20165205 第十周课下补做
课程内容总结
- 泛型类声明:class People
,People是泛型类的名字,E是其中的泛型 - 使用泛型类声明对象:
Cone<Ciecle> coneOne; coneOne=new Cone<Circle>(new Circle()); - LinkedList
泛型类: LinkedList<String> mylist=new LinkedList<String>(); - 添加结点:
mylist.add("hoe"); - 当前链表迭代器:
Iterator<String> iter=list.iterator(); public static sort(List<E>list)升序排序;int binarySearch(List<T>,Tkey,compareTo<T>c)折半查找list是否含有和参数key一样的元素。public static void shuffle(List<E>list)将list中数据按洗牌算法重新随机排列。- 堆栈:Stack
建立一个堆栈对象。压栈: public E push(E item);;弹栈:public E pop(); - 有类的源代码,针对某一成员变量排序,让类实现Comparable接口,调用Collection.sort(List)
- 没有类的源代码,或者多种排序,新建一个类,实现Comparator接口 调用Collection.sort(List, Compatator)
课上习题:
-
习题2
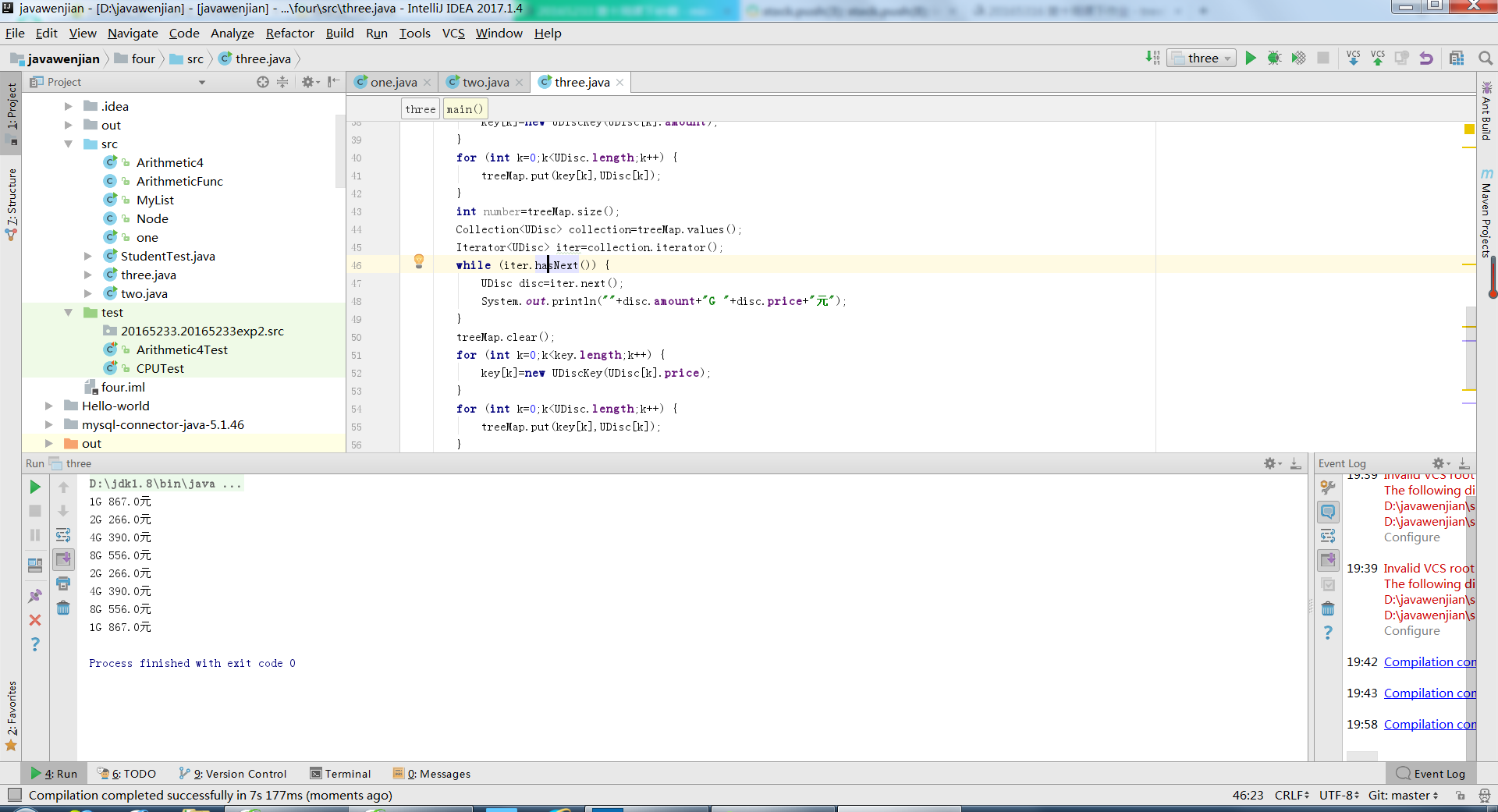
import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; import java.util.LinkedList; public class StudentTest { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Student> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add(new Student(20165207,"litianlin","male",60,89,67,89)); list.add(new Student(20165206,"hanxiao","male",60,79,66,45)); list.add(new Student(20165205,"liuzhejun","female",70,69,81,78)); list.add(new Student(20165204,"jiapuhan","male",80,69,56,76)); list.add(new Student(20165203,"jiahaisu","male",90,62,80,83)); SortByTotal_score