C++线性表之数组实现
线性表-数组描述
1. 线性表定义
1.1 文字描述
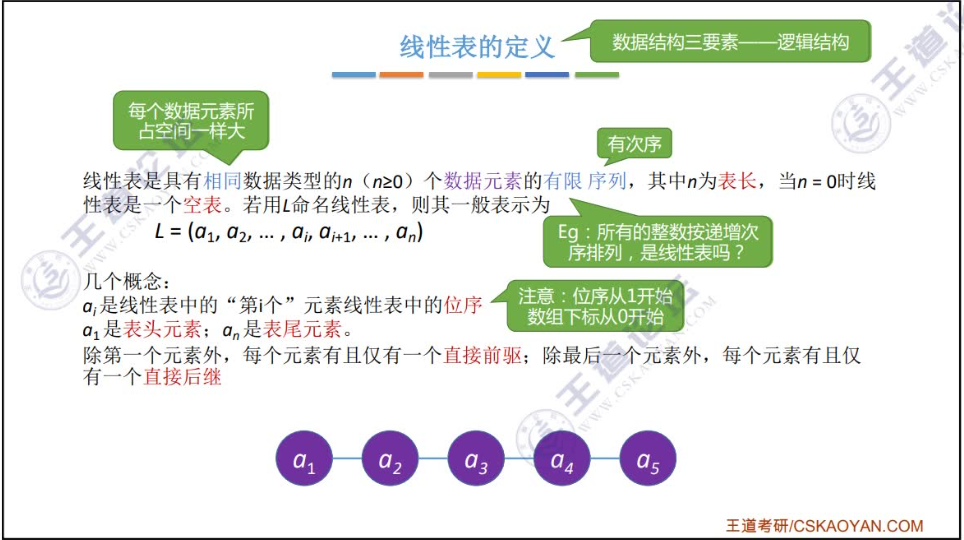
1.2 抽象数据结构(ADT)-linearList -- 数据结构三要素(逻辑结构、物理结构和数据的运算)
抽象数据类型 linearList{
实例:
有限个元素的有序集合; // 一般使用数组
操作:
empty();// 若表空,返回true,否则返回false
size(); // 返回线性表的大小(表中元素的个数)
get(index); // 返回线性表中索引为index的元素
indexOf(x); // 返回线性表中第一次出现x的索引。若x不存在,则返回-1
erase(index); // 删除索引为index的元素,索引大于index的元素其索引-1
insert(index,x); // 把x插入线性表中索引为index的位置上,索引大于等于index的元素其索引+1
output();// 输出表中元素
}
2. 抽象类 - linearList(ADT的C++代码描述)
C++使用抽象类来描述线性表的ADT
class linearList{ public: // 析构函数都是虚函数 virtual ~linearList(){}; // 不修改线性表的方法声明为常函数 virtual bool empty() const = 0; virtual int size() const = 0; virtual T& get(int index) const = 0; // 形参要加const,保护数据不被修改 virtual int indexOf(const T& theElement) = 0; virtual T earse(int theIndex) = 0; virtual T insert(int index,const T& theElement) = 0; // 把线性表插入输出流out中 virtual void output(ostream& out) = 0; // 末尾追加元素进线性表 virtual void empty_push(const T& theElement) = 0; };
3. 线性表的数组实现 -- 自定义
1.1 定义地址映射函数 --- 这个思想必须有,地址都是我们定义映射函数得到的
1.描述:
线性表中第i个元素存储在数组的哪个位置?2.地址映射公式
location(i) = i; --- 我们线性表使用这个地址映射公式 // 第i个线性表元素放到数组的第i个下标上 location(i) = arrayLength-i-1; --- 这个线性表也可以使用,但是一般不用// 从数组的右端一次存储线性表左边->右边的元素 location(i) = (location(0)+t)%arrayLength; --- 适合循环队列的地址映射函数 // 第1个线性表的元素放到数组的第t个位置,如果i+t>=arrayLength,则之后的线性表元素从0开始插入 // 1->t // 2->t+1 // ...i+t>=arrayLenth // i->0 // i+1->1 // ... 插入到t-1位置后,数组就满了
2.2 c++中迭代器iterator的结构
template<typename _Category, typename _Tp, typename _Distance = ptrdiff_t,
typename _Pointer = _Tp*, typename _Reference = _Tp&>
struct iterator
{
/// One of the @link iterator_tags tag types@endlink.
