软工实践寒假作业(2/2)
软工实践寒假作业(2/2)
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 2020春|S班 (福州大学) |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 软工实践寒假作业(2/2) |
| 这个作业的目标 | 学习github的使用、制定代码规范、阅读《构建之法》前三章、填写PSP表格、设计和发开疫情统计程序并进行单元测试、总结 |
| 作业正文 | 软工实践寒假作业(2/2) |
| 其他参考文献 | 博客园、简书等相关文章 |
Github仓库地址
PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 45 | 55 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 20 | 25 |
| Development | 开发 | 540 | 580 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 90 | 110 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 60 | 55 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 45 | 60 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 45 | 30 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 60 | 60 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 180 | 210 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 45 | 40 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 120 | 150 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 150 | 125 |
| Test Repor | 测试报告 | 30 | 25 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 20 | 30 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 50 |
| 合计 | 1510 | 1605 |
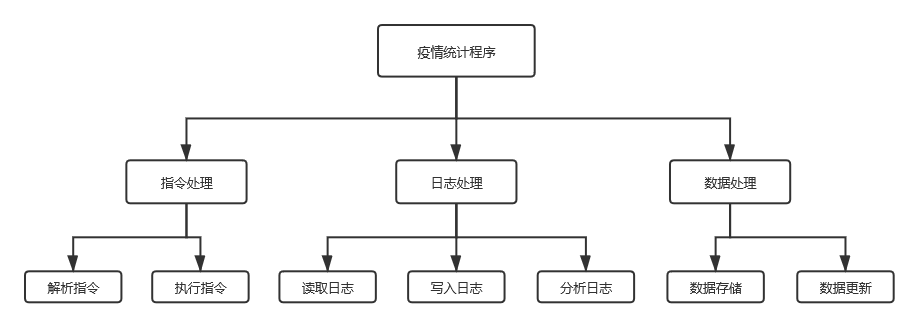
解题思路
-
程序大致流程如下所示
-
初拿到需求感到指令很陌生,不知道在控制台输入指令怎么向程序输入,以为list是自带的函数,搜索一番后恍然大悟,原来输入的指令存在String args[]里。
那么只要用for循环逐个读取指令的“项”,就能知道这条指令是为了“做什么”;然后再根据-log和-date的参数值读取相应的日志文件,逐行判断应进行的操作,就能实现对各省各个人群数量的修改,
随后再按-type和-province规定的格式输出-out到指定文件夹。 -
需要根据读取的文件的内容修改省的ip、sp、cure、dead,于是计划构建MyProvince类;因为输入的省名是字符串,考虑建立省名和省的MyProvince类的HashMap;
又因为日志中存在八种不同的操作情况,为这八个情况各设计一个MyProvince类的成员函数。根据有无-province参数有两种不同的输出情况,因此在MyProvince类中添加两个标记值,
以记录该省是在日志中被提到还是被指定输出;同时用变量isProvinceSpecified记录确定输出日志中提到的省份还是输出指定的省份。 -
通过switch-case分析读取到的控制台命令,如记录输入输出文件的路径,记录-type参数的参数值顺序,
标记-province参数值对应的省的MyProvince类实例。 -
将日志名里的日期与-date的日期相比较,获取需要的日志名列表(或提示-date参数值错误),
读取日志后逐行分析文件内容(略过空行和注释行),用空格拆分读到的行,随后通过if-else判断应进行哪些操作。 -
对各省人群操作完毕后,根据变量isProvinceSpecified和MyProvince的两个标记值确定输出日志中提到的省份还是输出指定的省份;
逐个输出需要的省份时,根据保存的type顺序(默认为ip sp cure dead)输出需要的人群。输出完成后加上注释。
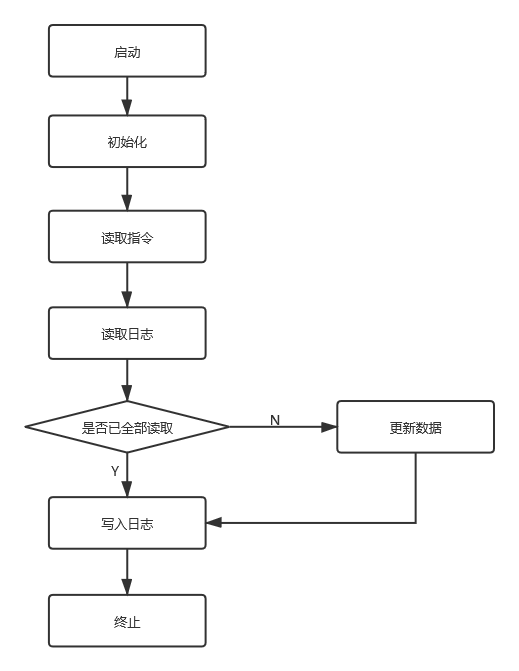