sortBytotal_score = new SortByTotal_score(); Collections.sort(list, sortBytotal_score); SortByID sortByID = new SortByID(); Collections.sort(list, sortByID); System.out.println("根据学生学号由低到高排序:"); for (Student student : list) { System.out.println(student); } Collections.sort(list, sortBytotal_score); System.out.println("根据学生成绩由低到高排序:"); for (Student student : list) { System.out.println(student); } } } class Student { private int id;//表示学号 private String name;//表示姓名 private int age;//表示年龄 private String sex; private double computer_score;//表示计算机课程的成绩 private double english_score;//表示英语课的成绩 private double maths_score;//表示数学课的成绩 private double total_score;// 表示总成绩 private double ave_score; //表示平均成绩 @Override public String toString() { return "Student[name:"+name+",age:"+age+",number:"+id+",total_score"+total_score+"]"; } public Student(int id, String name, String sex, int age,double computer_score, double english_score,double maths_score) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.age = age; this.computer_score = computer_score; this.english_score = english_score; this.maths_score = maths_score; } public int getId() { return id; }//获得当前对象的学号, public double getComputer_score() { return computer_score; }//获得当前对象的计算机课程成绩, public double getMaths_score() { return maths_score; }//获得当前对象的数学课程成绩, public double getEnglish_score() { return english_score; }//获得当前对象的英语课程成绩, public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }// 设置当前对象的id值, public void setComputer_score(double computer_score) { this.computer_score = computer_score; }//设置当前对象的Computer_score值, public void setEnglish_score(double english_score) { this.english_score = english_score; }//设置当前对象的English_score值, public void setMaths_score(double maths_score) { this.maths_score = maths_score; }//设置当前对象的Maths_score值, public double getTotalScore() { total_score=computer_score + maths_score + english_score; return total_score; }// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的总成绩。 public double getAveScore() { return getTotalScore() / 3; }// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的平均成绩。 } class SortByID implements Comparator<Student> { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return o1.getId() - o2.getId(); } } class SortByTotal_score implements Comparator<Student> { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return (int)( o1.getTotalScore() - o2.getTotalScore()); } }
-
习题3:
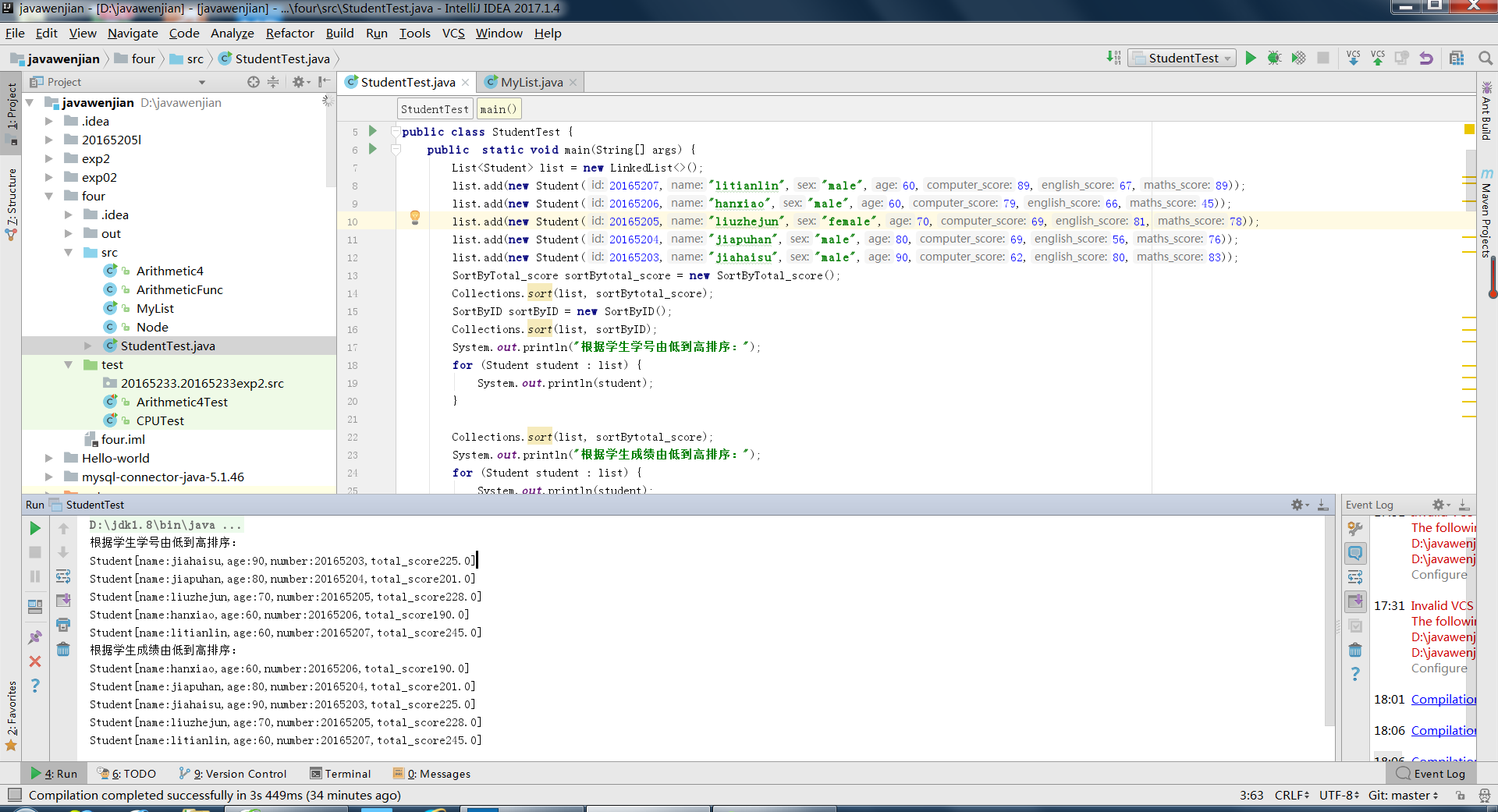
import java.util.*; public class MyList { public static void main(String [] args) { List<String> list=new LinkedList<String>(); list.add("20165203"); list.add("20165204"); list.add("20165206"); list.add("20165207"); System.out.println("打印初始链表"); //把上面四个节点连成一个没有头结点的单链表 Iterator<String> iter=list.iterator(); while(iter.hasNext()){ String te=iter.next(); System.out.println(te); } //遍历单链表,打印每个结点的 list.add("20165205"); //把你自己插入到合适的位置(学号升序) System.out.println("插入我的学号后排序,打印链表"); Collections.sort(list); iter=list.iterator(); while(iter.hasNext()){ String te=iter.next(); System.out.println(te); } //遍历单链表,打印每个结点的 list.remove("20165205"); //从链表中删除自己 System.out.println("删除我的学号后打印链表"); iter=list.iterator(); while(iter.hasNext()){ String te=iter.next(); System.out.println(te); } //遍历单链表,打印每个结点的 } }
课后编程题:
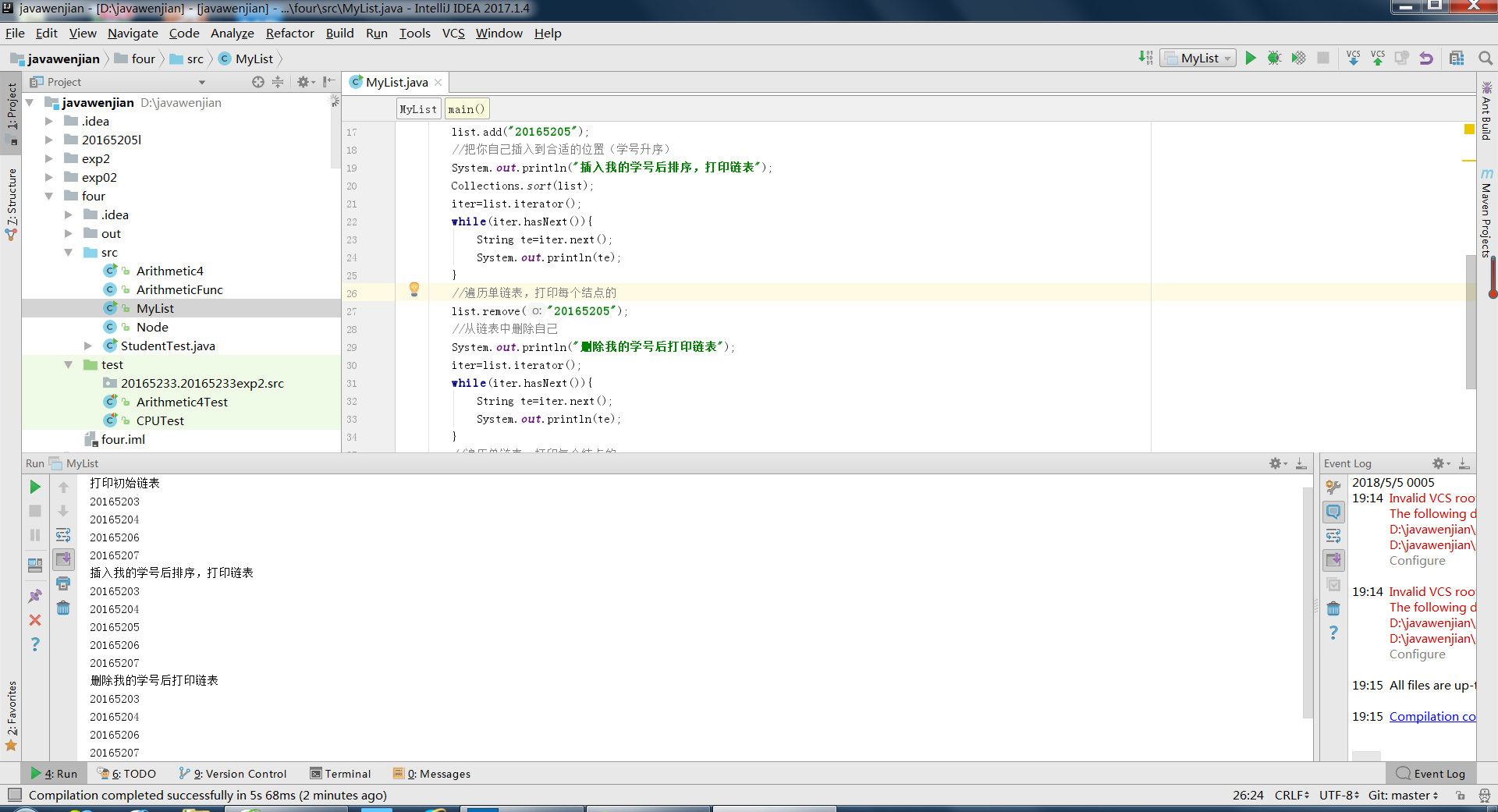
1.使用堆栈结构输出an的若干项,其中an=2an-1+2an-2,a1=3,a2=8。
import java.util.*;
public class ONE {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(3);
stack.push(8);
int k=1;
while (k<=10) {
for (int i=1;i<=2;i++) {
Integer F1=stack.pop();
int f1=F1.intValue();
Integer F2=stack.pop();
int f2=F2.intValue();
Integer temp= 2 * f1 + 2 * f2;
System.out.println(""+temp.toString());
stack.push(temp);
stack.push(F2);
k++;
}
}
}
}
2.将链表中的学生英语成绩单存放到一个树集中,使得按成绩自动排序,并输出排序结果
