java.lang(StringBuffer)
public final class StringBuffer
extends AbstractStringBuilder
implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence {
/**
* Constructs a string buffer with no characters in it and an
* initial capacity of 16 characters.
*/
public StringBuffer() {
super(16);
}
/**
* Constructs a string buffer with no characters in it and
* the specified initial capacity.
*/
public StringBuffer(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
/**
* Constructs a string buffer initialized to the contents of the
* specified string. The initial capacity of the string buffer is
* <code>16</code> plus the length of the string argument.
*
* @param str the initial contents of the buffer.
* @exception NullPointerException if <code>str</code> is <code>null</code>
*/
public StringBuffer(String str) {
super(str.length() + 16);
append(str);
}
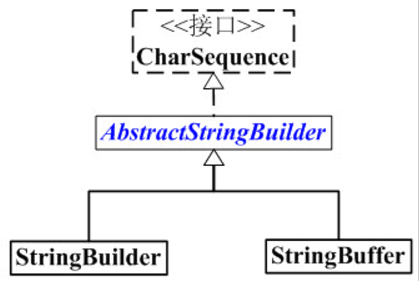
StringBuffer 是一个线程安全的可变的字符序列。它继承于AbstractStringBuilder,实现了CharSequence接口。
StringBuilder 也是继承于AbstractStringBuilder的子类;但是,StringBuilder和StringBuffer不同,前者是非线程安全的,后者是线程安全的。
StringBuffer的内部实现方式和String不同,StringBuffer在进行字符串处理时,不生成新的对象,在内存使用上要优于String类。
所以在实际使用时,如果经常需要对一个字符串进行修改,例如插入、删除等操作,使用StringBuffer要更加适合一些。
在StringBuffer类中存在很多和String类一样的方法,这些方法在功能上和String类中的功能是完全一样的。
但是有一个最显著的区别在于,对于StringBuffer对象的每次修改都会改变对象自身,这点是和String类最大的区别。
对于StringBuffer的append操作基本是在AbstractStringBuilder继承实现,看源码:
abstract class AbstractStringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence {
char[] value; //The value is used for character storage.
int count; //The count is the number of characters used.
//Appends the specified string to this character sequence.
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null) str = "null";
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
// Documentation in subclasses because of synchro difference
public AbstractStringBuilder append(StringBuffer sb) {
if (sb == null)
return append("null");
int len = sb.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
sb.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
// Documentation in subclasses because of synchro difference
public AbstractStringBuilder append(CharSequence s) {
if (s == null)
s = "null";
if (s instanceof String)
return this.append((String)s);
if (s instanceof StringBuffer)
return this.append((StringBuffer)s);
return this.append(s, 0, s.length());
}
/**
* Appends the string representation of the {@code char} array
* argument to this sequence.
*/
public AbstractStringBuilder append(char[] str) {
int len = str.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
System.arraycopy(str, 0, value, count, len);
count += len;
return this;
}
}
/***************其他追加字符方法省略介绍了***********/
添加字符时的扩容方法介绍:
/**
* This implements the expansion semantics of ensureCapacity with no
* size check or synchronization.
*/
void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
if (newCapacity < 0) {
if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
}
每次添加字符时扩容为:int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号