设计实现过程
包含整体逻辑和关键函数的流程图如下
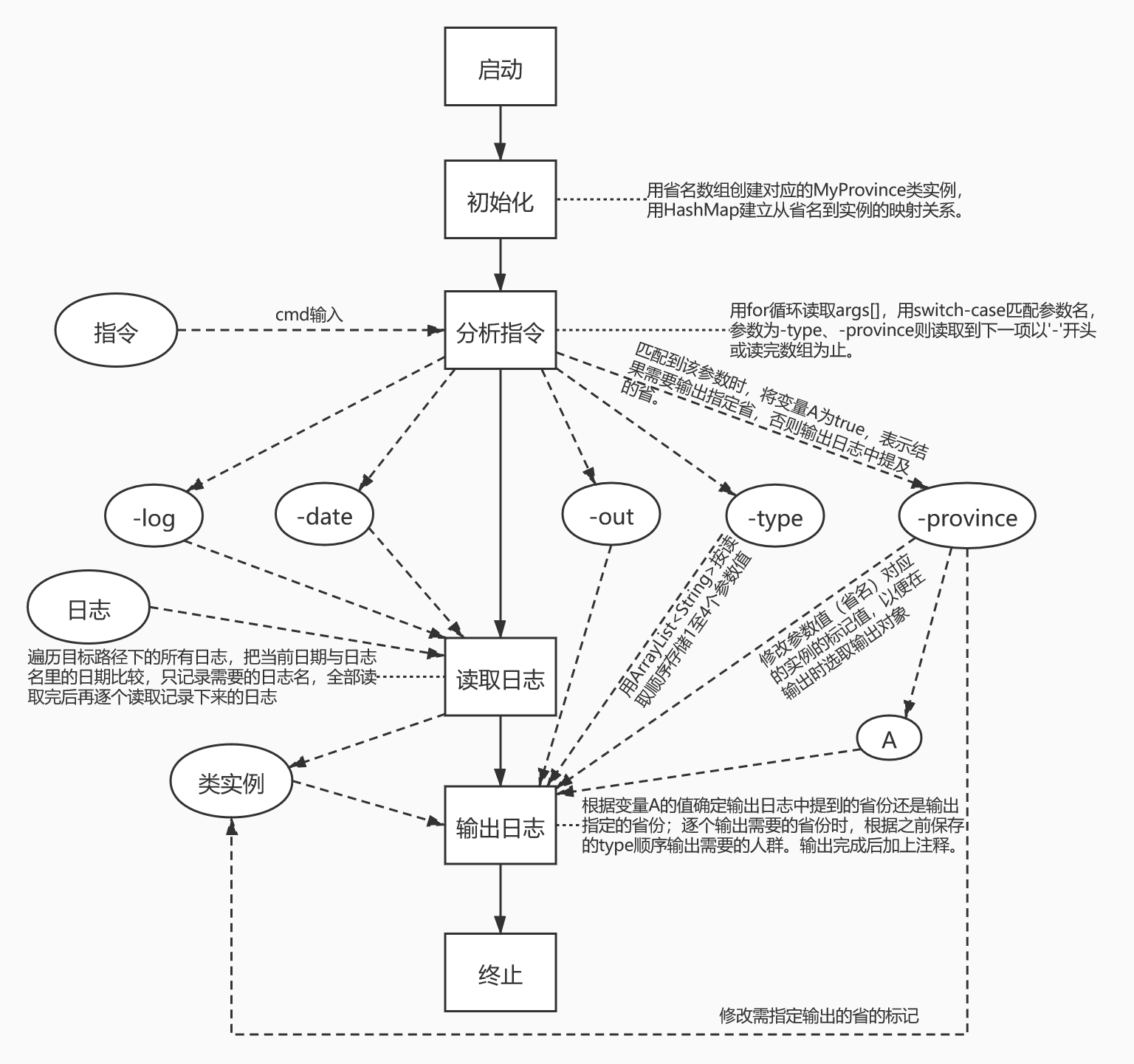
代码说明
- 类MyProvince的定义,包括省名、ip、sp、cure、dead、isMentioned(是否在日志中被提及)、isNeedPrint(是否被操作员指明需要列出)、八种人员变动情况对应的操作
class MyProvince {
public String provinceName;//“全国”,或省、直辖市的名称
public int ip;//确诊患者数量
public int sp;//疑似患者数量
public int cure;//治愈患者数量
public int dead;//死亡患者数量
public boolean isMentioned;//是否在日志中被提到过
public boolean isNeedPrint;//是否被操作员指明需要列出
public MyProvince(String provinceName) {
this.provinceName = provinceName;
this.ip = 0;
this.sp = 0;
this.cure = 0;
this.dead = 0;
this.isMentioned = false;
this.isNeedPrint = false;
if(provinceName.equals("全国")) {
this.isMentioned = true;
}
}
//<省> 新增 感染患者 n人
public void ipAdd(int n) {
this.isMentioned = true;
this.ip += n;
provinceMap.get("全国").ip += n;
}
//<省> 新增 疑似患者 n人
public void spAdd(int n) {
this.isMentioned = true;
this.sp += n;
provinceMap.get("全国").sp +=n;
}
//<省1> 感染患者 流入 <省2> n人
public void ipMove(String strProvinceName, int n) {
this.isMentioned = true;
this.ip -= n;
provinceMap.get(strProvinceName).isMentioned = true;
provinceMap.get(strProvinceName).ip += n;
}
//<省1> 疑似患者 流入 <省2> n人
public void spMove(String strProvinceName, int n) {
this.isMentioned = true;
this.sp -= n;
provinceMap.get(strProvinceName).isMentioned = true;
provinceMap.get(strProvinceName).sp += n;
}
//<省> 死亡 n人
public void peopleDead(int n) {
this.isMentioned = true;
this.ip -= n;
this.dead += n;
provinceMap.get("全国").ip -= n;
provinceMap.get("全国").dead += n;
}
//<省> 治愈 n人
public void peopleCured(int n) {
this.isMentioned = true;
this.ip -= n;
this.cure += n;
provinceMap.get("全国").ip -= n;
provinceMap.get("全国").cure += n;
}
//<省> 疑似患者 确诊感染 n人
public void spDiagnosed(int n) {
this.isMentioned = true;
this.sp -= n;
this.ip += n;
provinceMap.get("全国").sp -= n;
provinceMap.get("全国").ip += n;
}
//<省> 排除 疑似患者 n人
public void spExclude(int n) {
this.isMentioned = true;
this.sp -= n;
provinceMap.get("全国").sp -= n;
}
}
- main函数,init为初始化函数,processCmd为初步处理指令函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
InfectStatistic infectStatistic = new InfectStatistic();
infectStatistic.init();
infectStatistic.processCmd(args);
}
- 准备阶段,准备好需要的HashMap,方便之后通过省名字符串找到省实例
//建立省份名与省份类实例的HashMap
HashMap<String, MyProvince>provinceMap = new HashMap<String, MyProvince>();
//省份名数组,按首字母顺序排列,“全国”排最前
String [] AllProvinceName = {
"全国","安徽","北京","重庆","福建","甘肃","广东","广西",
"贵州","海南","河北","河南","黑龙江","湖北","湖南","吉林",
"江苏","江西","辽宁","内蒙古","宁夏","青海","山东","山西",
"陕西","上海","四川","天津","西藏","新疆","云南","浙江",
};
//初始化HashMap,建立对应关系
public void init() {
provinceMap.clear();
for(String strProvinceName:AllProvinceName) {
MyProvince myProvince = new MyProvince(strProvinceName);
provinceMap.put(strProvinceName, myProvince);
}
}
- 初步处理指令,将得到的处理后的参数值送往执行指令函数
//处理输入的命令
public void processCmd(String[] args) {
if(args.length>1 && args[0].equals("list")) {
String logPath = new String("");
String outPath = new String("");
String date = new String("");
//int[] type = new int[] {1,1,1,1};//默认输出四种人群。更新:难以按指定顺序输出。已修改
//默认依ip,sp,cure,dead顺序输出四种人群,读取-type参数时重置为空
ArrayList<String> type = new ArrayList<String>();
type.add("ip");
type.add("sp");
type.add("cure");
type.add("dead");
boolean isProvinceSpecified = false;//该项为false,输出所有日志中提到的省份,为true输出指定的省份
for(int index = 1;index<args.length;index++) {
switch(args[index]) {
case "-log":
logPath = args[index+1];
index++;
break;
case "-out":
outPath = args[index+1];
index++;
break;
case "-date":
date=args[index+1];
index++;
break;
case "-type":
type.clear();
while(index+1<args.length && args[index+1].charAt(0)!='-') {
if(args[index+1].equals("ip")||args[index+1].equals("sp")
||args[index+1].equals("cure")||args[index+1].equals("dead")) {
type.add(args[index+1]);
}
index++;
}
break;
case "-province":
isProvinceSpecified = true;
while(index+1<args.length && args[index+1].charAt(0)!='-') {
provinceMap.get(args[index+1]).isNeedPrint = true;
index++;
}
break;
}
}
excuteCmd(logPath,outPath,date,type,isProvinceSpecified);
}
}
- 执行指令函数,判断读、写路径是否为空后依次进行日志读取和写入操作
//执行输入的命令
public void excuteCmd(String logPath,String outPath,String date,ArrayList<String> type,boolean isProvinceSpecified) {
if(logPath.equals("")||outPath.equals("")) {
System.out.println("输入、输出路径均不能为空!");
