Density-invariant Features for Distant Point Cloud Registration论文阅读
Density-invariant Features for Distant Point Cloud Registration
2023 ICCV
*Quan Liu, Hongzi Zhu, Yunsong Zhou, Hongyang Li, Shan Chang, Minyi Guo*; Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023, pp. 18215-18225
- paper: [2307.09788] Density-invariant Features for Distant Point Cloud Registration (arxiv.org)
- code: [liuQuan98/GCL: ICCV 23] Density-invariant Features for Distant Point Cloud Registration (github.com)

Idea
面向outdoor LiDAR点云,利用multiple point clouds sample set(in the same spatial location), 基于Group-wise Contrastive Learning方法,应用dense feature extractor(FCGF, KPConv……),提取density-invariant geometric features,解决远距离激光雷达点云配准(distant outdoor LiDAR point cloud registration)任务。
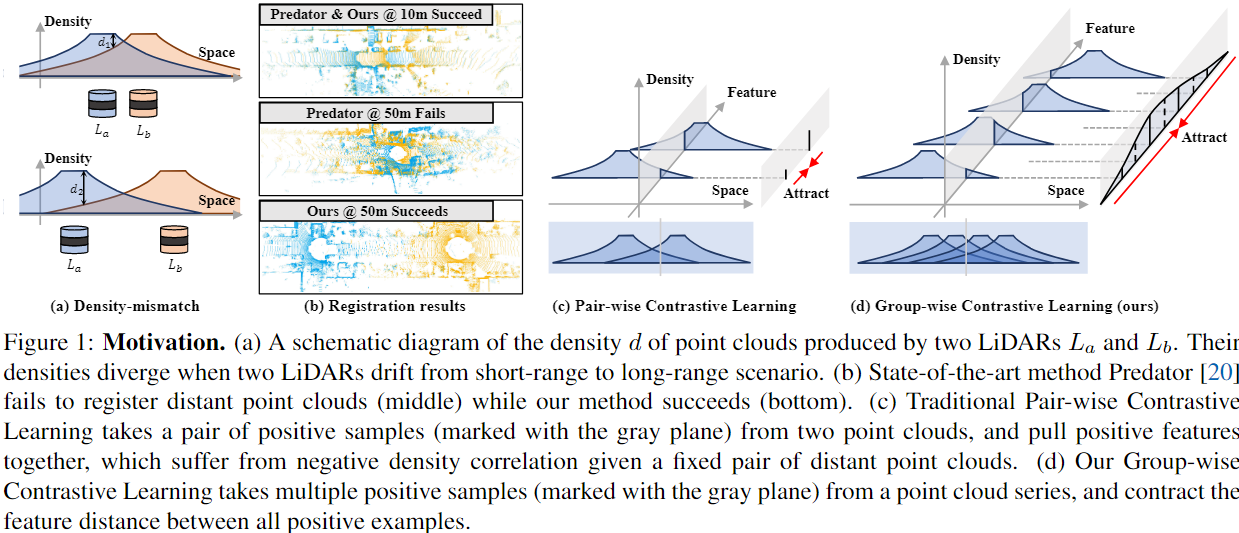
distant outdoor LiDAR point cloud registration的难点在于随着与LiDAR间隔距离的扩大,不同空间位置的点云密度会程二次曲线性质下降。这会造成不同点云重叠区域点云密度不同,深度学习方法对于该特性比较敏感,其配准性能会发生下降,也就是density-mismatch problem。
回顾以前的feature-based对比学习配准方法,每一个batch都是一对正样本待配准点云 ,然后取推理出各关键点正样本对的similar feature descriptor。根据文献[1] ,这么做能够收敛的前提是重叠区域点云样本独立同分布 ,简单来说就是密度和形状近似一致。但是显然这样训练出来的模型无法解决density-mismatch problem 。实验表明,无论是密度相关方法(e.g. voxelization) or 密度自适应方法都不能很好的配准distant outdoor point cloud.
作者提出的方法简单来说就是:既然训练时一对正样本达不到,那我就多用些正样本,用一组高overlap的正样本待配准点云来进group contrastive learning,通过这样数据增广的方式来实现density-invariant feature提取,使得模型能够克服density-mismatch问题。
原文:A large enough positive group can better approximate the underlying feature distribution .
