手写一个SpringMVC框架(转)
一:梳理SpringMVC的设计思路
本文只实现自己的@Controller、@RequestMapping、@RequestParam注解起作用,其余SpringMVC功能读者可以尝试自己实现。
1、读取配置
SpringMVC本质上是一个Servlet,这个 Servlet 继承自 HttpServlet。FrameworkServlet负责初始化SpringMVC的容器,并将Spring容器设置为父容器。因为本文只是实现SpringMVC,对于Spring容器不做过多讲解。
为了读取web.xml中的配置,我们用到ServletConfig这个类,它代表当前Servlet在web.xml中的配置信息。通过web.xml中加载我们自己写的MyDispatcherServlet和读取配置文件。
2、初始化阶段
-
加载配置文件
-
扫描用户配置包下面所有的类
-
拿到扫描到的类,通过反射机制,实例化。并且放到ioc容器中(Map的键值对 beanName-bean) beanName默认是首字母小写
-
初始化HandlerMapping,这里其实就是把url和method对应起来放在一个k-v的Map中,在运行阶段取出
3、运行阶段
每一次请求将会调用doGet或doPost方法,所以统一运行阶段都放在doDispatch方法里处理,它会根据url请求去HandlerMapping中匹配到对应的Method,然后利用反射机制调用Controller中的url对应的方法,并得到结果返回。按顺序包括以下功能:
-
异常的拦截
-
获取请求传入的参数并处理参数
-
通过初始化好的handlerMapping中拿出url对应的方法名,反射调用
二、实现自己的SpringMVC框架
工程文件及目录:
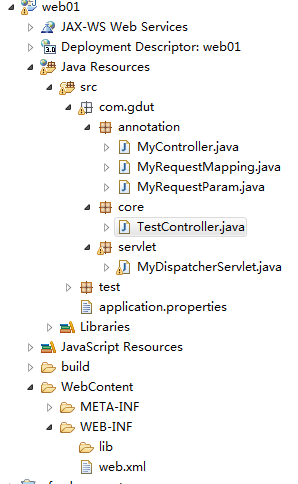
用到javax.servlet.jar
web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>web01</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> <servlet-name>MySpringMVC</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.gdut.servlet.MyDispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>application.properties</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>MySpringMVC</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
application.properties文件中只是配置要扫描的包到SpringMVC容器中。application.properties文件内容为:
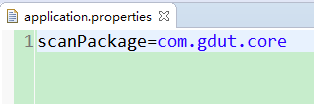
创建自己的Controller注解,它只能标注在类上面:
package com.gdut.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyController { /** * 表示给controller注册别名 * @return */ String value() default ""; }
RequestMapping注解,可以在类和方法上:
package com.gdut.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyRequestMapping { /** * 表示访问该方法的url * @return */ String value() default ""; }
RequestParam注解,只能注解在参数上
package com.gdut.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyRequestParam { /** * 表示参数的别名,必填 * @return */ String value(); }
然后创建MyDispatcherServlet这个类,去继承HttpServlet,重写init方法、doGet、doPost方法,以及加上我们第二步分析时要实现的功能:
package com.gdut.servlet; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.net.URL; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Properties; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.gdut.annotation.MyController; import com.gdut.annotation.MyRequestMapping; public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet { private Properties properties = new Properties(); private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<>(); private Map<String, Object> ioc = new HashMap<>(); private Map<String, Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<>(); private Map<String, Object> controllerMap = new HashMap<>(); @Override public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { // 1.加载配置文件 doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation")); // 2.初始化所有相关联的类,扫描用户设定的包下面所有的类 doScanner(properties.getProperty("scanPackage")); // 3.拿到扫描到的类,通过反射机制,实例化,并且放到ioc容器中(k-v beanName-bean) beanName默认是首字母小写 doInstance(); // 4.初始化HandlerMapping(将url和method对应上) initHandlerMapping(); } @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { try { // 处理请求 doDispatch(req, resp); } catch (Exception e) { resp.getWriter().write("500!! Server Exception"); } } private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception { if (handlerMapping.isEmpty()) { return; } String url = req.getRequestURI(); String contextPath = req.getContextPath(); url = url.replace(contextPath, "").replaceAll("/+", "/"); if (!this.handlerMapping.containsKey(url)) { resp.getWriter().write("404 NOT FOUND!"); return; } Method method = this.handlerMapping.get(url); // 获取方法的参数列表 Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); // 获取请求的参数 Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = req.getParameterMap(); // 保存参数值 Object[] paramValues = new Object[parameterTypes.length]; // 方法的参数列表 for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) { // 根据参数名称,做某些处理 String requestParam = parameterTypes[i].getSimpleName(); if (requestParam.equals("HttpServletRequest")) { // 参数类型已明确,这边强转类型 