System.exit(0);
}
//读取指定日期以及之前的所有log文件
readLogs(logPath,date);
try {
//带格式输出到指定文件
writeLog(outPath,type,isProvinceSpecified);
} catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("日志写入错误!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
- 把需要读取的文件存入File[] tempList,变量isDateAllowed用于判断当前日期是否可用(默认为不可用,出现不早于当前日期的日志时置为可用)
//读取指定日期以及之前的所有log文件
public void readLogs(String logPath,String date) {
ArrayList<String> files = new ArrayList<String>();
File file = new File(logPath);
File[] tempList = file.listFiles();
//isDateAllowed,默认为日期超出范围(false),直到出现不早于date的日期时,置为true
boolean isDateAllowed = false;
//将所有不晚于date的.log.txt文件的绝对路径添加到files,并判断日期是否超出范围
for (int i = 0; i < tempList.length; i++) {
if (tempList[i].isFile()) {
//若未指明日期,无需判断,读取所有logs
if (date.equals("")) {
isDateAllowed = true;
files.add(tempList[i].toString());
} else {//若指明日期,需要判断日期是否合理,选择不晚于该日期的logs
//fileName,不包含路径、后缀(也就是说只有日期yyyy-mm-dd)
String fileName = tempList[i].getName().substring(0,10);
//当d1早于d2,dateCompare返回-1,files只记录所有不晚于date的日期
if(dateCompare(date,fileName) != -1) {
files.add(tempList[i].toString());
}
if(dateCompare(date, fileName) != 1) {
isDateAllowed = true;
}
}
}
}
//日期超出范围提示
if(!isDateAllowed) {
System.out.println("日期超出范围!");
System.exit(0);
}
//逐个读取files中的路径对应的文件
for(int i = 0;i < files.size();i++) {
try{
readOneLog(files.get(i));
}catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("日志读取错误!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
- 逐行读取文件,对读取的每一行进行拆分,用if-else结构与八种情况进行匹配,并用MyProvince的成员函数执行相应操作
//读取单个文件
public void readOneLog(String logPathName) throws IOException {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(logPathName);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String line = new String("init");
while (line!=null){
line = bufferedReader.readLine();
if(line!=null && !line.startsWith("//")) {//忽略空行和注释
//line为当前行
String [] wordString = line.split("\\s+");//按空格分割当前行
if(wordString[1].equals("新增")) {
if(wordString[2].equals("感染患者")) {
int num = getPeopleNum(wordString[3]);
provinceMap.get(wordString[0]).ipAdd(num);
} else if(wordString[2].equals("疑似患者")) {
int num = getPeopleNum(wordString[3]);
provinceMap.get(wordString[0]).spAdd(num);
}
} else if(wordString[2].equals("流入")) {
if(wordString[1].equals("感染患者")) {
int num = getPeopleNum(wordString[4]);
provinceMap.get(wordString[0]).ipMove(wordString[3], num);
} else if(wordString[1].equals("疑似患者")) {
int num = getPeopleNum(wordString[4]);
provinceMap.get(wordString[0]).spMove(wordString[3], num);
}
} else if(wordString[1].equals("死亡")) {
int num = getPeopleNum(wordString[2]);
provinceMap.get(wordString[0]).peopleDead(num);
} else if(wordString[1].equals("治愈")) {
int num = getPeopleNum(wordString[2]);
provinceMap.get(wordString[0]).peopleCured(num);
} else if(wordString[2].equals("确诊感染")) {
int num = getPeopleNum(wordString[3]);
provinceMap.get(wordString[0]).spDiagnosed(num);
} else if(wordString[1].equals("排除")){
int num = getPeopleNum(wordString[3]);
provinceMap.get(wordString[0]).spExclude(num);
}
}
}
bufferedReader.close();
fileReader.close();
}
- 对各省人群操作完毕后,根据变量isProvinceSpecified(即上面流程图中的变量A)和MyProvince的两个标记值确定输出日志中提到的省份还是输出指定的省份; 逐个输出需要的省份时,根据保存的type顺序(默认为ip sp cure dead)输出需要的人群。输出完成后加上注释。
//带格式输出到指定文件
public void writeLog(String outPath,ArrayList<String> type,boolean isProvinceSpecified) throws IOException {
String outStr = new String();
//构建输出字符串
//没有"-province"参数时,列出全国的数据,以及日志中涉及到的省的数据
if(!isProvinceSpecified) {
for(int i = 0;i < AllProvinceName.length;i++) {
if(provinceMap.get(AllProvinceName[i]).isMentioned) {
outStr += getStrByType(type,provinceMap.get(AllProvinceName[i]));
}
}
}
//有"-province"参数时,指定的省必须列出
else {
for(int i=0;i<AllProvinceName.length;i++) {
if(provinceMap.get(AllProvinceName[i]).isNeedPrint) {
outStr += getStrByType(type,provinceMap.get(AllProvinceName[i]));
}
}
}
//加上注释
outStr += "// 该文档并非真实数据,仅供测试使用";
File file = new File(outPath);
BufferedWriter writer = null;
FileOutputStream writerStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(writerStream, "UTF-8"));
StringBuilder strBuild = new StringBuilder(outStr);
writer.write(strBuild.toString());
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
//按-type指定的顺序输出curProvince的防疫情况
