Unsupervised Binning
|
|
|
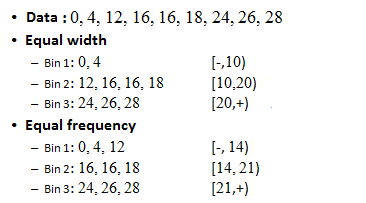
| Unsupervised binning methods transform numerical variables into categorical counterparts but do not use the target (class) information. Equal Width and Equal Frequency are two unsupervised binning methods. |
|
|
| |
|
|
1- Equal Width Binning
|
|
|
| The algorithm divides the data into k intervals of equal size. The width of intervals is: |
|
|
w = (max-min)/k
|
|
|
| And the interval boundaries are: |
|
|
min+w, min+2w, ... , min+(k-1)w
|
|
|
| |
|
|
2- Equal Frequency Binning
|
|
|
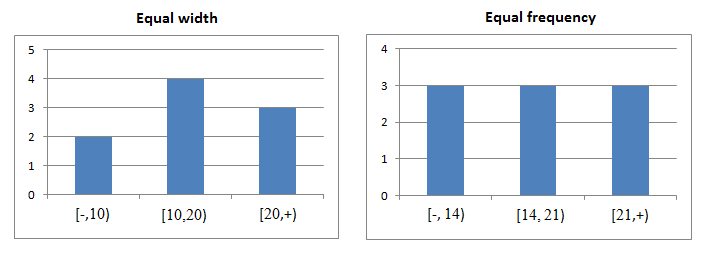
| The algorithm divides the data into k groups which each group contains approximately same number of values. For the both methods, the best way of determining k is by looking at the histogram and try different intervals or groups. |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Example: |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |





