Spherical Voxelization
Spherical Voxelization
- 标签: voxelization
- AI 摘要: 文档介绍了球面体素化的过程,包括重要的类和方法,如ConvertToSphericalVoxel和spherical_voxel_optimized,详细解释了参数及其作用。球面体素化通过将点云转换为球面坐标系,利用自适应采样权重来平衡不同纬度区域的点密度,从而有效捕捉几何特征。文中还提到C++绑定的sv.compute函数,负责体素特征的计算与填充,确保在特征计算中考虑邻近体素的信息。
- 最相关链接: https://github.com/CVLAB-Unibo/compass
Spherical Voxelization
参考链接:
- CVLAB-Unibo/compass: Repository containing the code of "Learning to Orient Surfaces by Self-supervised Spherical CNNs". (github.com)
- jonkhler/s2cnn: Spherical CNNs (github.com)
- qq456cvb/PRIN: Pointwise Rotation-Invariant Network (AAAI 2020) (github.com)
代码组成:
ConvertToSphericalVoxel类:最高接口,实例化一个converter类,调用convert转换局部点云
↓
spherical_voxel_optimized方法:在convert中调用,实现转换,先转换到球面坐标系,然后进行体素化
↓
spherical_voxel.compute方法:最终实现体素化,用pybind绑定C++代码最终实现
ConvertToSphericalVoxel
from utils import geometry as ug
class ConvertToSphericalVoxel():
"""
Convert point cloud to spherical voxel [beta = 2 * bandwidth, alfa = 2 * bandwidth, num_radial_division].
Alfa in [0, 2pi], Beta in [0, pi]
"""
def __init__(self, bandwidth, radius_support, num_radial_division, num_points, random_sampling):
self.bandwidth = bandwidth
self.radius_support = radius_support
self.num_radial_division = num_radial_division
self.num_points = num_points
self.random_sampling = random_sampling
def __call__(self, point_cloud):
features, pts_normed = ug.spherical_voxel_optimized(points=point_cloud,
size_bandwidth=self.bandwidth,
size_radial_divisions=self.num_radial_division,
radius_support=self.radius_support,
do_random_sampling=self.random_sampling,
num_random_points=self.num_points)
return features, pts_normed
……
参数解释:
- bandwidth: 球面体素化的带宽,通常用于定义球面信号的分辨率。它决定了角度方向上的采样密度(球面坐标系的\(\beta\),\(\alpha\)),影响了球面信号的分辨率,PRIN, LMVD, Compess等设置为24。
- radius_support: 支持半径,定义了local patch的支持半径,也就是说它确定了从关键点向外延伸的范围内哪些点将被纳入local patch。
- num_radial_division: 表示径向(从关键点向外辐射的方向)上的分割数目。它影响了在径向方向上球面信号的分辨率。
- num_points: 采样点的数量,这个值与local patch的固定点数一致(即1024点),确保输入到转换过程中的点数是一致的,这对于后续处理和模型输入非常重要。
- random_sampling: 控制是否在从点云中选择点时进行随机采样,设置为
True使得在局部区域内的点采样更加多样化,避免由于局部密度过高或过低而导致的信息丢失。随机采样可以让网络更具鲁棒性,适应不同点云的分布。
spherical_voxel_optimized
def spherical_voxel_optimized(points: np.ndarray, size_bandwidth: int, size_radial_divisions: int,
radius_support: float, do_random_sampling: bool, num_random_points: int) \
-> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""Compute spherical voxel using the C++ code.
Compute Spherical Voxel signal as defined in:
Pointwise Rotation-Invariant Network withAdaptive Sampling and 3D Spherical Voxel Convolution.
Yang You, Yujing Lou, Qi Liu, Yu-Wing Tai, Weiming Wang, Lizhuang Ma and Cewu Lu.
AAAI 2020.
:param points: the points to convert.
:param size_bandwidth: alpha and beta bandwidth.
:param size_radial_divisions: the number of bins along radial dimension.
:param radius_support: the radius used to compute the points in the support.
:param do_random_sampling: if true a subset of random points will be used to compute the spherical voxel.
:param num_random_points: the number of points to keep if do_random_sampling is true.
