[Nest] 01.初见nest.js
nest 介绍
Nest 是一个用于构建高效,可扩展的 Node.js 服务器端应用程序的框架.它使用渐进式 JavaScript,内置并完全支持 TypeScript(但仍然允许开发人员使用纯 JavaScript 编写代码)并结合了 OOP(面向对象编程),FP(函数式编程)和 FRP(函数式响应编程)的元素.
在底层,Nest 使用强大的 HTTP Server 框架,如 Express(默认)和 Fastify.Nest 在这些框架之上提供了一定程度的抽象,同时也将其 API 直接暴露给开发人员.这样可以轻松使用每个平台的无数第三方模块.
为什么用 nest
近年来,感谢 Node.js,JavaScript 已成为前端和后端应用程序的网络“通用语言”.这产生了令人敬畏的项目,如 Angular,React 和 Vue,它们提高了开发人员的工作效率,并能够构建快速,可测试和可扩展的前端应用程序.然而,虽然 Node(和服务器端 JavaScript )存在大量优秀的库,帮助器和工具,但它们都没有有效地解决主要问题 - 架构.
Nest 提供了一个开箱即用的应用程序架构,允许开发人员和团队创建高度可测试,可扩展,松散耦合且易于维护的应用程序
环境搭建
您可以使用 Nest CLI 构建项目,也可以克隆启动项目(两者都会产生相同的结果).
安装 cli
npm i -g @nestjs/cli
创建项目目录
nest new project-name
更简单些可以直接 clone 官方预设项目
git clone https://github.com/nestjs/typescript-starter.git project
cd project
npm install
npm run start
新创建的 project-name 目录结构
├── README.md
├── node_modules
├── nodemon-debug.json
├── nodemon.json
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
├── src
├── test
├── tsconfig.json
├── tsconfig.spec.json
├── tslint.json
└── webpack.config.js
src 是源码目录
├── app.controller.ts # 根控制器
├── app.controller.spec.ts # 根控制器测试文件
├── app.module.ts # 应用程序根模块
├── app.service.ts # 根服务
└── main.ts # 应用程序入口文件
main.ts 代码
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
async function bootstrap() {
// 创建实例
const app = await NestFactory.create();
// 监听6688端口
await app.listen(6688);
}
bootstrap();
通过 async 和 await 并使用了 NestFactory 核心类创建一个 Nest 应用实例.NestFactory 暴露了一些静态方法用于创建应用实例,create() 方法返回一个实现 INestApplication 接口的对象,.并且监听 6688 接口
开启应用
npm start
启动 HTTP 服务器,项目会启动并监听一个接口 6688,此时访问 localhost:6688 或者 127.0.0.1:6688 可以看到 nest 信息
Nest 可以在创建适配器后使用任何 Node HTTP 框架. 有两个支持开箱即用的 HTTP 平台:express 和 fastify. 您可以选择最适合您需求的产品.
express 和 fastify
当使用 express
npm i --save @nestjs/platform-express colors ip
main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { NestExpressApplication } from '@nestjs/platform-express';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import { blue } from 'colors';
import { address } from 'ip';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create<NestExpressApplication>(AppModule);
const port = 6333;
await app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(
blue(
`当前服务运行在 \n http://localhost:${port} \n http://${address()}:${port}`,
),
);
});
}
bootstrap();
当使用 fastify
npm i --save @nestjs/platform-fastify
main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import {
FastifyAdapter,
NestFastifyApplication,
} from '@nestjs/platform-fastify';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create<NestFastifyApplication>(
AppModule,
new FastifyAdapter(),
);
await app.listen(6688);
}
bootstrap();
不管是使用 express 还是 fastify,它都会暴露自己的应用程序界面.它们分别是 NestExpressApplication 和 NestFastifyApplication.将类型传递给 NestFactory.create() 方法时,就可以访问底层平台 API,app 对象可以调用 express 或者 fastify 的方法.当然该类型可以不指定.
快速创建模块
nest 主要有三个核心概念:模块 Module, 控制器 Controller, 服务与依赖注入 Provider
- 模块 Module: 用于将代码拆分为独立的和可重用的模块,例如用户信息模块,然后将该用户模块的控制器和服务集合进来,最后直接将用户模块导入到根 Module 就可以使用了.
