注解
1、 注解概念
它不是注释 注释是程序员写的,给程序员看
注解,用于描述程序如何运行及在什么阶段来运行。
注解现在在实际开发中,最大的功能是用于替换配置文件(xml)。
注解是jdk1.5的新特性
可以通过反射来让注解具有功能。
注解 @xxxx
2、 常见的的注解
@Override:检查子类确实是覆盖了父类的方法。
@Deprecated:说明已经过时了
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation"):抑制程序中的警告。
@Test
public class Animal {
public void eat() {
}
}
public class Dog extends Animal{
//检查子类确实覆盖了父类的方法,如果标记该注解的方法,父类没有就会报错
@Override
public void eat() {
}
//表示该方法过时
@Deprecated
public void cry() {
}
}
public class Test1 {
//单元测试
@Test
public void test1() {
Dog dog=new Dog();
dog.eat();
dog.cry();
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")//忽略警告
public void test2() {
Dog dog=new Dog();
dog.cry();
}
}


3、 自定义注解的语法:(肉体)
声明一个注解 @interface 注解名{}
public @interface MyAnnotation{}
public @interface MyAnnotation {
}
4、 注解的本质

注解它的本质就是一个接口,这个接口需要继承 Annotation接口。
分析注解中的成员 注解本质上就是接口,接口中可以有属性方法
属性 : 例:int age();
5、 关于注解属性的类型可以有哪些?
1. 基本类型
2. String
3. 枚举类型
4. 注解类型
5. Class类型
6. 以上类型的一维数组
6、 定义注解
public @interface MyAnnotation {
int age() default -1;
String name() default "xiaohei";
Class getClss();
String [] values();
}


注解就是在你的程序代码中的某个位置加了一个标记而已。
7、 注解的反射:(灵魂)
7.1 反射注解类
public interface AnnotatedElement
7.1.1 AnnotatedElement拥有的方法

1. default boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass)判断某个Class,Method,Filed是否标记有注解
2. <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass)获得自己身上的注解
3. Annotation[] getAnnotations():得到所有的注解,包含从父类继承下来的。
4. default boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass):判断 指定的注解有没有。
有Declared和没有的区别
没有的只能获取public
有能获取public,protected,private,和默认修饰的
Class、Method、Field、Constructor等实现了AnnotatedElement接口
7.1.2 用反射获取注解
Class cls=Dog.class;
//判断Dog 是否有@MyAnnotation注解
boolean ishava = cls.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class);
if(ishava) {
System.out.println(cls.getSimpleName()+"有@MyAnnotation注解");
}else {
System.out.println(cls.getSimpleName()+"没有@MyAnnotation注解");
}
//获取Dog的所有方法
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
//获取方法名
String methodNmae=method.getName();
if("eat".equals(methodNmae)) {
boolean ishas = method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class);
if(ishas) {
System.out.println(methodNmae+"有@MyAnnotation注解");
}else {
System.out.println(methodNmae+"没有@MyAnnotation注解");
}
}
}
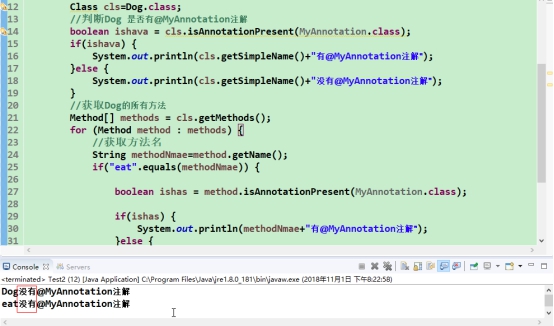
明明在类(Dog)和方法eat中标记了注解@MyAnnotation为什么获取不到
改写代码发现可以获取到@Deprecated的注解
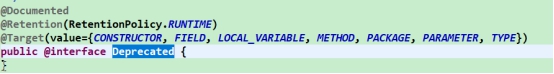
通过JDK的注解发现注解上还有注解(元注解)
7.2 元注解
自定义的注解的存活范围(生命周期):默认是CLASS。
@Retention:作用。改变自定义的注解的存活范围。
RetentionPolicy: SOURCE CLASS RUNTIME
@Target:作用,指定该注解能用在什么地方。
ElementType:TYPE: METHOD: FIELD:
@Documented:作用,使用了@MyAnnotation的注解的类,如果@MyAnnotation注解上面 有 @Documented 注 解 , 那 么 使 用 了 @MyAnnotation 的 注 解 的 类 的 API 文 档 中 会 出 现
@MyAnnotation的身影。
@Inherited:作用,说明该注解可以被继承下去。
@Target(value= {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
int age() default -1;
String name() default "xiaohei";
Class getClss();
String [] values();
}



