c++中的 static 关键字
注:若没有特指是 静态成员时,默认都是普通成员;
1 类中的普通成员
类中的成员变量 和 成员函数 是分开存储的。其中,
1)每个对象都有独立的成员变量;成员变量可以存储在 栈空间、堆空间、全局数据区;
2)所有对象共享类的成员函数;成员函数 只能存储在 代码段;
2 类中的静态成员(static)
类中的静态成员
1、用 static关键字 修饰;
2、可以用 类名::成员名 访问 静态成员;
3、静态成员 属于 整个类;
4、静态成员 是所属类的成员,其它类不能访问;
5、静态成员的内存分配 是 唯一的;
1) 静态成员变量
特征:1、静态成员变量 属于 整个类所有;
2、静态成员变量的生命周期不依赖任何对象;(静态成员变量的生命周期在程序的运行期)
3、所有对象共享类的静态成员变量;
4、可以通过 类名 直接访问公有的静态成员变量;
5、可以通过 对象名 访问公有的静态成员变量;
6、静态成员变量 需要在类外单独分配空间;(类内声明、类外定义并初始化)
7、静态成员变量 在程序内部位于全局数据区,不计入类的内存计算。
原因/好处:使用静态成员变量实现多个对象之间的数据共享不会破坏隐藏的原则,保证了安全性还可以节省内存。
使用方法:
1、在类的内部,使用 static 修饰普通成员变量;
2、在类的外部(全局作用域),使用 Type ClassName::VarName = value 初始化,并申请存储空间;
注:静态成员变量不属于类的任何对象,所以并不是对象建立时被定义的,所以它不能由类的构造函数初始化,一般也不能在类内初始化;
1 /* 2 静态成员变量 只能在类的内部声明,在类的外部(全局区)定义和初始化; 3 */ 4 5 #include <iostream> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 class Test{ 10 public: 11 int GetA() const{return a;} 12 private: 13 static int a; // 静态成员变量 14 }; 15 //int Test::a;如果这样定义不赋予初值,则初值为零 16 int Test::a = 1; 17 18 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 19 { 20 Test T; 21 22 cout << T.GetA() << endl; 23 24 return 0; 25 }
静态成员变量 被类的所有对象共享,包括派生类对象;
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Base{ 6 public: 7 static int a; // 静态成员变量 8 }; 9 10 // int Base::a;如果这样定义不赋予初值,则初值为零 11 int Base::a = 0; 12 13 class Derived : public Base{ 14 15 }; 16 17 18 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 19 { 20 Base B; 21 Derived D; 22 23 B.a++; 24 cout << B.a << endl; // 1 25 D.a++; 26 cout << D.a << endl; // 2 27 28 return 0; 29 }
静态成员变量可以作为普通成员函数的默认形参,而普通成员变量则不可以;
1 class Test{ 2 public: 3 static int a; //静态成员变量 4 int b; 5 void fun_1(int i = a); //正确 6 //void fun_2(int i = b); //报错 7 };
静态成员变量的类型 可以是所属类的类型,而普通成员变量则不可以。普通成员变量只能声明为 所属类类型的 指针或引用;
1 class Test{ 2 public: 3 static Test a; //正确 4 Test b; //报错 5 Test *pTest; //正确 6 Test &m_Test; //正确 7 static Test *pStaticObject; //正确 8 };
静态成员变量在const函数中可以修改,而普通的成员变量是万万不能修改的;
1 /* 2 const修饰的是当前this指针所指向的对象是const,但是静态成员变量不属于任何类的对象,它被类的所有对象修改,所以this指针不修饰静态的成员变量,所以可以更改。 3 */ 4 class Test{ 5 public: 6 static int a; 7 int b; 8 public: 9 Test():b(0){} 10 void test() const 11 { 12 a++; 13 //b++; // err // const指的是不能修改当前调用该函数对象的成员变量 14 } 15 }; 16 17 int Test::a;
2)静态成员函数
特征:1、静态成员函数 属于 整个类所有;
2、所有对象共享类的静态成员函数;
2、可以通过 类名 直接访问公有的静态成员函数;
3、可以通过 对象名 访问公有的静态成员函数;
4、静态成员函数 只能 访问静态成员,不能访问 非静态成员;
5、静态成员函数没有this指针,也就是说静态成员函数不能使用修饰符(也就是函数后面的const关键字);
原因:处理静态成员变量;
使用方法:直接用 static 修饰 普通成员函数(类内声明时),不需要 static 修饰(类外定义时);
总结: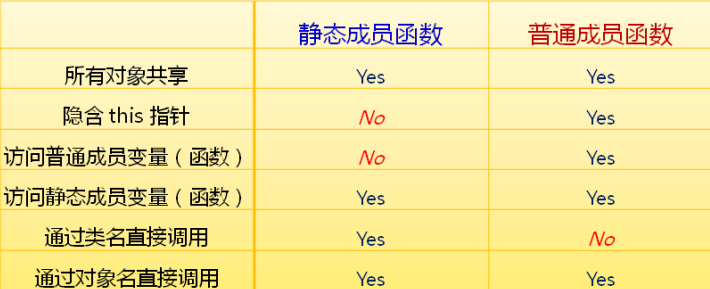
案例分析:

1 /** 2 * 统计某班选修课考试的平均成绩 3 */ 4 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <string> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 class Student 11 { 12 private: 13 string name; // 姓名 14 string gender; // 性别 15 float score; // 分数 16 string subject; // 课程 17 static float chinese_scores; // 语文分数 18 static float math_scores; // 数学分数 19 public: 20 static int total_counts; // 总人数 21 static int chinese_counts; // 语文课人数 22 static int math_counts; // 数学课人数 23 public: 24 Student(string name, string gender, float score, string subject); 25 ~Student(); 26 static float aveScores(string subject); 27 void printStudentInfo(); 28 void printAveScores(); 29 }; 30 int Student::total_counts = 0; 31 float Student::chinese_scores = 0; 32 int Student::chinese_counts = 0; 33 float Student::math_scores = 0; 34 int Student::math_counts = 0; 35 36 Student::Student(string name, string gender, float score, string subject) 37 { 38 this->name = name; 39 this->gender = gender; 40 this->score = score; 41 this->subject = subject; 42 43 if(subject == "chinese" || subject == "语文") 44 { 45 chinese_scores += score; 46 chinese_counts++; 47 total_counts++; 48 } 49 else if(subject == "math" || subject == "数学") 50 { 51 math_scores += score; 52 math_counts++; 53 total_counts++; 54 } 55 else 56 { 57 cout << "this is no the subect:" << subject << endl; 58 } 59 } 60 61 Student::~Student() 62 { 63 total_counts--; 64 65 if(subject == "chinese" || subject == "语文") 66 { 67 chinese_counts--; 68 } 69 if(subject == "math" || subject == "数学") 70 { 71 math_counts--; 72 } 73 } 74 75 float Student::aveScores(string subject) 76 { 77 float ave_score = 0; 78 79 if(chinese_counts > 0 && subject == "chinese" || subject == "语文") 80 { 81 ave_score = (chinese_scores / chinese_counts); 82 //cout << subject << "\t" << chinese_counts << "\t" << chinese_scores << endl; 83 } 84 else if(math_counts > 0 && subject == "math" || subject == "数学") 85 { 86 ave_score = (math_scores / math_counts); 87 //cout << subject << "\t" <<math_counts << "\t" << math_scores << endl; 88 } 89 90 return ave_score; 91 } 92 93 void Student::printStudentInfo() 94 { 95 cout << name << "\t" << gender << "\t" << score << "\t" << subject << endl; 96 } 97 98 void Student::printAveScores() 99 { 100 cout <<subject << " average score: " << aveScores(subject) << endl; 101 } 102 103 void function() 104 { 105 const int SIZE = 5; 106 Student stu[SIZE] = 107 { 108 Student("10001", "male", 92, "语文"), 109 Student("10002", "male", 91, "数学"), 110 Student("10003", "male", 91, "数学"), 111 Student("10004", "male", 93, "语文"), 112 Student("10005", "male", 92, "语文"), 113 }; 114 115 for(int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) 116 { 117 stu[i].printStudentInfo(); 118 } 119 120 stu[0].printAveScores(); 121 stu[1].printAveScores(); 122 123 cout << "语文" << " average score: " << Student::aveScores("语文") << endl; 124 cout << "数学" << " average score: " << Student::aveScores("数学") << endl; 125 126 cout << "总人数: " << Student::total_counts << endl; 127 } 128 129 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 130 { 131 function(); 132 133 cout << "语文课人数: " << Student::chinese_counts << endl; 134 cout << "数学课人数: " << Student::math_counts << endl; 135 cout << "总人数: " << Student::total_counts << endl; 136 137 return 0; 138 }