public String getStrByType(ArrayList<String> type,MyProvince curProvince) {
String str = new String();
str += curProvince.provinceName;
for(int i = 0;i < type.size();i++) {
switch(type.get(i)){
case "ip":
str += " " + "感染患者" + curProvince.ip + "人";
break;
case "sp":
str += " " + "疑似患者" + curProvince.sp + "人";
break;
case "cure":
str += " " + "治愈" + curProvince.cure + "人";
break;
case "dead":
str += " " + "死亡" + curProvince.dead + "人";
break;
}
}
str += "\n";
return str;
}
单元测试截图和描述
- 测试过程:
- 首先选择一条指令str1,和执行这条指令可以得到的正确的输出日志ListOut1.txt。
- 将指令分割并存在字符串数组中,将字符串数组输入main函数,如此测试类就会根据指令的内容将统计结果输出到output1.txt。
- 然后设计一个根据路径读取文件内容并以字符串类型返回文件内容的函数getFileString。
- 随后通过语句assertEquals(getFileName(ListOut1.txt),getFileName(output1.txt))判断程序是否通过该次测试。
- 取字符串str2~str10,重复以上操作。总共进行十组测试。
- 备注:两个文件的路径均是完整路径,此处为了方便阅读而写成文件名,与实际测试时无关。输出日志格式为UTF-8无BOM。
- 测试源码:
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class InfectStatisticTest {
String str1 = new String("list -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output1.txt -date 2020-01-22");
String str2 = new String("list -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output2.txt -date 2020-01-22 -province 福建 河北");
String str3 = new String("list -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output3.txt -date 2020-01-23 -type cure dead ip -province 全国 浙江 福建");
String str4 = new String("list -type cure dead ip -province 全国 浙江 福建 -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output4.txt -date 2020-01-23");
String str5 = new String("list -type cure dead ip -province 全国 浙江 福建 -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output5.txt -date 2020-01-27");
String str6 = new String("list -province 全国 浙江 福建 -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output6.txt -date 2020-01-27");
String str7 = new String("list -type cure dead ip -province 全国 浙江 福建 -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output7.txt");
String str8 = new String("list -type cure dead ip -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output8.txt -date 2020-01-27");
String str9 = new String("list -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output9.txt");
