Android之Surface绘制原理
一、Surface的Buffer是从哪里来的?
源码:frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
View触发绘制是通过requestLayout()函数或者setLayoutParms()函数:
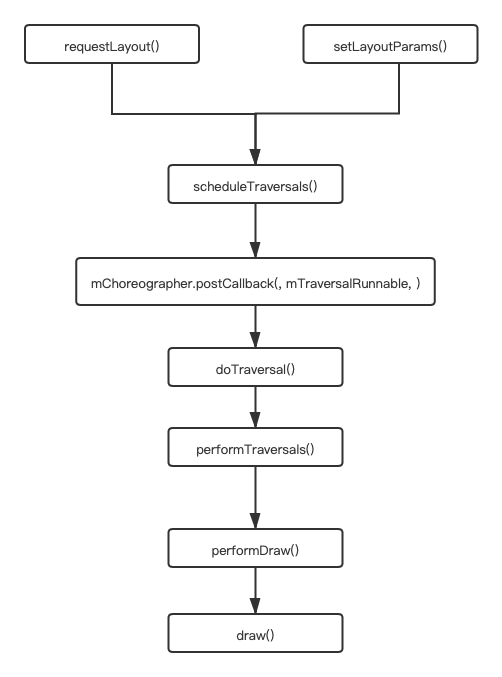
performTravsersals()函数实现:
private void performTraversals() { …… performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight); performDraw(); …… }
perfomrDraw()函数调用draw()函数开始绘制:
private void performDraw() { …… boolean canUseAsync = draw(fullRedrawNeeded); …… }
ViewRootImpl.draw()函数实现:
private boolean draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) { Surface surface = mSurface; …… if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset, scalingRequired, dirty, surfaceInsets)) { return false; } …… return useAsyncReport; }
drawSoftware()软件绘制,默认是软件绘制。
drawSoftware()函数软件绘制流程:
private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff, boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty, Rect surfaceInsets) { // Draw with software renderer. final Canvas canvas; …… canvas = mSurface.lockCanvas(dirty); …… mView.draw(canvas); …… surface.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas); }
获取:通过lockCanvas函数获取Canvas对象,
绘制:再通过mView.draw(canvas)函数向在canvas上绘制,
提交:最后通过surface.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas)函数提交Canvas。
通过lockCanvas()函数获取Canvas对象,lockCanvas()函数如何获取Canvas对象。
lockCanvas()函数实现:
/** * Gets a {@link Canvas} for drawing into this surface. * * After drawing into the provided {@link Canvas}, the caller must * invoke {@link #unlockCanvasAndPost} to post the new contents to the surface. * * @param inOutDirty A rectangle that represents the dirty region that the caller wants * to redraw. This function may choose to expand the dirty rectangle if for example * the surface has been resized or if the previous contents of the surface were * not available. The caller must redraw the entire dirty region as represented * by the contents of the inOutDirty rectangle upon return from this function. * The caller may also pass <code>null</code> instead, in the case where the * entire surface should be redrawn. * @return A canvas for drawing into the surface. * * @throws IllegalArgumentException If the inOutDirty rectangle is not valid. * @throws OutOfResourcesException If the canvas cannot be locked. */ public Canvas lockCanvas(Rect inOutDirty) throws Surface.OutOfResourcesException, IllegalArgumentException { synchronized (mLock) { checkNotReleasedLocked(); if (mLockedObject != 0) { // Ideally, nativeLockCanvas() would throw in this situation and prevent the // double-lock, but that won't happen if mNativeObject was updated. We can't // abandon the old mLockedObject because it might still be in use, so instead // we just refuse to re-lock the Surface. throw new IllegalArgumentException("Surface was already locked"); } mLockedObject = nativeLockCanvas(mNativeObject, mCanvas, inOutDirty); return mCanvas; } }
通过Native层android_view_Surface.cpp的nativeLockCanvas(mNativeObject, mCanvas, inOutDirty)函数获取,mNativeOjbect参数是Java层的Surface在Native层对应的Surface对象的指针。mCanvas是Surface的变量,在lockCanvas()函数调用时mCanvas是空的。
在调用nativeLockCanvas()函数后mCanvas就有值了,最后返回mCanvas对象。
static jlong nativeLockCanvas(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jlong nativeObject, jobject canvasObj, jobject dirtyRectObj) { // (1) sp<Surface> surface(reinterpret_cast<Surface *>(nativeObject)); …… // (2) ANativeWindow_Buffer buffer; status_t err = surface->lock(&buffer, dirtyRectPtr); …… // (3) graphics::Canvas canvas(env, canvasObj); canvas.setBuffer(&buffer, static_cast<int32_t>(surface->getBuffersDataSpace())); …… // (4) // Create another reference to the surface and return it. This reference // should be passed to nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost in place of mNativeObject, // because the latter could be replaced while the surface is locked. sp<Surface> lockedSurface(surface); lockedSurface->incStrong(&sRefBaseOwner); return (jlong) lockedSurface.get(); }
(1) 获取Native层的Surface对象。
(2) 获取Native层的Surface对象的Buffer。
(3) 将Buffer设置给Canvas,这里Canvas就有一个Buffer了。在每次都申请一个新的Buffer给Canvas对象。
(4) 向Java层返回Native的Surface对象,这里返回的是一个Long型数据,这个Long型数据是Surface指针。
获取Buffer实现,surface -> lock(&buffer, ),这里传入Buffer地址:
源码:frameworks/native/libs/gui/Surface.cpp
