Java多线程
一、线程的创建
创建一个Thread类,或者一个Thread子类的对象
创建一个实现Runnable接口的类的对象
Thread类
构造方法:
Thread();创建一个线程对象
Thread(String name);创建一个具有指定名称的线程对象
Thread(Runnable target);创建一个基于Runnable接口实现类的线程对象
Thread(Runnable target,String name);创建一个基于Runnable接口实现类,并且具有指定名称的线程对象
常用方法:
void run();线程相关的代码写在该方法中,一般需要重写
void start();启动线程
static void sleep(long m);线程休眠m毫秒
void join();优先执行调用join方法的线程
Runnable接口
只有一个方法run();
Runnable是Java中用以实现线程的接口
任何实现线程功能的类都必须实现该接口
案例1:通过继承Thread类创建线程
public class MyThread extends Thread{ public void run(){ System.out.println(getName()+"该线程正在执行!"); } }
public class ThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //线程何时获得cpu的使用权是随机的 System.out.println("主线程1"); MyThread myThread=new MyThread(); myThread.start();//启动线程,start()方法只能被调用一次 System.out.println("主线程2"); } }
案例2:实现Runnable接口创建线程
为什么要实现Runnable接口?
- Java不支持多继承
- 不打算重写Thread类的其他方法
class PrintRunnable implements Runnable{ int i=1; @Override //run()方法中的代码可以被多个线程共享, public void run() { while(i<=10) System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在运行第"+(i++)+"次"); } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //多个线程处理同一个资源 PrintRunnable pr=new PrintRunnable(); Thread t1=new Thread(pr); t1.start(); Thread t2=new Thread(pr); t2.start(); } }
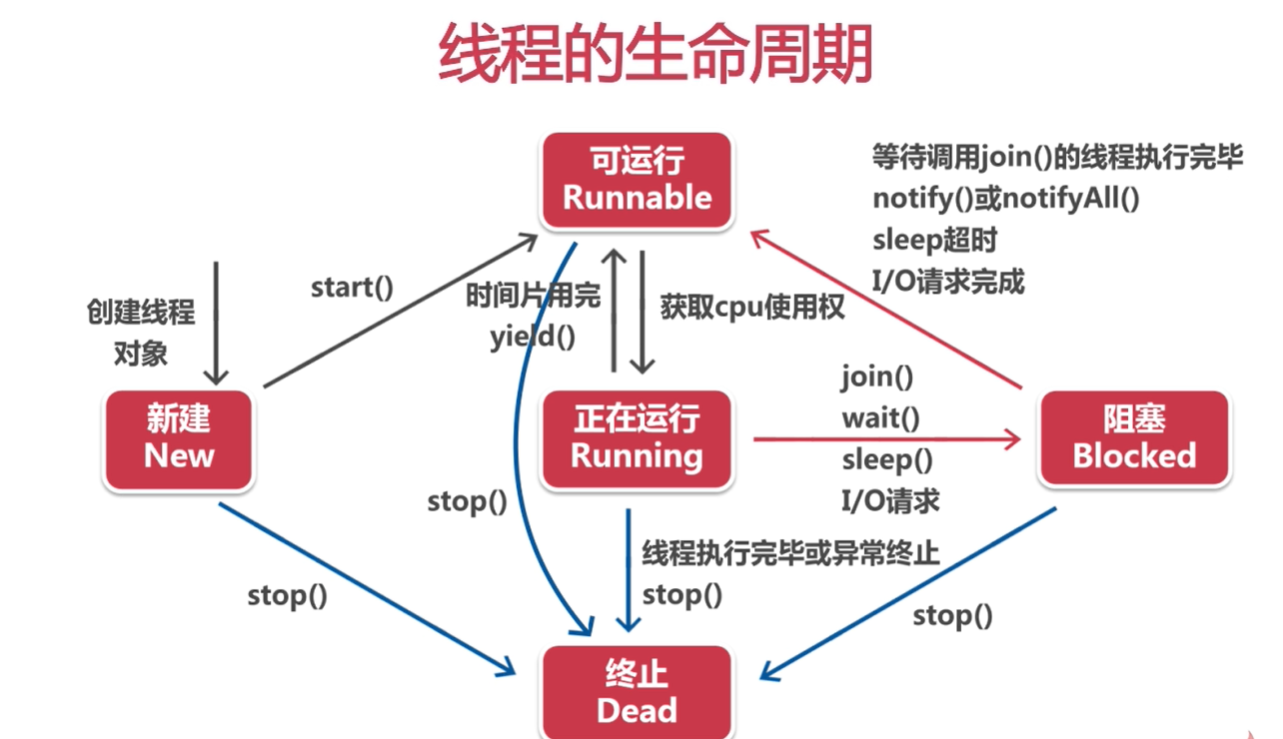
二、线程的状态和生命周期
线程的5个状态
- 新建(New)
- 可运行(Runnable)
- 正在运行(Running)
- 阻塞(Blocked)
- 终止(Dead)
sleep方法的应用
puble static void sleep(long milles)
作用:在指定的毫秒数内让正在执行的线程休眠(暂停执行)
参数为休眠时间,单位是毫秒
