花授粉优化算法-python/matlab
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import random # 初始化种群 def init(n_pop, lb, ub, nd): """ :param n_pop: 种群 :param lb: 下界 :param ub: 上界 :param nd: 维数 """ p = lb + (ub - lb) * np.random.rand(n_pop, nd) return p # 适应度函数 def sphere(x): y = np.sum(x ** 2, 1) return y f_score = sphere # 函数句柄 # Levy飞行Beale def Levy(nd, beta=1.5): num = np.random.gamma(1 + beta) * np.sin(np.pi * beta / 2) den = np.random.gamma((1 + beta) / 2) * beta * 2 ** ((beta - 1) / 2) sigma_u = (num / den) ** (1 / beta) u = np.random.normal(0, sigma_u ** 2, (1, nd)) v = np.random.normal(0, 1, (1, nd)) z = u / (np.abs(v) ** (1 / beta)) return z def FPA(Max_g, n_pop, Pop, nd, lb, ub, detail): # FPA算法 """ :param Max_g: 迭代次数 :param n_pop: 种群数目 :param Pop: 花粉配子 :param nd: 维数 :param lb: 下界 :param ub: 上界 :param detail: 显示详细信息 """ # 计算初始种群中最好个体适应度值 pop_score = f_score(Pop) g_best = np.min(pop_score) g_best_loc = np.argmin(pop_score) g_best_p = Pop[g_best_loc, :].copy() # 问题设置 p = 0.8 best_fit = np.empty((Max_g,)) # 迭代 for it in range(1, Max_g + 1): for i in range(n_pop): if np.random.rand() < p: new_pop = Pop[i, :] + Levy(nd) * (g_best_p - Pop[i, :]) new_pop = np.clip(new_pop, lb, ub) # 越界处理 else: idx = random.sample(list(range(n_pop)), 2) new_pop = Pop[i, :] + np.random.rand() * (Pop[idx[1], :] - Pop[idx[0], :]) new_pop = np.clip(new_pop, lb, ub) # 越界处理 if f_score(new_pop.reshape((1, -1))) < f_score(Pop[i, :].reshape((1, -1))): Pop[i, :] = new_pop # 计算更新后种群中最好个体适应度值 pop_score = f_score(Pop) new_g_best = np.min(pop_score) new_g_best_loc = np.argmin(pop_score) if new_g_best < g_best: g_best = new_g_best g_best_p = Pop[new_g_best_loc, :].copy() best_fit[it - 1] = g_best if detail: print("----------------{}/{}--------------".format(it, Max_g)) print(g_best) print(g_best_p) return best_fit, g_best if __name__ == "__main__": pop = init(30, -100, 100, 2) fitness, g_best = FPA(1000, 30, pop, 2, -100, 100, True) # 可视化 plt.figure() # plt.plot(fitness) plt.semilogy(fitness) # 可视化 # fig = plt.figure() # plt.plot(p1, fit) plt.show()
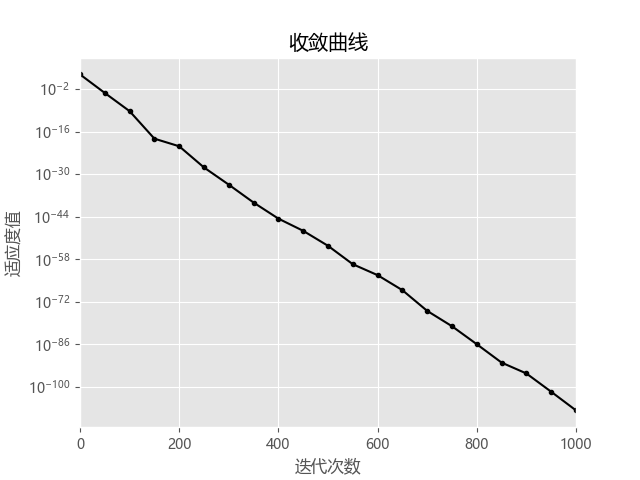