1 /** 2 * 案例:有一场篮球赛,红队与蓝队各有5名队员,统计各个球队的得分情况(总分、平均分),并将获胜球队的球员信息输出 3 */ 4 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <string> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 class Player 11 { 12 public: 13 int number; // 编号 14 string gender; // 性别 15 int age; // 年龄 16 float score; // 个人分数 17 18 public: 19 Player(int number = 0, int age = 0, float score = 0, string gender = "male") 20 { 21 this->number = number; 22 this->age = age; 23 this->score = score; 24 this->gender = gender; 25 } 26 }; 27 28 class Team 29 { 30 private: 31 string name; // 球队名称 32 int sum; // 球队总分 33 34 //static int COUNT; // 球队人数 35 static const int COUNT = 5; // 球队人数 36 Player player[COUNT]; // 球队队员信息 37 public: 38 Team(string name) 39 { 40 this->name = name; 41 for(int i = 0; i < Team::COUNT; i++) 42 { 43 player[i] = Player(10001 + i, 20 + i, 0); 44 } 45 } 46 string getName() 47 { 48 return name; 49 } 50 static int playersCount() 51 { 52 return COUNT; 53 } 54 int totalScore() 55 { 56 sum = 0; 57 for(int i = 0; i < Team::COUNT; i++) 58 { 59 sum += player[i].score; 60 } 61 62 return sum; 63 } 64 float aveScore() 65 { 66 if(sum == 0) 67 { 68 totalScore(); 69 } 70 return (sum/Team::COUNT); 71 } 72 bool setPlayer(int index, int num, int age, float score, bool isMale = true) 73 { 74 bool ret = true; 75 76 if(index >= 0 && index < Team::COUNT) 77 { 78 player[index].number = num; 79 player[index].age = age; 80 player[index].score = score; 81 isMale == true ? player[index].gender = "male" : player[index].gender = "female"; 82 } 83 else 84 { 85 cout << "the index of array is out of range, the max index should less than " << Team::COUNT << endl; 86 ret = false; 87 } 88 89 return ret; 90 } 91 bool PK(Team &team) 92 { 93 int ret = this->sum > team.sum; 94 95 if(ret) 96 { 97 cout << this->name + " 获胜" << endl; 98 } 99 else 100 { 101 cout << team.name + " 获胜" << endl; 102 } 103 104 return ret; 105 } 106 void print() 107 { 108 cout << "Team Name:" << name << endl; 109 for(int i = 0; i < Team::COUNT; i++) 110 { 111 cout << player[i].number << "\t" << player[i].gender << "\t" << player[i].age << "\t" << player[i].score << endl; 112 } 113 cout << name << " get total score:" << totalScore() << endl; 114 cout << name << " get average score:" << aveScore() << endl; 115 } 116 117 118 }; 119 //int Team::COUNT = 5; // 初始化每支球队共有5名球员 120 121 122 123 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 124 { 125 Team t1("Red Team"); 126 127 t1.setPlayer(0, 10001, 22, 91); 128 t1.setPlayer(1, 10003, 32, 93); 129 t1.setPlayer(2, 10005, 23, 94); 130 t1.setPlayer(3, 10007, 25, 95, false); 131 t1.setPlayer(4, 10009, 28, 88); 132 // t1.print(); 133 // cout << t1.getName() << " get total score:" << t1.totalScore() << endl; 134 // cout << t1.getName() << " get average score:" << t1.aveScore() << endl; 135 136 cout << endl; 137 138 Team t2("Blue Team"); 139 140 t2.setPlayer(0, 20001, 22, 81); 141 t2.setPlayer(1, 20003, 32, 83); 142 t2.setPlayer(2, 20005, 23, 84); 143 t2.setPlayer(3, 20007, 25, 85); 144 t2.setPlayer(4, 20009, 28, 88); 145 // t2.print(); 146 // cout << t2.getName() << " get total score:" << t2.totalScore() << endl; 147 // cout << t2.getName() << " get average score:" << t2.aveScore() << endl; 148 149 if( t1.PK(t2) ) 150 { 151 t1.print(); 152 } 153 else 154 { 155 t2.print(); 156 } 157 158 return 0; 159 }