Contribution
- 从理论上分析了distant point clouds registration 的困难,提出构建更多的 i.i.d (independently and identically distributed) positive samples 是训练出density-invariant feature descriptor的关键;
- 基于group-wise contrastive learning,提出有效的density-invariant feature descriptor 训练方案和相应的loss;
- 在KITTI和nuScenes的远距离点云配准样本下刷SOTA(KITTI:+40.9%; nuScenes: +26.9% -> reigistration recall)
论文中说对比学习方案设计更多考虑怎么提取更加困难的负样本,很少研究怎么提升正样本带来的训练效果 (A noticeable trend is that sampling more and harder negative samples will improve feature quality due to elevated stability and informativeness, but improvements on positive samples are scarce.),虽然group contrastive learning不是什么新概念,但是据我浅薄的学识来看,确实是第一次用在本文的任务上。
Description
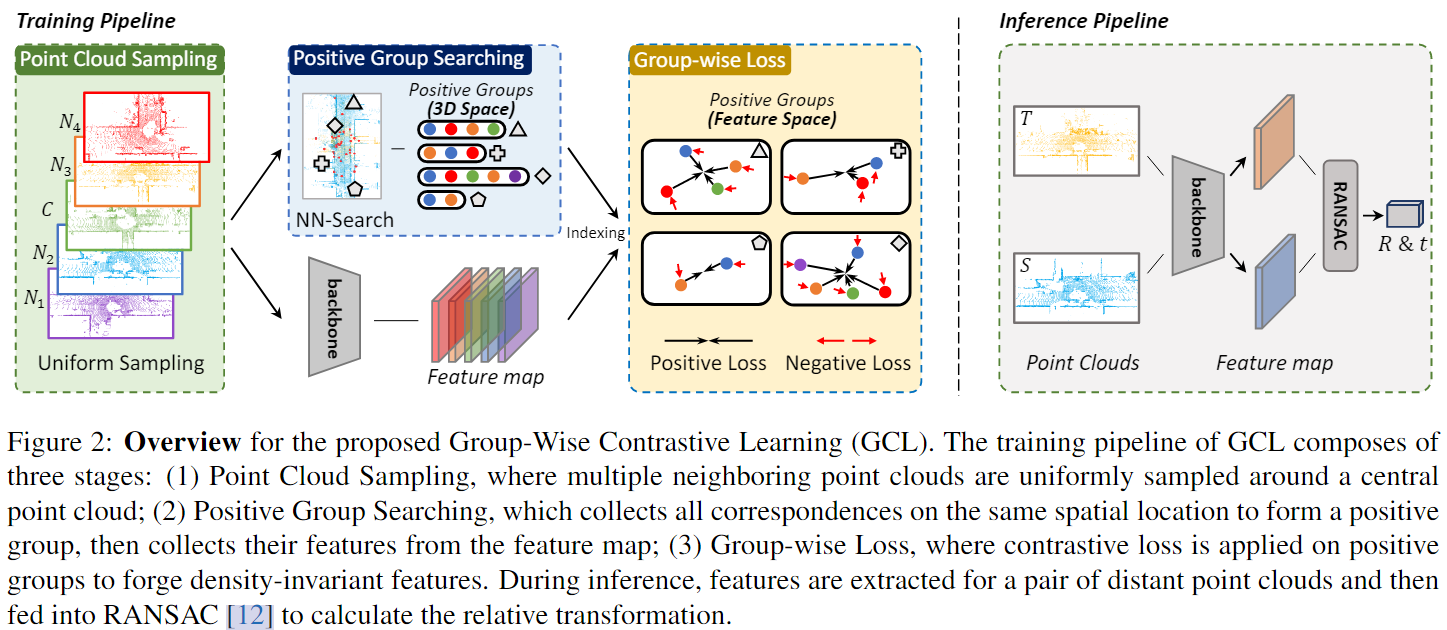
pipline还是比较清晰的四个步骤:
- 以 \(C\) frame为中心,在 \([-60m, 60m]\) 区域内选择N个segment,并对segment进行均匀采样得到点云(对于这个选择segment方式我还没有理清楚😭)。
- 使用fully convolutional features descriptor (FCGF、KPConv)为点云中每个点提取feature;