typedef _Category iterator_category;
/// The type "pointed to" by the iterator.
typedef _Tp value_type;
/// Distance between iterators is represented as this type.
typedef _Distance difference_type;
/// This type represents a pointer-to-value_type.
typedef _Pointer pointer;
/// This type represents a reference-to-value_type.
typedef _Reference reference;
};
C++迭代器
为了简化迭代器的开发和基于迭代器的通用算法的分类,C++的STL定义了5种迭代器,输入、输出、向前、双向和随机访问。 所有的迭代器都具备操作符==,!=,*的重载。
2.3 arrayList的类的定义 -- 带迭代器实现
template<class T>
class arrayList:public linearList<T>{
public:
arrayList(int inintialCapacity = 10);
// 复制构造函数
arrayList(const arrayList<T>&);
~arrayList(){delete []element;cout<<"arrayList destructor";}
// ADT方法
bool empty() const {return listSize == 0;}
int size() const {return listSize;}
T& get(int index) const ;
int indexOf(const T &theElement) const ;
void erase(int index);
void insert(int theIndex,const T& theElement);
void output(ostream&);
void empty_push(const T &theElement) override;
// 定义访问元素的迭代器 -- 迭代器实现,读者要重点看一下
// 核心:*重载,构造函数定义
class iterator{
public:
// 用c++的typedef语句实现双向迭代器
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef T* pointer;
typedef T& reference;
// 构造函数
iterator(T* thePosition = 0){position = thePosition;};
// 迭代器必须有的重载==,!=,*
// 解引用操作符 --- 迭代器访问数组元素,靠的就是"*"运算符的重载
T& operator*()const {return *position;}
T* operator->()const {return &*position;}
//==,!=运算符重载
bool operator==(const iterator right) const {return position == right.position;}
bool operator!=(const iterator right) const {return position != right.position;}
//迭代器可选重载
//++,--运算符重载
iterator& operator++(){
position++;
return *this;
}
iterator& operator++(int){
iterator it = *this;
position++;
return it;
}
iterator& operator--(){
--position;
return *this;
}
iterator& operator--(int){
iterator it = *this;
--position;
return it;
}
protected:
// 指向表中元素的指针
T* position;
};
iterator begin() const{return iterator(element);}
iterator end() const {return iterator(element+listSize);}
// 友元函数重载<<,输出线性表
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& a,const arrayList<T>& t);
protected:
// 存储线性元素的一维动态数组
T* element;
// 一维数组的长度
int arrayLenth;
// 线性表元素的个数
int listSize;
// 检查下标
void checkIndex(int theIndex) const ;
// 扩容函数
void changeLength(T*& a,int oldLength,int newLength);
};
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(int inintialCapacity) {
if (inintialCapacity < 1){
ostringstream s;
s<<"Initial capacity = "<<inintialCapacity<<"Must be > 0";
throw "illegalParameterValue"+s.str();
}
arrayLenth = inintialCapacity;
listSize = 0;
element = new T[arrayLenth];
}
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(const arrayList<T> & theList) {
listSize = theList.listSize;
arrayLenth = theList.arrayLenth;
element = new T[arrayLenth];
// 把theList.element中元素复制给element
copy(theList.element,theList.element + listSize,element);
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const {
// 检查下标是否合法
if (theIndex <0 || theIndex >= arrayLenth){
ostringstream s;
s<<"index = "<<theIndex<<" size = "<<listSize;
throw "illegaParameter"+s.str();
}
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::changeLength(T *&a, int oldLength, int newLength) {
if (newLength < 0)
throw "illegal newLength";
T* temp = new T[newLength];
int number = min(oldLength,newLength);
copy(a,a+number,temp);
delete [] a;
a = temp;
