Spring Cloud Config 配置中心
对于一些简单的项目来说,我们一般都是直接把相关配置放在单独的配置文件中,以 properties 或者 yml 的格式出现,更省事儿的方式是直接放到 application.properties 或 application.yml 中。但是这样的方式有个明显的问题,那就是,当修改了配置之后,必须重启服务,否则配置无法生效。
一、实现最简单的配置中心
最简单的配置中心,就是启动一个服务作为服务方,之后各个需要获取配置的服务作为客户端来这个服务方获取配置。
现在github中建立配置文件,我这里使用的是码云:https://gitee.com/。
新建一个仓库SpringCloudConfig,在仓库根路径下创建一个文件夹config,目录结构如下:

配置文件的内容大致如下,用于区分,略有不同。
data:
env: config-single-dev
user:
username: single-client-user
password: 1291029102
注意文件的名称不是乱起的,例如上面的 config-single-client-dev.yml 和 config-single-client-prod.yml 这两个是同一个项目的不同版本,项目名称为 config-single-client(spring.application.name配置的值), 一个对应开发版,一个对应正式版。
创建配置中心服务端
1、新建 Spring Boot 项目,引入 config-server 和 starter-web
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- spring cloud config 服务端包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId> </dependency>
2、配置 config 相关的配置项
bootstrap.yml 文件
spring:
application:
name: config-single-server # 应用名称
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://gitee.com/linhongwei/SpringCloudConfig #配置文件所在仓库
username: github 登录账号
password: github 登录密码
default-label: master #配置文件分支
search-paths: config #配置文件所在根目录
application.yml
server: port: 3301
3、在启动类上增加相关注解 @EnableConfigServer
@EnableConfigServer @SpringBootApplication public class ConfigServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args); } }
Spring Cloud Config 有它的一套访问规则,我们通过这套规则在浏览器上直接访问就可以。
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
{application} 就是应用名称,对应到配置文件上来,就是配置文件的名称部分,例如我上面创建的配置文件。
{profile} 就是配置文件的版本,我们的项目有开发版本、测试环境版本、生产环境版本,对应到配置文件上来就是以 application-{profile}.yml 加以区分,例如application-dev.yml、application-sit.yml、application-prod.yml。
{label} 表示 git 分支,默认是 master 分支,如果项目是以分支做区分也是可以的,那就可以通过不同的 label 来控制访问不同的配置文件了。
因为我这里的配置文件都是 yml 格式的。根据这三条规则,我们可以通过以下地址查看配置文件内容:
http://localhost:3301/config-single-client/dev/master http://localhost:3301/config-single-client/prod http://localhost:3301/config-single-client-dev.yml http://localhost:3301/config-single-client-prod.yml http://localhost:3301/master/config-single-client-prod.yml
通过访问以上地址,如果可以正常返回数据,则说明配置中心服务端一切正常。
创建配置中心客户端
配置中心服务端好了,配置数据准备好了,接下来,就要在我们的项目中使用它了。
1、、引入相关的maven包
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- spring cloud config 客户端包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency>
2、配置文件
bootstrap.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
spring:
profiles: prod
application:
name: config-single-client # 与配置文件的名称部分要对应
cloud:
config:
uri: http://localhost:3301
label: master
profile: prod
---
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: config-single-client # 与配置文件的名称部分要对应
cloud:
config:
uri: http://localhost:3301
label: master
profile: dev
配置了两个版本的配置,并通过 spring.profiles.active 设置当前使用的版本,例如本例中使用的 dev 版本。
application.yml
server:
port: 3302
data:
env: NaN
user:
username: NaN
password: NaN
data 部分是当无法读取配置中心的配置时,使用此配置,以免项目无法启动。
3、要读取配置中心的内容,需要增加相关的配置类,Spring Cloud Config 读取配置中心内容的方式和读取本地配置文件中的配置是一模一样的。可以通过 @Value 或 @ConfigurationProperties 来获取。
使用 @Value 的方式:
@Component public class GitConfig { @Value("${data.env}") private String env; @Value("${data.user.username}") private String username; @Value("${data.user.password}") private String password; public String getEnv() { return env; } public void setEnv(String env) { this.env = env; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
使用 @ConfigurationProperties 的方式:
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "data") public class GitAutoRefreshConfig { public static class UserInfo { private String username; private String password; public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } @Override public String toString() { return "UserInfo{" + "username='" + username + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + '}'; } } private String env; private UserInfo user; public String getEnv() { return env; } public void setEnv(String env) { this.env = env; } public UserInfo getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(UserInfo user) { this.user = user; } }
4、增加一个 RESTController 来测试使用配置
@RestController public class GitController { @Autowired private GitConfig gitConfig; @Autowired private GitAutoRefreshConfig gitAutoRefreshConfig; @GetMapping(value = "show") public Object show(){ return gitConfig; } @GetMapping(value = "autoShow") public Object autoShow(){ return gitAutoRefreshConfig; } }
5、启动项目,访问 RESTful 接口:
http://localhost:3302/show,返回如下:

http://localhost:3302/autoShow,返回如下:

二、实现自动刷新
Spring Cloud Config 在项目启动时加载配置内容这一机制,导致了它存在一个缺陷,修改配置文件内容后,不会自动刷新。例如我们上面的项目,当服务已经启动的时候,去修改 github 上的配置文件内容,这时候,再次刷新页面,对不起,还是旧的配置内容,新内容不会主动刷新过来。
但是,总不能每次修改了配置后重启服务吧。如果是那样的话,还是不要用它了为好,直接用本地配置文件岂不是更快。
它提供了一个刷新机制,但是需要我们主动触发。那就是 @RefreshScope 注解并结合 actuator ,注意要引入 spring-boot-starter-actuator 包。
1、在config client 侧引入actuator依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>
2、在 config client 端配置中增加 actuator 配置
management:
endpoint:
shutdown:
enabled: false
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
其实这里主要用到的是 refresh 这个接口。
3、在需要读取配置的类上增加 @RefreshScope 注解,我们是 controller 中使用配置,所以加在 controller 中。
@RestController @RefreshScope public class GitController { @Autowired private GitConfig gitConfig; @Autowired private GitAutoRefreshConfig gitAutoRefreshConfig; @GetMapping(value = "show") public Object show() { return gitConfig; } @GetMapping(value = "autoShow") public Object autoShow() { return gitAutoRefreshConfig; } }
注意,以上都是在 client 端做的修改。
之后,重启 client 端,重启后,我们修改 github 上的配置文件内容,并提交更改,再次刷新页面,没有反应。没有问题。
接下来,我们发送 POST 请求到 http://localhost:3302/actuator/refresh 这个接口,用 postman 之类的工具即可,此接口就是用来触发加载新配置的,返回内容如下:
[
"config.client.version",
"data.env"
]
之后,再次访问 RESTful 接口,http://localhost:3302/autoShow 这个接口获取的数据已经是最新的了,说明 refresh 机制起作用了。
而 http://localhost:3302/show 获取的还是旧数据,这与 @Value 注解的实现有关,所以,我们在项目中就不要使用这种方式加载配置了。
使用 Spring Cloud Bus 实现自动刷新多个端
Spring Cloud Bus 将分布式系统的节点与轻量级消息代理链接。这可以用于广播状态更改(例如配置更改)或其他管理指令。一个关键的想法是,Bus 就像一个扩展的 Spring Boot 应用程序的分布式执行器,但也可以用作应用程序之间的通信渠道。
Spring Cloud Config配合Spring Cloud Bus自动刷新配置有两种架构设计:
1)利用消息总线触发一个客户端/bus/refresh,而刷新所有客户端的配置