- 使用nearest neighbor search 以 \(C\) 点云每个点寻找在其他点云下的对应正样本点,并丢弃找不到多余1个对应点的参考点,称为positive group search;
- 之后计算Group-wise Loss:
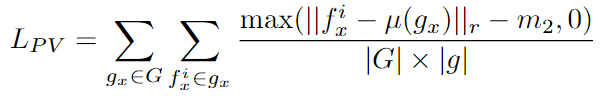
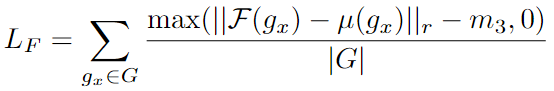
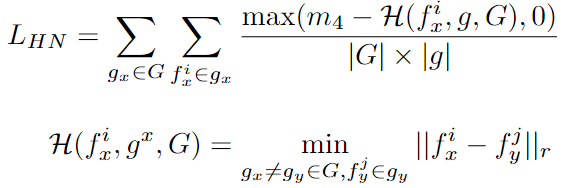
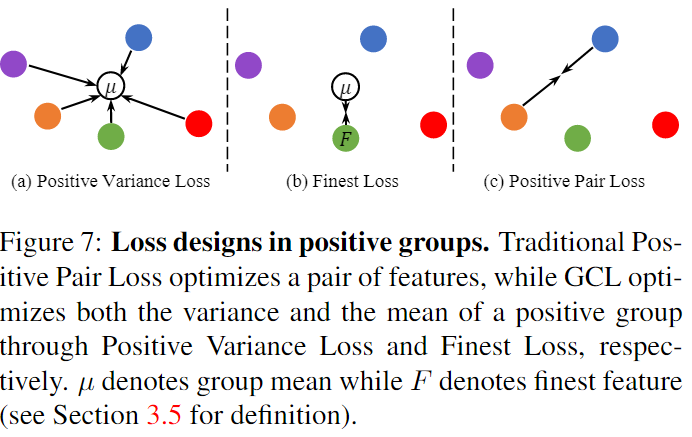
- \(L_{PV}\) : positive variance loss( \(\mu(·)\) is the average of all feature descriptors \(f_x^i\) of \(g_x\) correspondence group)
- \(L_F\) : Finest loss( \(\mathcal{F}(·)\) is the finest feature for \(g_x\) correspondence group)
- \(L_{HN}\) : the hardest negative loss
Experiment
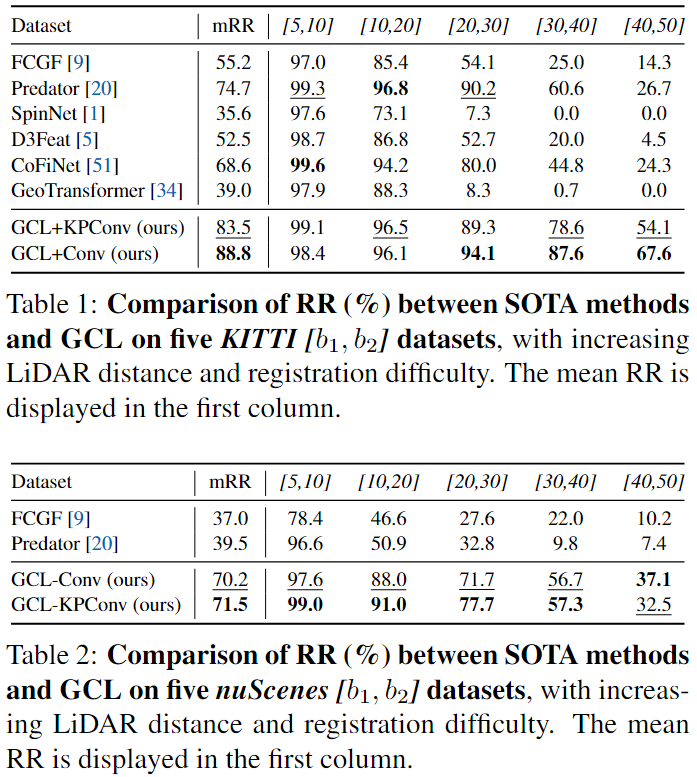
实话说,确实厉害,这个提点
Ablation
对于multi positive point cloud set中point cloud的数目:
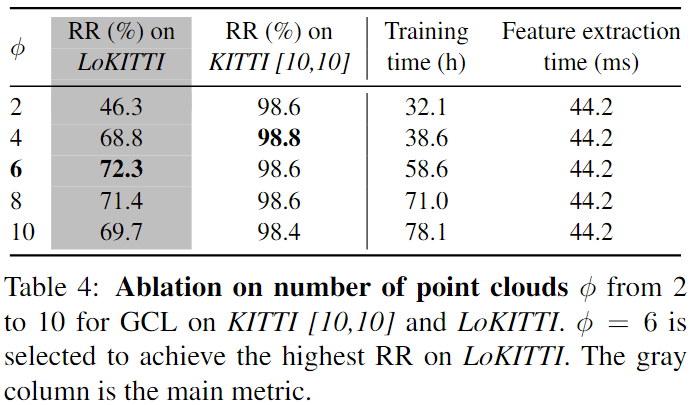
可以看到很明显,增多了正样本点云数量确实对于提取density-invariant feature很有帮助。
Saunshi, Nikunj, et al. "A theoretical analysis of contrastive unsupervised representation learning." International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019. ↩︎



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号