paramValues[i] = req; continue; } if (requestParam.equals("HttpServletResponse")) { paramValues[i] = resp; continue; } if (requestParam.equals("String")) { for (Entry<String, String[]> param : parameterMap.entrySet()) { String value = Arrays.toString(param.getValue()) .replaceAll("\\[|\\]", "").replaceAll(",\\s", ","); paramValues[i] = value; } } } // 利用反射机制来调用 try { method.invoke(this.controllerMap.get(url), paramValues);// 第一个参数是method所对应的实例 // 在ioc容器中 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private void doLoadConfig(String location) { // 把web.xml中的contextConfigLocation对应value值的文件加载到流里面 InputStream resourceAsStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader() .getResourceAsStream(location); // 用Properties文件加载文件里的内容 try { properties.load(resourceAsStream); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (resourceAsStream != null) { try { resourceAsStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } private void doScanner(String packageName) { // 把所有的.替换成/ URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader() .getResource("/" + packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/")); File dir = new File(url.getFile()); for (File file : dir.listFiles()) { if (file.isDirectory()) { // 递归读取包 doScanner(packageName + "." + file.getName()); } else { String className = packageName + "." + file.getName().replace(".class", ""); classNames.add(className); } } } private void doInstance() { if (classNames.isEmpty()) { return; } for (String className : classNames) { try { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className); if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)) { ioc.put(toLowerFirstWord(clazz.getSimpleName()), clazz.newInstance()); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private void initHandlerMapping() { if (ioc.isEmpty()) { return; } try { for (Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) { Class<? extends Object> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass(); if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)) { continue; } // 拼url时,是controller头的url拼上方法上的url String baseUrl = ""; if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)) { MyRequestMapping annotation = clazz .getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class); baseUrl = annotation.value(); } Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)) { continue; } MyRequestMapping annotation = method .getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class); String url = annotation.value(); url = (baseUrl + "/" + url).replaceAll("/+", "/"); handlerMapping.put(url, method); controllerMap.put(url, clazz.newInstance()); System.out.println(url + "," + method); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 把字符串的首字母小写 * * @param name * @return */ private String toLowerFirstWord(String name) { char[] charArray = name.toCharArray(); charArray[0] += 32; return String.valueOf(charArray); } }
这里我们就开发完了自己的SpringMVC,现在我们测试一下:
package com.gdut.core; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.gdut.annotation.MyController; import com.gdut.annotation.MyRequestMapping; import com.gdut.annotation.MyRequestParam; @MyController @MyRequestMapping("/test") public class TestController { @MyRequestMapping("/doTest") public void test1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @MyRequestParam("param") String param){ System.out.println(param); try { response.getWriter().write( "doTest method success! param:"+param); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @MyRequestMapping("/doTest2") public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){ try { response.getWriter().println("doTest2 method success!"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
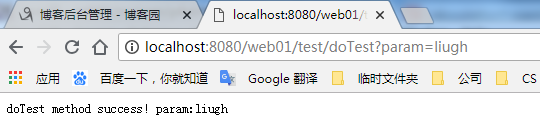
访问http://localhost:8080/web01/test/doTest?param=liugh如下:
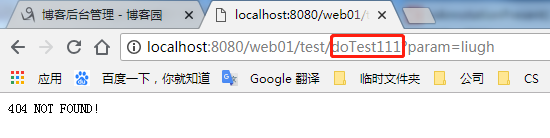
访问一个不存在的试试:
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/java1024/p/8556519.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号