Spring深入浅出(一),基本概念,HelloWorld实例
什么是Spring
Spring是一个分层的Java SE/EE full-stack(一站式)轻重级开源框架,它以IoC(Inversion of Control,控制反转)和AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程)为内核,使用基本JavaBean来完成以前只能由EJB完成的工作,取代了EJB臃肿、低效的开发模式。
Spring框架优点
- 非侵入式设计
- 方便解耦、简化开发
- 支持AOP
- 支持声明式事务式处理
- 方便集成各种优秀框架
- 降低Java EE API的使用难度
Spring体系结构
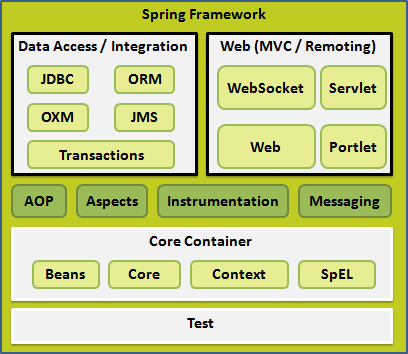
- Core Container(核心容器),包括Beans模块、Core核心模块、Context-support模块、SpEL模块
- Data Acess/Integration(数据访问/集成),包括JDBC模块、ORM模块、OXM模块、JMS模块、Transactions模块
- Web,包括WebSocket模块、Servlet模块、Web模块、Portlet模块
- 其他模块,包括AOP模块、Apsects模块、Instrumentation模块、Messaging模块、Test模块
一、假设你已经搭建好Spring开发环境,包括:
1. Java 开发工具包,参考:Java SE Downloads
2. Apache Commons Logging API,参考: http://commons.apache.org/logging/
3. MyEclipse2020,参考:https://www.myeclipsecn.com/download/
4. Spring 5.2.3版本,参考:https://repo.spring.io/libs-release-local/org/springframework/spring/5.2.3.RELEASE/spring-5.2.3.RELEASE-dist.zip
并且,至少将下列文件引用到类库(MyEclipse中,Build Path -> Configure Build Path):
- spring-core-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar 包含Spring框架基本的核心工具类
- spring-beans-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar 所有应用都要用到的Jar包,它包含访问配置文件、创建和管理Bean以及进行IoC或者DI操作相关的所有类
- spring-context-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar 提供在基础IoC功能上的扩展服务
- spring-expression-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar 定义Spring的表达式语言
- commons-logging-1.2.jar Spring依赖的第三方Jar包,记录日志用
二、创建HelloWorld程序
1. 创建实体Bean
package com.clzhang.spring.demo; public class HelloWorld { private String message; public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } public void getMessage() { System.out.println("The Message is:" + message); } }
2. 创建调用程序
package com.clzhang.spring.demo; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); HelloWorld objA = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld"); objA.getMessage(); } }
3. 创建配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.clzhang.spring.demo.HelloWorld"> <property name="message" value="Hello World!" /> </bean> </beans>
4. 运行程序MainApp
The Message is:Hello World!
三、解读
IoC 容器是 Spring 的核心,也可以称为 Spring 容器。Spring 提供 2 种不同类型的 IoC 容器,即 BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext 容器。ApplicationContext 继承了 BeanFactory 接口,由 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext 接口定义,对象在启动容器时加载。
BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext 都是通过 XML 配置文件加载 Bean 的。二者的主要区别在于,如果 Bean 的某一个属性没有注入,使用 BeanFacotry 加载后,第一次调用 getBean() 方法时会抛出异常,而 ApplicationContext 则会在初始化时自检,这样有利于检查所依赖的属性是否注入。
在实际开发中,通常都选择使用 ApplicationContext,只有在系统资源较少时,才考虑使用 BeanFactory。
ApplicationContext 接口有两个常用的实现类,具体如下:
1)ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
该类从类路径 ClassPath 中寻找指定的 XML 配置文件,并完成 ApplicationContext 的实例化工作,具体如下所示:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation);
2)FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
该类从指定的文件系统路径中寻找指定的 XML 配置文件,并完成 ApplicationContext 的实例化工作,具体如下所示:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation);
它与 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的区别是:在读取 Spring 的配置文件时,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 不会从类路径中读取配置文件,而是通过参数指定配置文件的位置。即 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 可以获取类路径之外的资源,如“F:/workspaces/Beans.xml”。这种采用绝对路径的方式,会导致程序的灵活性变差,所以这个方法一般不推荐使用。
本文参考:
http://c.biancheng.net/spring/ioc.html
https://www.w3cschool.cn/wkspring/dgte1ica.html


