第一步: 进行特征的可视化操作
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import datetime import matplotlib.pyplot as plt features = pd.read_csv('temps.csv') # 可视化图形 print(features.head(5)) #使用日期构造可视化图像 dates = [str(int(year)) + "-" + str(int(month)) + "-" + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(features['year'], features['month'], features['day'])] dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, "%Y-%m-%d") for date in dates] # 进行画图操作 plt.style.use("fivethirtyeight") fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 10)) fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=45) ax1.plot(dates, features["temp_1"]) ax1.set_xlabel('') ax1.set_ylabel('Temperature') ax1.set_title("Previous max Temp") ax2.plot(dates, features["temp_2"]) ax2.set_xlabel('') ax2.set_ylabel('Temperature') ax2.set_title("Two day Prio max Temp") ax3.plot(dates, features["friend"]) ax3.set_xlabel('') ax3.set_ylabel('Temperature') ax3.set_title("Friend Estimate") ax4.plot(dates, features["actual"]) ax4.set_xlabel('') ax4.set_ylabel('Temperature') ax4.set_title("Max Temperature") plt.tight_layout(pad=2) plt.show()
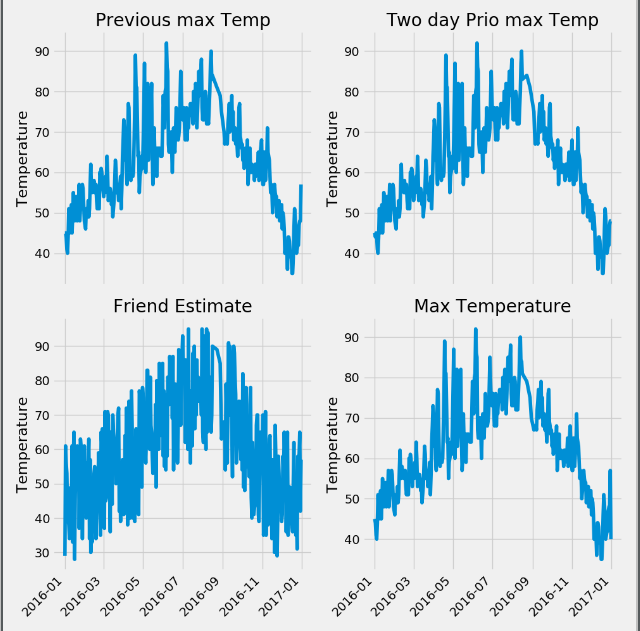
第二步: 对非数字的特征进行独热编码,使用温度的真实值作为标签,去除真实值的特征作为输入特征,同时使用process进行标准化操作
# 构造独热编码 # 遍历特征,将里面不是数字的特征进行去除 for feature_name in features.columns: print(feature_name) try: float(features.loc[0, feature_name]) except: for s in set(features[feature_name]): features[s] = 0 #根据每一行数据在时间特征上添加为1 for f in range(len(features)): features.loc[f, [features.iloc[f][feature_name]]] = 1 # 去除对应的week特征 features = features.drop(feature_name, axis=1) # 构造独热编码也可以使用 # features = pd.get_dummies(features) # 构造标签 labels = np.array(features['actual']) # 构造特征 features = features.drop('actual', axis=1) # 进行torch网络训练 import torch # 对特征进行标准化操作 from sklearn import preprocessing input_feature = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(features) print(input_feature[:, 5])
第三步: 对特征和标签进行torch.tensor处理,转换为tensor格式,初始化weigh和biases, 使用batch_size进行迭代优化,利用weight.grad 和 biases.grad进行学习率的梯度优化
# 构建神经网络 x = torch.tensor(input_feature, dtype=torch.float) y = torch.tensor(labels, dtype=torch.float) weight = torch.randn((14, 128), dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) biases = torch.randn(128, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) weight2 = torch.randn((128, 1), dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) biases2 = torch.randn(1, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) learning_rate = 0.001 losses = [] batch_size = 16 for i in range(1000): # 计算隐层 batch_loss = [] for start in range(0, len(input_feature), batch_size): end = start + batch_size if start + batch_size < len(input_feature) else len(input_feature) xx = torch.tensor(input_feature[start:end], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) yy = torch.tensor(labels[start:end], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True) hidden = xx.mm(weight) + biases # 加入激活函数 hidden = torch.sigmoid(hidden) #预测结果 predictions = hidden.mm(weight2) + biases2 # 计算损失值 loss = torch.mean((predictions - yy) ** 2) loss.backward() # 更新参数 weight.data.add_(- learning_rate * weight.grad.data) biases.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases.grad.data) weight2.data.add_(- learning_rate * weight2.grad.data) biases2.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases2.grad.data) # 每次迭代都记得清空 weight.grad.data.zero_() biases.grad.data.zero_() weight2.grad.data.zero_() biases2.grad.data.zero_() batch_loss.append(loss.data.numpy()) if i % 100 == 0: losses.append(np.mean(batch_loss)) print(i, np.mean(batch_loss))
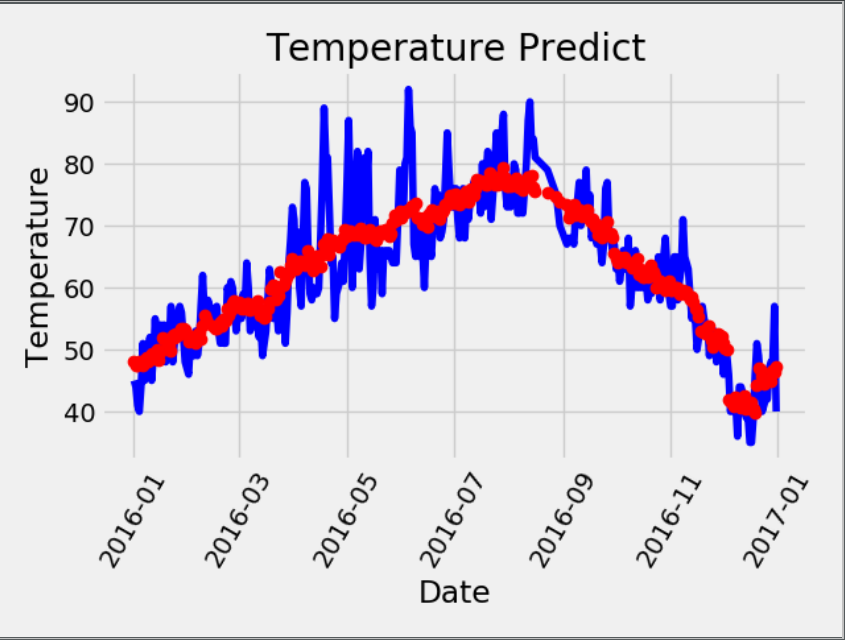
第四步: 将x重新输入到网络中,计算获得最终的prediction,进行最终的作图
hidden = x.mm(weight) + biases # 加入激活函数 hidden = torch.sigmoid(hidden) # 预测结果 prediction = hidden.mm(weight2) + biases2 prediction = prediction.detach().numpy() plt.plot(dates, y, 'b-', label='actual') plt.plot(dates, prediction, 'ro', label='predit') plt.xticks(rotation=60) plt.title("Temperature Predict") plt.xlabel("Date") plt.ylabel("Temperature") plt.show()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号