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt plt.style.use('ggplot') plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ["Microsoft YaHei"] plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False def sphere(x): y = 0 for e in x.flatten(): y += e ** 2 return y class FPA: def __init__(self, num_pop, dim, ub, lb, f_obj, verbose): self.num_pop = num_pop # 种群数目 self.dim = dim # 维数 self.ub = ub # 上界 self.lb = lb # 下界 self.pop = np.empty((num_pop, dim)) # 种群 self.f_obj = f_obj # 目标函数 self.f_score = np.empty((num_pop, 1)) self.verbose = verbose # 显示 self.p_best = None # 最好个体 self.f_best = None # 最好适应度值 self.iter_f_score = [] def initialize(self): """ 种群初始化 :return: 初始化种群和种群分数 """ for i in range(self.num_pop): self.pop[i, :] = self.lb + (self.ub - self.lb) * np.random.rand(1, self.dim).flatten() self.f_score[i] = self.f_obj(self.pop[i, :]) return [self.pop, self.f_score] def get_best(self): """ 获取最优解 :return: 最优索引和最优得分 """ idx = np.argmin(self.f_score) self.p_best = self.pop[idx, :] self.f_best = np.min(self.f_score) return [self.p_best, self.f_best] def Levy(self, beta=1.5): """ 莱维飞行 :param beta: 固定参数 :return: 随机数 """ sigma = (np.random.gamma(1 + beta) * np.sin(np.pi * beta / 2) / ( np.random.gamma((1 + beta) / 2) * beta * 2 ** ((beta - 1) / 2))) ** (1 / beta) # print(sigma) u = np.random.normal(0, sigma, (1, self.dim)) v = np.random.normal(0, 1, (1, self.dim)) levy = u / (np.abs(v) ** (1 / beta)) return levy def fit(self, max_generation, p=0.8): """ 算法迭代 :param max_generation: 最大迭代次数 :param p: 切换概率 :return: 最优值和最优个体 """ self.pop, self.f_score = self.initialize() # 初始化 self.p_best, self.f_best = self.get_best() # 当前最优个体 self.iter_f_score.append(self.f_best) # 迭代 for i in range(max_generation): for j in range(self.num_pop): if np.random.rand() < p: # 异花授粉公式 new_pop = self.pop[j, :] + self.Levy() * (self.pop[j, :] - self.p_best) else: # 自花授粉公式 idx_set = np.random.choice(range(self.num_pop), 2) new_pop = self.pop[j, :] + np.random.rand(1, self.dim) * (self.pop[idx_set[0], :] - self.pop[idx_set[1], :]) # 越界处理 new_pop = np.clip(new_pop.flatten(), self.lb, self.ub) new_f_score = self.f_obj(new_pop) # 进化算法 if new_f_score < self.f_score[j]: self.pop[j, :] = new_pop self.f_score[j] = new_f_score if new_f_score < self.f_best: self.p_best = new_pop self.f_best = new_f_score self.iter_f_score.append(self.f_best) if self.verbose: print("============{}/{}==============".format(i, max_generation)) print(self.f_best) return [self.iter_f_score, self.f_best] # 测试 if __name__ == "__main__": n_pop = 20 d = 2 upper = 100 lower = -100 max_iter = 1000 fpa = FPA(n_pop, d, upper, lower, sphere, True) iter_score, _ = fpa.fit(max_iter) xx = [int(i) for i in range(0, 1001, 50)] yy = np.array(iter_score) plt.figure() plt.title("收敛曲线") plt.semilogy(xx, yy[xx], c='k', marker='.') plt.xlim([0, 1000]) plt.xlabel("迭代次数") plt.ylabel("适应度值") plt.show()
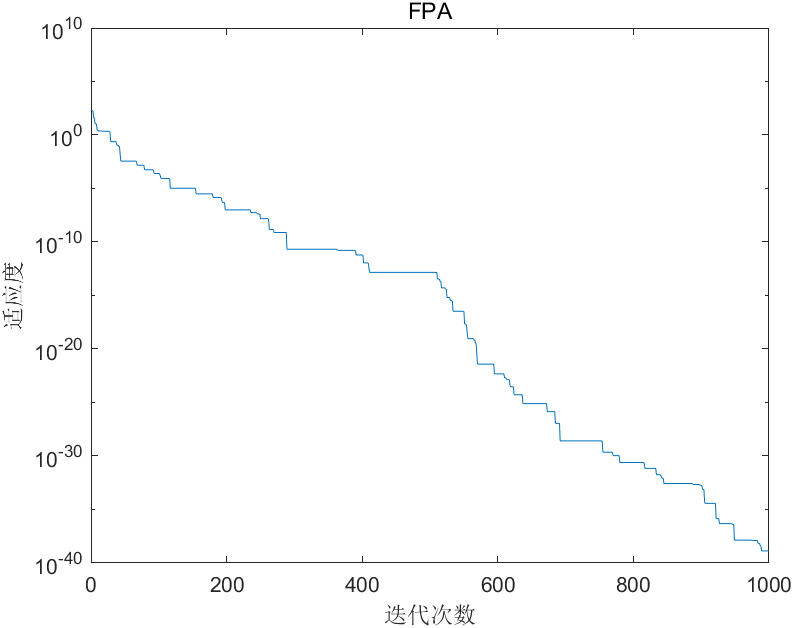
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 | 花授粉算法Matlab代码% 清屏和工作空间变量clcclearStep 1: 问题定义npop = 30; % 种群数目dpop = 2; % 种群维数ub = 100; % 种群的上界lb = -100; % 种群的下界Step 2: 初始化种群 pop = lb + rand(npop, dpop).*(ub - lb); % pop是初始种群Step 3:适应度函数 fScore = @ sphereStep 4:Levy飞行levy = @ LevyStep 5:计算初始种群最好的适应度值popScore = fScore(pop);[bestscore, loc] = min(popScore);bestpop = pop(loc, :);Step 6:参数设置iterMax = 1000; % 最大迭代次数p = 0.8; % 转换概率BestScore = ones(iterMax, 1);Step 7:越界处理Clip = @ clip; % 越界处理函数Step 8:迭代for it=1:iterMax for i = 1:npop if rand < p newpop = pop(i, :) + levy(1, dpop).*(bestpop - pop(i, :)); % 异花授粉 else idx = randsample(30, 2); newpop = pop(i, :) + rand*(pop(idx(1), :) - pop(idx(2), :)); % 自花授粉 end newpop = Clip(newpop, ub, lb); % 越界处理 if fScore(newpop) < fScore(pop(i, :)) pop(i, :) = newpop; % 更新种群 end end popScore = fScore(pop); [newBestScore, Loc] = min(popScore); if newBestScore < bestscore bestscore = newBestScore; bestpop = pop(loc, :); end BestScore(it) = bestscore; disp(['Iteration ' num2str(it) ': Best Cost = ' num2str(bestscore)]); disp(['Bestpop ' num2str(bestpop)])endStep 9:可视化figuresemilogy(BestScore)% plot(BestScore)xlim([0 1000])xlabel('迭代次数')ylabel('适应度')title('FPA') |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | function L=Levy(d)%% Levy飞行 beta=3/2; sigma=(gamma(1+beta)*sin(pi*beta/2)/(gamma((1+beta)/2)*beta*2^((beta-1)/2)))^(1/beta); u=random('normal', 0, sigma, 1, d); v=random('normal', 0, 1, 1, d); L=0.01*u./abs(v).^(1/beta);end |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | function s=simplebounds(s,Lb,Ub)%% 越界处理函数 ns_tmp=s; I=ns_tmp<Lb; ns_tmp(I)=Lb(I); J=ns_tmp>Ub; ns_tmp(J)=Ub(J); s=ns_tmp;end |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | function [y] = Sphere(xx)%% 目标函数 d = length(xx); sum = 0; for ii = 1:d xi = xx(ii); sum = sum + xi^2; end y = sum;end |





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端