1.画两个条形图,bar和barh, 同时axes[0].axhline画一条横线,axes[1].axvline画一条竖线
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(0) x = np.arange(5) y = np.random.randint(-5, 5, 5) # 分成两个方框,一行两列 fig,axes = plt.subplots(ncols=2) # 对第一个方框进行画图bar axes[0].bar(x, y, color='r') # 对第二个方框进行画图barh axes[1].barh(x, y, color='g') # 对第一个方框画一条横线,axhline axes[0].axhline(0, color='grey', linewidth=2) # 对第二个方框画一条竖线, axvline axes[1].axvline(0, color='grey', linewidth=2) plt.show()
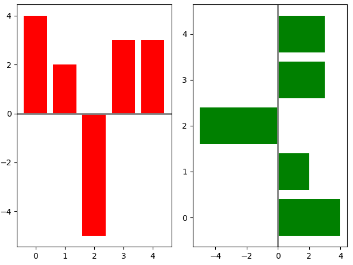
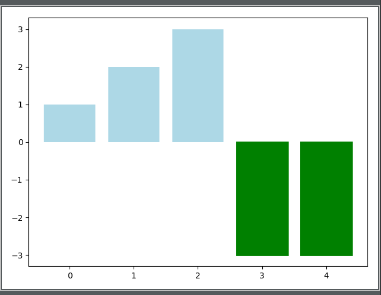
2.根据条形图y的大小设置每个条形图的颜色
np.random.seed(0) fig, ax = plt.subplots() v_bars = ax.bar(x, y, color='lightblue') for bars, height in zip(v_bars, y): if height < 0: bars.set(edgecolor='darkred', color='green', linewidth=2) plt.show()
3.fill_between 进行填充操作, .consum 表示的是进行累加操作,将前一个值累加到当前值
x = np.random.randn(100).cumsum() y = np.linspace(0, 100, 100) fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.fill_between(x, y, color='lightblue') plt.show()
4. fill_between 对两个函数之间进行填充操作
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 200) y1 = 2*x + 1 y2 = 3*x + 1.2 y_mean = 0.5*x*np.cos(2*x) + 2.5*x + 1.1 fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# 填充函数之间的值 ax.fill_between(x, y1, y2, color='red') plt.plot(x, y_mean, color='black') plt.show()

5. 误差棒的设置plt.bar(yerr=variance) # variance表示误差的大小
mean_values = [1, 2, 3] # variance表示误差 variance = [0.2, 0.4, 0.5] bar_label = ['bar1', 'bar2', 'bar3'] # 设置x轴的范围 x_pos = list(range(len(mean_values))) # yerr用来设置误差棒 plt.bar(x_pos, mean_values, color='r', yerr=variance) max_y = max(zip(mean_values, variance)) # 设置y轴的显示范围 plt.ylim([0, (max_y[0] + max_y[1]) * 1.2]) # 设置x轴的标签,x_pos表示标签的位置,bar_label表示标签名 plt.xticks(x_pos, bar_label) plt.ylabel('variable_y') plt.show()
6. 画横向并排的条形图
x1 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) x2 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) bar_label = ['bar1', 'bar2', 'bar3'] fig = plt.figure(figsize=[8, 6]) y_pos = list(np.arange(len(x1))) plt.barh(y_pos, x1, color='r',) plt.barh(y_pos, -x2, color='b',) # 为了使得图形美观,设置xlim和ylim的范围 plt.xlim([-max(x2)-1, max(x1) + 1]) plt.ylim(-1, max(y_pos) + 1) plt.show()
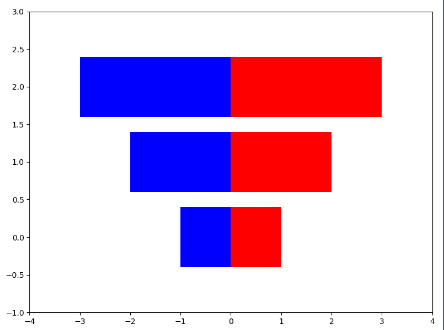
7.设置位置的宽度进行并排
green_data = [1, 2, 3] blue_data = [3, 2, 1] red_data = [2, 3, 3] labels = ['group1', 'group2', 'group3'] # 设置x_pos的位置 x_pos = list(range(len(green_data))) print(x_pos) width = 0.2 plt.bar(x_pos, green_data, width=width, color='g', label=labels[0], alpha=0.6) plt.bar([x+width for x in x_pos], blue_data, width=width, color='b', label=labels[1], alpha=0.6) plt.bar([x+2*width for x in x_pos], red_data, width=width, color='r', label=labels[2], alpha=0.6) plt.legend(loc='best', framealpha=0.05) plt.show()
8. 在画的条形图上加竖线ax.axvline(data.min()) 在条形图的后面加上%plt.text 通过获得每个条形图的位置信息
data = np.arange(200, 225, 5) bar_labels = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] y_pos = list(np.arange(len(data))) fig, ax = plt.subplots() # ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False) # 去除右边的框图 ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False) plt.yticks(y_pos, bar_labels) v_bars = plt.barh(y_pos, data) # 加横线 ax.axvline(data.min(), linestyle='--', color='k') # 进行对每一个条形块文本标注 for b, d in zip(v_bars, data): plt.text(b.get_width(), b.get_y()+b.get_height()/2, '{0:.2%}'.format(d/min(data))) plt.show()

9. 构造colormap来建立条形图的颜色 使用colormap构造条形图cm.ScalarMappable(col.Normalize())
import matplotlib.colors as col import matplotlib.cm as cm mean_values = range(10, 18) x_pos = range(len(mean_values)) # 构造colormap, cm.hot表示风格 cmap1 = cm.ScalarMappable(col.Normalize(min(mean_values), max(mean_values), cm.hot)) cmap2 = cm.ScalarMappable(col.Normalize(0, 20, cm.hot)) plt.subplot(121) # cmap1.to_rgba(mean_values) # 将color_map使用到mean_values plt.bar(x_pos, mean_values, color=cmap1.to_rgba(mean_values)) plt.subplot(122) plt.bar(x_pos, mean_values, color=cmap2.to_rgba(mean_values)) plt.show()
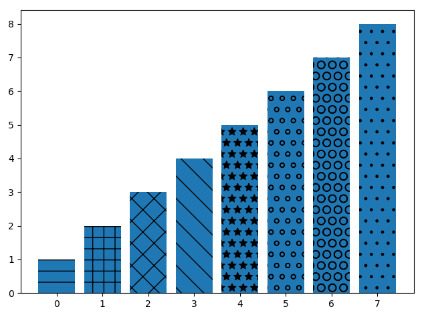
10. b.set_hatch('o') # 画出不同填充风格的条形图
patterns = ('-', '+', 'x', '\\', '*', 'o', 'O', '.') data = range(1, len(patterns) + 1 ) x_pow = range(len(data)) bars = plt.bar(x_pow, data) for b, p in zip(bars, patterns): b.set_hatch(p) plt.show()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号