Uva--1331(区间动规,计算几何)
2014-08-27 22:17:30
| Root | |
1331 - Minimax TriangulationTime limit: 3.000 seconds |
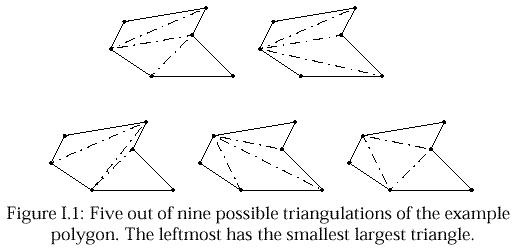
Triangulation of surfaces has applications in the Finite Element Method of solid mechanics. The objective is to estimate the stress and strain on complex objects by partitioning them into small simple objects which are considered incompressible. It is convenient to approximate a plane surface with a simple polygon, i.e., a piecewise-linear, closed curve in the plane on m distinct vertices, which does not intersect itself. A chord is a line segment between two non-adjacent vertices of the polygon which lies entirely inside the polygon, so in particular, the endpoints of the chord are the only points of the chord that touch the boundary of the polygon. A triangulation of the polygon, is any choice of m -3 chords, such that the polygon is divided into triangles. In a triangulation, no two of the chosen chords intersect each other, except at endpoints, and all of the remaining (unchosen) chords cross at least one of the chosen chords. Fortunately, finding an arbitrary triangulation is a fairly easy task, but what if you were asked to find the best triangulation according to some measure?
Input
On the first line of the input is a single positive integer n, telling the number of test scenarios to follow. Each scenario begins with a line containing one positive integer 2 < m < 50, being the number of vertices of the simple polygon. The following m lines contain the vertices of the polygon in the order they appear along the border, going either clockwise or counter clockwise, starting at an arbitrary vertex. Each vertex is described by a pair of integers x y obeying 0 ≤ x ≤ 10 000 and 0 ≤ y ≤ 10 000.
Output
For each scenario, output one line containing the area of the largest triangle in the triangu-lation of the polygon which has the smallest largest triangle. The area should be presented with one fractional decimal digit.
Sample Input
1 6 7 0 6 2 9 5 3 5 0 3 1 1
Sample Output
9.0
思路:这题结合了动规和计算几何,挺好的题。首先要用到的动规知识是小白书里的“最优三角剖分”,设dp[i][j]为子多边形i,i+1,...,j-1,j(i<j)的最优解(即最小的最大三角形面积),状态转移方程为:dp[i][j] = min{dp[i][j],max(S[i][j][k],dp[i][k],dp[k][j])} (i < k < j),其中S[i][j][k]为三角型i-j-k的面积,S是需要预处理的,在处理过程中:通过三角形三个顶点的坐标求三角形面积是用叉积来做。
这题唯一的 trick 在于:在DP过程中,如果三角形i-j-k中还有其他顶点,则不能剖分,仔细思考,所以在选取了一个三角形i-j-k后,要对所有顶点检索,看看这些点是否在这个三角形内,方法是判断 S[i][j][k] ?= S[i][j][p] + S[i][k][p] + S[j][k][p] (1 <= p <= ,p != i,p != j,p != k)。
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: 1331.cpp 3 > Author: Nature 4 > Mail: 564374850@qq.com 5 > Created Time: Wed 27 Aug 2014 07:55:10 PM CST 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <cstdio> 9 #include <cstring> 10 #include <cstdlib> 11 #include <cmath> 12 #include <iostream> 13 #include <algorithm> 14 using namespace std; 15 const int INF = 1 << 30; 16 const double eps = 1e-8; 17 18 int Case; 19 int m; 20 double x[55]; 21 double y[55]; 22 double s[55][55][55]; 23 double dp[55][55]; 24 25 double cross(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2){ 26 return x1 * y2 - x2 * y1; 27 } 28 29 void Cal_area(){ 30 for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) 31 for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) 32 for(int k = 1; k <= m; ++k) 33 s[i][j][k] = fabs(cross(x[i],y[i],x[j],y[j]) + cross(x[j],y[j],x[k],y[k]) - 34 cross(x[i],y[i],x[k],y[k])) / 2.0; 35 } 36 37 bool Judge(int a,int b,int c){ 38 double area = s[a][b][c]; 39 double tmp; 40 for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){ 41 if(i == a || i == b || i == c) continue; 42 tmp = s[a][b][i] + s[a][c][i] + s[b][c][i]; 43 if(fabs(area - tmp) < eps) 44 return false; 45 } 46 return true; 47 } 48 49 int main(){ 50 scanf("%d",&Case); 51 while(Case--){ 52 scanf("%d",&m); 53 for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) 54 scanf("%lf%lf",&x[i],&y[i]); 55 Cal_area(); 56 memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); 57 for(int len = 2; len < m; ++len){ 58 for(int i = 1,j = i + len; i <= m - len; ++i,++j){ 59 dp[i][j] = INF; 60 for(int k = i + 1; k < j; ++k){ 61 if(!Judge(i,j,k)) continue; 62 dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j],max(s[i][k][j],max(dp[i][k],dp[k][j]))); 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 printf("%.1lf\n",dp[1][m]); 67 } 68 return 0; 69 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号