用 300 行代码手写提炼 Spring 核心原理 [1]
系列文章
- 用 300 行代码手写提炼 Spring 核心原理 [1]
- 用 300 行代码手写提炼 Spring 核心原理 [2]
- 用 300 行代码手写提炼 Spring 核心原理 [3]
手写一个 mini 版本的 Spring 框架是一个很好的实践项目,可以让你对框架的核心概念和实现有更深刻的理解。接下来我们从 0-1 逐层深入,一步一步揭开 Spring 的神秘面纱。

自定义配置
配置 application.properties
为了解析方便,我们用 application.properties 来代替 application.xml 文件,具体的配置内容如下:
scanPackage=org.example.minispring
配置 web.xml
所有依赖于 Web 容器的项目都是从读取 web.xml 文件开始的,我们先配置好 web.xml 中的内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>MiniSpring</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher-servlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.example.minispring.framework.v1.MyDispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>application.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher-servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
其中 MyDispatcherServlet 是模拟 Spring 实现的核心功能类。
自定义注解
- @MyService 注解
package org.example.minispring.framework.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface MyService {
String value() default "";
}
- @MyAutowired 注解
package org.example.minispring.framework.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface MyAutowired {
String value() default "";
}
- @MyController 注解
package org.example.minispring.framework.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface MyController {
String value() default "";
}
- @MyRequestMapping 注解
package org.example.minispring.framework.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
public @interface MyRequestMapping {
String value() default "";
}
- @MyRequestParam 注解
package org.example.minispring.framework.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
public @interface MyRequestParam {
String value() default "";
}
配置注解
- 配置业务实现类 DemoService
按照规范,先定义接口类 IDemoService
package org.example.minispring.service;
public interface IDemoService {
public String get(String name);
}
再定义实现类:
package org.example.minispring.service.impl;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyService;
import org.example.minispring.service.IDemoService;
@MyService
public class DemoService implements IDemoService {
@Override
public String get(String name) {
return "Hello " + name + "!";
}
}
- 配置请求入口类 DemoAction
package org.example.minispring.action;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyAutowired;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyController;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyRequestMapping;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyRequestParam;
import org.example.minispring.service.IDemoService;
@MyController
@MyRequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoAction {
@MyAutowired
private IDemoService demoService;
@MyRequestMapping("/query")
public void query(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp,
@MyRequestParam("name") String name) {
String result = demoService.get(name);
try {
resp.getWriter().write("<html><h2>" + result + "</h2></html>");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
容器初始化
所有核心逻辑全部写在 MyDispatcherServlet 的 init() 方法中:
package org.example.minispring.framework.v1;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyAutowired;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyController;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyRequestMapping;
import org.example.minispring.framework.annotation.MyService;
public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
// 保存beanName -> bean的映射关系
private Map<String, Object> beanMapping = new HashMap<>();
// 保存url -> method的映射关系
private Map<String, Object> handlerMapping = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
doDispatch(req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
resp.getWriter().write("500 Exception " + Arrays.toString(e.getStackTrace()));
}
}
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
String url = req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = req.getContextPath();
url = url.replace(contextPath, "").replaceAll("/+", "/");
if (!this.handlerMapping.containsKey(url)) {
resp.getWriter().write("404 Not Found");
return;
}
// 根据url找到对应的方法
// 此处method为DemoAction.query(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, String)
