这是一种用于前馈卷积神经网络的简单而有效的注意模块。 给定一个中间特征图,我们的模块会沿着两个独立的维度(通道和空间)依次推断注意力图,然后将注意力图乘以输入特征图以进行自适应特征修饰。 由于CBAM是轻量级的通用模块,因此可以以可忽略的开销将其无缝集成到任何CNN架构中,并且可以与基础CNN一起进行端到端训练。
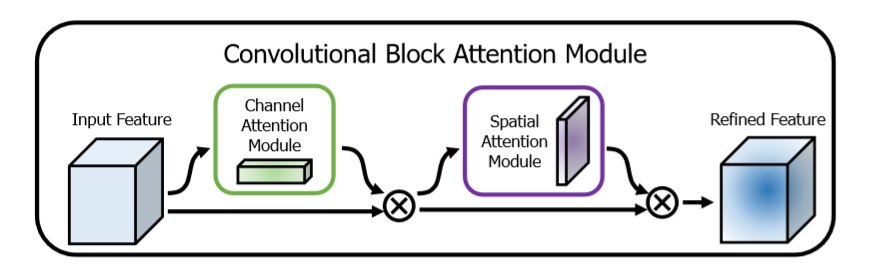
为了实现这一目标,我们依次应用频道和空间关注模块(如图1所示),以便每个分支机构都可以分别学习在频道和空间轴上参与的“内容”和“位置”。结果,我们的模块通过学习要强调或抑制的信息来有效地帮助网络中的信息流。将结果先通过通道加权模块,再通过空间位置加权模块
这里对网络做一个实际性的分析,
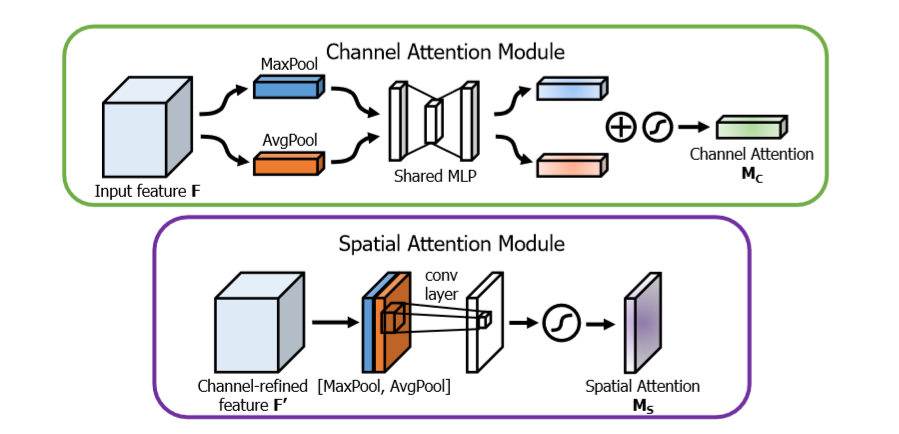
channel attention Module 主要是关注哪些通道对网络的最后输出结果起到作用,即文章中提到的‘什么’,即哪些特征对最终的预测起到了决定性的作用
channel 特征分析,输入通过一个最大值池化和均值池化
最大值池化分析:首先通过对宽度和高度进行最大值池化,然后对特征通道进行全连接,为了减少参数,这里的输出通道为 channel / 8, 下一步再进行全连接,使得输出通道为 channel。
均值池化分析:首先通过对宽度和高度进行均值池化,然后对特征通道进行全连接,为了减少参数,这里的输出通道为channel / 8, 下一步再使用全连接,使得输出通道为channel。
下一步:将两个进行加和,然后通过sigmoid进行输出,最后的结果与输入结果进行相乘操作,进行注意机制加权。
Spatial Attention Module 主要是关注哪些位置对网络的最后输出结果起到作用,即文章中提到的‘哪里’,即哪些位置信息对最终的预测起到了决定性的作用
spatial 特征分析:输入通过一个最大值池化和均值池化
最大值池化分析:对通道求取最大值池化
均值池化:对通道求取均值池化
下一步:将两个特征进行axis=3的通道串接,进行卷积操作,保证axis=3的特征数为1,进行sigmoid输出,最后结果与输入进行相乘操作,进行注意机制加权
attention_module.py
import tensorflow as tf def cbam_block(input_feature, name, ratio=8): """Contains the implementation of Convolutional Block Attention Module(CBAM) block. As described in https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.06521. """ with tf.variable_scope(name): attention_feature = channel_attention(input_feature, 'ch_at', ratio) # 通道注意机制 attention_feature = spatial_attention(attention_feature, 'sp_at') print("CBAM Hello") return attention_feature def channel_attention(input_feature, name, ratio=8): kernel_initializer = tf.contrib.layers.variance_scaling_initializer() # 通道的参数卷积初始化 bias_initializer = tf.constant_initializer(value=0.0) # 偏置的初始化 with tf.variable_scope(name): channel = input_feature.get_shape()[-1] # 输入的通道数 avg_pool = tf.reduce_mean(input_feature, axis=[1, 2], keepdims=True) # 进行均值平均 assert avg_pool.get_shape()[1:] == (1, 1, channel) avg_pool = tf.layers.dense(inputs=avg_pool, units=channel // ratio, activation=tf.nn.relu, kernel_initializer=kernel_initializer, bias_initializer=bias_initializer, name='mlp_0', reuse=None) assert avg_pool.get_shape()[1:] == (1, 1, channel // ratio) avg_pool = tf.layers.dense(inputs=avg_pool, units=channel, kernel_initializer=kernel_initializer, bias_initializer=bias_initializer, name='mlp_1', reuse=None) assert avg_pool.get_shape()[1:] == (1, 1, channel) max_pool = tf.reduce_max(input_feature, axis=[1, 2], keepdims=True) assert max_pool.get_shape()[1:] == (1, 1, channel) max_pool = tf.layers.dense(inputs=max_pool, units=channel // ratio, activation=tf.nn.relu, name='mlp_0', reuse=True) assert max_pool.get_shape()[1:] == (1, 1, channel // ratio) max_pool = tf.layers.dense(inputs=max_pool, units=channel, name='mlp_1', reuse=True) assert max_pool.get_shape()[1:] == (1, 1, channel) scale = tf.sigmoid(avg_pool + max_pool, 'sigmoid') return input_feature * scale def spatial_attention(input_feature, name): kernel_size = 7 kernel_initializer = tf.contrib.layers.variance_scaling_initializer() with tf.variable_scope(name): avg_pool = tf.reduce_mean(input_feature, axis=[3], keepdims=True) assert avg_pool.get_shape()[-1] == 1 max_pool = tf.reduce_max(input_feature, axis=[3], keepdims=True) assert max_pool.get_shape()[-1] == 1 concat = tf.concat([avg_pool, max_pool], 3) assert concat.get_shape()[-1] == 2 concat = tf.layers.conv2d(concat, filters=1, kernel_size=[kernel_size, kernel_size], strides=[1, 1], padding="same", activation=None, kernel_initializer=kernel_initializer, use_bias=False, name='conv') assert concat.get_shape()[-1] == 1 concat = tf.sigmoid(concat, 'sigmoid') return input_feature * concat


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号