- 控制器 Controller: 负责处理客户端传入的请求参数并向客户端返回响应数据.nest.js 提供许多 http 请求的装饰器,如例如@Body(),@Post()等.控制器不需要定义任何诸如从客户端获取数据、验证用户输入等工作,这些都是交给服务 Provider 处理,通过把任务委托给各种服务,可以让控制器类更加精简、高效.
- 服务 Provider :在这里处理所有请求执行逻辑,在控制器中通过 constructor 函数以依赖注入的方式实现.
直接用命令的方式创建模块,控制器 , 服务
// 新建模块
nest g mo user
// 新建controller
nest g co user
// 新建service
nest g s user
nest 命令全称和简称
- class (alias: cl) 类
- controller (alias: co) 控制器
- decorator (alias: d) 装饰器
- exception (alias: e) 异常捕获
- filter (alias: f) 过滤器
- gateway (alias: ga) 网关
- guard (alias: gu) 守卫
- interceptor (alias: i) 拦截器
- middleware (alias: mi) 中间件
- module (alias: mo) 模块
- pipe (alias: pi) 管道
- provider (alias: pr) 供应商
- service (alias: s) 服务
cli 还有个好用的命令是nest info用来查询当前项目的情况
创建路由
修改 user/user.controller.ts
import { Controller, Post, Body, Get } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
@Get()
public renderLoginPage(): string {
return `<div style="color:blue">
<form action="/collect/create" method="post">
<div>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input name="name" type="text" id="name">
</div>
<div>
<label for="mail">E-mail:</label>
<input name="email" type="email" id="mail">
</div>
<div>
<label for="msg">description:</label>
<textarea name="description" id="description"></textarea>
</div>
<button type="submit">Send your message</button>
</form>
</div>`;
}
@Post('login')
public login(
@Body() loginInfo: { name: string; email: string; description: string },
): string {
return `<div>${loginInfo.name} + ${loginInfo.email} + ${loginInfo.description}</div>`;
}
}
重新执行 start 命令,然后在http://localhost:6333/user进行表单填写,然后就是进入 login 查看新息
Nest 请求装饰器
- @Get()
- @Post()
- @Put()
- @Delete()
- @Patch()
- @Options()
- @Head()
- @All()
HTTP 没有 All 方法,这是一个快捷方法用来接收任何类型的 HTTP 请求.
nodemon
nodemon 用来监视 node.js 应用程序中的任何更改并自动重启服务,非常适合用在开发环境中.
npm install --save-dev nodemon
在 nodemon.json 中添加配置
{
"watch": ["src"],
"ext": "ts,tsx",
"ignore": [
"src/**/*.spec.ts",
"dist/*",
"docs/*",
"node_modules/*",
"public/*",
"test/*",
"static/*"
],
"delay": "2500",
"exec": "ts-node -r tsconfig-paths/register ./src/main.ts"
}
在 package.json 中 scripts 中添加
"dev": "export NODE_ENV=development && nodemon",
随便修改内容会发现服务会自动重启,适合用于开发模式
设置视图-hbs模板引擎
Nest 默认使用 Express 库,为了创建一个简单的 MVC(模型 - 视图 - 控制器)应用程序,我们必须安装一个模板引擎
npm install --save hbs
然后在 main.ts 文件中进行设置
const app = await NestFactory.create<NestExpressApplication>(AppModule);
// 设置public文件存放文件夹
app.useStaticAssets(join(__dirname, '..', 'public'), {
prefix: '/public/',
});
// 设置静态文件存放文件夹
app.useStaticAssets(join(__dirname, '..', 'static'), {
prefix: '/static/',
});
// 设置视图文件夹
app.setBaseViewsDir(join(__dirname, '..', '/views'));
// 设置视图引擎
app.setViewEngine('hbs');
// 设置视图部件的文件夹
registerPartials(join(__dirname, '..', '/views/partials'));
新建 hbs 文件
hbs 的基本使用
- {{value}}, handlebars 模板会自动匹配相应的数值,对象甚至是函数
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
<p>{{content}}</p>
- 分离 html 模块,小模板分离
// 直接引入login_view.hbs
{{> login_view}}
- hbs 的 foreach 循环
{{#each items}}
{{label}}: {{@foo}}
{{/each}}
- if 判断
{{#if names.length}}
<ul>
{{#each names}}
<li>{{this}}</li>
{{/each}}
</ul>
{{/if}}
在 views 文件夹中新建 login.hbs
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>login</title>
</head>
<body>
{{ login }}
</body>
</html>
同时修改 user.controller.ts
import { Controller, Post, Get, Render } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('')
export class UserController {
@Get('login')
@Render('login.hbs')
public login(): string {
return '';
}
@Get('register')
@Render('register.hbs')
public register(): string {
return '';
}
}
添加 webpack 进行文件监听
npm i --save-dev webpack webpack-cli webpack-node-externals ts-loader
配置 webpack
然后,我们需要在根目录创建一个 webpack.config.js.
