
alert(id_reg.test("62172118850265478X"));
</script>4. 验证中文字符串
<script>
let chinese_reg = /^[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+$/;
alert(chinese_reg.test("前端脚本"));
</script>表单验证与密码强度:
1.验证用户名的合法性,包括用户名的长度,字母开头,只能包含数字,字母,下划线
2. 密码强度验证,包括密码的长度,强度等级划分
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
let tag_userName = $("username");
let tag_password = $("passwd");
let tag_span = $("username-span");
let tag_code = $("code");
let tag_testCode = tag_code.getElementsByTagName("div");
tag_userName.onblur = function () {
let username = tag_userName.value;
// 判断长度
if(username.length < 6 || username.length >18)
{
tag_span.innerHTML = "!用户名长度6~18";
tag_span.style.color = "red";
}
//判断首字母开头
else if(! /[a-zA-Z]/.test(username[0]))
{
tag_span.innerHTML = "!用户名必须以字母开头";
tag_span.style.color = "red";
}
else if (/\W/.test(username))
{
tag_span.innerHTML = "!用户名只能包含数字字母下划线";
tag_span.style.color = "red";
}
else
{
tag_span.innerHTML = "!该用户名可注册";
tag_span.style.color = "green";
}
};
tag_password.onkeyup = function () {
let password = tag_password.value;
if(password.length >= 6)
{
// 可以开始验证密码强度
// 分类
// 1. 弱密码: 纯数字 纯小写 纯大写
// 2. 中密码: 两者混合
// 3. 三种混合
if (/^[0-9]+$/.test(password) || /^[a-z]+$/.test(password) ||/^[A-Z]+$/.test(password))
{
tag_testCode[0].style.background = "orange";
tag_testCode[1].style.background = "gray";
tag_testCode[2].style.background = "gray";
}
else if(/\d/.test(password) && /[a-z]/.test(password) && /[A-Z]/.test(password))
{
tag_testCode[0].style.background = "gray";
tag_testCode[1].style.background = "gray";
tag_testCode[2].style.background = "orange";
}
else
{
tag_testCode[0].style.background = "gray";
tag_testCode[1].style.background = "orange";
tag_testCode[2].style.background = "gray";
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
#form{
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 1px solid black;
background: #66c5b4;
text-align: center;
}
#form #username{
margin: 40px 5px 10px 5px;
}
#username-span{
display: block;
font-size: 10px;
height: 16px;
line-height: 16px;
color: gray;
}
#passwd{
margin: 10px 0 0 0;
}
#code
{
height: 30px;
margin: 10px 60px 0 60px;
}
#code .testCode{
width: 60px;
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
background: gray;
color: black;
text-align: center;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="form">
<input id="username" type="text" placeholder="邮箱">
<span id="username-span">字母,数字,下划线,长度6~18</span>
<input id="passwd" type="password" placeholder="密码">
<!--密码轻度-->
<div id="code">
<div class="testCode">若</div>
<div class="testCode">中</div>
<div class="testCode">强</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
localStore本地存储:
在HTML5中,加入了一个localStorage特性,主要用来作为本地存储使用,解决了cookie存储空间不足的问题,cookie中每条cookie的存储空间为4k,localStorage中浏览器支持的是5M大小。
例如,首次登陆,点击记住用户名和密码,下次登陆就无需在输入用户名和密码
本地存储技术:
localStorage: 1. 永久存储 2.最大支持5M (客户端微型数据库) 3. 只能存储字符串
cookie: 1. 可以设置过期时间 2. 最大可以存储4k 3. 每一个域名下最多可以存储50条数据
sessionStorage : (结合后台使用)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
localStorage对象:
1. setItem(name, value)
2. getItem(name, value)
3. removeItem(name, value)
<script>
if (!window.localStorage)
{
alert("不支持localStore");
}
else
{
localStorage.setItem("name", "kitty");
localStorage.setItem("age", "33");
}
window.onclick = function () {
alert(localStorage.getItem("name"));
localStorage.removeItem("age");
}
</script>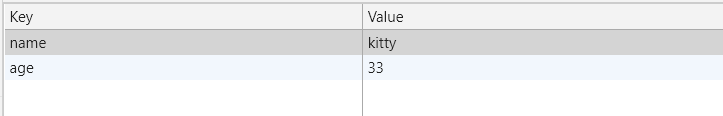
localStorage应用:
在页面刷新后,依然能够保持页面的状态:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script rel="script" src="../JavaScript/tool.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
let slide = $("slide");
let full = $("full");
let block = $("block");
// 加载本地存储的位置信息
if (!window.localStorage)
{
alert("不支持localStorage");
}
else
{
let pos = localStorage.getItem("position");
if (pos){