String str10 = new String("list -province 全国 浙江 福建 湖北 -type cure sp -log D:\\log_in\\ -out D:\\log_out\\output10.txt");
String [] strA = str1.split("\\s+");
String [] strB = str2.split("\\s+");
String [] strC = str3.split("\\s+");
String [] strD = str4.split("\\s+");
String [] strE = str5.split("\\s+");
String [] strF = str6.split("\\s+");
String [] strG = str7.split("\\s+");
String [] strH = str8.split("\\s+");
String [] strI = str9.split("\\s+");
String [] strJ = str10.split("\\s+");
public static String getFileString(String logPathName) throws IOException {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(logPathName);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String line = new String("init");
String str = new String("");
while (line!=null){
line = bufferedReader.readLine();
if(line!=null && !line.startsWith("//")) {//忽略空行和注释
str += line;
}
}
bufferedReader.close();
fileReader.close();
return str;
}
@Test
void testMain() {
InfectStatistic.main(strA);
InfectStatistic.main(strB);
InfectStatistic.main(strC);
InfectStatistic.main(strD);
InfectStatistic.main(strE);
InfectStatistic.main(strF);
InfectStatistic.main(strG);
InfectStatistic.main(strH);
InfectStatistic.main(strI);
InfectStatistic.main(strJ);
try{
//若两文件内容一致,则可以通过测试
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strA[4]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut1.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strB[4]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut2.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strC[4]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut3.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strD[12]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut4.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strE[12]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut5.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strF[8]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut6.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strG[12]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut7.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strH[8]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut8.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strI[4]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut9.txt"));