const webpack = require('webpack');
const path = require('path');
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals');
module.exports = {
entry: ['webpack/hot/poll?100', './src/main.ts'],
watch: true,
target: 'node',
externals: [
nodeExternals({
whitelist: ['webpack/hot/poll?100'],
}),
],
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.tsx?$/,
use: 'ts-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/,
},
],
},
mode: 'development',
resolve: {
extensions: ['.tsx', '.ts', '.js'],
},
plugins: [new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin()],
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'server.js',
},
};
热模块更换
在 main.ts 中添加 webpack 的配置
declare const module: any;
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create<NestExpressApplication>(AppModule);
addEngine(app);
const port = 6333;
await app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(blue(`http server is start at ===> http://localhost:${port}`));
});
if (module.hot) {
module.hot.accept();
module.hot.dispose(() => app.close());
}
}
bootstrap();
在 package.json 中添加
"webpack": "webpack --config webpack.config.js"
关闭 node 进程,重新执行 dev 和 webpack 命令
添加 swagger
npm install --save @nestjs/swagger swagger-ui-express
在 main.ts 中添加 swagger
import { DocumentBuilder, SwaggerModule } from '@nestjs/swagger';
......
const options = new DocumentBuilder()
.setTitle('平头哥')
.setDescription('后端API接口文档')
.setVersion('1.0')
.addTag('nestjs')
.build();
const document = SwaggerModule.createDocument(app, options);
SwaggerModule.setup('swagger', app, document);
......
然后输入http://localhost:6333/swagger/就可以看到swagger自动生成的文档
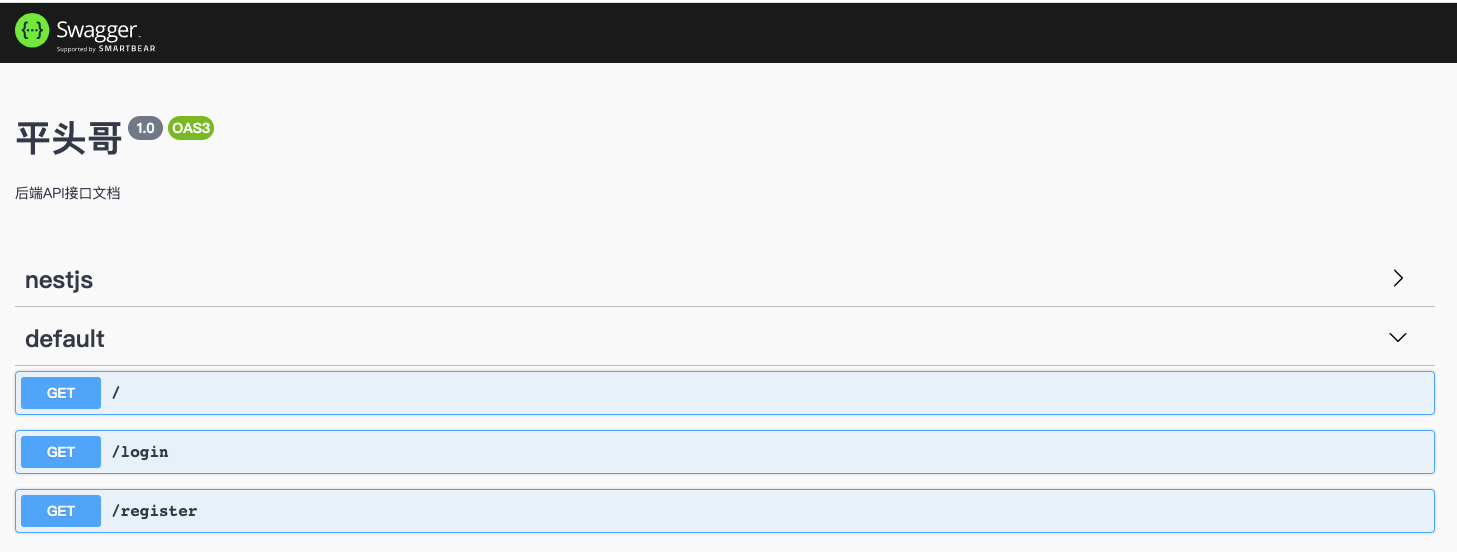
常用装饰器
- ApiProperty 标注 dto 的字段
- ApiQuery 发起查询的字段
- ApiBody 请求主体输入
- ApiTags 添加指定标签
- ApiHeader 添加自定义标头
- ApiResponse 添加自定义响应
添加数据库
为了与 SQL 和 NoSQL 数据库集成,Nest 提供了 @nestjs/typeorm 包.Nest 使用 TypeORM 是因为它是 TypeScript 中最成熟的对象关系映射器( ORM ).因为它是用 TypeScript 编写的,所以可以很好地与 Nest 框架集成.