2)利用消息总线触发一个服务端ConfigServer的/bus/refresh端点,而刷新所有客户端的配置
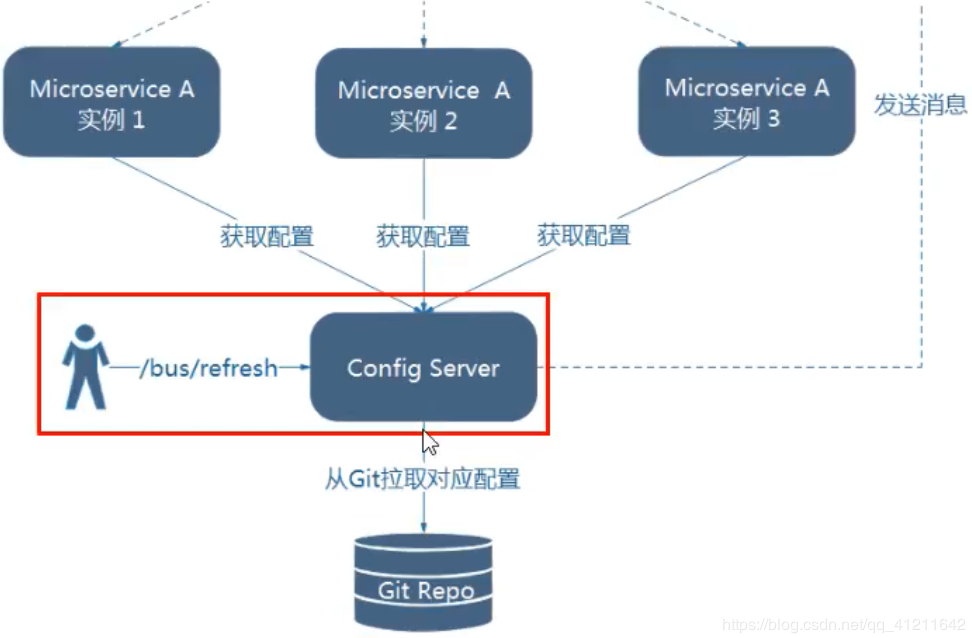
图二的架构显然更加合适,图一不合适的原因如下:
- 打破了微服务的职责单一性,因为微服务本身是业务模块,它本不应该承担配置刷新的职责
- 破坏了微服务各节点的对等性
- 有一定的局限性。例如,微服务在迁移时,它的网络地址常常会发生变化,此时如果想要做到自动刷新,那就需要增加更多的修改
1、Spring Cloud Bus 核心原理其实就是利用消息队列做广播,所以要先有个消息队列,目前官方支持 RabbitMQ 和 kafka。
这里用的是 RabbitMQ, 所以先要搭一套 RabbitMQ 环境,然后安装了 rabbitmq-management 插件,这样就可以在浏览器访问 15672 查看 UI 管理界面了。如何安装,请看我另外一篇文章:Windows下RabbitMQ安装及配置
2、配置中心服务端添加消息总线支持
<!--添加消息总线RbbitMQ支持--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>
applicaiton.yml添加rabbitmq和actuator的配置项
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672 # 15672是插件的端口,在这里应该使用5672
username: guest
password: guest
management:
endpoint:
shutdown:
enabled: false
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "bus-refresh"
3、config client添加消息总线支持
<!--添加消息总线rabbitMQ支持--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>
application.yml添加rabbitmq的配置项
#rabbit相关配置 15672是web管理界面的端口,5672是MQ访问的端口
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest #这是客户端,不需要刷新
4、启动config server和两个config client(3302、3303)。
分别打开 http://localhost:3302/autoShow 和 http://localhost:3303/autoShow,查看内容,然后修改 github 上配置文件的内容并提交。再次访问这两个地址,数据没有变化。
访问其中一个的 actuator/bus-refresh 地址(如:http://localhost:3301/actuator/bus-refresh),注意还是要用 POST 方式访问。然后再访问前面两个地址,发现数据变了,说明刷新生效了。
三、结合Eureka使用Spring Cloud Config
以上讲了 Spring Cloud Config 最基础的用法,但是如果我们的系统中使用了 Eureka 作为服务注册发现中心,那么 Spring Cloud Config 也应该注册到 Eureka 之上,方便其他服务消费者使用,并且可以注册多个配置中心服务端,以实现高可用。
接下来就来集成 Spring Cloud Config 到 Eureka 上。
在 github 仓库中增加配置文件
前提:启动eureka server
配置 Spring Cloud Config 服务端
服务端和前面的相比也就是多了注册到 Eureka 的配置,其他地方都是一样的。
1、在 pom 中引入相关的包
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- spring cloud config 服务端包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- eureka client 端包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency>
2、配置文件做修改
bootstrap.yml
spring:
application:
name: config-eureka-server # 应用名称
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://gitee.com/linhongwei/SpringCloudConfig #配置文件所在仓库
username: github 登录账号
password: github 登录密码
default-label: master #配置文件分支
search-paths: config #配置文件所在根目录
force-pull: true
application.yml
server:
port: 3301
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
defaultZone: http://test:123456@localhost:9090/os/eureka/
instance:
preferIpAddress: true
3、在启动类上添加@EnableDiscoveryClient注解
4、启动服务,之后访问 Eureka ,可以看到服务已注册成功
配置 Spring Cloud Config 客户端
1、pom 中引入相关的包
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency>
2、配置文件做修改
bootstrap.yml
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
defaultZone: http://test:123456@localhost:9090/os/eureka/
instance:
preferIpAddress: true
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
spring:
profiles: prod
application:
name: config-eureka-client
cloud:
config:
label: master
profile: prod
discovery:
enabled: true
service-id: config-eureka-server
---
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: config-eureka-client
cloud:
config:
label: master #指定仓库分支
profile: dev #指定版本 本例中建立了dev 和 prod两个版本
discovery:
enabled: true # 开启
service-id: config-eureka-server # 指定配置中心服务端的server-id
application.yml
server:
port: 3302
data:
env: NaN
user:
username: NaN
password: NaN
除了注册到 Eureka 的配置外,就是配置和配置中心服务端建立关系。
其中 service-id 也就是服务端的application name。
3、启动类上添加@EnableDiscoveryClient注解
4、另外的配置实体类和 RESTController 和上面的一样,没有任何更改。
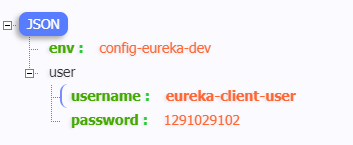
5、启动 client 端,访问 http://localhost:3302/autoShow,即可看到配置文件内容。
四、注意事项
1、在 git 上的配置文件的名字要和 config 的 client 端的 application name 对应;
2、在结合 eureka 的场景中,关于 eureka 和 git config 相关的配置要放在 bootstrap.yml 中,否则会请求默认的 config server 配置,这是因为当你加了配置中心,服务就要先去配置中心获取配置,而这个时候,application.yml 配置文件还没有开始加载,而 bootstrap.yml 是最先加载的。
五、可配置项







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决