assertEquals(InfectStatisticTest.getFileString(strJ[12]),InfectStatisticTest.getFileString("D:\\log_out\\result\\ListOut10.txt"));
} catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("日志读取错误!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
-
测试截图(取部分例子):
-
如图,这是测试前的文件夹,result文件夹用于存放正确输出日志,log_out文件夹用于存放测试输出日志

-
如图,这是测试后的状态,可以看到testMain里的十个例子均通过测试
-
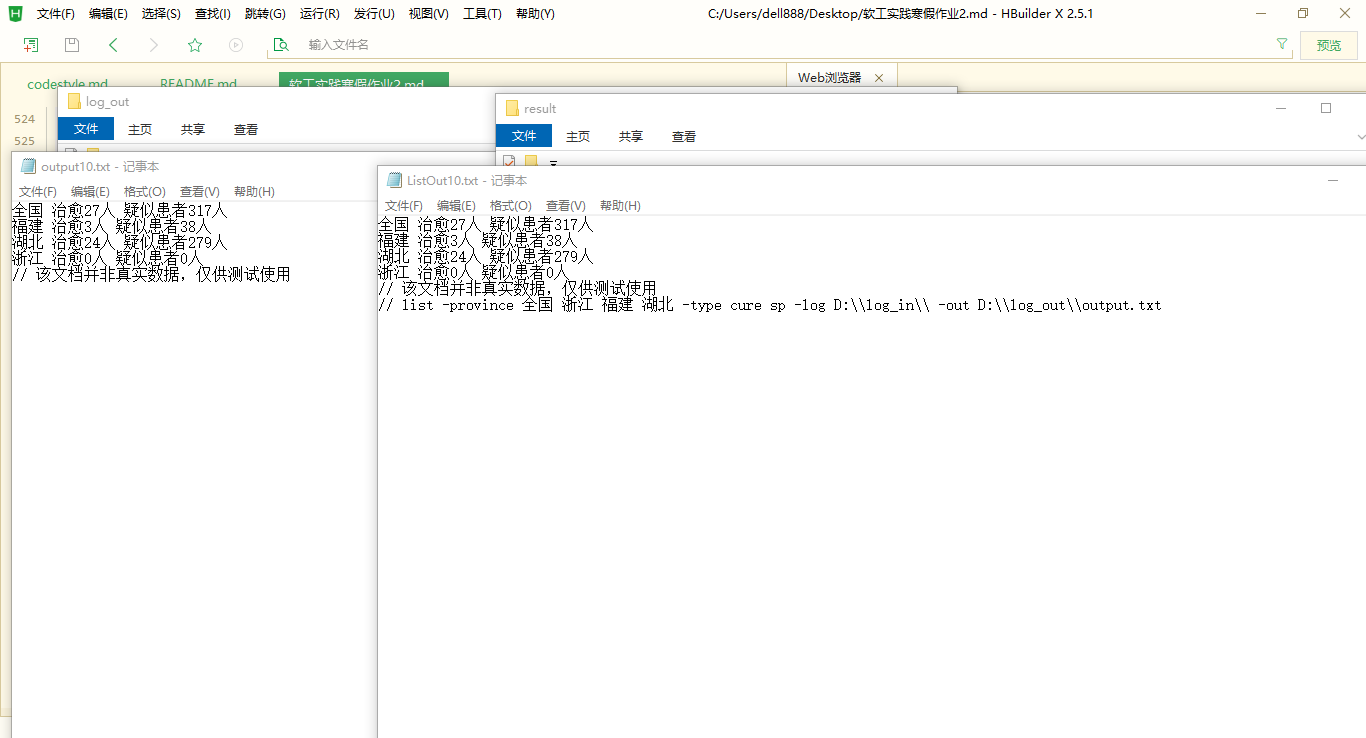
如图,这是测试后的文件夹,output1~output10是测试过程中产生的文件

-
如图,随机打开两个文件夹中对应的文件(数字编号相同),可以发现他们的内容(除了注释),是一样的——当然,测试程序已经自动检验过十组文件每组中的两个是否一致了
单元测试覆盖率优化和性能测试
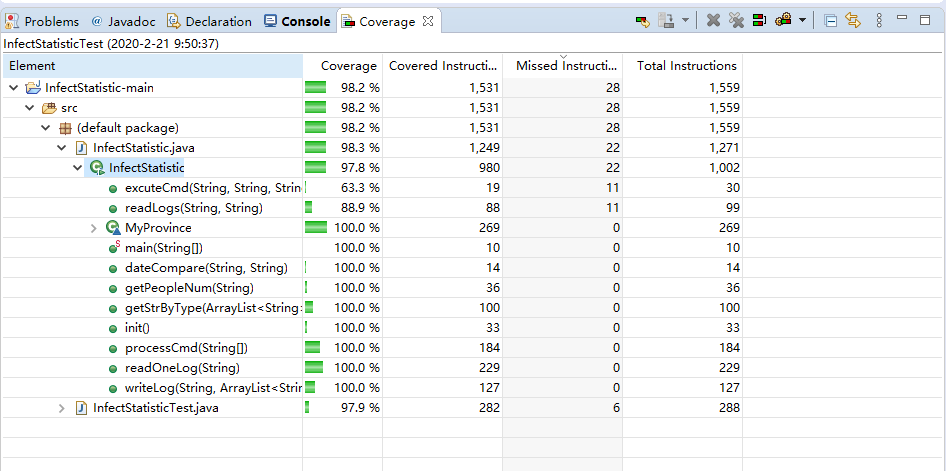
- 覆盖率如图,可以看到覆盖率很高,最低的excuteCmd函数具体代码在图片下方,原因可能是判断是否输入了路径和catch部分的代码没有被测试
//执行输入的命令
public void excuteCmd(String logPath,String outPath,String date,ArrayList<String> type,boolean isProvinceSpecified) {
if(logPath.equals("")||outPath.equals("")) {
System.out.println("输入、输出路径均不能为空!");
System.exit(0);
}
//读取指定日期以及之前的所有log文件
readLogs(logPath,date);
try {
//带格式输出到指定文件
writeLog(outPath,type,isProvinceSpecified);
} catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("日志写入错误!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
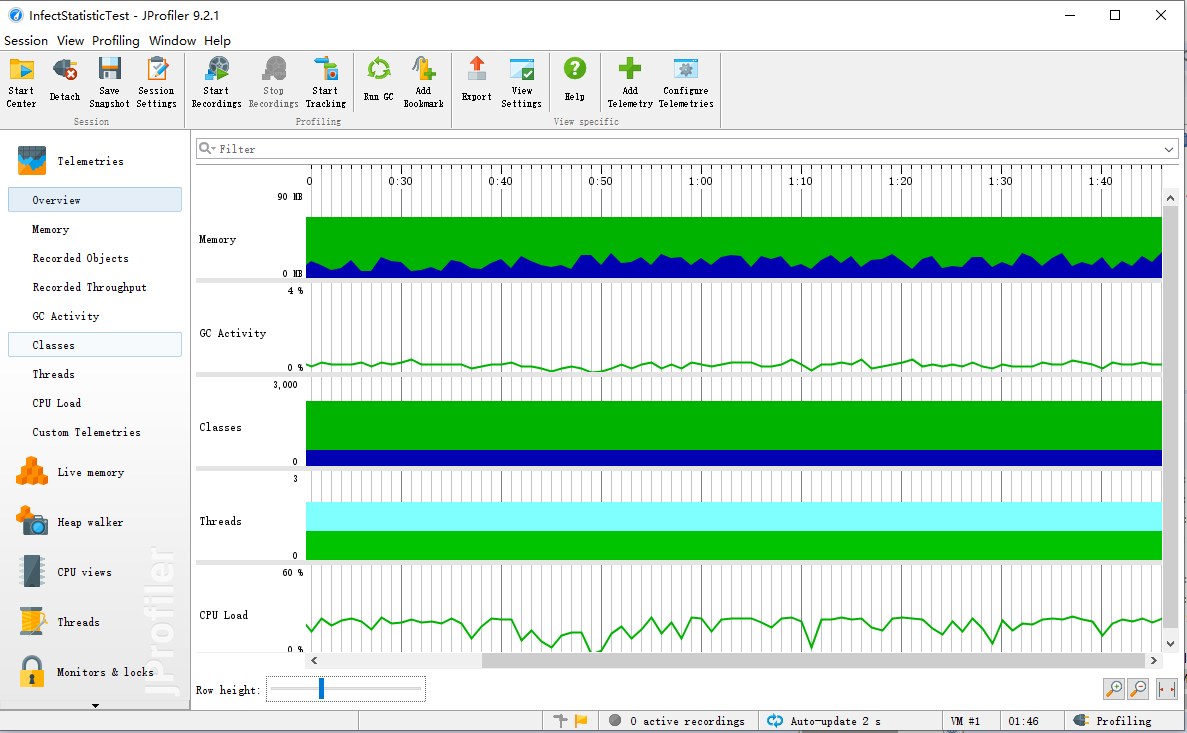
- 性能测试如图
代码规范
心路历程与收获
- 从大一以来所写的程序基本都是“莽”出来的,基本没有所谓的规划,用在检验程序可靠性上的时间也寥寥无几。
因此拿出来的程序基本都毫无拓展性可言,也不能应对复杂的情况——比如需要处理的数据提升若干数量级,或者有预期之外的输入,是否还能在可以接受的时间范围内,保持程序的正确性,
给出需要的结果。换句话说,基本没有考虑程序的效率和可靠性。当然,也没有太多的考虑程序的规范性和可读性...... - 然而,在解决实际问题的过程中,程序在保证正确率的情况下,提高程序处理问题的效率,以及面对新需求时是否能很好的拓展新功能,是很重要的。
- 就像作者说的那样,也许2000行的程序还能“埋头苦写”,但是到了20000行甚至数十万行,情况就完全不一样了。
因此,在处理某个项目时,需要先做好各个阶段的规划工作,以及在软件本身完成后,设计一套有效的、自动化的、可以维护的自动化测试流程也是很重要的。
这样可以及时地发现软件或程序中地错误并修改。 - 我们须不断提升自身的技术和能力,学习用工程的思维分析问题,以团队的方式处理问题,以期有一天能创造出“合格”的软件。
学习路线相关的5个仓库
Spring Boot入门学习项目。适合对Spring Boot不熟悉的新手。
《Spring Boot基础教程》的程序样例。
Java设计模式,是在设计应用程序或系统时可用来解决常见问题的参考手册。
用spring mvc写的个人博客网站。项目很小但较为完整。
mall项目是一套电商系统,包括前台商城系统及后台管理系统,基于SpringBoot+MyBatis实现,采用Docker容器化部署。