为了开始使用它,我们首先安装所需的依赖项.在本章中,我们将演示如何使用流行的 Mysql , TypeORM 提供了对许多关系数据库的支持,比如 PostgreSQL 、Oracle、Microsoft SQL Server、SQLite,甚至像 MongoDB 这样的 NoSQL 数据库.我们在本章中介绍的过程对于 TypeORM 支持的任何数据库都是相同的.您只需为所选数据库安装相关的客户端 API 库.
npm install --save @nestjs/typeorm typeorm mysql moment
修改 app.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { TypeOrmModule } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
@Module({
imports: [TypeOrmModule.forRoot()],
})
export class AppModule {}
创建 ormconfig.json,可以将 forRoot()配置抽离出来,不传入没有任何选项调用 forRoot()
{
"type": "mysql",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 3306,
"username": "root",
"password": "root",
"database": "test",
"entities": ["dist/**/*.entity{.ts,.js}"], // 自动加载实体
"synchronize": true
}
一旦完成,TypeORM 连接和 EntityManager 对象就可以在整个项目中注入(不需要导入任何模块)
创建 user/entity/user.entity.ts
import { Entity, Column, OneToMany, PrimaryGeneratedColumn } from 'typeorm';
import { ApiProperty } from '@nestjs/swagger';
@Entity({ name: 'user' })
export class User {
@ApiProperty()
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
public id: number;
@ApiProperty()
@Column({ length: 40 })
public account: string;
@ApiProperty()
@Column({ length: 100 })
public avatarUrl: string;
@ApiProperty()
@Column({ length: 40 })
public name: string;
@ApiProperty()
@Column({ length: 40 })
public role: string;
@ApiProperty()
@Column('int')
public createdAt: number;
@ApiProperty()
@Column('int')
public updatedAt: number;
@ApiProperty()
@Column({ length: 250 })
public password: string;
}
user 的增删改查
修改 user/user.controller.ts
import { ApiTags } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import {
Controller,
Get,
Param,
Post,
Body,
Delete,
Put,
Render,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { User } from './entity/user.entity';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
interface IResult {
code: number;
message: string;
data?: any;
}
@Controller('')
export class UserController {
constructor(private readonly userService: UserService) {}
@Get('login')
@Render('login.hbs')
public renderLogin(): string {
return '';
}
@Get('register')
@Render('register.hbs')
public async renderRegister() {
return '';
}
/**
* 用户注册
* @param user
*/
@ApiTags('用户注册')
@Post('api/user/register')
public async register(
@Body()
user: {
account: string;
password: string;
},
): Promise<IResult> {
const result = await this.userService.register(user);
return { code: 200, message: '注册成功', data: result };
}
@ApiTags('删除用户')
@Delete('api/user/:id')
async remove(@Param() id: number): Promise<IResult> {
const data = await this.userService.remove(id);
return { code: 200, message: '删除用户成功', data };
}
@ApiTags('更新用户')
@Put('api/user/:id')
async update(@Param() id: number, updateInput: User): Promise<IResult> {
const data = await this.userService.update(id, updateInput);
return { code: 200, message: '更新用户成功', data };
}
@ApiTags('查找用户')
@Get('api/user/:id')
async findOne(@Param() id: number): Promise<IResult> {
const data = await this.userService.findOneWithPostsById(id);