Method method = (Method) this.handlerMapping.get(url);
// 获取请求参数, 此处为: name = [浏览器传来的值]
Map<String, String[]> params = req.getParameterMap();
// 1. method.getDeclaringClass().getName()
// 本例为org.example.minispring.action.DemoAction
// 2. beanMapping.get(beanName): 根据beanName获取到对应的bean实例,例如:
// org.example.minispring.action.DemoAction@51e3ce14
// 3. method.invoke调用的就是
// org.example.minispring.action.DemoAction@51e3ce14.query(req, resp, name)
String beanName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
method.invoke(this.beanMapping.get(beanName), new Object[] { req, resp, params.get("name")[0] });
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
Properties configContext = new Properties();
try {
configContext.load(is);
String scanPackage = configContext.getProperty("scanPackage");
// 扫描相关的类,本例中scanPackage=org.example.minispring
doScanner(scanPackage);
for (String className : beanMapping.keySet()) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
// 解析@MyController注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)) {
// 保存className和@MyController实例的对应关系
beanMapping.put(className, clazz.newInstance());
String baseUrl = "";
// 解析@MyController上的@MyRequestMapping注解,作为当前Controller的baseUrl
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)) {
MyRequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl = requestMapping.value();
}
// 解析@MyController中方法上的@MyRequestMapping注解
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)) {
continue;
}
MyRequestMapping requestMapping = method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
// 组合方法签名上的完整url,正则替换是为防止路径中出现多个连续多个"/"的不规范写法
String url = (baseUrl + "/" + requestMapping.value()).replaceAll("/+", "/");
// 保存url -> method的对应关系
handlerMapping.put(url, method);
System.out.println("Mapped " + url + " -> " + method);
}
}
// 解析@MyService注解
else if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyService.class)) {
MyService service = clazz.getAnnotation(MyService.class);
String beanName = service.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)) {
beanName = clazz.getName();
}
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
// 保存className和@MyService实例的对应关系
beanMapping.put(beanName, instance);
for (Class<?> i : clazz.getInterfaces()) {
beanMapping.put(i.getName(), instance);
}
}
}
// 解析对象之间的依赖关系,依赖注入
for (Object object : beanMapping.values()) {
if (object == null) {
continue;
}
Class<?> clazz = object.getClass();
// 向MyController中注入MyService
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)) {
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAutowired.class)) {
continue;
}
MyAutowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(MyAutowired.class);
String beanName = autowired.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)) {
beanName = field.getType().getName();
}
// 只要加了@MyAutowired注解都要强制赋值
// 反射中叫做暴力访问
field.setAccessible(true);
// 用反射机制动态给字段赋值
// 赋值后DemoAction.demoService = DemoService@c97ae21
// 也即DemoService实例被注入到了DemoAction对象中,这就是依赖注入
field.set(beanMapping.get(clazz.getName()), beanMapping.get(beanName));
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 扫描相关的类,本例中scanPackage=org.example.minispring
*/
private void doScanner(String scanPackage) {
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File classDir = new File(url.getFile());
for (File file : classDir.listFiles()) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
// 递归扫描子文件夹
doScanner(scanPackage + "." + file.getName());
} else {
String clazzName = scanPackage + "." + file.getName().replace(".class", "");
beanMapping.put(clazzName, null);
}
}
}
}
运行演示
到此为止我们就实现了 mini-spring 的 1.0 版本。
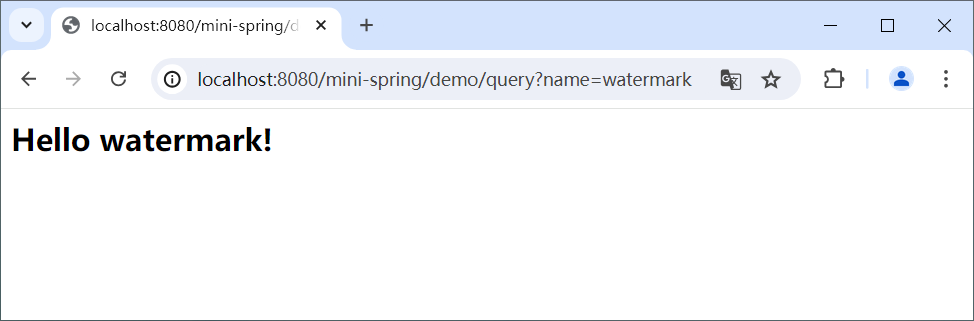
1.0 版本具备了初步的功能,但是代码不够优雅,接下来我们在此基础上进行优化,采用常用的设计模式(工厂模式、单例模式、委派模式、策略模式)将 init() 方法中的代码进行封装,请看下篇 用 300 行代码手写提炼 Spring 核心原理 [2]。
参考
[1] 《Spring 5 核心原理与 30 个类手写实战》,谭勇德著。

![用 300 行代码手写提炼 Spring 核心原理 [1]](https://img2024.cnblogs.com/blog/2850366/202409/2850366-20240911162610795-890862520.png) 手写一个 mini 版本的 Spring 框架是一个很好的实践项目,可以让你对框架的核心概念和实现有更深刻的理解。接下来我们从 0-1 逐层深入,一步一步揭开 Spring 的神秘面纱。
手写一个 mini 版本的 Spring 框架是一个很好的实践项目,可以让你对框架的核心概念和实现有更深刻的理解。接下来我们从 0-1 逐层深入,一步一步揭开 Spring 的神秘面纱。


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!