RTL 时间的处理
有关时间的内容应该被拆分为两部分:硬件和库环境 在使用nemu时,硬件部分由nemu充当,在nemu里对时间的处理如下:
首先查看/nemu/src/device/timer.c,
static void rtc_io_handler(uint32_t offset, int len, bool is_write) { assert(offset == 0 || offset == 4); if (!is_write && offset == 4) { uint64_t us = get_time(); rtc_port_base[0] = (uint32_t)us; rtc_port_base[1] = us >> 32; } } #ifndef CONFIG_TARGET_AM //不用看 static void timer_intr() { if (nemu_state.state == NEMU_RUNNING) { extern void dev_raise_intr(); dev_raise_intr(); } } #endif void init_timer() { rtc_port_base = (uint32_t *)new_space(8); #ifdef CONFIG_HAS_PORT_IO add_pio_map ("rtc", CONFIG_RTC_PORT, rtc_port_base, 8, rtc_io_handler); #else add_mmio_map("rtc", CONFIG_RTC_MMIO, rtc_port_base, 8, rtc_io_handler); #endif IFNDEF(CONFIG_TARGET_AM, add_alarm_handle(timer_intr)); }
我们只需要关注 init_timer 和 io_handle 两段,在这里定义了0xa0000048作为时钟的地址,通过add_poi_map注册,为之后运行时的抽象寄存器做准备。为了让各个平台都能正确使用,所以将rtc_port_base拆成了两个uint32数。
rtc_io_handle 这个函数里调用了 get_time() 这个函数,get_time() 位于 utils/timer.c 。这里才是更靠近底层的代码:
static uint64_t boot_time = 0; static uint64_t get_time_internal() { #if defined(CONFIG_TARGET_AM) uint64_t us = io_read(AM_TIMER_UPTIME).us;
#elif defined(CONFIG_TIMER_GETTIMEOFDAY) //默认用gettimeofday struct timeval now; gettimeofday(&now, NULL); uint64_t us = now.tv_sec * 1000000 + now.tv_usec;
#else struct timespec now; clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC_COARSE, &now); uint64_t us = now.tv_sec * 1000000 + now.tv_nsec / 1000; #endif
return us; } uint64_t get_time() { //给src/device/timer.c调用 if (boot_time == 0) boot_time = get_time_internal(); uint64_t now = get_time_internal(); return now - boot_time; }
这里展示了get_time和get_time_interval两个函数,头文件根据情况调用。在POSIX下,gettimeodday这个函数要引用sys/time.h,time.h是C语言的库,二者不同。gettimeofday这个函数会给出一个结构体,包含秒和毫秒两变量,记录从UNIX时间开始到现在的总毫秒数。gettimeofday将时间写入now这个结构体,然后再转换成毫秒数并返回。
get_time的基本思路,就是首先记录一次boot_time作为启动时的时间,然后每次都记录一次当前时间,和boot_time做对比,他们的都是uint64,单位是毫秒。
----------------------------------
然后再看运行时环境这一边。在这一部分,nemu和npc公用一份运行时寄存器和函数定义,但nemu有nemu.h,npc没有,代码也是分开实现,但写法基本是一样的。总的来说,就是在time.c这个函数里,__am_timer_init函数读取一次地址,设置初始时间,然后__am_timer_uptime函数读取地址,并减去初始时间即可。
(注意,读地址的时候先读高位)
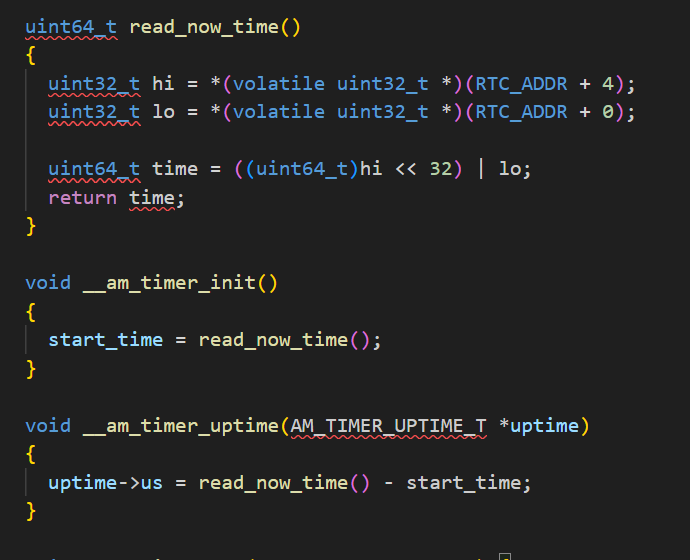
由于npc版代码没有nemu.h,也没有riscv.h,有的宏定义缺失,所以需要手动直接写代码,不要用宏。
-----------------------------
然后再看npc这边,我们可以参考讲义,不需要实现什么太多的内容,只需要实现和nemu的timer.c思路差不多、代码也差不多的函数。在pmem_read里增加条件,申请读时间的两个地址时,就调用npc的时间函数,返回总毫秒数的高低32位即可。注意高位也要右移。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具