import java.util.*;
class CollegeStu implements Comparable {
int english=0;
String name;
CollegeStu(int english,String name) {
this.name=name;
this.english=english;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object b) {
CollegeStu stu=(CollegeStu)b;
return (this.english-stu.english);
}
}
public class two {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<CollegeStu> list=new LinkedList<CollegeStu>();
int score []={67, 66, 90, 56, 80};
String name []={"贾海粟","贾普涵","刘喆君","韩啸","李天林"};
for (int i=0;i<score.length;i++) {
list.add(new CollegeStu(score[i],name[i]));
}
Iterator<CollegeStu> iter=list.iterator();
TreeSet<CollegeStu> mytree=new TreeSet<CollegeStu>();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
CollegeStu stu=iter.next();
mytree.add(stu);
}
Iterator<CollegeStu> te=mytree.iterator();
while (te.hasNext()) {
CollegeStu stu=te.next();
System.out.println(""+stu.name+" "+stu.english);
}
}
}
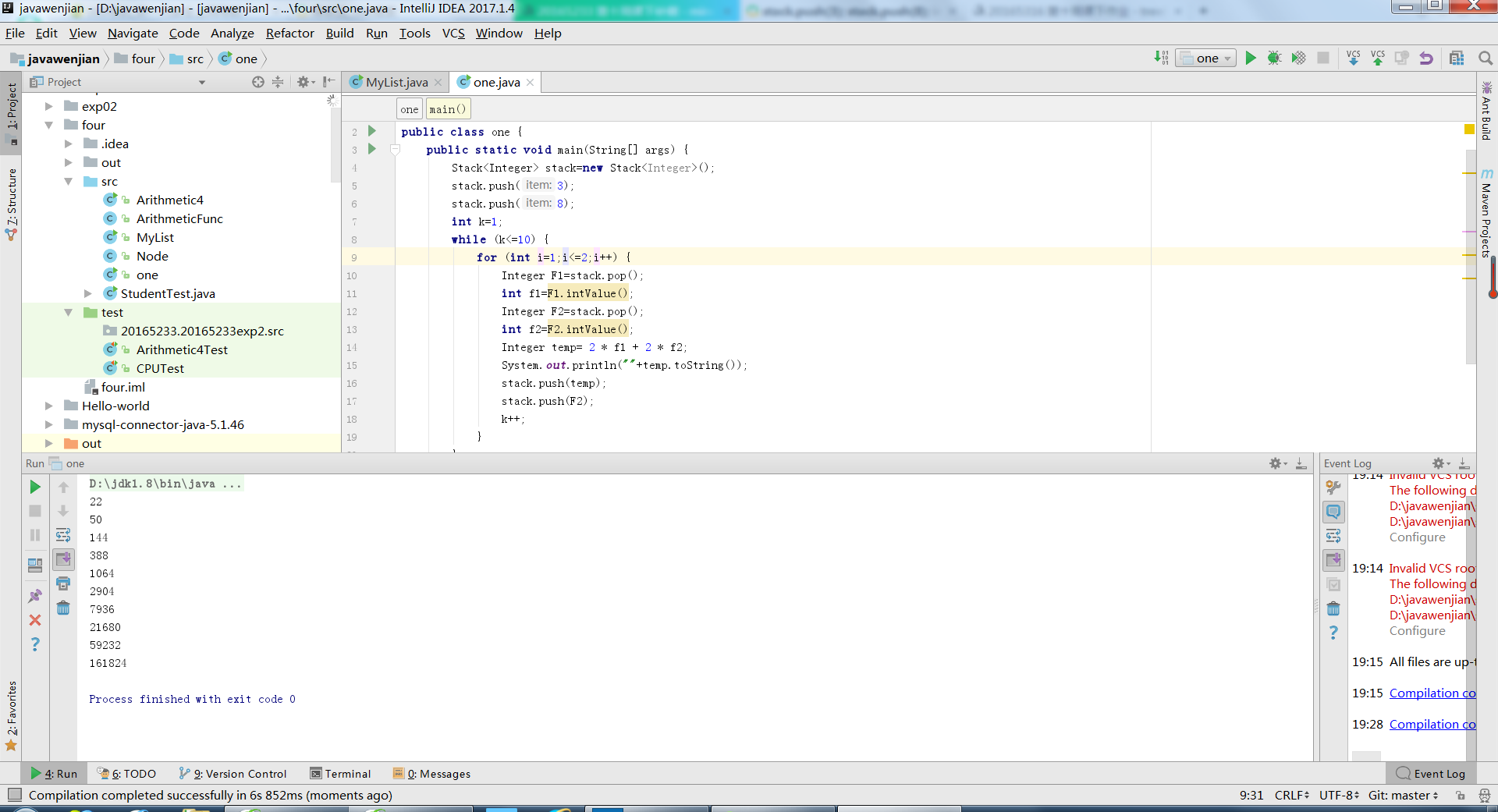
3.有10个U盘,有两个重要的属性:价格和容量,编写一个应用程序,使用TreeMap<K,V>类,分别按照价格和容量排序输出10个U盘的详细信息。
import java.util.*;
class UDiscKey implements Comparable {
double key = 0;
UDiscKey(double d) {
key = d;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object b) {
UDiscKey disc = (UDiscKey) b;
if ((this.key - disc.key) == 0) {
return -1;
}
else
{
return (int) ((this.key - disc.key) * 1000);
}
}
}
class UDisc {
int amount;
double price;
UDisc(int m,double e) {
amount=m;
price=e;
}
}
public class three {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc> treeMap=new TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc>();
int amount[]={1,2,4,8,16};
double price[]={867,266,390,556};
UDisc UDisc[]=new UDisc[4];
for (int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
UDisc[k]=new UDisc(amount[k],price[k]);
}
UDiscKey key[]=new UDiscKey[4];
for (int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].amount);
}
for (int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treeMap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]);
}
int number=treeMap.size();
Collection<UDisc> collection=treeMap.values();
Iterator<UDisc> iter=collection.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
treeMap.clear();
for (int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].price);
}
for (int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treeMap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]);
}
number=treeMap.size();
collection=treeMap.values();
iter=collection.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
}
}