:return: A tuple containing:
The spherical voxel, shape(size_radial_divisions, 2 * size_bandwidth, 2 * size_bandwidth).
The points used to compute the signal normalized according the the farthest point.
"""
if do_random_sampling:
min_limit = 1 if points.shape[0] > 1 else 0
indices_random = np.random.randint(min_limit, points.shape[0], num_random_points)
points = points[indices_random]
pts_norm = np.linalg.norm(points, axis=1)
# Scale points to fit unit sphere
pts_normed = points / pts_norm[:, None]
pts_normed = np.clip(pts_normed, -1, 1)
pts_s2_coord = S2.change_coordinates(pts_normed, p_from='C', p_to='S')
# Convert to spherical voxel indices
pts_s2_coord[:, 0] *= 2 * size_bandwidth / np.pi # [0, pi]
pts_s2_coord[:, 1] *= size_bandwidth / np.pi # raw 2*size_bandwidth/2*np.pi
pts_s2_coord[:, 1][pts_s2_coord[:, 1] < 0] += 2 * size_bandwidth
# Adaptive sampling factor sin{pi*[(1/2,..., 2*size_bandwidth+1/2)/(2*size_bandwidth)]}
# 能更好的聚合点云信息,但是也会导致更多的形变,有得必有失
daas_weights = np.sin(np.pi * (2 * np.arange(2 * size_bandwidth) + 1) / 4 / size_bandwidth).astype(np.float32)
voxel = np.asarray(sv.compute(pts_on_s2=pts_s2_coord,
pts_norm=pts_norm,
size_bandwidth=size_bandwidth,
size_radial_divisions=size_radial_divisions,
radius_support=radius_support,
daas_weights=daas_weights))
pts_normed = points / np.max(pts_norm)
return voxel.astype(np.float32), pts_normed.astype(np.float32)
pts_norm是local patch的点云径向距离,所以local patch输入的时候最好经过对于关键点的中心化操作,不然径向距离会是关于坐标系原点的。S2.change_coordinates用于将点云从笛卡尔坐标系转换成球面坐标系,球面坐标系解释见WIKI,简单来说就是两个坐标,维度角度坐标\beta,和经度角度坐标\alpha- daas_weights是自适应权重:
- 采样密度平衡:在球面坐标系中,由于纬度(通常用
β表示)不同区域的面积差异,不同区域的点密度会有所不同。例如,在球面的极地区域(纬度接近0或π的区域),同样的角度变化可能覆盖的球面面积较小,而在赤道区域,面积较大。为了避免在这些区域中出现过度或不足的采样,自适应采样权重用于平衡不同纬度区域的影响。 - 信息保持:通过在不同的纬度上使用不同的采样权重,可以更精确地保留球面上重要的几何特征,特别是在特定的关键区域。这样可以确保球面信号在高纬度和低纬度区域都能有效地捕捉到有意义的几何信息。
- 采样密度平衡:在球面坐标系中,由于纬度(通常用
sv.compute用于体素转换。
sv.compute
该函数是用pybind绑定的C++方法,文件为spherical_voxel.cc ,代码解释如下:
初始化
const float interval = radius_support / (size_radial_divisions);
std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<float> > > > > grids;
std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<float> > > features;
grids.resize(size_radial_divisions);
features.resize(size_radial_divisions);
for (auto &beta: grids) {
beta.resize(2 * size_bandwidth);
for (auto &alpha: beta) {
alpha.resize(2 * size_bandwidth);
}
}
for (auto &beta: features) {
beta.resize(2 * size_bandwidth);
for (auto &alpha: beta) {
alpha.resize(2 * size_bandwidth, 0);
}
}
- interval表示径向分割下每个体素的径向长度
- grids用来存储每个体素覆盖的所有点,可以通过下面的初始化看到,会初始化径向,维度,经度,每个体素是一种voxel
- feature用来存储最终每个体素的特征(特征是密度特征)
grids填充
// mapping the points to the voxel grid
for (size_t i = 0; i < pts_on_s2.size(); i++) {
int r_idx = int(pts_norm[i] / interval);
// except for the points radius larger than radius_support
if (r_idx > size_radial_divisions - 1) r_idx = size_radial_divisions - 1;
int beta_idx = int(pts_on_s2[i][0] + 0.5f);
if (beta_idx > 2 * size_bandwidth - 1) beta_idx = 2 * size_bandwidth - 1;
int alpha_idx = int(pts_on_s2[i][1] + 0.5f);
if (alpha_idx > 2 * size_bandwidth - 1) alpha_idx = 2 * size_bandwidth - 1;
grids[r_idx][beta_idx][alpha_idx].emplace_back(std::vector<float>{pts_norm[i], pts_on_s2[i][0], pts_on_s2[i][1]});
}
这里会遍历每个点,计算每个点的径向体素所用r_idx,纬度体素索引beta_idx,经度体素索引alpha_idx ,然后push到对应的体素里面。
feature计算
首先计算每个体素的经度左右特征计算边界left、right(也就是说每个体素的特征计算并不仅仅只考虑本体素内部,还有一些可能出现的相邻体素),这里计算左右边界就用到自适应权重,维度高的,左右边界会宽一些。
之后根据左右边界访问对应体素,并取出体素中所有点,基于径向距离确定点是否靠近本体素中心,越靠近该点的特征权重越大([0, 1])。
然后考虑径向相邻体素内部的点,用于本体素的特征计算,因为从径向考虑,点分布相对连续,需要补充这样的信息。
最后计算本体素的特征(密度特征(加过权的点个数))
// compute the feature of each voxel
for (size_t i = 0; i < size_radial_divisions; i++) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < 2 * size_bandwidth; j++) {
for (size_t k = 0; k < 2 * size_bandwidth; k++) {
const float left = std::max(0.f, k - 0.5f / daas_weights[j]);
const float right = std::min(2.f * size_bandwidth, k + 0.5f / daas_weights[j]);
float sum = 0.f;
int cnt = 0;
for (int m = int(left + 0.5f); m < int(right + 0.5f); m++) {
for (int n = 0; n < grids[i][j][m].size(); n++) {
if (grids[i][j][m][n][2] > left && grids[i][j][m][n][2] < right) {
sum += 1.f - std::abs(grids[i][j][m][n][0] / interval - (i + 1)); // radial feature weight
cnt++;
}
}
// 在实际情况中,点云数据可能分布在两个相邻的径向分割之间,
// 尤其是当点的径向距离位于两个径向分割的边界附近时。
// 为了防止因单纯考虑当前径向分割而导致信息的丢失,
// 代码会查找相邻径向分割中满足条件的点,并将它们的贡献也加到当前体素单元的特征值中。
if (i < size_radial_divisions - 1) {
for (int n = 0; n < grids[i + 1][j][m].size(); n++) {
if (grids[i + 1][j][m][n][2] > left && grids[i + 1][j][m][n][2] < right) {
sum += 1.f - std::abs(grids[i + 1][j][m][n][0] / interval - (i + 1));
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
// 与径向分割不同,纬度分割(即 beta 方向)代表的是球面坐标中的角度,
// 分割的区域代表不同的“环”或“带”。
// 在这种情况下,每个纬度分割对应的球面区域是明确的,
// 且这些分割区域之间没有交叉,因此点不会“跨越”到另一个纬度分割。
if (cnt > 0) {
features[i][j][k] = sum / cnt;
}
}
}
}


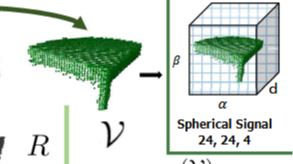 介绍了球面体素化的过程,包括重要的类和方法,如ConvertToSphericalVoxel和spherical_voxel_optimized,详细解释了参数及其作用。球面体素化通过将点云转换为球面坐标系,利用自适应采样权重来平衡不同纬度区域的点密度,从而有效捕捉几何特征。文中还提到C++绑定的sv.compute函数,负责体素特征的计算与填充,确保在特征计算中考虑邻近体素的信息
介绍了球面体素化的过程,包括重要的类和方法,如ConvertToSphericalVoxel和spherical_voxel_optimized,详细解释了参数及其作用。球面体素化通过将点云转换为球面坐标系,利用自适应采样权重来平衡不同纬度区域的点密度,从而有效捕捉几何特征。文中还提到C++绑定的sv.compute函数,负责体素特征的计算与填充,确保在特征计算中考虑邻近体素的信息

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号