return { code: 200, message: '查询用户成功', data };
}
@ApiTags('查找全部用户')
@Get('api/user/')
async findAll(): Promise<IResult> {
const data = await this.userService.findAll();
return { code: 200, message: '查询所有用户成功', data };
}
}
修改 user/user.service.ts
import { HttpException, Injectable, OnModuleInit } from '@nestjs/common';
import { User } from './entity/user.entity';
import { InjectRepository } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
import { Repository } from 'typeorm';
import * as moment from 'moment';
@Injectable()
export class UserService implements OnModuleInit {
async onModuleInit() {
if (await this.findOneByAccount('admin')) {
return;
}
// 初始化系统管理员
const admin = this.userRepository.create({
account: 'admin',
password: 'admin',
name: '系统管理员',
role: 'admin',
avatarUrl: '',
createdAt: moment().unix(),
updatedAt: moment().unix(),
});
await this.userRepository.save(admin);
}
constructor(
@InjectRepository(User)
private readonly userRepository: Repository<User>,
) {}
public async findAll(): Promise<User[]> {
return await this.userRepository.find();
}
public async register(createUserData: any): Promise<User> {
const user = await this.findOneByAccount(createUserData.account);
if (user) {
throw new HttpException('账号已存在', 409);
}
const assign = {
...createUserData,
name: '系统管理员',
role: 'admin',
avatarUrl: '',
createdAt: moment().unix(),
updatedAt: moment().unix(),
password: createUserData.password,
};
return await this.userRepository.save(assign);
}
/**
* 用户登录
* @param account 登录账号
* @param password 登录密码
*/
public async login(account: string, password: string): Promise<User> {
const user = await this.findOneByAccount(account);
if (!user) {
throw new HttpException('登录账号有误', 406);
}
if (!user.password) {
throw new HttpException('登录密码有误', 409);
}
return user;
}
/**
* 删除用户
* @param id 用户ID
*/
public async remove(id: number): Promise<void> {
const existing = await this.userRepository.findOne(id);
if (!existing) {
throw new HttpException(`删除失败,ID 为 '${id}' 的用户不存在`, 404);
}
await this.userRepository.remove(existing);
}
/**
* 更新用户
* @param id 用户ID
* @param updateInput updateInput
*/
public async update(id: number, updateInput: User) {
const existing = await this.userRepository.findOne(id);
if (!existing) {
throw new HttpException(`更新失败,ID 为 '${id}' 的用户不存在`, 404);
}
if (updateInput.account) {
existing.account = updateInput.account;
}
if (updateInput.password) {
existing.password = updateInput.password;
}
if (updateInput.name) {
existing.name = updateInput.name;
}
return await this.userRepository.save(existing);
}
/**
* 通过登录账号查询用户
* @param account 登录账号
*/
public async findOneByAccount(account: string): Promise<User> {
return await this.userRepository.findOne({ account });
}
/**
* 查询用户及其帖子的信息
* @param id 用户ID
*/
public async findOneWithPostsById(id: number): Promise<User> {
return await this.userRepository.findOne(id, { relations: ['posts'] });
}
}
输入http://localhost:6333/register,填写注册信息进行注册,实际只有账号和密码两个字段是有效字段
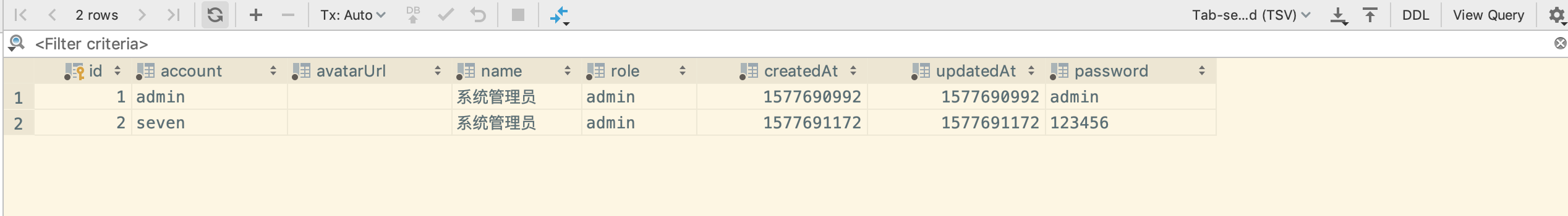
这里将 render 和 api 放到了一起,这是为了凑成一个文件