block.style.left = pos + "px";
full.style.width = pos + "px";
}
else{
pos = 0;
block.style.left = pos + "px";
full.style.width = pos + "px";
}
}
block.onmousedown = function (ev) {
let e = ev || window.event;
let offset_x = e.clientX - slide.offsetLeft;
document.onmousemove = function (ev) {
let e = ev || window.event;
let current_x = e.clientX - slide.offsetLeft;
if (current_x < 0)
{
current_x = 0;
}
if(current_x > slide.offsetWidth - block.offsetWidth)
{
current_x = slide.offsetWidth - block.offsetWidth;
}
block.style.left = current_x + "px";
full.style.width = current_x + "px";
// 对滑块的位置进行存储到本地
if (window.localStorage) {
localStorage.setItem("position", current_x.toString());
}
else {
alert("不支持storage");
}
}
};
window.onmouseup = function () {
document.onmousemove = null;
};
}
</script>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
#slide{
position: relative;
width: 600px;
height: 30px;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 100px auto;
}
#block{
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
background-color: blue;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
}
#full
{
width: 0;
height: 30px;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="slide">
<div id="full"></div>
<div id="block"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>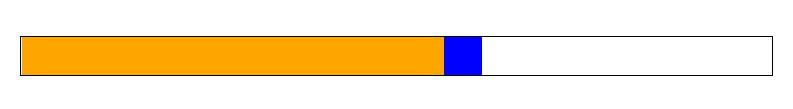
在页面上拖动进度条之后,即使刷新页面,也会保持上次的进度条的位置。
强制改变this指向:
每一个函数中都有一个内置的变量this,this指向当前函数的主人,函数的主人需要根据上下文进行判断
强制数据类型转换:强制使得this指向统一的对象
1. call
例如,定义show(x, y)函数
格式:通过show.call()调用函数
参数:show.call(newObj, x, y) newObj表示新绑定的对象,后面的表示函数参数
<script>
function show(x, y) {
alert(this); // this->window
alert(x + "," + y);
}
show(1,2);
show.call("call", 1, 2); // this->call
</script>2.apply()方法
格式:show.apply()
参数: show.apply(newObj, [x, y]);
<script>
function show(x, y) {
alert(this); // this->window
alert(x + "," + y);
}
show(1,2);
show.apply("call", [1, 2]); // this->call
</script>3. bind()方法:预设this指向
格式:show.bind(newObj)
返回值:在执行show.bind(newObj)之后,show函数并不会被执行,而是会返回一个show()函数,但是此时的show()函数中this已经指向了newObj。
<script>
function show(x, y) {
alert(this); // this->window
alert(x + "," + y);
}
show(1,2);
let show1 = show.bind("call");
show1(4,5);
</script>apply使用技巧,在Math.min()和Math.max()中,查找数组的最大最小值,由于Math.min()和Math.max()只能传入一个一个的数,如果想找到数组中的最值,可以借助apply方法:
<script>
alert(Math.max(1,2,3,4,5));
alert(Math.max.apply("null", [1,2,3,4,5]));
</script>let和const关键字:
let关键字:用于声明变量,变量作用域范围更小,只要遇到大括号,就形成作用域,例如,for循环,if判断,switch条件判断
var关键字:用于声明变量,且声明的变量是要遵循内存的垃圾回收机制,即将当前函数所在的大括号最为一个作用域进行处理。
所以将let关键字形成的作用域称为块作用域,将var关键字形成的作用域称为局部作用域。
例如:
<script>
window.onload = function () {
let btns = document.getElementsByTagName("button");
for (var i=0; i<btns.length; i++)
{
btns[i].onclick = function () {
alert(i);
}
} // 每个按钮都哦输出的是3,for循环下是整个作用域
for (let i=0; i<btns.length; i++)
{
btns[i].onclick = function () {
alert(i);
}
} // 因为每次循环,都会i都会产生一个独立的作用域,所以会生成三个独立的作用域
// 所以输出的是0,1,2;
}
</script>const关键字:用于声明常量,变量的值只能在声明的时候确定,后续不能修改
箭头函数
一种新的函数的写法,只是写法上的一种改变,并没有实质上新的功能,也没有对程序的执行效率有所提高,且这样的代码可读性不好。由于不推荐,就不深入学习了。
<script>
window.onload = function () {
function add(x) {
return x+10;
}
// 箭头函数的写法
var add = x => x + 10;
}
</script>解构与ECMA6字符串:
解构:
1. 中括号解构
2. 大括号解构
<script>
window.onload = function () {
// 中括号解构
let x, y, z = [1, 2, 3];
alert(x + "," + y + "," + z);
// 大括号解构
let {name, age} = {
name: "wang",
age: "23"
}
}
</script>解构的应用:
1. 可以很方便的交换两个变量的值
2. 使得函数可以返回多个值
3. 函数定义参数,传入参数的顺序
<script>
window.onload = function () {
// 1. 交换值
[x, y] = [1, 2];
[x, y] = [y, x];
// 2. 返回值
function test() {
return [12, 45, 11];
}
[a, b, c] = test();
// 3. 传参顺序
function show({name, age=13, sex}) {
alert("I am " + name + "," + age + "years old" + "," +sex);
}
show({ // 参数的顺序可以打乱, 参数还可以有默认值
age: 13,
sex: "female",
name: "zhang"
})
}
</script>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号