status_t Surface::lock(ANativeWindow_Buffer* outBuffer, ARect* inOutDirtyBounds) { …… // (1) ANativeWindowBuffer* out; status_t err = dequeueBuffer(&out, &fenceFd); …… // (2) sp<GraphicBuffer> backBuffer(GraphicBuffer::getSelf(out)); …… // (3) void* vaddr; status_t res = backBuffer->lockAsync(GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_READ_OFTEN | GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_WRITE_OFTEN, newDirtyRegion.bounds(), &vaddr, fenceFd); …… // (4) mLockedBuffer = backBuffer; // (5) outBuffer->bits = vaddr; …… }
(1) 获取dequeueBuffer()函数在SurfaceFlinger的Buffer队列中获取Buffer。
(2) 创建GraphicBuffer对象backBuffer。在SharedBufferStack中有双缓冲机制,分别为FontBuffer和BackBuffer。
-
- FontBuffer:代表当前将显示在屏幕的Buffer数据。属于前台Buffer。
- BackBuffer:代表绘制的Buffer数据,是准备渲染的数据Buffer。属于后台Buffer。
(3) 锁定Buffer,并将Buffer地址返回,将返回的Buffer地址给Canvas的Buffer。
(4) 切换Buffer,将后台BackBuffer切换到前台,交给mLockedBuffer。FontBuffer的变量就是mLockedBuffer。
(5) 将vaddr赋值给outBuffer->bits,bits最后赋值给Canvas的Buffer,就是BkBitmap,作为Canvas的缓冲区。
dequeteBuffer()是如何获取Buffer的,dequeteBuffer()函数实现:
int Surface::dequeueBuffer(android_native_buffer_t** buffer, int* fenceFd) { …… int buf = -1; // (1) status_t result = mGraphicBufferProducer->dequeueBuffer(&buf, &fence, reqWidth, reqHeight, reqFormat, reqUsage, &mBufferAge, enableFrameTimestamps ? &frameTimestamps : nullptr); …… // (2) sp<GraphicBuffer>& gbuf(mSlots[buf].buffer); …… // (3) if ((result & IGraphicBufferProducer::BUFFER_NEEDS_REALLOCATION) || gbuf == nullptr) { if (mReportRemovedBuffers && (gbuf != nullptr)) { mRemovedBuffers.push_back(gbuf); } result = mGraphicBufferProducer->requestBuffer(buf, &gbuf); if (result != NO_ERROR) { ALOGE("dequeueBuffer: IGraphicBufferProducer::requestBuffer failed: %d", result); mGraphicBufferProducer->cancelBuffer(buf, fence); return result; } } …… // (4) *buffer = gbuf.get(); }
(1) 通过mGaphicBufferProducer->dequeteBuffer()函数在远端的Buffer slots中获得一个空闲的Buffer,返回远端Buffer地址指针。
(2) 通过gbp从本地Buffer Slots里获取Buffer,在(1)中从远端,在(2)中从本地,这里涉及远端Buffer queue与本地Buffer queue同步问题。
(3) 负责本地Buffer与远端Buffer同步,远端返回的Buffer的result是BUFFER_NEEDS_REALLOCATION或者本地的gbp是null,通过gbp的requestBuffer()获取新的远端Buffer指针地址。mGaphicBufferProducer->requestBuffer()函数。
(4) 获取Buffer。
二、Surface的Buffer是如何提交的?
通过surface.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas)向远端提交更新的Buffer,unlockCanvasAndPost()函数实现:
/** * Posts the new contents of the {@link Canvas} to the surface and * releases the {@link Canvas}. * * @param canvas The canvas previously obtained from {@link #lockCanvas}. */ public void unlockCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas) { synchronized (mLock) { unlockSwCanvasAndPost(canvas); } } private void unlockSwCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas) { try { nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost(mLockedObject, canvas); } finally { nativeRelease(mLockedObject); mLockedObject = 0; } }
最后调用到Native层的nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost(mLockedObject, canvas)。
Native层,nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost()函数实现:
static void nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jlong nativeObject, jobject canvasObj) { // (1) sp<Surface> surface(reinterpret_cast<Surface *>(nativeObject)); // (2) // detach the canvas from the surface graphics::Canvas canvas(env, canvasObj); canvas.setBuffer(nullptr, ADATASPACE_UNKNOWN); // (3) // unlock surface status_t err = surface->unlockAndPost(); }
(1) 获取对应Java层的Native层的Surface对象。
(2) 获取对应Java层的Native层的Canvas对象。
(3) 将本地Buffer更新到远端的Buffer queue中。
Native层更新远端Buffer queue,surface->unlockAndPost()函数实现:
源码:frameworks/native/libs/gui/Surface.cpp
status_t Surface::unlockAndPost() { if (mLockedBuffer == nullptr) { ALOGE("Surface::unlockAndPost failed, no locked buffer"); return INVALID_OPERATION; } int fd = -1; status_t err = mLockedBuffer->unlockAsync(&fd); ALOGE_IF(err, "failed unlocking buffer (%p)", mLockedBuffer->handle); err = queueBuffer(mLockedBuffer.get(), fd); ALOGE_IF(err, "queueBuffer (handle=%p) failed (%s)", mLockedBuffer->handle, strerror(-err)); mPostedBuffer = mLockedBuffer; mLockedBuffer = nullptr; return err; }
通过函数queueBuffer(mLockedBuffer.get(), )函数实现更新:
int Surface::queueBuffer(android_native_buffer_t* buffer, int fenceFd) { …… // (1) int i = getSlotFromBufferLocked(buffer); …… // (2) status_t err = mGraphicBufferProducer->queueBuffer(i, input, &output); …… return err; }
(1) 获取Buffer的index。
(2) 通过mGraphicBufferProducer->queueBuffer(i, )函数,将本地的Buffer同步到远端Buffer queue中。
三、总结




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号