public class Letter implements Runnable{ char letter[]=new char[26]; public Letter(){ for(int i=0;i<26;i++){ letter[i]=(char)(97+i); } } @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<26;i++){ System.out.print(letter[i]); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { Letter letter=new Letter(); Thread t=new Thread(letter); t.start(); } }
join方法的应用
public final void join()
作用:等待调用该方法的线程结束后才能执行
public final void join(long millis)
作用:等待该线程终止的时间最长为millis毫秒
class MyThread1 extends Thread{ public void run(){ for(int i=1;i<=500;i++) System.out.println(getName()+"正在执行第"+i+"次"); } } public class JoinDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread1 mt=new MyThread1(); mt.start(); try { mt.join(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for(int i=1;i<=3;i++) System.out.println("主线程运行第"+i+"次"); System.out.println("主线程运行结束"); } }
线程优先级
- Java为线程类提供了10个优先级,数字越大优先级越高
- 优先级可以用整数1-10表示,超出范围会抛出异常
- 主线程默认优先级为5
- 也可以用优先级常量表示线程的优先级
MAX_PRIORITY:线程的最高优先级10
MIN_PRIORITY:线程的最小优先级1
NORM_PRIORITY:线程的默认优先级5
优先级相关的方法:
public int getPrority() 获取线程优先级
public void setPrority() 设置线程优先级
三、线程同步
多线程运行问题:
1.各个线程通过竞争cpu时间而获得运行机会的
2.各线程什么时候得到cpu时间,占用多久,是不可预测的
3.一个正在运行的线程在什么地方被暂停是不确定的
同步
synchronized关键字用在
- 成员方法
- 静态方法
- 语句块
可以确保共享对象在同一时刻只能被一个线程访问
public synchronized void saveAccount(){}
public static synchronized void saveAccount(){}
synchronized(obj){……}
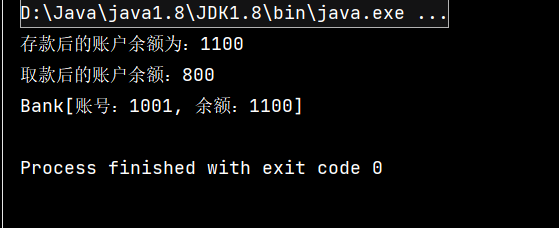
由于线程运行的随机性,可能会出现数据丢失的问题:

public class Bank { private String account;//账号 private int balance;//账户余额 public Bank(String account, int balance) { this.account = account; this.balance = balance; } public String getAccount() { return account; } public void setAccount(String account) { this.account = account; } public int getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(int balance) { this.balance = balance; } @Override public String toString() { return "Bank[账号:"+ account + ", 余额:" + balance + "]"; } //存款 public void saveAccount(){ //可以在不同的位置处添加sleep方法 //获取当前的账号余额 int balance=getBalance(); try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } //修改余额,存100元 balance+=100; //修改账户余额 setBalance(balance); //输出存款后的账户余额 System.out.println("存款后的账户余额为:"+balance); } //取款 public void drawAccount(){ //获取当前的账户余额 int balance=getBalance(); //修改金额,取200 balance=balance-200; try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } //修改账户余额 setBalance(balance); System.out.println("取款后的账户余额:"+balance); } }

//取款 public class DrawAccount implements Runnable{ Bank bank; public DrawAccount(Bank bank){ this.bank=bank; } @Override public void run() { bank.drawAccount(); } }

//存款 public class SaveAccount implements Runnable{ Bank bank; public SaveAccount(Bank bank){ this.bank=bank; } @Override public void run() { bank.saveAccount(); } }

//测试 public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建账户,给定金额1000 Bank bank=new Bank("1001",1000); //创建线程对象 SaveAccount sa=new SaveAccount(bank); DrawAccount da=new DrawAccount(bank); Thread save=new Thread(sa); Thread draw=new Thread(da); save.start(); draw.start(); try { save.join(); draw.join(); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(bank); } }
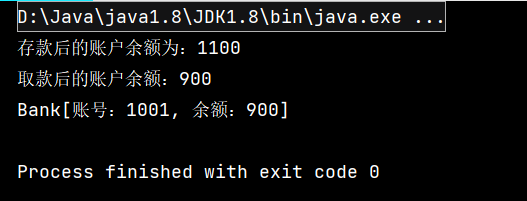
使用synchronized关键字对Bank对象进行锁定后可解决执行被打断这一问题
案例3:synchronized的应用

//存款 public synchronized void saveAccount(){ //获取当前的账号余额 int balance=getBalance(); try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } //修改余额,存100元 balance+=100; //修改账户余额 setBalance(balance); //输出存款后的账户余额 System.out.println("存款后的账户余额为:"+balance); } //取款 public void drawAccount(){ synchronized (this){ //获取当前的账户余额 int balance=getBalance(); //修改金额,取200 balance=balance-200; try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } //修改账户余额 setBalance(balance); System.out.println("取款后的账户余额:"+balance); } }
四、线程间通信
wait()方法:中断方法的执行,使线程等待
notify()方法:唤醒处于等待的某一个线程,使其结束等待
notifyAll()方法:唤醒所有处于等待的线程,使它们结束等待
案例4:天气生产与读取

public class Weather { private int tempeature; private int humidity; private boolean flag=false; public int getTempeature() { return tempeature; } public void setTempeature(int tempeature) { this.tempeature = tempeature; } public int getHumidity() { return humidity; } public void setHumidity(int humidity) { this.humidity = humidity; } public synchronized void generate(){ if(flag){ try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } int t=(int)(Math.random() *40); int h=(int)(Math.random() *100); setTempeature(t); setHumidity(h); System.out.println("生成天气数据[温度:"+t+",湿度:"+h+"]"); flag=true; notifyAll(); } public synchronized void read(){ if(!flag){ try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } int t=getTempeature(); int h=getHumidity(); System.out.println("读取天气数据[温度:"+t+",湿度:"+h+"]"); flag=false; notifyAll(); } }

public class GenerateWeather implements Runnable{ Weather weather; public GenerateWeather(Weather weather){ this.weather=weather; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ weather.generate(); try { Thread.sleep(800); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }

public class ReadWeather implements Runnable{ Weather weather; public ReadWeather(Weather weather){ this.weather=weather; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ weather.read(); try { Thread.sleep(800); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }

public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Weather weather=new Weather(); new Thread(new GenerateWeather(weather)).start(); new Thread(new ReadWeather(weather)).start(); } }







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!