}
template<class T>
T& arrayList<T>::get(int index) const {
// 元素不存在则抛出异常
checkIndex(index);
return element[index];
}
template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::indexOf(const T &theElement) const {
// 返回元素第一次出现的索引,没找到返回-1
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; ++i) {
if (element[i] == theElement)
return i;
}
return index;
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::erase(int index) {
// 检查下标是否合法
checkIndex(index);
// index后面的元素向前移动一个单位
copy(element+index+1,element+listSize,element+index);
// 调用析构函数
element[--listSize].~T();
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T &theElement) {
// 插入位置不合法
if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex > listSize){
ostringstream s;
s<<"Index = "<<theIndex<<" size = "<<listSize;
throw "illegalParameter"+s.str();
}
// 判断数组是否满了
if (listSize == arrayLenth){
changeLength(element,arrayLenth,arrayLenth<<1);
arrayLenth == arrayLenth<<1;
}
copy_backward(element+theIndex,element+listSize,element+listSize+1);
element[theIndex] = theElement;
listSize++;
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::output(ostream &out) {
// 把线性表插入到输出流中
// ostream_iterator头文件 iterator
copy(element,element+listSize,ostream_iterator<T>(cout," "));
}
template<class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const linearList<T>*& t){
t->ouput(out);
return out;
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::empty_push(const T &theElement) {
// 判断线性表是否满了
if (listSize == arrayLenth){
changeLength(element,arrayLenth,arrayLenth<<1);
arrayLenth = arrayLenth<<1;
}
element[listSize] = theElement;
listSize++;
}
4.线性表基于数组实现vector -- STL标准库自带的
特点:
1.vector是一个可变大小数组的容器
2.vector采用连续存储空间来进行元素存储
3.vector使用动态分配数组来存储它的元素
4.支持下标随机访问元素
方法:
增(insert,push_back,empty_back)删(erase,pop_back,clear)改(下标,assign)查(下标,迭代器)
4.0 头文件
#include<vector>
4.1 构造函数
1.vector<T> v; // 空数组
2.vector<T> v(int size,int initialValue); // 长度为size的,每个空间都存储initialValue的数组
3.vector<T> v(const vector& t); // 复制t给v
4.2 末尾追加元素
vector<int> arr;
1.arr.push_back(1); // 追加1
2.arr.emplace_back(2); // 追加2
4.3 插入元素 -- 使用迭代器地址插入元素
iterator insert(iterator it,const T& x):向量中迭代器指向元素前增加一个元素x
iterator insert(iterator it,int n,const T& x):向量中迭代器指向元素前增加n个相同的元素x
iterator insert(iterator it,const_iterator first,const_iterator last):向量中迭代器指向元素前插入另一个相同类型向量的[first,last)间的数据
4.4 删除元素 -- 使用迭代器地址删除元素
iterator erase(iterator it):删除向量中迭代器指向元素
iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last):删除向量中[first,last)中元素
void pop_back():删除向量中最后一个元素
void clear():清空向量中所有元素
4.5 修改元素 -- 使用下标修改
1.使用下标修改
vector<int> a(0,1); a[0] = 12;2.使用assign函数赋值
void assign(int n,const T& x):设置向量中前n个元素的值为x void assign(const_iterator first,const_iterator last):向量中[first,last)中元素设置成当前向量元素 // 例如 arr.assign(a.begin(),a.end()); // 把arr元素变为a中元素,完全复制后,arr就是a的一个副本
4.6 遍历元素
reference at(int pos):返回pos位置元素的引用
// 返回首尾元素的引用
reference front():返回首元素的引用
reference back():返回尾元素的引用
// 返回迭代器地址(指针地址)
iterator begin():返回向量头指针,指向第一个元素
iterator end():返回向量尾指针,指向向量最后一个元素的下一个位置
reverse_iterator rbegin():反向迭代器,指向最后一个元素
reverse_iterator rend():反向迭代器,指向第一个元素之前的位置
4.7 容量函数
int size() const:返回向量中元素的个数
int capacity() const:返回当前向量所能容纳的最大元素值
int max_size() const:返回最大可允许的vector元素数量值
4.8 判空函数
bool empty() const:判断向量是否为空,若为空,则向量中无元素



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现